2025 GROUP B PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES: Complete Monograph (2630 pages)
36 kitchen related proposals were reviewed during our precious sesssion
2024 GROUP A PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES: Complete Monograph (2658 pages)
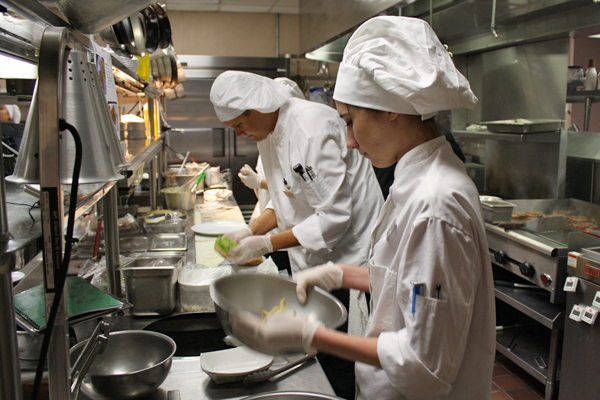
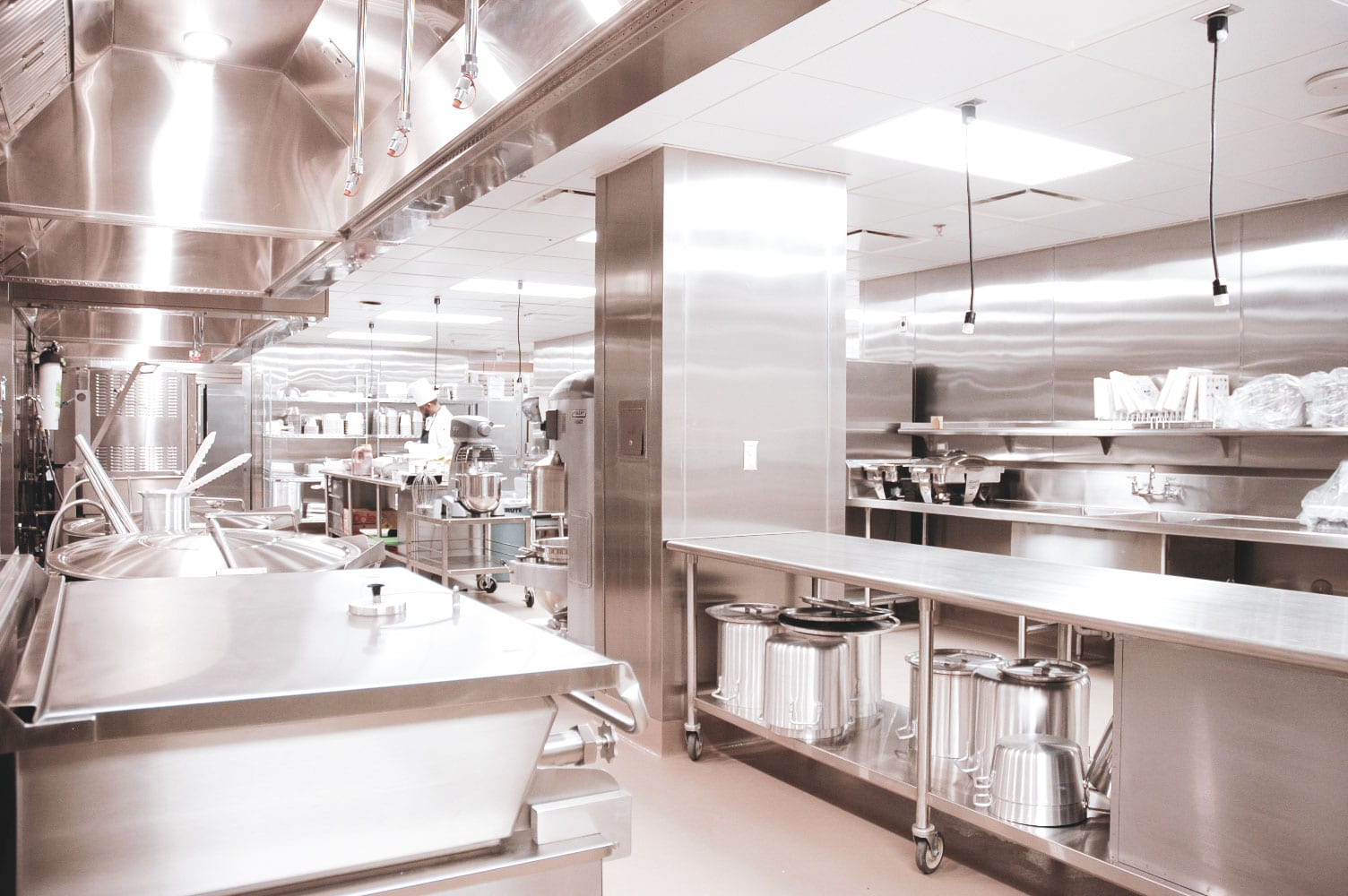
Commercial kitchens offer several benefits, such as efficient food preparation and large-scale production, allowing businesses to meet high demand. They provide professional-grade equipment and ample space, enabling chefs to explore culinary creativity. Commercial kitchens also promote hygiene and food safety standards, with dedicated cleaning protocols and inspections. However, hazards can arise from the high-temperature cooking equipment, sharp tools, and potentially hazardous substances. There is also a risk of burns, slips, and falls, emphasizing the importance of proper training and safety measures. Adequate ventilation and fire safety systems are vital to prevent accidents and maintain a healthy working environment.
The International Code Council is re-configuring its code development process in nearly every dimension. While that situation stabilizes let us review the back-and-forth on this topic during the previous revision cycle (linked below):
2021 International Building Code Section 306 Factory Group F Moderate Hazard
2021 International Fire Code Section 606 Commercial Cooking Equipment and Systems
The International Code Council has recently re-configured its code development calendar:
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
Public hearings on the proposed changes happen in Orlando, April 7-16.
This is a summary of the actions taken on the 2024 Comments on Proposed Changes to the ICC International Codes at the October 23-28, 2024 Committee Action Hearings #2 held at the Long Beach Convention Center, Long Beach, California. Balloting of local building code officials is now underway.
Commercial kitchen electrical power wiring requirements are covered extensively in Article 210 through Article 215 of the National Electrical Code. Standards action in this domain is referred to IEEE Education & Healthcare Facility Committee.
ASHRAE International: Calculating Airflow Rates, Cooking Loads in Commercial Kitchens
Related
International Mechanical Code: Chapter 10 Boilers, Water Heaters and Pressure Vessels
AGA Response to The Atlantic Article about Natural Gas Cooking
Thomas Edison State University: Undergraduate Certificate in Gas Distribution