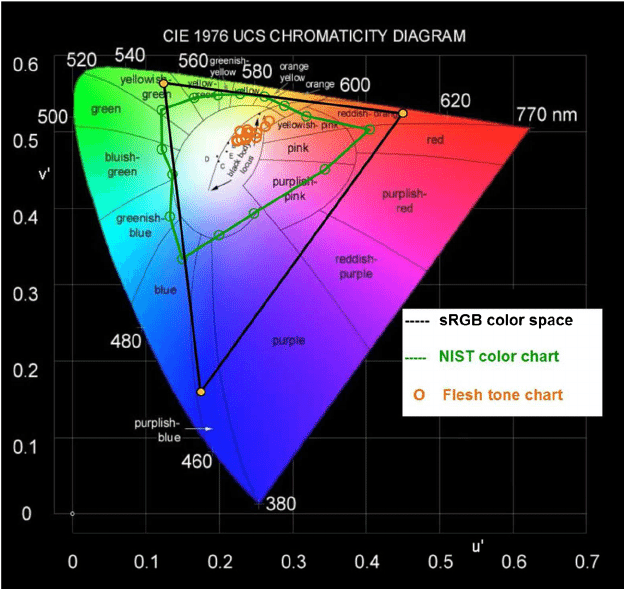
Range of colors chart used in NIST measurements
The National Institute of Standards and Technology measures color through a combination of sophisticated instrumentation and established standards:
1. Standards and Calibration
-
- Primary Standards: NIST maintains primary color standards, such as spectral reflectance and transmittance standards, that are traceable to international measurement systems.
- Calibration of Instruments: Instruments used for color measurement are calibrated using these standards to ensure accuracy and consistency.
2. Instrumentation
-
- Spectrophotometers: These instruments measure the intensity of light at different wavelengths. They are used to obtain the spectral reflectance or transmittance of a sample.
- Colorimeters: These are simpler instruments that measure color using a few broad wavelength bands. They are often used for less precise applications.
3. Measurement Process
-
- Sample Preparation: The sample to be measured is prepared according to specific protocols to ensure uniformity and consistency.
- Spectral Measurement: The spectrophotometer or colorimeter measures the light reflected or transmitted by the sample across the visible spectrum.
- Data Collection: The data collected includes the spectral power distribution, which indicates how much light is reflected or transmitted at each wavelength.
4. Data Analysis
-
- Color Spaces and Models: The raw spectral data is converted into color space coordinates (e.g., CIE XYZ, Lab) using mathematical models. These models account for human vision characteristics and provide a numerical representation of color.
- Comparison and Reporting: The measured color can be compared to standard references or reported in various formats depending on the application (e.g., color difference ΔE).
5. Quality Control and Assurance
-
- Repeatability and Reproducibility: NIST ensures the repeatability and reproducibility of color measurements by using rigorous quality control protocols.
- Uncertainty Analysis: The uncertainty associated with the measurements is analyzed and reported to provide a clear understanding of the precision of the measurements.
Example Instruments and Techniques
-
- Goniospectrophotometers: These measure the color of materials that change appearance with viewing angle.
- Integrating Spheres: These are used with spectrophotometers to measure diffuse reflectance or transmittance.
- Laser-based Systems: Advanced systems that use lasers for highly precise color measurements.
NIST’s methods are designed to provide highly accurate and reliable color measurements that can be used across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, textiles, and digital imaging.
Standards Michigan: National Institute of Standards and Technology
The gems color wheel is useful to identify potential gems in specific colors for jewelers.
[✏️ suigemstone] pic.twitter.com/0sVHQgTWMr
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) September 11, 2024
The surprising invisibility effect of painting chicken wire blackpic.twitter.com/OlTFyahUyQ
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) October 17, 2024
They destroyed art,
they stole colors,
that’s why the world is depressed. pic.twitter.com/7ZYY4xBXwz— The Figen (@TheFigen_) August 22, 2025








