Tag Archives: Massachusetts
- Home
- Posts tagged "Massachusetts" (Page 3)

Legal Grounds Café
Facilities Management | A Look At BC Master Planning: Past, Present, And Future
.@BC_CSON has launched a master’s degree in nurse-midwifery, which aims to address the crisis of maternal mortality and the shortage of maternal health care workers.https://t.co/QGb3FRpR3B
— Boston College (@BostonCollege) March 13, 2025
Sundry:
National Fire Protection Association: Quincy Massachusetts
History of Irish Americans in Boston
Boston Tea Party
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Hillside Cafe
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Eggnogg
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Varieties of Innovation
History News Network: Why Do So Many Professors Hate America?
Business innovation involves creating new or improved business processes, models, or strategies to achieve organizational goals and gain a competitive advantage. It focuses on enhancing efficiency, customer experience, and overall business performance. Business innovation may encompass changes in marketing, operations, management, or other aspects of the business ecosystem.
On the other hand, technology innovation revolves around the development and application of new technologies or the improvement of existing ones. It aims to introduce novel solutions, products, or services by leveraging advancements in technology. Technology innovation can be driven by scientific research, engineering breakthroughs, or the integration of emerging technologies to address specific needs.
While business innovation is broad and encompasses various facets of organizational improvement, technology innovation specifically centers on advancements in technology and their strategic implementation. Successful companies often integrate both types of innovation to stay competitive, using business innovation to optimize processes and technology innovation to enable novel solutions and capabilities.
Noteworthy innovations relevant to the development and maintenance of the real assets of education settlements:
- Proptech Platforms: Various proptech (property technology) platforms have emerged to streamline property management tasks, including tenant communication, rent collection, and maintenance requests. Examples include Buildium, AppFolio, and Propertyware.
- Blockchain in Real Estate: Blockchain technology is being explored for its potential to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in real estate transactions. Smart contracts on blockchain can automate and secure property transactions.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies are being used for virtual property tours, allowing potential buyers or tenants to explore properties remotely. This helps in saving time and making more informed decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: Data analytics and machine learning are being employed to analyze market trends, predict property values, and assess investment opportunities. This enables more data-driven decision-making in real estate.
- IoT (Internet of Things): IoT devices are being integrated into buildings for smart property management. This includes smart thermostats, security systems, and energy-efficient solutions, enhancing overall property performance.
- Automated Valuation Models (AVMs): AVMs leverage algorithms and data analysis to estimate property values. These tools provide quick and automated property valuations, aiding in pricing decisions.
- Digital Transaction Platforms: Platforms that facilitate end-to-end digital real estate transactions are gaining popularity. These platforms aim to simplify the buying and selling process, reducing paperwork and increasing efficiency.
- Energy-efficient Technologies: Sustainable and energy-efficient solutions are becoming integral to real estate development. Innovations include smart building systems for energy management, green construction materials, and renewable energy integration.
- Crowdfunding for Real Estate: Crowdfunding platforms allow individuals to invest in real estate projects with smaller amounts of capital. This democratizing approach to real estate investment provides opportunities for a broader range of investors.
- Facial Recognition and Biometrics: Some property management systems are incorporating facial recognition and biometric technologies for enhanced security in access control and building management.
Celebrating the 150th Birthday of Gustav Holst
A British composer best known for The Planets suite Gustav Holst has had a profound impact on the Anglosphere by bridging classical music with broader cultural narratives and modernity. The Planets, with its bold orchestration and thematic explorations of astrological symbolism, has resonated deeply across English-speaking countries, shaping the orchestral landscape and inspiring generations of composers, particularly in film.
Holst’s music marries English folk influences with European classical traditions, embodying a distinctly English voice that celebrates both innovation and heritage. His works emphasize emotion and mysticism, reflecting a British identity while connecting to universal themes.
In the Anglosphere, Holst’s contributions have expanded the appreciation of orchestral music, influencing composers from Benjamin Britten to John Williams, whose iconic film scores owe much to Holst’s pioneering style. Holst’s legacy endures as a touchstone of British musical identity, evoking wonder, tradition, and a cosmic scope that resonates globally.
Sir Winston Churchill – Funeral (I Vow To Thee) – The Nation’s Farewell
Mabon Breakfast
Tufts University Financial Statement: $4.602B
The word “fecund” comes from the Latin word “fecundus,” which means fertile or fruitful. Historically, it has been used to describe land, animals, or people that are capable of producing abundant offspring or vegetation.
The term conveys a sense of richness and productivity, often associated with fertility and the ability to generate new life or growth. In a broader sense, it can also be applied metaphorically to describe creative or intellectual productivity.
Related:
Boston Public Library: The Origins and Practices of Mabon
Standards Michigan: Kitchen Safety & Sustainability
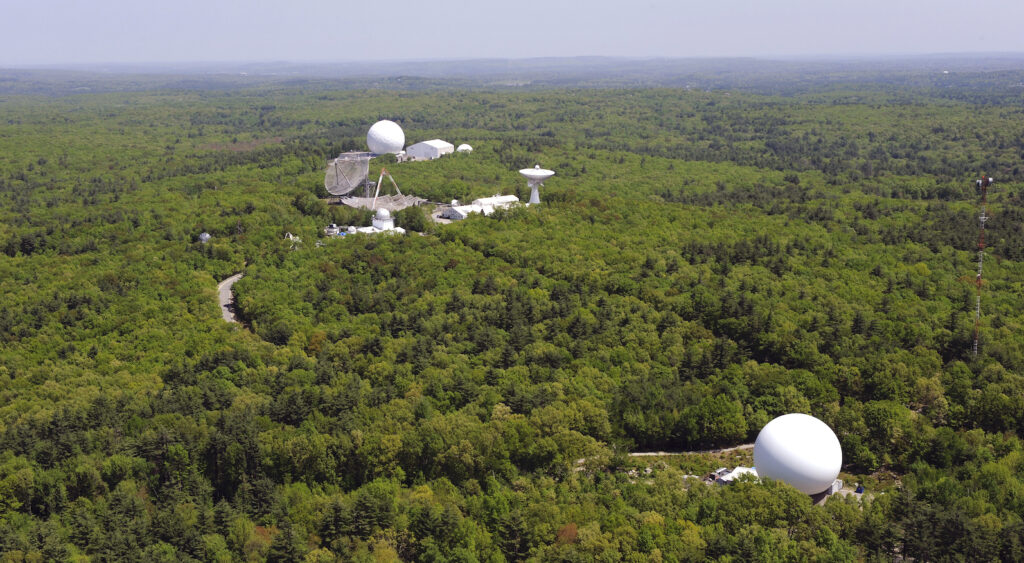
Haystack Observatory
The Haystack Observatory is a research facility primarily focused on radio astronomy, geodesy, and atmospheric science research. Although WMBR and the Haystack Observatory are both associated with MIT, they serve distinct purposes; with WMBR focuses on providing a platform for student radio programming and community engagement in the Cambridge region.
The transmitter for student-run radio station, WMBR 88.1 FM, is located in the town of Belmont about 3 miles from campus; situated on a tower at 150 Pleasant Street in Belmont. This location allows WMBR’s signal to cover a significant portion of the greater Boston area, reaching listeners in Cambridge, Boston, and surrounding communities.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670