Information and communications technology (ICT) is a fast-moving economic space in which a mix of consensus, consortia and open-source standards form the broad contours of leading practice. ICT standards tend to follow international developments — more so than, say, fire safety standards which are more familiar to education facility leadership. All school districts, colleges, universities and university-affiliated health care systems have significant product, system, firmware and labor resources allocated toward ICT.
The Building Industry Consulting Service International (BICSI) is a professional association supporting the advancement of the ICT community in all markets. This community is roughly divided between experts who deal with “outside-plant” systems and “building premise” systems on either side of the ICT demarcation (or Point-of-Presence). BICSI standards cover the wired and wireless spectrum of voice, data, electronic safety & security, project management and audio & video technologies. Its work is divided among several committees as shown in the landing page of its standards setting enterprise, linked below:
BICSI International Standards Program
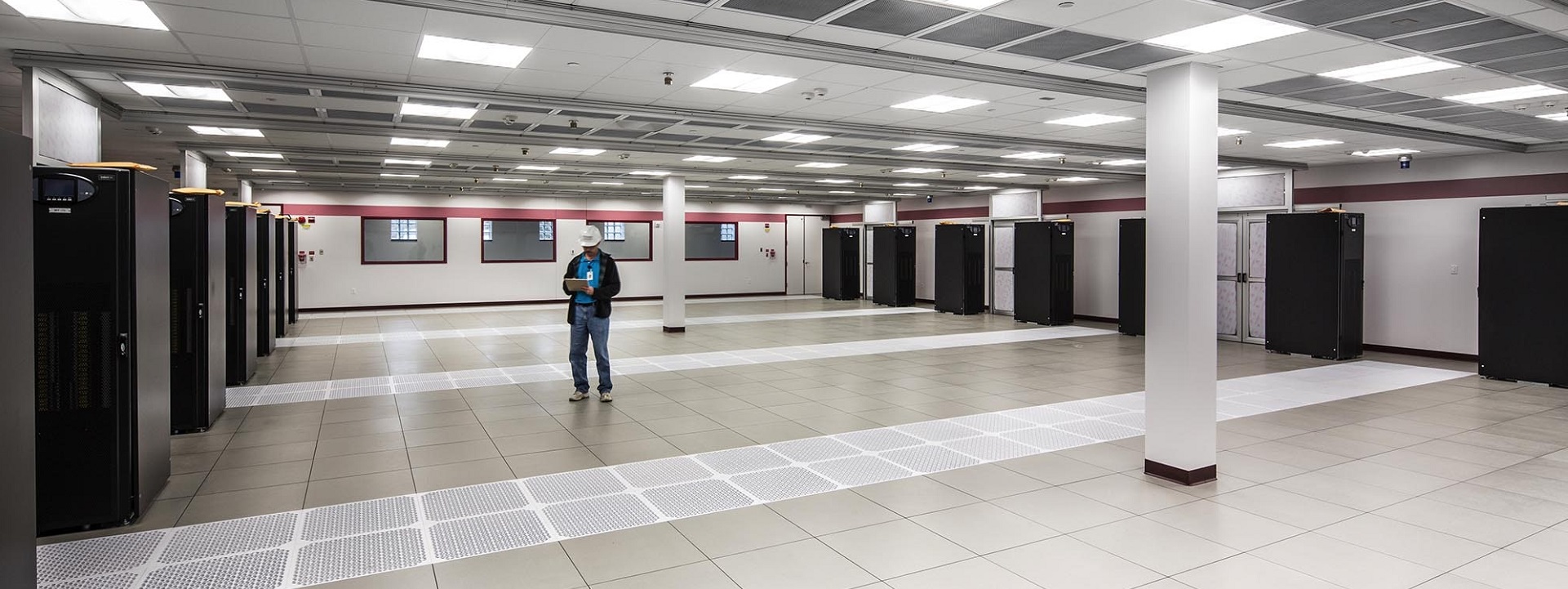
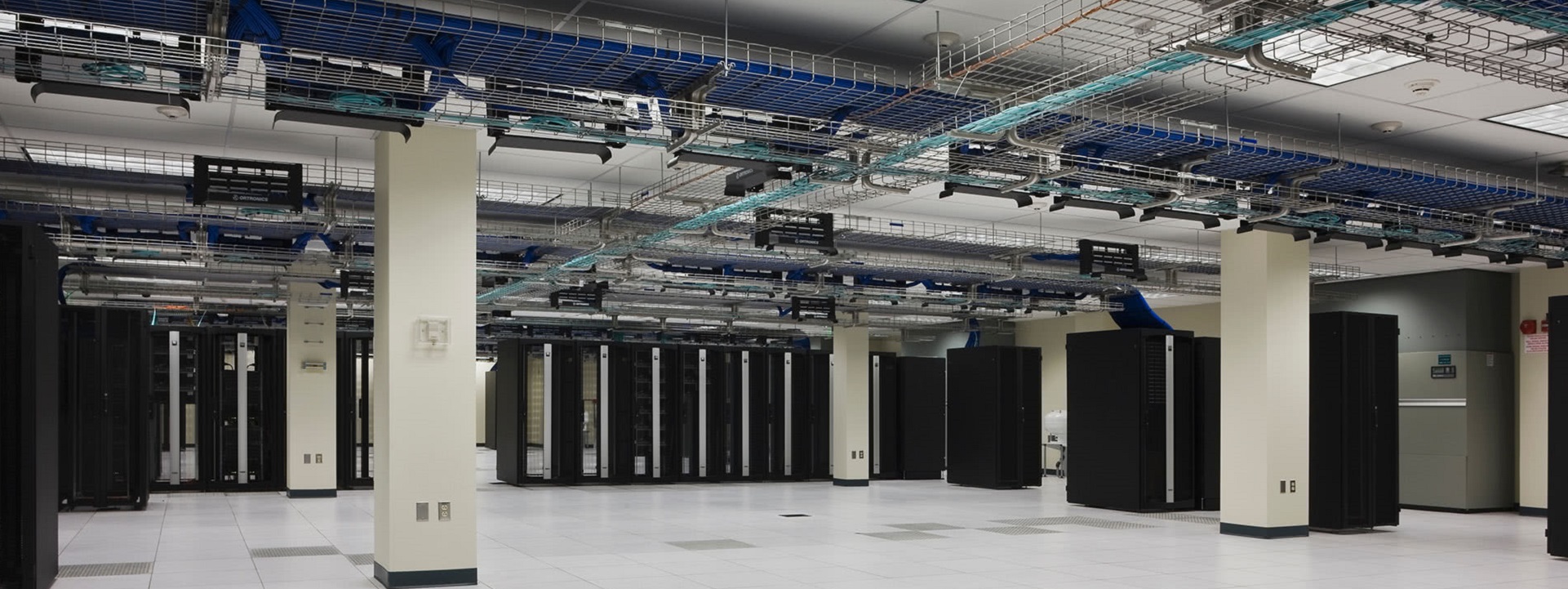
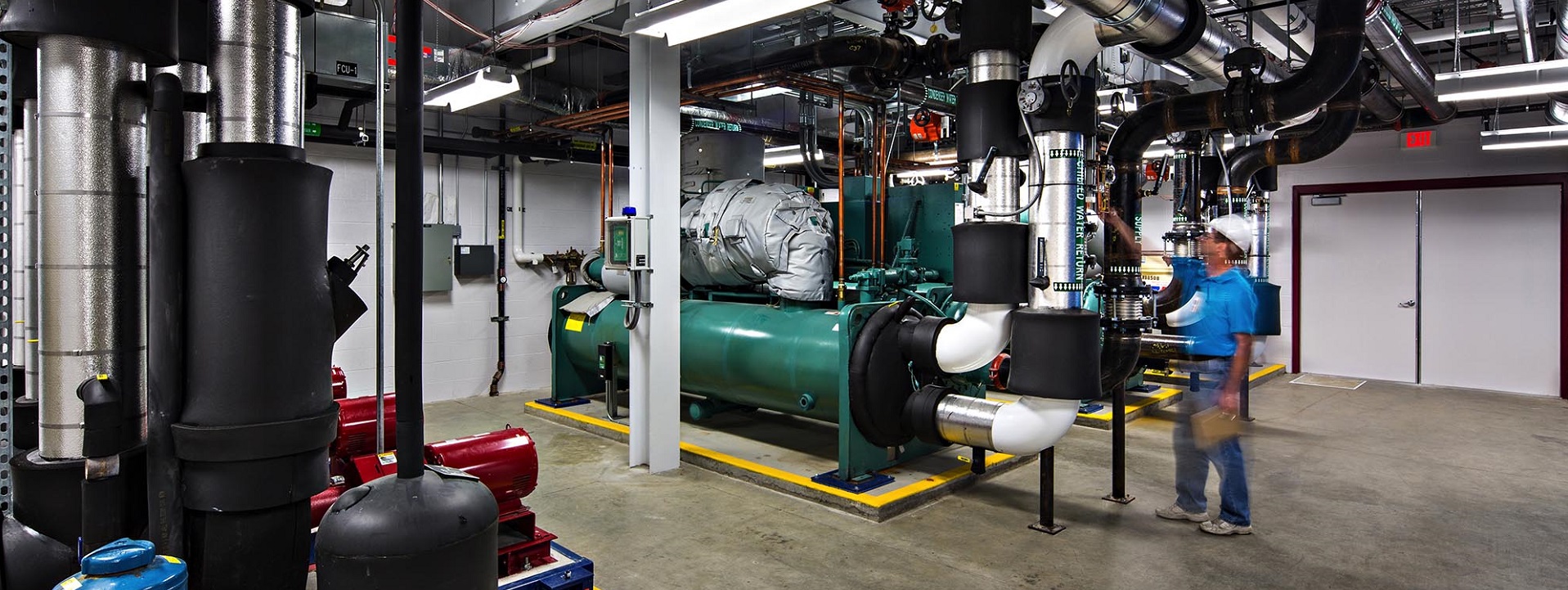
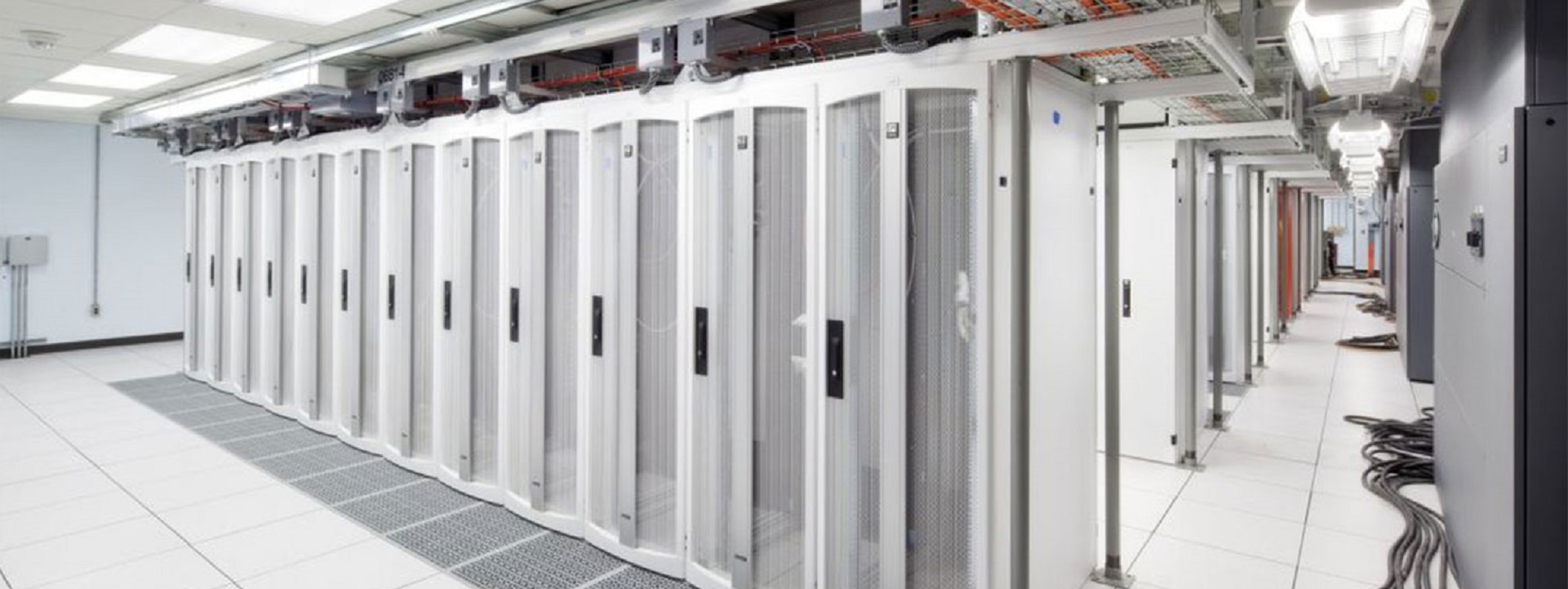
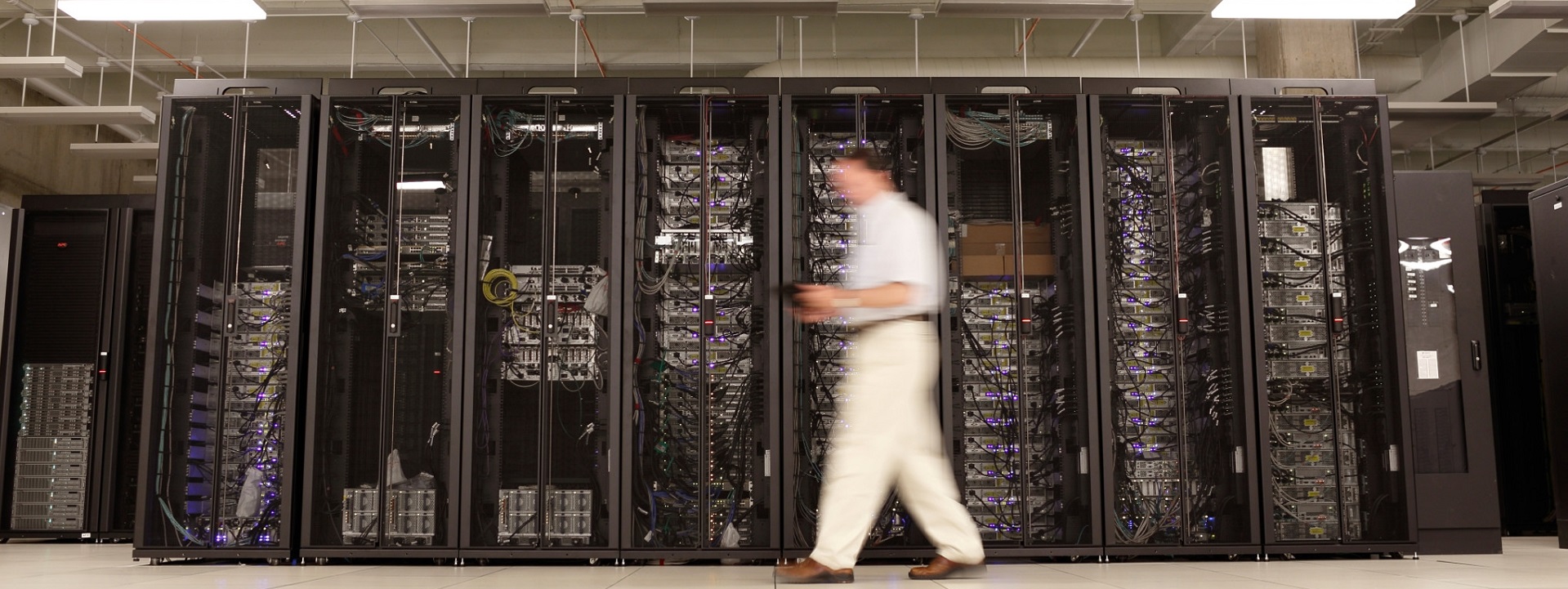
Education communities are stewards of significant information and communication technology infrastructure. Accordingly, we track the development of BICSI 009 Data Center Operations and Maintenance Best Practices. This title provides requirements, recommendations, and best practices for the operation and maintenance of data centers including but not limited to standard operating procedures, emergency operating procedures, maintenance, governance, and management. Those comments are now being integrated into a revised standard to be released as soon as the restrictions of the pandemic are eased. For more information you may communicate directly with Jeff Silveira (jSilveira@bicsi.org)
As of this posting, all BICSI best practice titles are stable and current; though our recent communication with its leadership indicates that BICSI standards setting has been slowed by the pandemic.
A fair amount of content in BICSI standards are inspired by movement in safety concepts of the National Electrical Code; particularly on matters involving wiring, grounding and lightning protection. We maintain all BICSI best practice titles on the standing agenda of our Infotech 200 teleconference. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to the public. On this topic we collaborate with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee meets four times monthly in European and American time zones; also open to the public.
Issue: [19-30]
Category: Telecommunications, Infotech
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Michael Hiler
LEARN MORE:
Did you know BICSI offers a complete library of our award winning technical manuals and published standards? Available in print or electronic download, this set is a perfect resource for your company. Learn more: https://t.co/fzBA8hqve9 pic.twitter.com/y9duVe0fCG
— BICSI (@BICSI) December 15, 2018