Author Archives: mike@standardsmichigan.com
- Home
- Articles posted by mike@standardsmichigan.com (Page 31)

Baked Potato Strips
Maine Major Capital School Construction Programs | Maine Farm Safety Programs
Maine Extension Homemakers Newsletter, January-February-March 2025
Our volunteers are busy, 78.3% of our volunteers serve other organizations.
Maine 4-H Volunteers, where else do you volunteer?
FMI on how you can give a little or give a lot of your time: https://t.co/9CZycRe80H #NE4HVolunteer
N E Reg Vol Impact Survey, 2020 pic.twitter.com/8q6MSEGfYj— UMaine Extension (@UMaineExtension) April 22, 2022
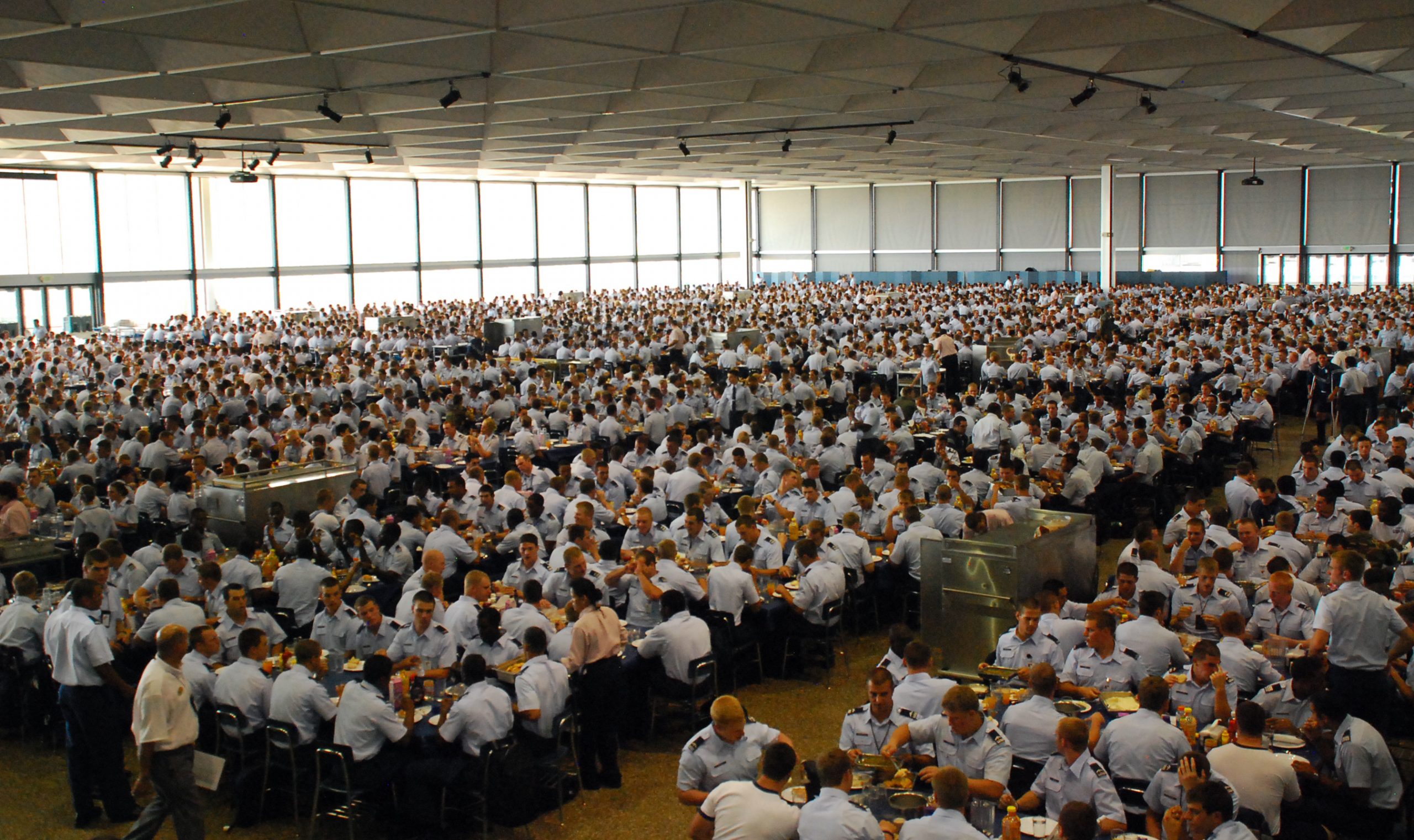
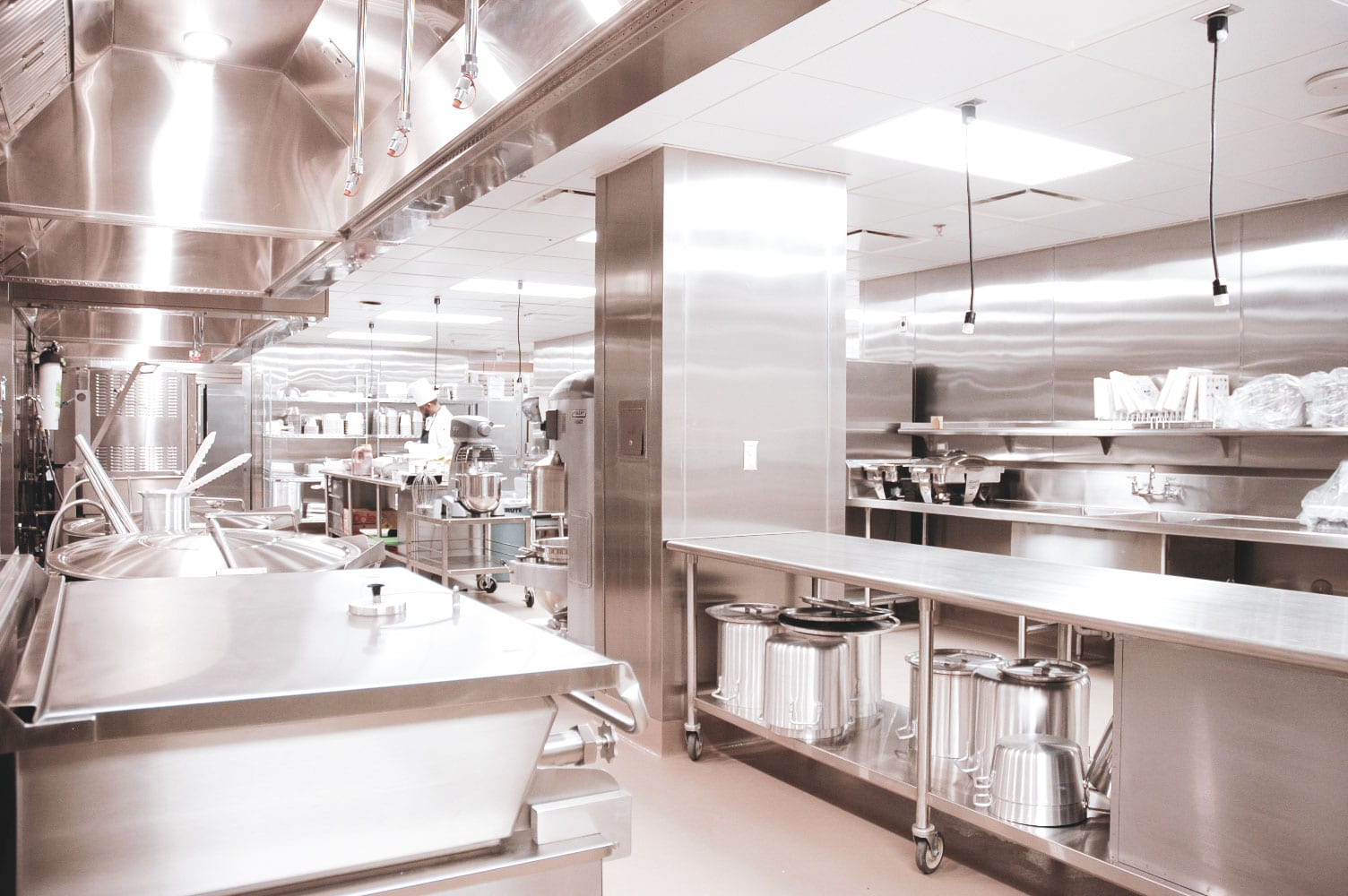
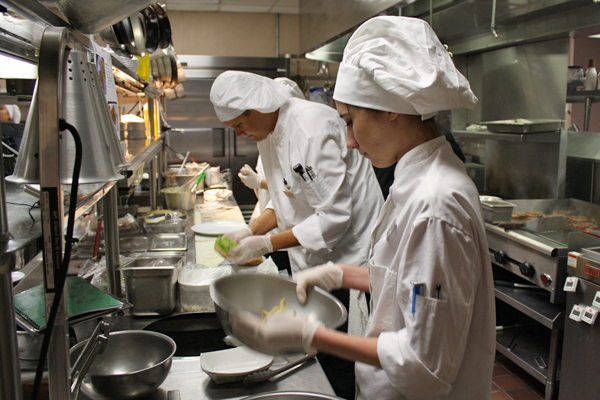
Kitchens 300
Commercial kitchens in school cafeterias and college dormitories are designed to meet strict health and safety standards, accommodate high-volume food production, and provide nutritious meals to students in an efficient and organized manner. Some common features:
- Industrial-grade cooking equipment: This may include commercial ovens, grills, ranges, fryers, steamers, and other specialized cooking equipment designed for high-volume cooking.
- Food preparation areas: These may include spacious prep tables, cutting boards, sinks, and other food preparation stations for washing, chopping, and assembling ingredients.
- Walk-in refrigerators and freezers: These are used for storing large quantities of perishable food items at appropriate temperatures to maintain freshness and safety.
- Food storage facilities: These may include shelves, racks, and cabinets for storing dry goods, canned goods, and other non-perishable food items.
- Dishwashing area: This may include commercial dishwashers capable of handling a large number of dishes and utensils efficiently.
- Serving stations: These may include counters, warming stations, and other facilities for serving food to students.
- Ventilation and exhaust systems: These are essential for maintaining a clean and safe kitchen environment by properly removing smoke, steam, and odors generated during cooking.
- Safety features: These may include fire suppression systems, emergency exits, and other safety measures to ensure compliance with local health and safety regulations.
Owing to the complexity of the domain, starting 2023 we will break down the standards for education community safety and sustainability into two separate colloquia:
Kitchens 100 will deal primarily safety — fire, shock hazard, sanitation, floors, etc.
Kitchens 300 will deal with sustainability criteria in large commercial kitchens common in school cafeterias, dormitories, sports venues and hospitals.
Owing to the complexity of the domain, starting 2023 we will break down the standards for education community safety and sustainability into two separate colloquia:
Kitchens 100 will deal primarily safety — fire, shock hazard, sanitation, floors, etc.
Kitchens 300 will deal with sustainability criteria in large commercial kitchens common in school cafeterias, dormitories, sports venues and hospitals.
Relevant catalogs:
3-A Sanitary Standards
AGA Response to The Atlantic Article about Natural Gas Cooking
ASHRAE International
Ventilation for Commercial Cooking Operations
ASTM International
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
Noteworthy Research:
Design Application of Smart Kitchen for Aging Based on Interactive Behavior Analysis
A Futuristic Kitchen Assistant – Powered by Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
Environmental analyses of waste cooking oil recycling and complete use practices in Bogor, Indonesia
IAPMO International
Prefabricated Gravity Grease Interceptors
International Code Council
International Building Code Sections 303 Commercial Kitchens
National Fire Protection Association
National Electrical Code
Standard for the Installation of Air-Conditioning and Ventilating Systems
The Association for Packaging and Processing Technologies
We will also review federal and state-level regulatory action. Open to everyone. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
Related:
Kitchen Exhaust
God walks among the pots and pans.
— Saint Teresa of Ávila c.1582
One of the concentrated risk aggregations in any school district, college, university and technical school, athletic venues and university-affiliated healthcare systems, rests in the food preparation units. On a typical large research university there are hundreds of kitchens in dormitories, student unions, athletic venues, hospitals and — to a surprising degree — kitchen facilities are showing up in classroom buildings. Kitchens that used to be located on the periphery of campus and run by private industry are now moving into instructional spaces and operated by private food service vendors.
Food preparation facilities present safety challenges that are on the same scale as district energy plants, athletic concession units, media production facilities and hospital operating rooms. There are 20 accredited standards setting organizations administering leading practice discovery in this space. Some of them concerned with fire safety; others concerned with energy conservation in kitchens, still others concerned with sanitation. The International Kitchen Exhaust Cleaning Association is one of the first names in this space and maintains an accessible standards development home page; linked below:
The IKECA catalog of titles establish a standard of care for cleaning activity that fills gaps in related ASHRAE, ASME, ICC and NFPA titles. For example:
IKECA I10 Standard for the Methodology for Inspection of Commercial Kitchen Exhaust Systems
IKECA C10 Standard for the Methodology for Cleaning Commercial Kitchen Exhaust Systems
Hazards posed by un-maintained exhaust systems are covered in the NFPA Report: Structure Fires in Eating and Drinking Establishments
We encourage subject matter experts in food enterprises in the education industry to communicate directly with John Dixon at IKCEA (jdixon@fernley.com) or Elizabeth Franks, (215) 320-3876, information@ikeca.org, International Kitchen Exhaust Cleaning Association, 100 North 20th Street, Suite 400, Philadelphia, PA 19103.
We are happy to get specific about how the IKECA suite contributes to lower education community cost during our Food teleconferences. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [18-24]
Category: Facility Asset Management
Colleagues: Larry Spielvogel, Richard Robben
LEARN MORE:
Dormitories, Fraternities, Sororities and Barracks
Keele University “Look When You Cook”
Commercial Kitchen Ventilation
Traps, Interceptors and Separators
Commercial Kitchens
2025 GROUP B PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES: Complete Monograph (2630 pages)
36 kitchen related proposals were reviewed during our precious sesssion
2024 GROUP A PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES: Complete Monograph (2658 pages)
Commercial kitchens offer several benefits, such as efficient food preparation and large-scale production, allowing businesses to meet high demand. They provide professional-grade equipment and ample space, enabling chefs to explore culinary creativity. Commercial kitchens also promote hygiene and food safety standards, with dedicated cleaning protocols and inspections. However, hazards can arise from the high-temperature cooking equipment, sharp tools, and potentially hazardous substances. There is also a risk of burns, slips, and falls, emphasizing the importance of proper training and safety measures. Adequate ventilation and fire safety systems are vital to prevent accidents and maintain a healthy working environment.
The International Code Council is re-configuring its code development process in nearly every dimension. While that situation stabilizes let us review the back-and-forth on this topic during the previous revision cycle (linked below):
2021 International Building Code Section 306 Factory Group F Moderate Hazard
2021 International Fire Code Section 606 Commercial Cooking Equipment and Systems
The International Code Council has recently re-configured its code development calendar:
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
Public hearings on the proposed changes happen in Orlando, April 7-16.
This is a summary of the actions taken on the 2024 Comments on Proposed Changes to the ICC International Codes at the October 23-28, 2024 Committee Action Hearings #2 held at the Long Beach Convention Center, Long Beach, California. Balloting of local building code officials is now underway.
Commercial kitchen electrical power wiring requirements are covered extensively in Article 210 through Article 215 of the National Electrical Code. Standards action in this domain is referred to IEEE Education & Healthcare Facility Committee.
ASHRAE International: Calculating Airflow Rates, Cooking Loads in Commercial Kitchens
Related
International Mechanical Code: Chapter 10 Boilers, Water Heaters and Pressure Vessels
AGA Response to The Atlantic Article about Natural Gas Cooking
Thomas Edison State University: Undergraduate Certificate in Gas Distribution
Teaching Kitchen
Net Position: $393.3M (Page 13)
Behind the scenes of our Falcon Family holiday photo.. we’ve all been there 🎥👀 pic.twitter.com/5d2907GoPn
— Bowling Green State University (@bgsu) December 12, 2025
Ventilation for Commercial Cooking Operations
Kitchen cooking ranks high as the causes of fire hazard in the built environment. ASHRAE 154 provides design criteria for the performance of commercial cooking ventilation systems. Education communities have hundreds of food preparation enterprises in school districts, residence halls, hospitals and athletic venues. It is not intended to circumvent any safety, health or environmental requirement; however we find a fair amount of drama regarding the competing requirements of fire safety and sustainability among subject matter experts. The stabilized version is dated 2022.
A noteworthy title in the ASHRAE standards catalog is ASHRAE 154 Ventilation for Commercial Cooking Operations. Food preparation enterprises in school districts, residence halls, hospitals and athletic venues and central features in education communities. Access to the 2022 edition is linked below:
The purpose of ASHRAE 154 is to provide design criteria for the performance of commercial cooking ventilation systems. It covers kitchen hoods, exhaust systems and replacement air systems, It is not intended to circumvent any safety, health or environmental requirement; however we find a fair amount of drama between partisans of air movement controls and energy conservation interests. Fire safety and the sustainability advocates are well funded voices.
There are no open consultations at the moment; but you may track release of any at the link below:
Public Review Draft Standards / Online Comment Database
Titles in the ASHRAE catalog move swiftly; many of them consultations lasting less than 45 days.
Interior environmental air safety is a concern that cuts across many professional disciplines. Accordingly, we maintain this title on the standing agendas of several colloquia — Mechanical Engineering, Energy and Housing. Starting 2022 we will break out this the subject of a separate, dedicated colloquium See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [14-92]
Category: Mechanical, Electrical, Energy, Facility Asset Management
Colleagues: David Conrad, Richard Robben, Larry Spielvogel
Kitchen cooking ranks high as the causes of fire hazard in the built environment. ASHRAE 154 provides design criteria for the performance of commercial cooking ventilation systems. Education communities have hundreds of food preparation enterprises in school districts, residence halls, hospitals and athletic venues. It is not intended to circumvent any safety, health or environmental requirement; however we find a fair amount of drama regarding the competing requirements of fire safety and sustainability among subject matter experts. The stabilized version is dated 2022.
Children’s Rights Management
The Icelandic Standards Body has proposed a new ISO standard: Children’s rights management (Page 45). Public comment will be received until December 10th.
Icelandic Standards Children’s Rights Management Proposal
(Our response to ANSI at the bottom of this page)
December 12, 2025
Dear Madeline, Sara and Rachel:
Hope all is well.
Thank you for the opportunity to comment on this proposal. This statement is our formal recommendation that ANSI find a way for the USA to participate. If you need this recommendation on our letterhead please let me know. I am happy to discuss over the phone at your convenience, also.
The recommendations listed below are informed by University of MIchigan and Standards Michigan engagement with ANSI and ISO for the better part of twenty years*. I, personally, have met with ISO staff several times in Geneva over the past 20 years and have been graciously received. I admire their processes and integrity of purpose.
Now, after having read the Business Plan, just a few bullet points:
-
The boundaries between children’s rights and education will quickly become fuzzy. The length of the list of incumbent references in the Business Plan reveals a requirement for cross-cultural sensitivities.
-
A US TAG will need substantial funding — usually a high bar for non-profits but less so for for-profit manufacturers, insurance companies, inspection and compliance. The mortality rate of ANSI TAGs, from our point of view, seems high.
-
Viability of the project – using successful ISO work on Quality Control, for example – will have to track in regulations that fund compliance revenue. It will take decades, at best half decades, for that to happen.
Looks like a lot of meetings. We applaud Icelandic leadership.
Hope this helps // Mike
xc: Christine Fischer
* List of ISO projects The University of Michigan and Standards Michigan has been involved with since about 2010.
ISO/IEC JTC 4 Smart and sustainable cities and communities • ISO/TC 48 Laboratory equipment • ISO/TC 205 Building environment design • ISO/TC 232 Education and learning services • ISO/TC 260 Human resource management • ISO/TC 267 Facility management • ISO/TC 292 Security and resilience • ISO/TC 301 Energy management and energy savings ISO/TC 304 Healthcare organization management • ISO/TC 336 Laboratory design
• INCITS ISO/IEC/JTC electrotechnology committees
Also: See our ABOUT
Eurocodes
Erasmus+ EU programme for education, training, youth and sport
The Eurocodes are ten European standards (EN; harmonised technical rules) specifying how structural design should be conducted within the European Union. These were developed by the European Committee for Standardization upon the request of the European Commission. The purpose of the Eurocodes is to provide:
- A means to prove compliance with the requirements for mechanical strength and stability and safety in case of fire established by European Union law.[2]
- A basis for construction and engineering contract specifications.
- A framework for creating harmonized technical specifications for building products (CE mark).
Since March 2010 the Eurocodes are mandatory for the specification of European public works and are intended to become the de facto standard for the private sector. The Eurocodes therefore replace the existing national building codes published by national standard bodies, although many countries have had a period of co-existence. Additionally, each country is expected to issue a National Annex to the Eurocodes which will need referencing for a particular country (e.g. The UK National Annex). At present, take-up of Eurocodes is slow on private sector projects and existing national codes are still widely used by engineers.
Eurocodes appear routinely on the standing agendas of several of our daily colloquia, among them the AEDificare, Elevator & Lift and Hello World! colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
So proud to announce the @ellisoninst is beginning construction on our new campus at the @UniofOxford and broadening our mission: Science & Engineering for Humanity. EIT develops & deploys technology in pursuit of solving four of humanity’s most challenging & enduring problems.… pic.twitter.com/vSkHWSS8EK
— David Agus (@DavidAgus) October 15, 2023
More
REGULATION (EU) No 305/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
Global Consistency in Presenting Construction & Life Cycle Costs
Research from the World Economic Forum has shown that improvements in the design and construction process can be achieved by using international standards like ICMS to gain comparable and consistent data. ICMS provides a high-level structure and format for classifying, defining, measuring, recording, analysing and presenting construction and other life-cycle costs.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670