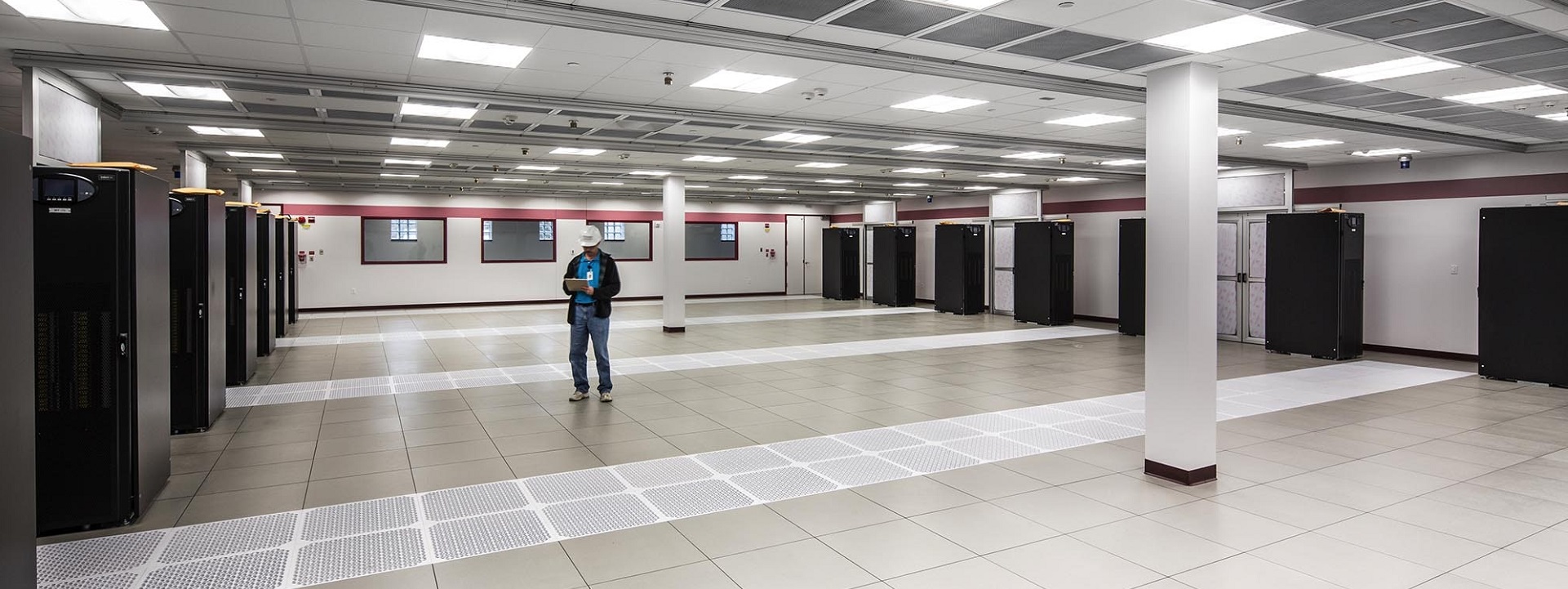
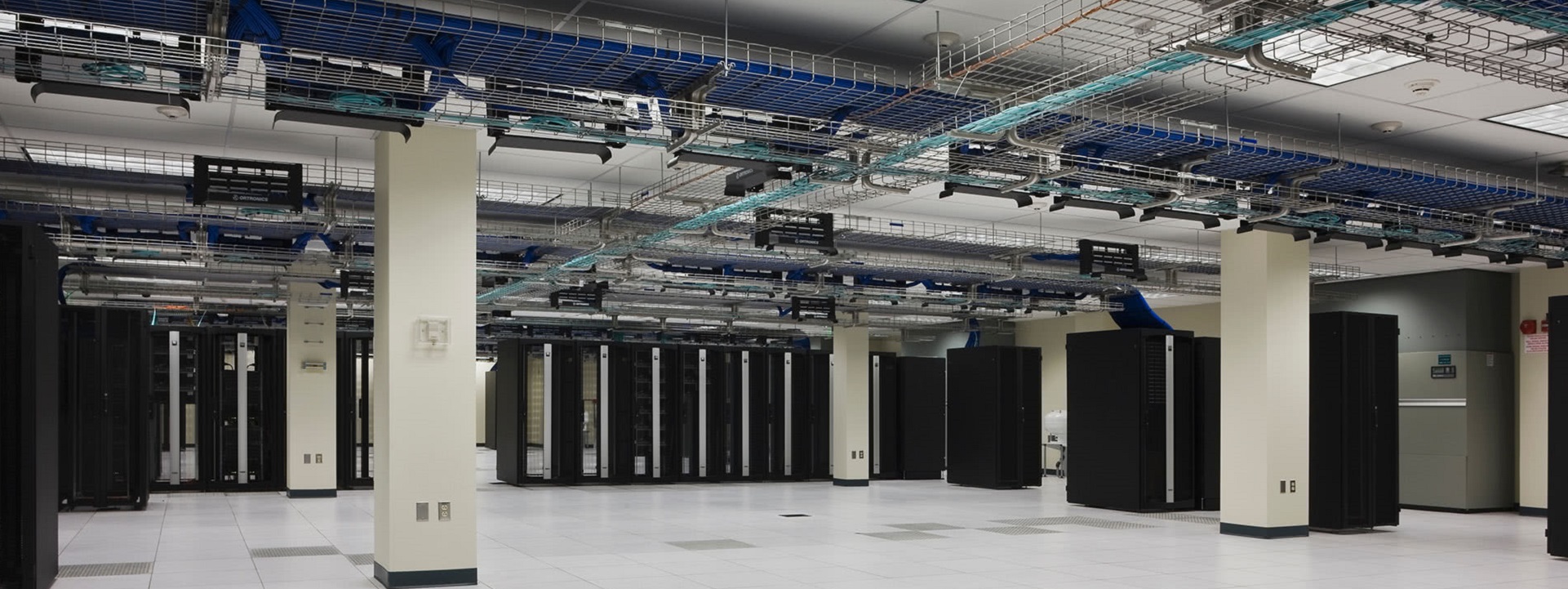
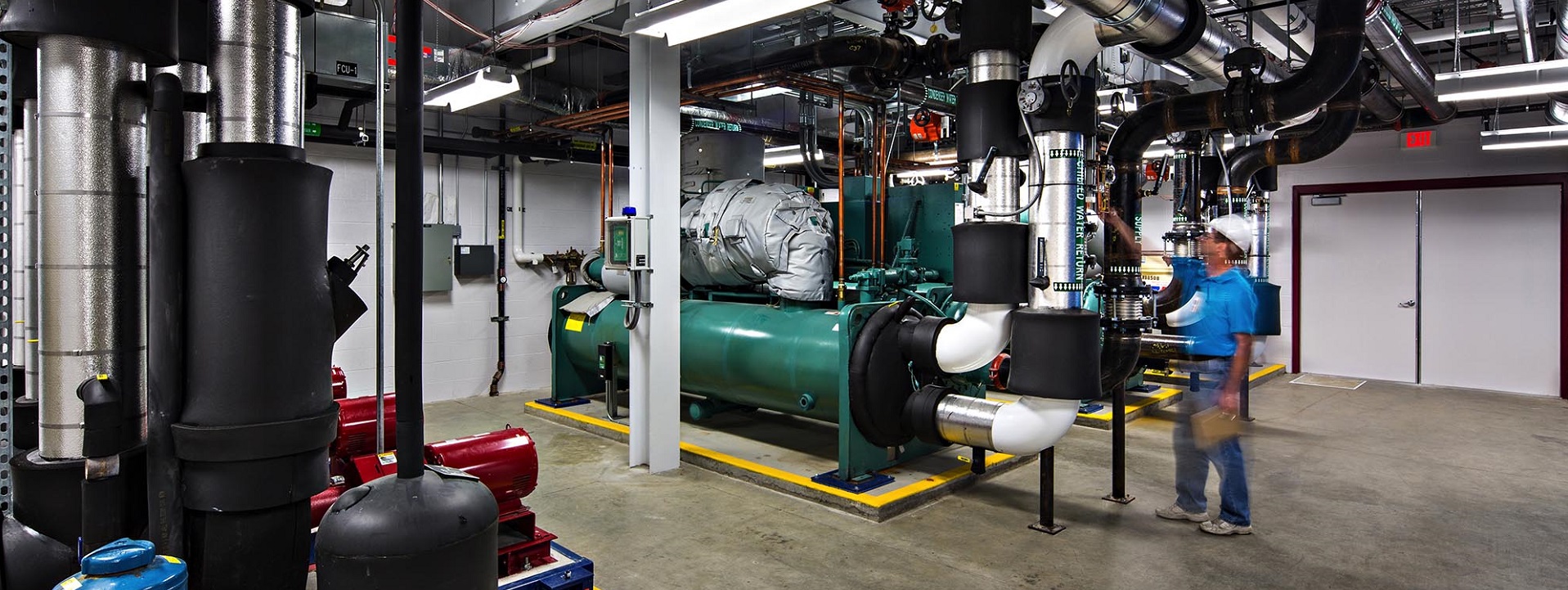
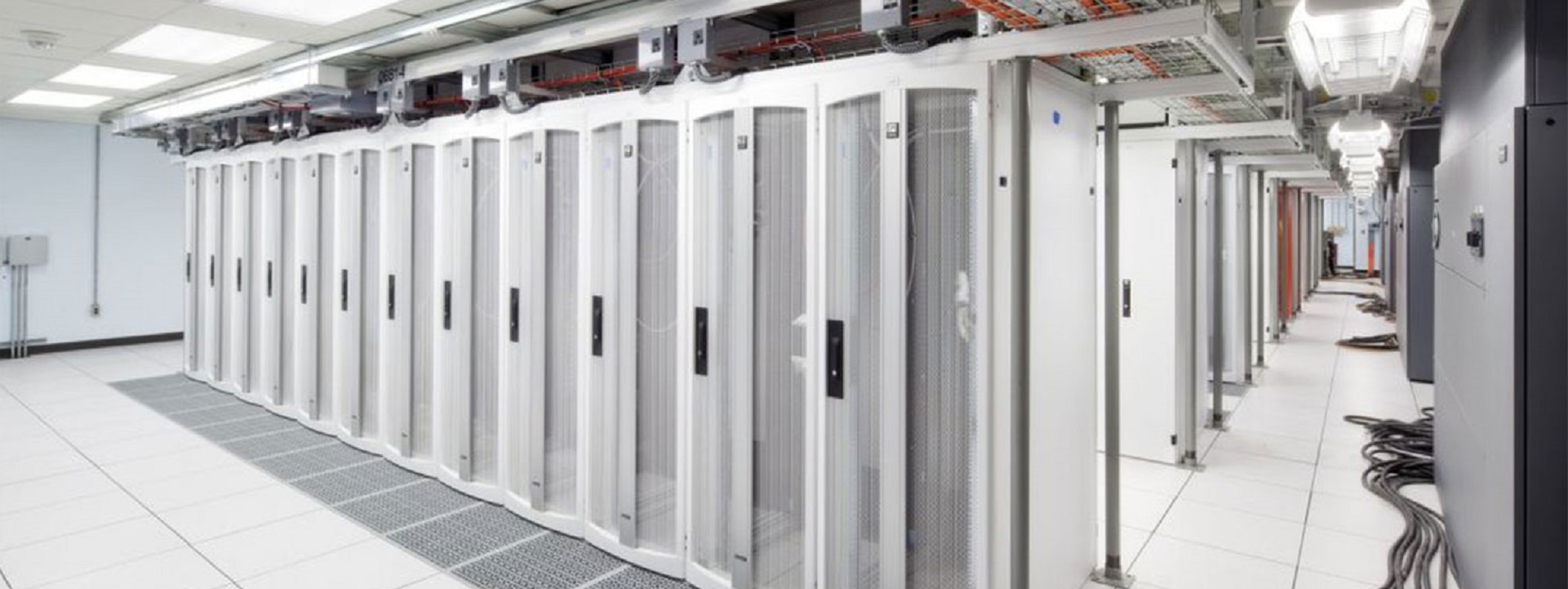
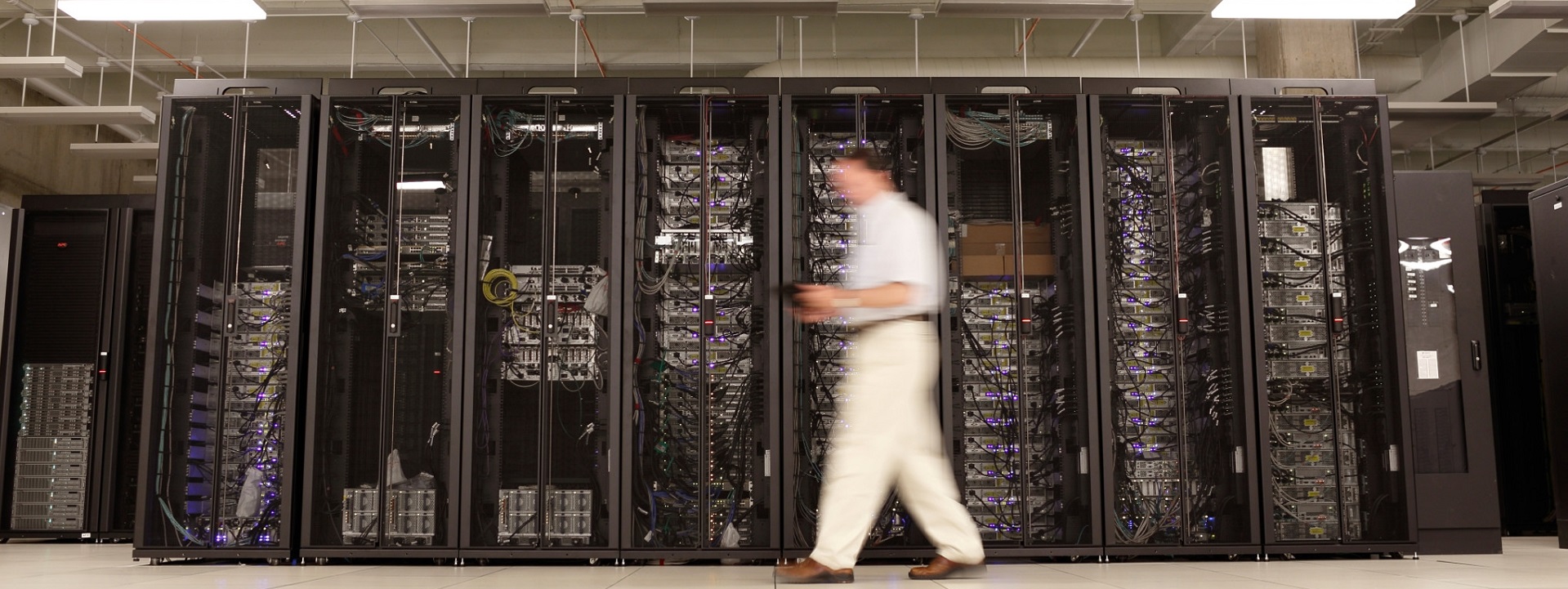
Data centers in colleges and universities are crucial for supporting the extensive technological infrastructure required for modern education and research. These centers house critical servers and storage systems that manage vast amounts of data, ensuring reliable access to academic resources, administrative applications, and communication networks. They enable the secure storage and processing of sensitive information, including student records, faculty research, and institutional data.
Uptime Institute Tier Classification
Moreover, data centers facilitate advanced research by providing the computational power needed for data-intensive studies in fields like bioinformatics, climate science, and artificial intelligence. They support virtual learning environments and online course management systems, essential for the increasingly prevalent hybrid and online education models. Efficient data centers also contribute to campus sustainability goals by optimizing energy use through modern, eco-friendly technologies.
ANSI/TIA 942 Data Center Infrastructure Standard
Additionally, robust data center infrastructure enhances the university’s ability to attract top-tier faculty and students by demonstrating a commitment to cutting-edge technology and resources. They also play a vital role in disaster recovery and business continuity, ensuring that educational and administrative functions can resume quickly after disruptions. Overall, data centers are integral to the academic mission, operational efficiency, and strategic growth of colleges and universities.
We have followed development of the technical standards that govern the success of these “installations” since 1993; sometimes nudging technical committees — NFPA, IEEE, ASHRAE, BICSI and UL. The topic is vast and runs fast so today we will review, and perhaps respond to, the public consultations that are posted on a near-daily basis. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
Related:
Ernst & Young LLP: Why there is no silver bullet for data center financing
Power Management For Data Centers Challenges And Opportunities