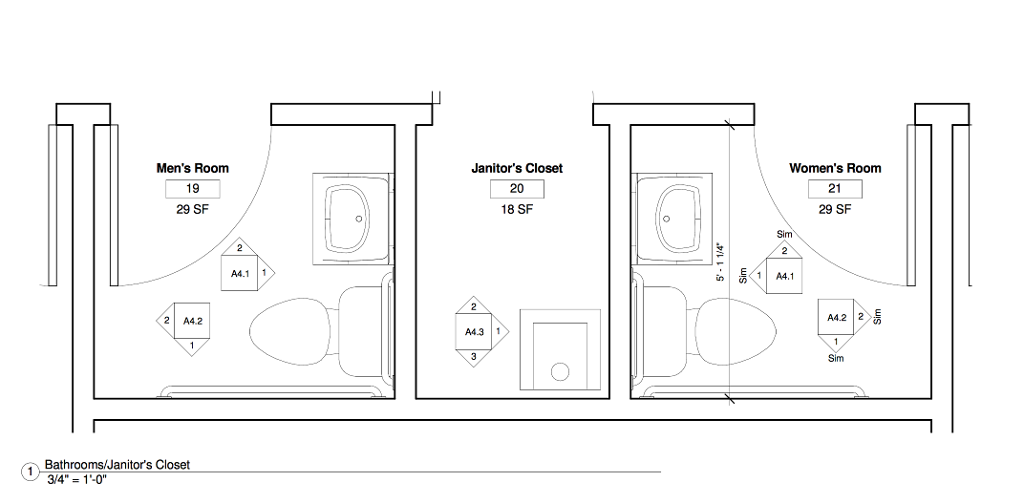
Today we examine relatively recent transactions in electrotechnologies — power, information and communication technology — that are present (and usually required) in patient care settings. At a patient’s bedside in a hospital or healthcare setting, various electrical loads or devices may be present to provide medical care, monitoring, and comfort. Some of the common electrical loads found at a patient’s bedside include:
Hospital Bed: Electric hospital beds allow for adjustments in height, head position, and leg position to provide patient comfort and facilitate medical procedures.
Patient Monitor: These monitors display vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate, helping healthcare professionals keep track of the patient’s condition.
Infusion Pumps: These devices administer medications, fluids, and nutrients intravenously at a controlled rate.
Ventilators: Mechanical ventilators provide respiratory support to patients who have difficulty breathing on their own.
Pulse Oximeter: This non-invasive device measures the oxygen saturation level in the patient’s blood.
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Machine: It records the electrical activity of the heart and is used to diagnose cardiac conditions.
Enteral Feeding Pump: Used to deliver liquid nutrition to patients who cannot take food by mouth.
Suction Machine: It assists in removing secretions from the patient’s airway.
IV Poles: To hold and support intravenous fluid bags and tubing.
Warming Devices: Devices like warming blankets or warm air blowers are used to maintain the patient’s body temperature during surgery or recovery.
Patient Call Button: A simple push-button that allows patients to call for assistance from the nursing staff.
Overbed Tables: A movable table that allows patients to eat, read, or use personal items comfortably.
Reading Lights: Bedside lights that allow patients to read or perform tasks without disturbing others.
Television and Entertainment Devices: To provide entertainment and alleviate boredom during the patient’s stay.
Charging Outlets: Electrical outlets to charge personal electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
It’s important to note that the specific devices and equipment present at a patient’s bedside may vary depending on the level of care required and the hospital’s equipment standards. Additionally, strict safety measures and electrical grounding are essential to ensure patient safety when using electrical devices in a healthcare setting.
We have been tracking the back-and-forth on proposals, considerations, adoption and rejections in the 3-year revision cycles of the 2023 National Electrical Code and the2021 Healthcare Facilities Code. We will use the documents linked below as a starting point for discussion; and possible action:
NFPA 99:
Electrical Systems (HEA-ELS) Public Input
Electrical Systems (HEA-ELS) Public Comment
NFPA 70:
National Electrical Code CMP-15
Fire Protection Research Foundation:
Electric Circuit Data Collection: An Analysis of Health Care Facilities (Mazetti Associates)
iDesign Services
Matt Dozier, Principal CMP-15
IEEE Education & Healthcare Facility Electrotechnology
There are many other organizations involved in this very large domain — about 20 percent of the US Gross Domestic Product.
Ahead of the September 7th deadline for new proposals for Article 517 for the 2026 National Electrical Code we will examine their influence in other sessions; specifically in our Health 100,200,300 and 400 colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
2026 National Electrical Code Workspace
Plug Load Management: Department of Energy By the National Renewable Energy Laboratory