Despite the name given to this ISO technical committee blockchain and distributed ledger technology are related concepts but they are not exactly the same thing.
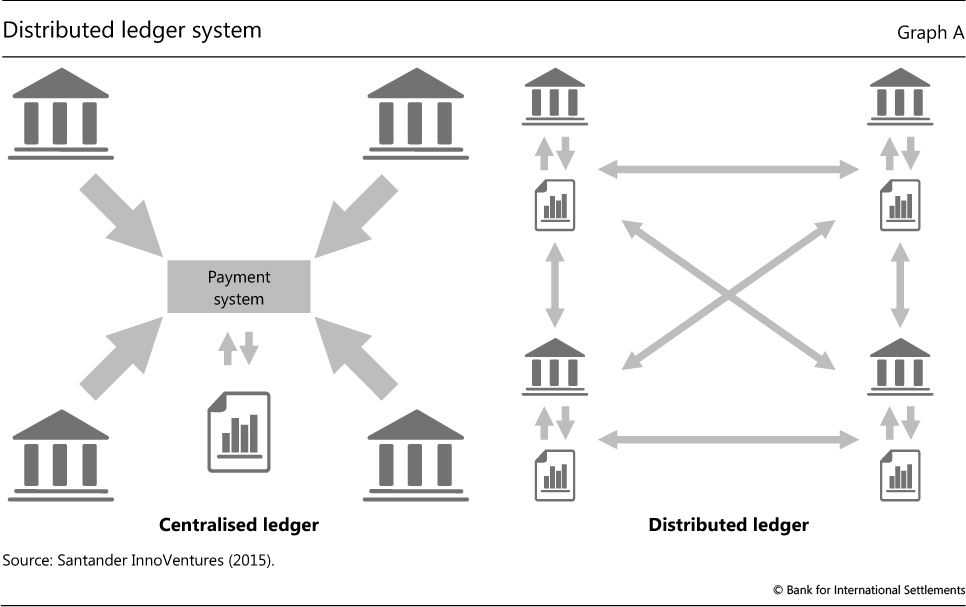
• A distributed ledger is a database that is spread across a network of computers or nodes, where each node has a copy of the same database. When a new transaction is made on the network, it is verified by multiple nodes and added to the ledger, which creates a permanent and tamper-evident record of the transaction.
• Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that uses blocks of transactions that are linked together in a chain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, which creates an unbreakable link between the blocks. This creates a tamper-evident and secure ledger that is resistant to modification.
While blockchain is a specific type of distributed ledger, not all distributed ledgers use blockchain technology. Other types of distributed ledgers include directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), Hashgraph, Holochain and Cordo.
The key difference between blockchain and distributed ledger technology is that blockchain is a specific type of distributed ledger that uses blocks of transactions that are linked together in a chain, whereas distributed ledger technology refers to any database that is spread across a network of computers or nodes.
Blockchain technology is changing the financial underpinnings of all economic sectors including the education industry in every nation. Accordingly, the International Standardization Organization has set up a relatively new technical committee — ISO/TC 307, blockchain and distributed ledger technologies — to meet the need for standardization in this area by providing internationally agreed ways of working with blockchain and distributed ledger technology to improve security, privacy and facilitate worldwide use of the technology through the highest possible level of interoperability.
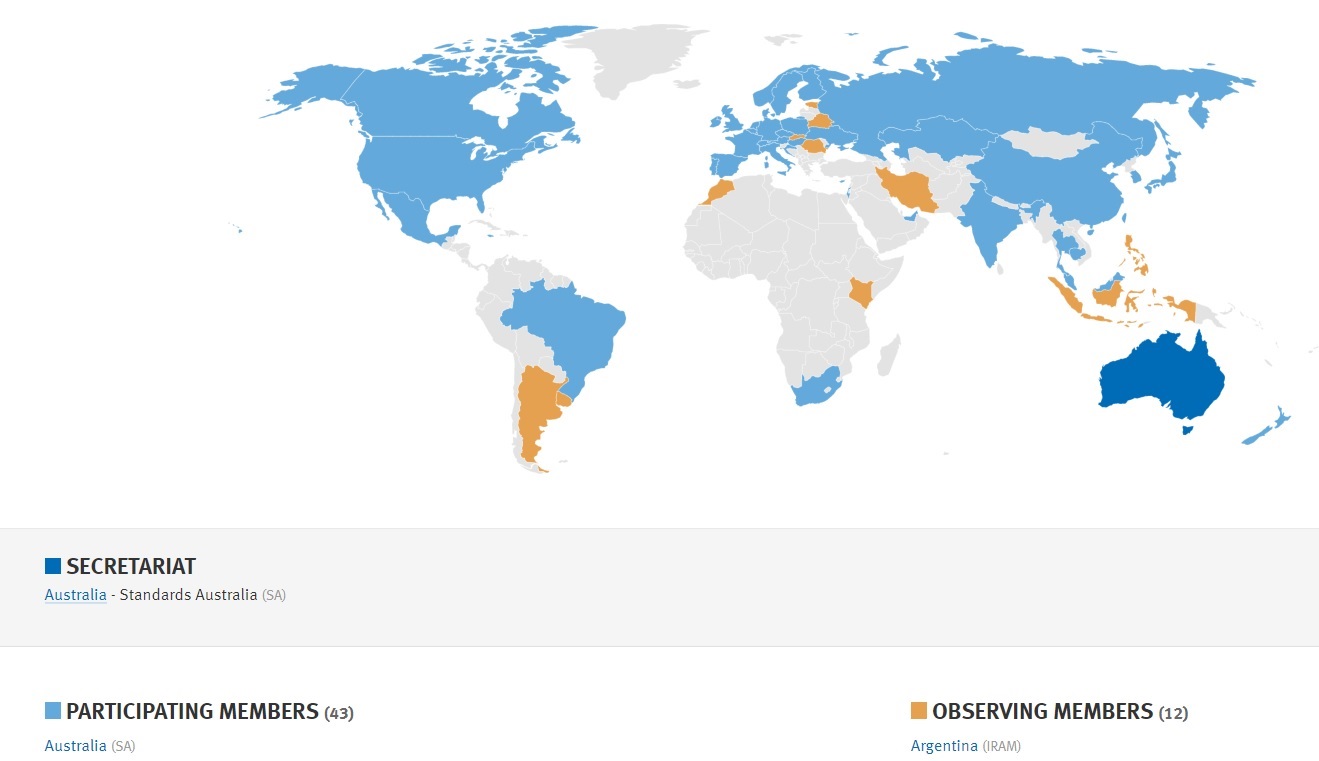
The consensus products emerging TC 307 will be relevant not only to not only education industry trade associations who claim an educational/accreditation mission but to college and university marketing departments that can, and should be interested in the ISO 307 products if for no other reason than to secure their claim to mastery of (in the argot of the moment) the most “woke” technologies for students and parents. The executive summary and global participation map is linked below:
STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLAN ISO/TC 307
In our 20+ year engagement with ANSI accredited standards-setting organizations; and nearly 20-year involvement in international standards promulgated by the ISO, IEC and ITU, we find early drafts of international standards are fairly dilutive; owing to the need to find agreed-upon definitions and the need to assemble an informed, durable and funded group of subject matter experts that can withstand the long-haul. A few of the focus areas we recommend for leaders of the US #WiseCampus zietgeist are listed below:
- Legally binding smart contracts
- Interactions between smart contracts in blockchain and distributed ledger technology systems
- Discover issues related to interoperability
- Guidelines for governance
The public working area identifies committee activity during October-November; characteristic of early-stage ISO product development. US stakeholders — which should include education communities — should communicate directly with INCTIS.
Standards Australia is the Global Secretariat. Our US colleagues are encouraged to communicate directly with ANSI’s ISO Team and/or the Chair of the US Technical Advisory Group InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS) 1101 K Street NW, Suite 610, Washington, DC 20005, Phone: (202) 626-5737. This standard is on the standing agenda of each of our Blockchain, Global, Infotech and Finance colloquia. See our CALENDAR.
Issue: [17-351]
Category: Finance & Management, International
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Christine Fischer, Jack Janveja, Richard Robben
LEARN MORE: