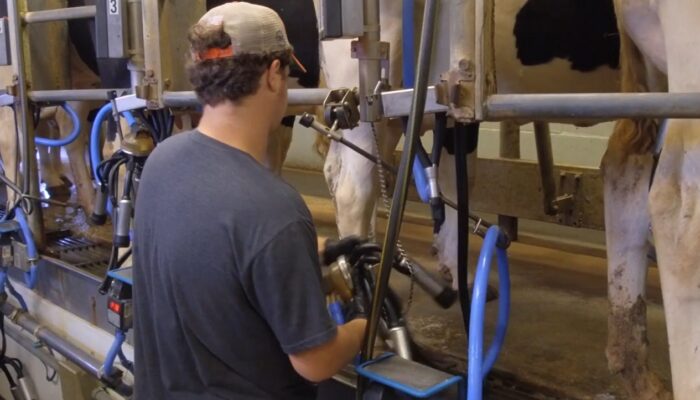
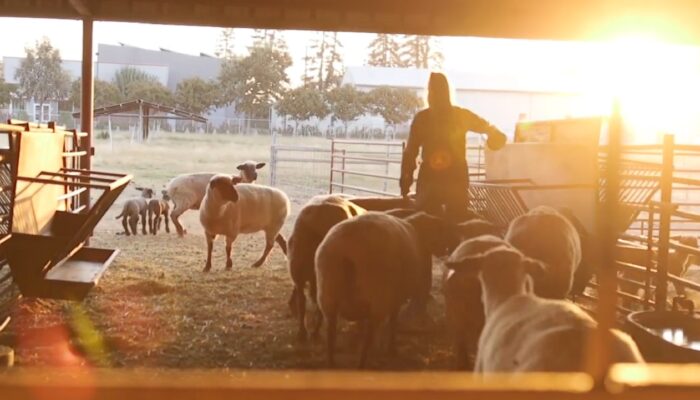
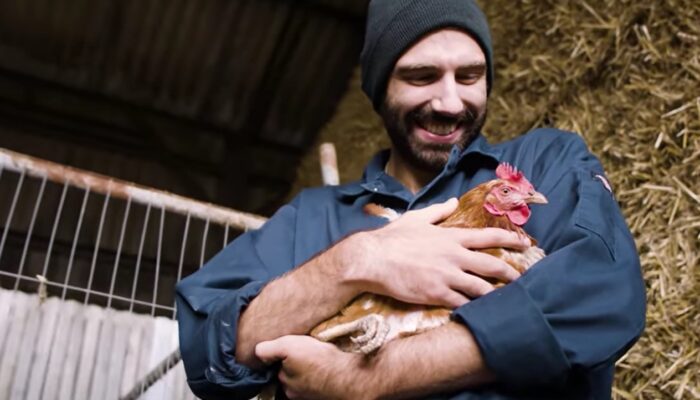
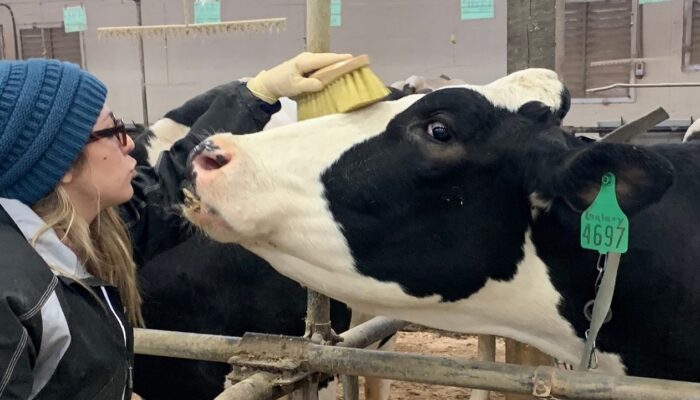
Many land grant colleges and universities are stewards of agricultural facilities that require reliable electrical power that is safe and sustainable for livestock well off the core campus distribution grid. Today we examine the 2026 National Electrical Code safe electric service rules with an eye toward the close date of April 6th for public input on the 2029 NEC.
Updated: September 3, 2024
Article 547: Agricultural Buildings
Public Input with Responses from CMP-7 (Start at PDF Page 187)
Many land grant colleges and universities are stewards of agricultural facilities that require reliable electrical power that is safe and sustainable for livestock and animal habitat for sporting.
FREE ACCESS: 2023 National Electrical Code
The premise wiring rules for hazardous university owned buildings have been relatively stable. Electrical professionals are guided by:
- Farm Load Calculations of Part V of Article 220,
- Corrosion mitigation with appropriate specification of power chain wiring
- Stray voltage and the equipotential plane
- Interactivity with regulated utility power sources.
Public response to the First Draft of the 2026 National Electrical Code will be received until August 28, 2024. We coordinate our approach to the entire NFPA electrical suite with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee which meets 4 times monthly. We typically refer to previous transcripts of technical committee actions to inform any changes (improvements) that we propose, if any.
We maintain this issue on the standing agenda of our Power and Nourriture (Food) colloquia. Feel free to join us with the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
More:
Cornell University Agricultural Safety and Health Program
National Safety Council (22 deaths by electrocution on farms per 100,000 in 2017)
National Agricultural Safety Database
Electrical Wiring for Barns, Riding Arenas, Animal Habitat and Feed Storage