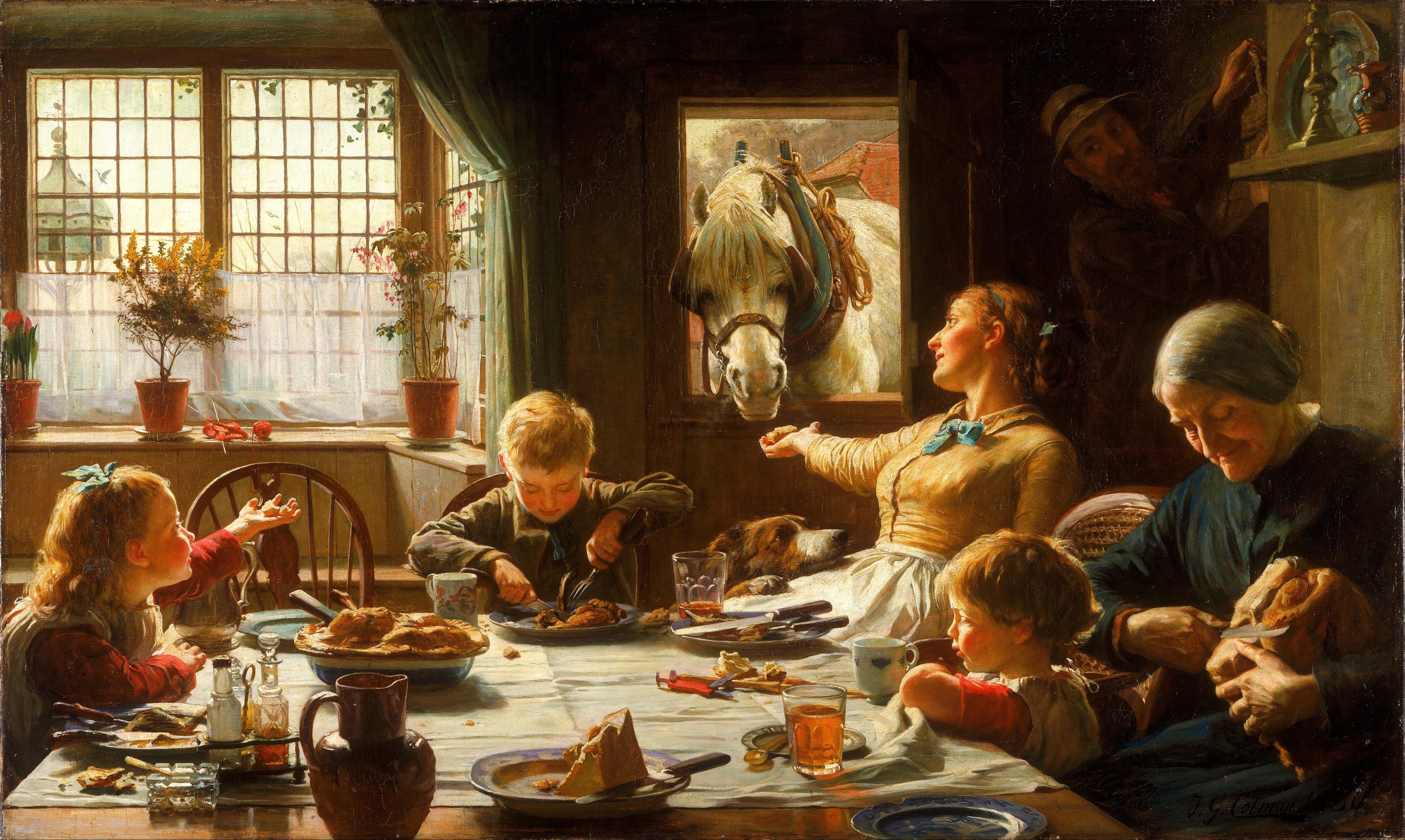
“One of the Family” 1880 | Frederick George Cotman

NFPA 150 Fire and Life Safety in Animal Housing Facilities Code has entered its s025 revision cycle. Many education communities are responsible for animal safety in academic units, research enterprises. museums and even — as in the United Kingdom — large farm animals that wander freely on campus with students, faculty and staff. The number of colleges and universities that permit students to live with their pets has expanded; and with it the responsibilities of university administration.
From the document scope:
This standard shall provide the minimum requirements for the design, construction, fire protection, and classification of animal housing facilities. The requirements of NFPA 150 recognize the following fundamental principles:
(1) Animals are sentient beings with a value greater than that of simple property.
(2) Animals, both domesticated and feral, lack the ability of self-preservation when housed in buildings and other structures.
(3) Current building, fire, and life safety codes do not address the life safety of the animal occupants. The requirements found in NFPA 150 are written with the intention that animal housing facilities will continue to be designed, constructed, and maintained in accordance with the applicable building, fire, and life safety codes.
The requirements herein are not intended to replace or rewrite the basic requirements for the human occupants. Instead, NFPA 150 provides additional minimum requirements for the protection of the animal occupants and the human occupants who interact with those animals in these facilities.
A full description of the project is linked below:
Fire and Life Safety in Animal Housing Facilities Code
Access to the 2025 Edition is linked below:
FREE ACCESS NFPA 150
We provide the transcript of the back-and-forth on the current 2022 edition to inform how education communities can contribute to the improvement of this title; a subject that stirs deep feelings about animal safety in research enterprises.
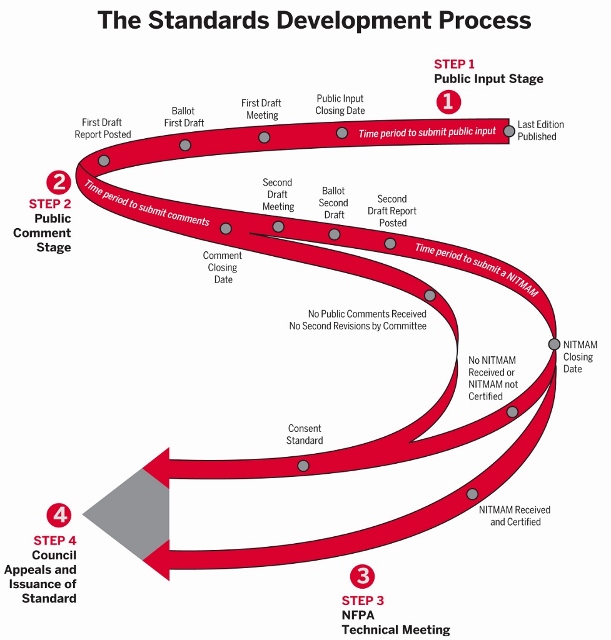
NFPA 150 First Draft Agenda
NFPA 150 Second Draft Report
Public comment on the Second Draft of the 2025 Edition will be received until March 27, 2024.
We have been advocating risk-informed animal safety concepts in this document since the 2013 Edition and have found that it is nearly impossible to overestimate the sensitivity of educational communities to the life safety of animals — either for agriculture or medical research.
We maintain the entire NFPA catalog on the standing agenda of our Prometheus colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.

Issue: [11-1] and [19-5]
Category: Fire Protection, Facility Asset Management, Academic, Risk Management
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Josh Elvove, Joe DeRosier
More:
Protecting Animals When Disaster Strikes
Animals 300
Bibliography:
25 Most Pet-Friendly Colleges
National Institute of Health: Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals
International Building Code: Section 304 (Business Group B): Animal hospitals, kennels and pounds
Terrestrial Animal Health Code
IEEE Guide for Animal Deterrents for Electric Power Supply Substations
ASHRAE Animal Facilities
IEEE Livestock Monitoring System
Ventilation Design Handbook on Animal Research Facilities
HVAC Design in Animal Facilities
USDA Animal Welfare Information Center
ISO Assistance Dogs
US Department of Agriculture: Animal Welfare Act and Animal Welfare Regulations
S. 4288: Reducing Animal Testing Act
Guaranteeing safety of animals under risk of fire: conceptual framework and technical issues analysis
Protecting Animals When Disaster Strikes