Educational and Day-Care Occupancies (July 23, 2025 Second Draft Transcript)
The Life Safety Code addresses those construction, protection, and occupancy features necessary to minimize danger to life from the effects of fire, including smoke, heat, and toxic gases created during a fire. It is widely incorporated by reference into public safety statutes; typically coupled with the consensus products of the International Code Council. It is a mighty document — one of the NFPA’s leading titles — so we deal with it in pieces; consulting it for decisions to be made for the following:
(1) Determination of the occupancy classification in Chapters 12 through 42.
(2) Determination of whether a building or structure is new or existing.
(3) Determination of the occupant load.
(4) Determination of the hazard of contents.
There are emergent issues — such as active shooter response, integration of life and fire safety systems on the internet of small things — and recurrent issues such as excessive rehabilitation and conformity criteria and the ever-expanding requirements for sprinklers and portable fire extinguishers with which to reckon. It is never easy telling a safety professional paid to make a market for his product or service that it is impossible to be alive and safe. It is even harder telling the dean of a department how much it will cost to bring the square-footage under his stewardship up to the current code.
The 2021 edition is the current edition and is accessible below:
NFPA 101 Life Safety Code Free Public Access
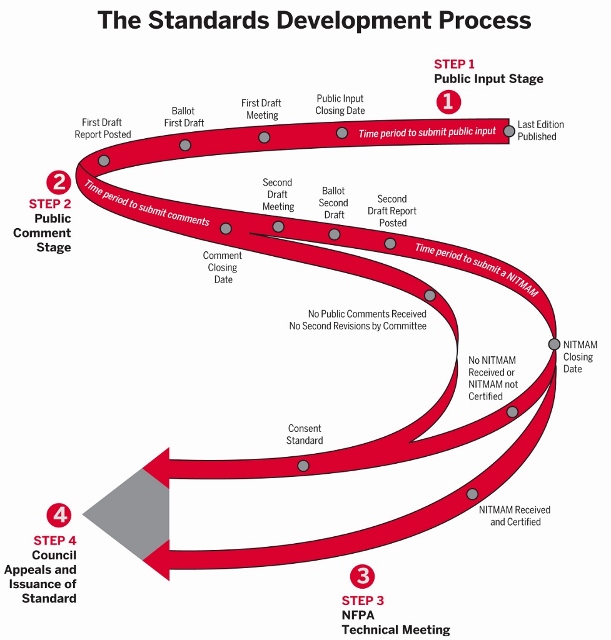
Public input on the 2027 Revision will be received until June 4, 2024. Public comment on the Second Draft 2027 Revision will be received until March 31, 2026.
Since the Life Safety Code is one of the most “living” of living documents — the International Building Code and the National Electric Code also move continuously — we can start anywhere and anytime and still make meaningful contributions to it. We have been advocating in this document since the 2003 edition in which we submitted proposals for changes such as:
• A student residence facility life safety crosswalk between NFPA 101 and the International Building Code
• Refinements to Chapters 14 and 15 covering education facilities (with particular attention to door technologies)
• Identification of an ingress path for rescue and recovery personnel toward electric service equipment installations.
• Risk-informed requirement for installation of grab bars in bathing areas
• Modification of the 90-minute emergency lighting requirements rule for small buildings and for fixed interval testing
• Modification of emergency illumination fixed interval testing
• Table 7.3.1 Occupant Load revisions
• Harmonization of egress path width with European building codes
There are others. It is typically difficult to make changes to stabilized standard though some of the concepts were integrated by the committee into other parts of the NFPA 101 in unexpected, though productive, ways. Example transcripts of proposed 2023 revisions to the education facility chapter is linked below:
Chapter 14 Public Input Report: New Educational Occupancies
Educational and Day Care Occupancies: Second Draft Public Comments with Responses Report
Since NFPA 101 is so vast in its implications we list a few of the sections we track, and can drill into further, according to client interest:
Chapter 3: Definitions
Chapter 7: Means of Egress
Chapter 12: New Assembly Occupancies
Chapter 13: Existing Assembly Occupancies
Chapter 16 Public Input Report: New Day-Care Facilities
Chapter 17 Public Input Report: Existing Day Care Facilities
Chapter 18 Public Input Report: New Health Care Facilities
Chapter 19 Public Input Report: Existing Health Care Facilities
Chapter 28: Public Input Report: New Hotels and Dormitories
Chapter 29: Public Input Report: Existing Hotels and Dormitories
Chapter 43: Building Rehabilitation
Annex A: Explanatory Material
As always we encourage front-line staff, facility managers, subject matter experts and trade associations to participate directly in the NFPA code development process (CLICK HERE to get started)
![]()
NFPA 101 is a cross-cutting title so we maintain it on the agenda of our several colloquia —Housing, Prometheus, Security and Pathways colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [18-90]
Category: Fire Safety, Public Safety
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Josh Elvove, Joe DeRosier, Marcelo Hirschler
More
When lives are at stake, alternative approaches are welcome. #LifeSafety #AlternativeApproaches #Code #NFPA101 @NFPA
https://t.co/JvWyyZtuLP— ANSI (@ansidotorg) December 20, 2018