Bibliography:
Tag Archives: D2/1
- Home
- Posts tagged "D2/1" (Page 2)

Elettrotecnico Lingua Franca
In our collaboration with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee we are sensitive to the point of view of our research and standards setting colleagues in other nations; among them CEN (European Committee for Standardization) and CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization) are two standardization organizations in Europe, and they have some similarities and differences.
- CEN develops standards for a wide range of products, services, and processes, including construction, consumer goods, food and agriculture, and many others.
- CENELEC, on the other hand, focuses specifically on electrotechnical standards, including electrical equipment, electronic components, and telecommunications.
Another key difference between CEN and CENELEC is their membership. CEN has members from 34 European countries, including national standardization bodies, industry associations, and consumer organizations. CENELEC has members from 34 European countries as well, but they are limited to national electrotechnical committees, which are responsible for electrotechnical standardization in their respective countries.
Despite their differences, both CEN and CENELEC play important roles in the development and promotion of European standards, and their standards are widely recognized and used across Europe and beyond. Its leadership committees meet this week in Brussels. CLICK HERE to access videolinks.
We had the pleasure to welcome the new CENELEC President Elect Mr Riccardo Lama at our offices, for a moment to engage with the CEN and CENELEC senior management team and the CEN and CENELEC Presidents Mr Stefano Calzolari and Mr Wolfgang Niedziella.@CEInorme @IECStandards pic.twitter.com/ynk9ViWb60
— CEN and CENELEC (@Standards4EU) January 17, 2024
Electropedia: The World’s Online Electrotechnical Vocabulary
Topology of Continuous Availability for LED Lighting Systems
Topology of Continuous Availability for LED Lighting Systems
Giuseppe Parise – Marco Allegri
Luigi Parise
Raffaele Pennacchia – Fabrizio Regoli
Giorgio Vasselli
Abstract: Lighting systems with a big number of luminaires in large halls are a case of distributed loads that need topologies with modularity, whenever possible to ensure a uniform distribution of the supplying circuits, an easier installation, management, and maintenance. The light emitting diode (LED) luminaires give a great impact on the system operation due to their auxiliary series devices and to the high inrush currents of the ac-dc switching power supplies. This article proposes a topology to design LED lighting systems, configured in a modular scheme of a main ac distribution and a branch dc distribution supplying luminaires clusters. Each cluster is provided as a “double-dual corded” equipment with double power supply and double control type, digital, and analogic. The suggested topology aims to make available a system that allows overcoming fault situations by design and permits maintenance activities limiting and recovering degradation conditions. In this way, the lighting system of special locations, for which there is the willingness-to-accept greater financial costs against loss service risks, can satisfy the requirement of continuous availability system. To provide more details on the proposed design criteria this article describes, as case study, the lighting system of a parliamentary hall with one thousands of luminaires.
CLICK HERE to order complete paper
https://t.co/NumxiedKbR
print(“Illumination”)@beatricedegraaf @UniofOxford pic.twitter.com/DBIvns5k4K— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) February 17, 2022
Enhancing the Sustainability of Outdoor Floodlighting for Cultural Heritage Buildings
Enhancing the Sustainability of Outdoor Floodlighting for Cultural Heritage Buildings
Matej B. Kobav, et al
Faculty of Electrical engineering, University of Ljubljana Slovenia
Abstract: Improperly lit architectural heritage sites contribute to intrusive light, impacting the environment. To combat this, a methodology using specialized luminaires with silhouette-based aperture was implemented during the renovation of Slovenian churches. By precisely directing light and minimizing spillage, this approach significantly reduced intrusive light. Real-life example of the Church of St. Thomas exemplifies its success. Such sustainable strategies ensure the preservation of cultural heritage while minimizing environmental impact.
Related:
Principles of Energy Saving in Buildings. A Survey
Smart Grid Blockchains
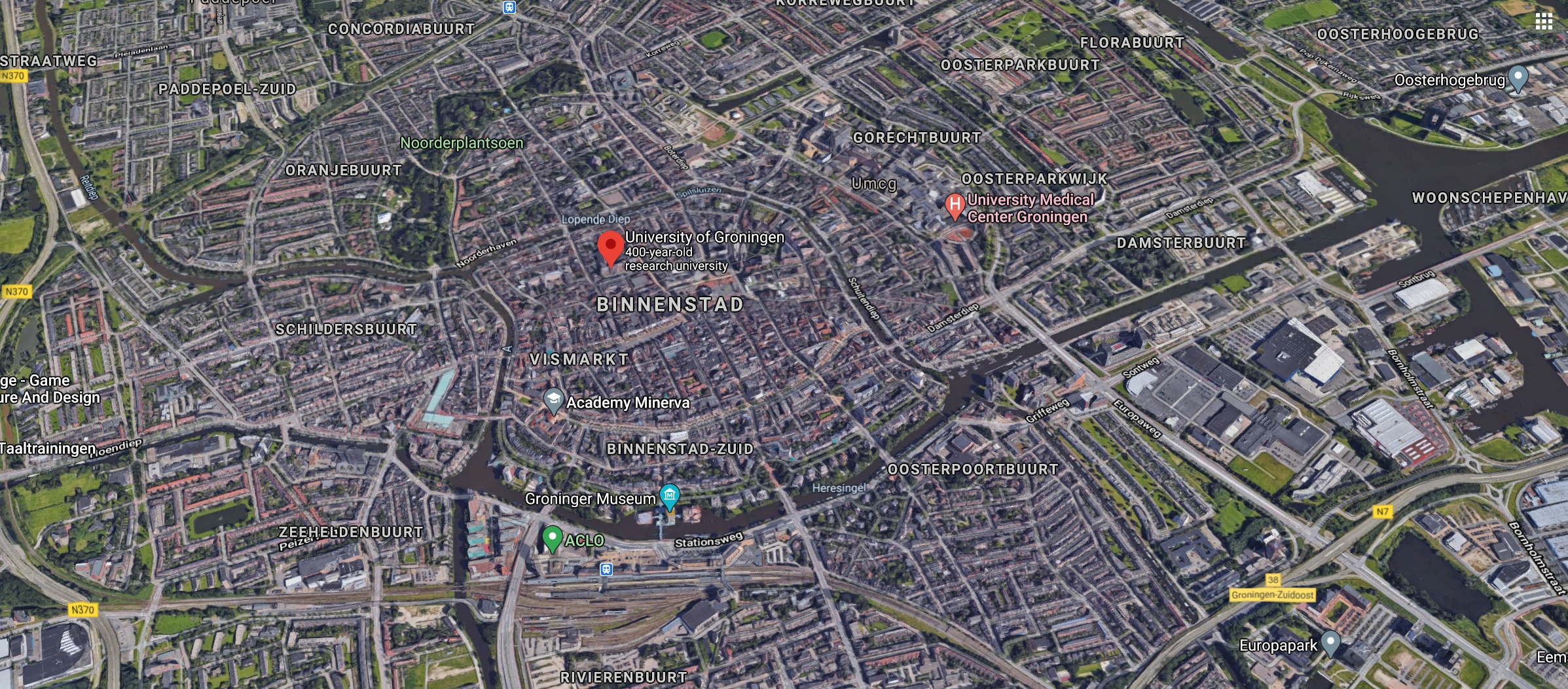
Department of European and Economic Law and Groningen Centre of Energy Law
Building Electrical Wiring Based on Microsystem Criteria
Electrical Distribution Systems Based on Microsystem Criteria
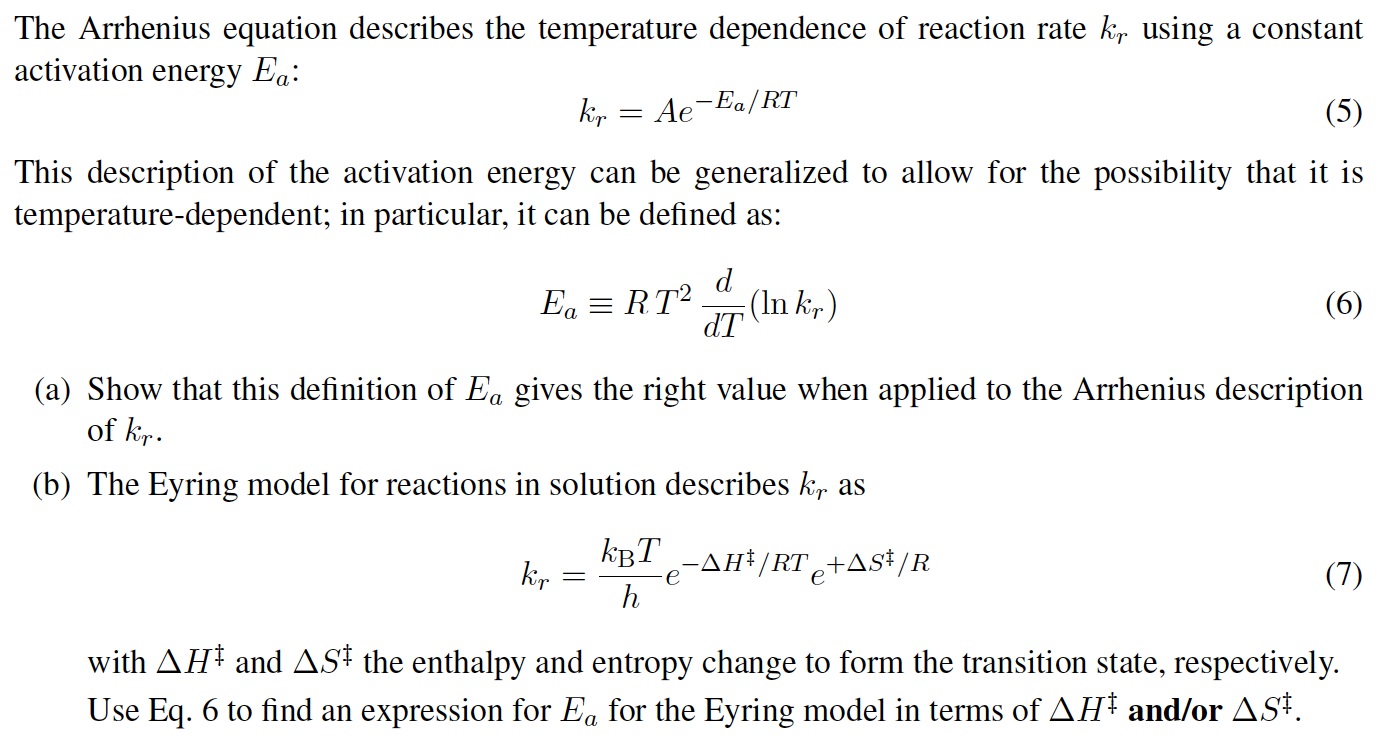
This paper deals with an innovative design strategy of building power systems by introducing criteria based on both the “installation approach” and the “operating approach” applying plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle. The In-Op design of the electrical power systems takes care of the worst cases of configurations, adequate gaps on load in selecting the rating of components, the actual mean losses to evaluate their energetic operation, and to avoid excessive gaps on the lifetime of components. With this aim, the authors suggest consideration of the thermal aging model of Arrhenius to review the actual gap on load in selecting the rating of components. In reference to IEC standards, this paper underlines in the circuits design the cable steady and transient current densities, the load current torque density as “natural” parameters that allow applying a thumb rule in the classic sizing of the cross-sectional area of circuit conductors. Microsystem criteria in power systems design allow structuring their configuration with components of smaller size to reduce radically the volume of circuit conductors with more sensitive results in the branch distribution. The authors suggest why not reconsider the series of commercial cross section areas of power cables.
This paper was presented at the IEEE Industrial Applications Society meetings in 2015 and is now available in IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications ( Volume: 54 , Issue: 1 , Jan.-Feb. 2018 ). The authors revisit the first principles of conductor ampacities and conclude by asking a question: What Innovations Without Cultural Changes?
In the United States, and most of North America, the National Fire Protection Association has the largest platform, and the longest history in electrical power engineering for buildings. In other words: the conversation about electrical safety within buildings is informed by the perspective of fire safety professionals. In Europe, not so much. The inspiration for European electrical safety is found in a shock protection.
The IEEE effectively ceded administration of building electrical safety to the NFPA and spent decades providing the platform for leading practice discovery for electrical power generation and distribution outside buildings — i.e. public utilities. In retrospect this “division of labor” roughly follows the money flows to and from manufacturers and insurance companies.
The cultural question raised in the paper is reproduced, in part, below:
“…For an actual safety program, a comparative analysis of international electrical approaches on distribution systems will facilitate an understanding of their similarities and differences and will promote the design of new equipment of high efficiency like AM Transformers and new integrated common solutions, like a new series of commercial cross section areas of the power cables efficient for reducing conductors volume in balance with the costs….”
We collaborate closely with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee which meets 4 times monthly in European and American time zones. Risk managers, electrical safety inspectors, facility managers and others are welcomed to click into those teleconferences also. We expect that concepts and recommendations this paper will find their way into future revisions of US and international electrical safety codes and standards.
Issue: [19-129]
Category: Electrical, Facility Asset Management, Fire Safety, International
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Christel Hunter, Giuseppe Parise, Luigi Parise
Virtual Power Plant Data
Simulation Concept of a Virtual Power Plant Based on Real-Time Data Acquisition
Presented at 2019 54th International Universities Power Engineering Conference
David-Cătălin Urcan
University Politehnica, Bucharest, Romania
Dorin BicẶ
University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Sciences and Technology of Târgu-Mureç, Romania
Abstract: The paper presents a comprehensive survey on the virtual power plant (VPP) concept. The survey covers the virtual power plant definitions, components, frame work and highlights the different techniques that can be used for VPP operation optimization. At the end of the works will be presented a virtual power plant infrastructure available on a web interface where it will be possible to control a virtual micro-grid that has acquire data from virtual smart meters which provide several load profiles for load consumption and distributed generation points.
CLICK HERE to order complete paper
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670