Current Referenda | Ballotpedia
Perspective:
- The largest school bond referendum on ballots in November 2025 is the $1.4 billion package for Richardson Independent School District (ISD) in Texas.
- University of Michigan’s 2025 $2 billion general revenue bonds
- New York University’s 2025 $2.18 billion bonds through the Dormitory Authority of the State of New York
- The largest school bond referendum on ballots in November 2024 was Measure US for the Los Angeles Unified School District (LAUSD) in California, totaling $9 billion.
- In the November 2022 elections, a significant number of school bond referenda were presented to voters across the United States. For example, in Wisconsin alone, there were 57 successful capital referenda amounting to nearly $2.1 billion in authorized debt (Wisconsin Policy Forum)
- In Texas, Central Texas schools had a total of $4.24 billion in bonds on the ballot, covering various propositions for school facilities, technology improvements, and athletic facilities (Fox 7 Austin)
- In California and Arkansas, bond measures totaling $74 million — including school choice — were aimed at addressing school facility improvements (The74Million)
- Voters in 16 North Carolina counties approved bond issues totaling $4.27 billion, with $3.08 billion dedicated to K-12 public school construction and improvements (EducationNC)
“The cure for high prices, is high prices” — They say.
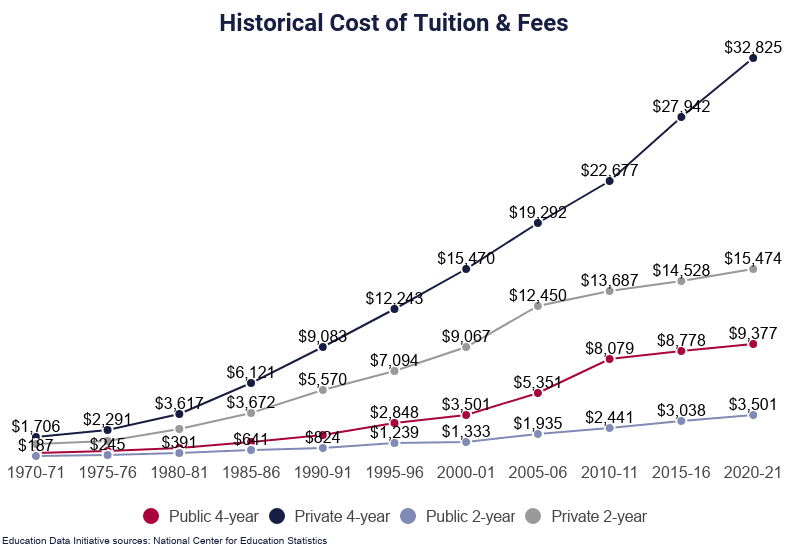
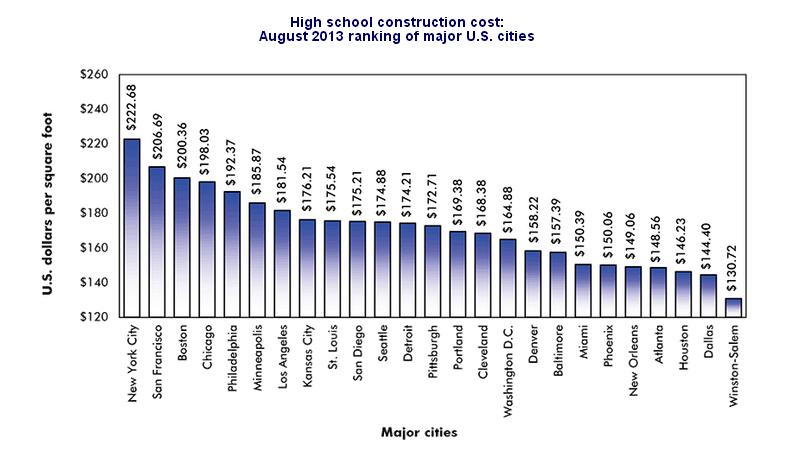
Today we explore fiscal runaway in the US education “industry” with particular interest in the financing instruments for building the real assets that are the beating heart of culture in neighborhoods, cities, counties and states. We steer clear of social and political issues. The marketing of these projects — and how the loans are paid off — provides insight into the costs and benefits of this $100+ billion industry; the largest non-residential building construction market in the United States.
We cannot do much to stop the hyperbolically rising cost of administrative functionaries but we can force the incumbents we describe in our ABOUT to work a little harder to reduce un-used (or un-useable) space and reduce maintenance cost. Sometimes simple questions result in obvious answers that result in significant savings.
More recently hybrid teaching and learning space, owing the the circumstances of the pandemic, opens new possibilities for placing downward pressure on cost.
Regulation or Money-Laundering?
After Architect-Engineers and Building Construction Contractors (many of whom finance election advocacy enterprises) the following organizations are involved in placing a bond on the open market:
- School Districts: Individual school districts issue bonds to fund construction or renovation of school facilities, purchase equipment, or cover other educational expenses. Each school district is responsible for managing its own bond issuances.
- Colleges and Universities: Higher education institutions, such as universities and colleges, issue bonds to finance campus expansions, construction of new academic buildings, dormitories, research facilities, and other capital projects.
- State-Level Agencies: Many states have agencies responsible for overseeing and coordinating bond issuances for schools and universities. These agencies may facilitate bond sales, help ensure compliance with state regulations, and provide financial assistance to educational institutions.
- Municipal Finance Authorities: Municipal finance authorities at the state or local level often play a role in facilitating bond transactions for educational entities. They may act as intermediaries in the bond issuance process.
- Investment Banks and Underwriters: Investment banks and underwriters assist educational institutions in structuring and selling their bonds to investors. They help determine bond terms, market the bonds, and manage the offering.
- Bond Counsel: Bond counsel, typically law firms, provide legal advice to educational institutions on bond issuances. They help ensure that the bond issuance complies with all legal requirements and regulations.
- Rating Agencies: Rating agencies, such as Moody’s, Standard & Poor’s, and Fitch Ratings, assess the creditworthiness of the bonds and assign credit ratings. These ratings influence the interest rates at which the bonds can be issued.
- Investors: Various institutional and individual investors, including mutual funds, pension funds, and individual bond buyers, purchase school and university bonds as part of their investment portfolios.
- Financial Advisors: Financial advisory firms provide guidance to educational institutions on bond issuances, helping them make informed financial decisions related to borrowing and debt management.
- Regulatory Authorities: Federal and state regulatory authorities, such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and state-specific agencies, oversee and regulate the issuance of bonds to ensure compliance with securities laws and financial regulations.
These organizations collectively contribute to the process of issuing, selling, and managing school and university bonds in the United States, allowing educational institutions to raise the necessary funds for their capital projects and operations. The specific entities involved may vary depending on the size and location of the educational institution and the nature of the bond issuance.
Bond issuances affect local property values.