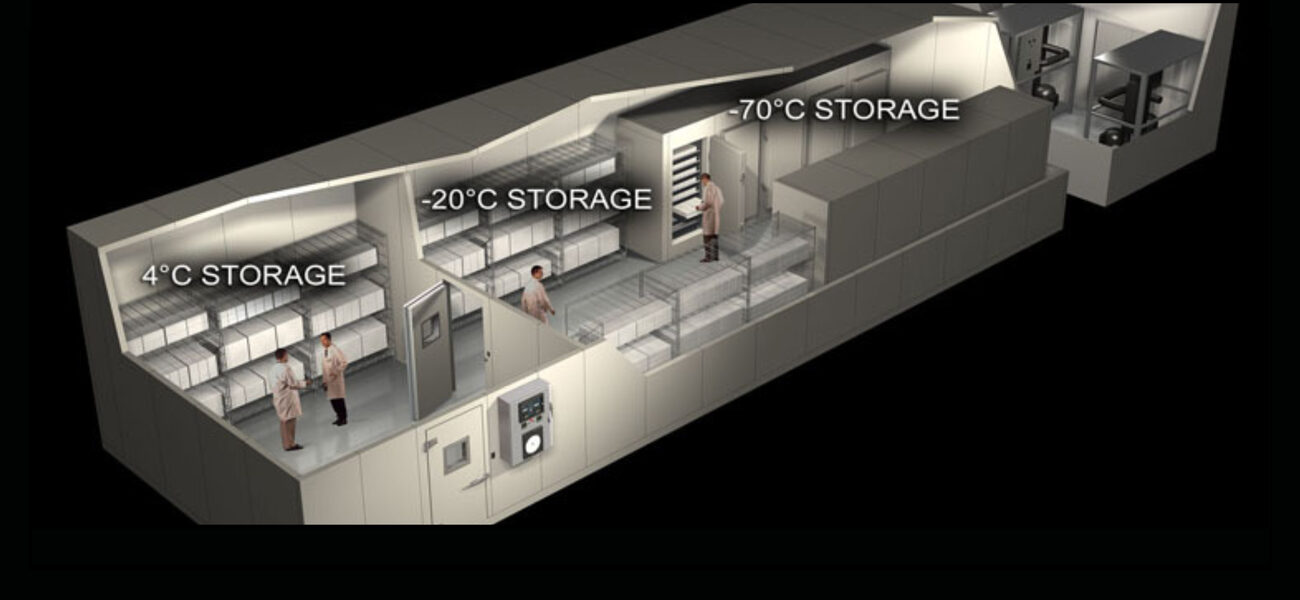
Walk-in refrigerators play a crucial role in food preparation areas in education communities; residence halls, hospitals, research laboratories and large football stadium not the least of them:
- Food Storage: They provide space for perishable foods, such as fruits, vegetables, meats, dairy products, and prepared dishes. They help maintain the freshness and quality of ingredients by keeping them at the appropriate temperature.
- Temperature Control: They allow precise temperature control, ensuring that food items are kept at the correct temperature to prevent spoilage and bacterial growth. Different shelves or zones within the refrigerator can be set to various temperatures to accommodate various types of food.
- Extended Storage: Compared to reach-in refrigerators or freezers, walk-ins offer a larger storage capacity. This is especially beneficial for residential kitchens that need to store bulk quantities of ingredients, prepared dishes, and food supplies.
- Organization: Walk-in refrigerators are designed with shelving, racks, and storage options that enable proper organization of food items. This organization makes it easier for kitchen staff to access ingredients quickly during busy service times.
- Prep Space: In addition to storage, some walk-in refrigerators are equipped with prep tables or counters. This feature allows chefs and kitchen staff to work directly within the cold storage area, making it more convenient to prepare ingredients and assemble dishes.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern walk-in refrigerators are designed with energy-efficient features, including well-insulated panels and energy-efficient compressors, helping to reduce energy consumption and operating costs.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many health and safety regulations require commercial kitchens to store perishable foods at specific temperatures. Walk-in refrigerators are designed to meet these regulatory requirements.
ASHRAE 15 sets the standard of care for safe design, construction, installation and operation of refrigeration systems. It establishes safeguards for life, limb, health, and property and prescribes safety requirements. This standard does not apply to refrigeration systems using ammonia (R-717) as the refrigerant. (ASHRAE Standard 34-2022, Designation and Safety Classification of Refrigerants covers that domain.)
As of this posting we find only one markup on proposed changes to ASHRAE 15; that one having more to do with correlation with changes to the one of the ASME Boiler Code (a lower tier priority for us).
Proposed Addendum a to Standard 15-2022, Safety Standard for Refrigeration Systems
Consultation on that markup closes October 22, 2023.
Other ASHRAE committees post their consultations at the link below:
Online Standards Actions & Public Review Drafts
We maintain the ASHRAE catalog on the standing agenda of nearly every topic we cover every day. See our CALENDAR.
Issue: [Various]
Category: Mechanical, Electrical, Energy Conservation, Facility Asset Management, US Department of Energy, #SmartCampus
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Larry Spielvogel, Richard Robben
The basis for modern refrigerators was created in 1755 AD, when Scottish professor William Cullen designed a small refrigerating machine. This machine had a pump and a container of ether. (24/26) pic.twitter.com/nw7GiSgbIE
— Bucknell_Thermo (@BucknellThermo) April 24, 2020