We have always taken a forward-looking approach to the National Electrical Code (NEC) because there is sufficient supply of NEC instructors and inspectors and not enough subject matter experts driving user-interest ideas into it. Today we approach the parts of the 2023 NEC that cover wiring safety for microgrid systems; a relatively new term of art that appropriates safety and sustainability concepts that have existed in electrotechnology energy systems for decades.
Turn to Part II of Article 705 Interconnected Electric Power Production Sources:
Free Access 2023 National Electrical Code
You will notice that microgrid wiring safety is a relatively small part of the much larger Article 705 Content. There were relatively minor changes to the 2017 NEC in Section 705.50 — but a great deal of new content regarding Microgrid Interconnection Devices, load side connections, backfeeding practice and disconnecting means — as can be seen in the transcripts of Code-Making Panel 4 action last cycle:
Code‐Making Panel 4 Public Input Report (692 Pages)
Code-Making Panel 4 Public Comment Report (352 Pages)
Keep in mind that the NEC says nothing (or nearly very little, in its purpose stated in Section 90.2) about microgrid economics or the life cycle cost of any other electrical installation. It is the claim about economic advantages of microgrids that drive education facility asset management and energy conservation units to conceive, finance, install, operate and — most of all — tell the world about them.
In previous posts we have done our level best to reduce the expectations of business and finance leaders of dramatic net energy savings with microgrids — especially on campuses with district energy systems. Microgrids do, however, provide a power security advantage during major regional contingencies — but that advantage involves a different set of numbers.
Note also that there is no user-interest from the education facility industry — the largest non-residential building construction market in the the United States — on Panel 4. This is not the fault of the NFPA, as we explain in our ABOUT.
The 2023 NEC was released late last year.
The 2026 revision cycle is in full swing with public comment on the First Draft receivable until August 24, 2024. Let’s start formulating our ideas using the 2023 CMP-4 transcripts. The link below contains a record of work on the 2023 NEC:
We collaborate with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facility Committee which meets online 4 times per month in European and American time zones. Since a great deal of the technical basis for the NEC originates with the IEEE we will also collaborate with other IEEE professional societies.
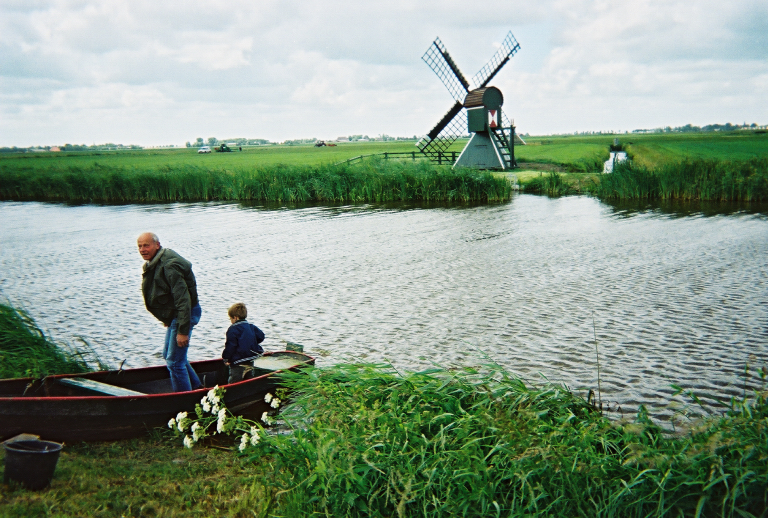

Mike Anthony’s father-in-law and son maintaining the electrical interactive system installed in the windmill that provides electricity to drive a pump that keeps the canal water at an appropriate level on the family farm near Leeuwarden, The Netherlands.
Issue: [19-151]
Category: Electrical, Energy
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Kane Howard, Jose Meijer