Tag Archives: United Kingdom
- Home
- Posts tagged "United Kingdom" (Page 3)

Fire Safety
Fire safety leadership usually finds itself involved in nearly every dimension of risk on the #WiseCampus; not just the built environment but security of interior spaces with combustibles but along the perimeter and within the footprint of the education community overall.
The Campus Fire Marshal, for example, usually signs the certificate of occupancy for a new building but may be drawn into meetings where decisions about cybersecurity are made. Fire protection systems coincide with evacuation systems when there is no risk and both may be at risk because of cyber-risk.
The job description of a campus fire safety official is linked below offers some insight into why fire safety technologies reach into every risk dimension:
University of California Santa Cruz Office of Emergency Services
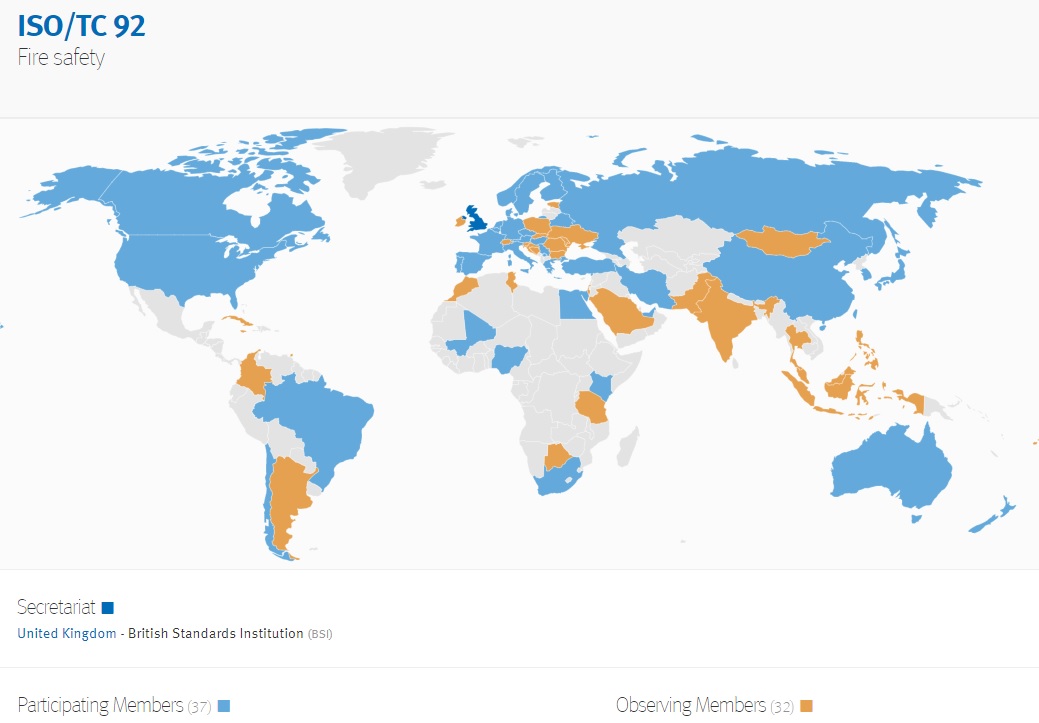
The development of the highest level fire safety consensus product in the world is led by the British Standards Institute, under the administration of the International Standardization Organization, with Committee E05 on Fire Standards of ASTM International as the US Technical Advisory Group Administrator. The business plan and the map of global participants is linked below:
BUSINESS PLAN ISO/TC 92 Fire safety EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The consensus products developed by TC 92 are intended to save lives, reduce fire losses, reduce technical barriers to trade, provide for international harmonization of tests and methods and bring substantial cost savings in design. ISO/TC 92 standards are expected to be of special value to developing countries, which are less likely to have national standards. As with all ISO standards, the TC 92 consensus product is a performance standard suitable for use in prescriptive regulations and provide for a proven route to increased fire safety.
We do not advocate in this standard at the moment; we only track it. The International Fire Code and the Fire Code have been our priorities since 2006. The fire safety space is well populated with knowledgeable facility professionals because conformity budgets in the fire safety world — i.e. the local or state fire marshal — usually has a budget. When you have a budget you usually have people keeping pace with best practice.
We encourage our colleagues in the United States on either the business or academic side of the education facility industry to communicate directly with ANSI’s ISO Team and/or the ASTM Contact: Tom O’Toole, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 Phone: (610) 832-9739, Email: totoole@astm.org
We maintain this title on the agenda of our periodic Global and Prometheus colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [19-104]
Category: Fire Safety, Fire Protection, International
Contact: Mike Anthony, Joe DeRosier, Alan Sactor, Joshua Elvove, Casey Grant
More:
The Challenges of Storage and Not Enough Space, Alan Sactor
Family Names
BSI Group: The Role of Standards in Shaping Careers and a Fairer Future
Growth for tech innovation in Bristol as Future Space expands
“Immoderate Greatness: Why Civilizations Fail, and Apologies to the Grandchildren” | William Ophuls
A great weekend! pic.twitter.com/9QQS6xvzVx
— Huw Llandre (@Llandre) April 2, 2024
English royal family tree traced back to the 9th century pic.twitter.com/DSQIqWq6dU
— ThinkingWest (@thinkingwest) August 6, 2024
They are the sons and daughters of Life’s longing for itself.
They come through you but not from you,
And though they are with you yet they belong not to you.
For they have their own thoughts.
You may house their bodies but not their souls,
For their souls dwell in the house of tomorrow,
English Viticulture and Oenology
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Cambridge Center for Smart Infrastructure & Construction
“No village or individual shall be compelled to make bridges at river banks,
except those who from of old are legally bound to do so.”
— Magna Cara Clause 23 (Limiting forced labor for infrastructure)

“Clare Hall and King’s College Chapel, Cambridge, from the Banks of the River Cam” / Joseph Mallord William Turner (1793)
Smart Infrastructure: Getting More From Strategic Assets
Dr Jennifer Schooling, Director of CSIC
Dr Ajith Parlikad, CSIC Co-Investigator and Senior Lecturer
Mark Enzer, Global Water Sector Leader
Mott MacDonald; Keith Bowers, Principal Tunnel Engineer, London Underground
Ross Dentten, Asset Information and Configuration Manager, Crossrail
Matt Edwards, Asset Maintenance and Information Manager, Anglian Water Services
Jerry England, Group Digital Railway Director, Network Rail
Volker Buscher, Director, Arup Digital
Smart Infrastructure is a global opportunity worth £2trn-4.8trn. The world is experiencing a fourth industrial revolution due to the rapid development of technologies and digital abundance.
Smart Infrastructure involves applying this to economic infrastructure for the benefit of all stakeholders. It will allow owners and operators to get more out of what they already have, increasing capacity, efficiency and resilience and improving services.
It brings better performance at lower cost. Gaining more from existing assets is the key to enhancing service provision despite constrained finance and growing resource scarcity. It will often be more cost-effective to add to the overall value of mature infrastructure via digital enhancements than by physical enhancements – physical enhancements add `more of the same’, whereas digital enhancements can transform the existing as well.
Smart Infrastructure will shape a better future. Greater understanding of the performance of our infrastructure will allow new infrastructure to be designed and delivered more efficiently and to provide better whole-life value.
Data is the key – the ownership of it and the ability to understand and act on it. Industry, organisations and professionals need to be ready to adjust in order to take advantage of the emerging opportunities. Early adopters stand to gain the most benefit. Everyone in the infrastructure sector has a choice as to how fast they respond to the changes that Smart Infrastructure will bring. But everyone will be affected.
Change is inevitable. Progress is optional. Now is the time for the infrastructure industry to choose to be Smart.
LEARN MORE:
Cambridge Centre for Smart Infrastructure and Construction
Perspective: Since this paper is general in its recommendations, we provide examples of specific campus infrastructure data points that are difficult, if not impossible, to identify and “make smart” — either willfully, for lack of funding, for lack of consensus, for lack of understanding or leadership:
-
- Maintenance of the digital location of fire dampers in legacy buildings or even new buildings mapped with BIM. Doors and ceiling plenums are continually being modified and the As-Built information is usually not accurate. This leads to fire hazard and complicates air flow and assuring occupant temperature preferences (i.e. uncontrollable hot and cold spots)
- Ampere readings of feeder breakers downstream from the electric service main. The power chain between the service substation and the end-use equipment is a “no-man’s land” in research facilities that everyone wants to meter but few ever recover the cost of the additional metering.
- Optimal air flow rates in hospitals and commercial kitchens that satisfies both environmental air hazards and compartmentalized air pressure zones for fire safety.
- Identification of students, staff and faculty directly affiliated with the campus versus visitors to the campus.
- Standpipe pressure variations in municipal water systems
- Pinch points in municipal sewer systems in order to avoid building flooding.
- How much of university data center cost should be a shared (gateway) cost, and how much should be charged to individual academic and business units?
- Should “net-zero” energy buildings be charged for power generated at the university central heating and electric generation plant?
- How much staff parking should be allocated to academic faculty versus staff that supports the healthcare delivery enterprises; which in many cases provides more revenue to the university than the academic units?
- Finally, a classical conundrum in facility management spreadsheets: Can we distinguish between maintenance cost (which should be covered under an O&M budget) and capital improvement cost (which can be financed by investors)
Received Pronunciation
Come see ‘Pygmalion’ this weekend at Arno Gustin Hall on campus! University of Mary students bring this classic to life in a riveting weekend of performances. 🎬
Showtimes:
Friday – 7:00pm
Saturday – 2:00pm & 7:00pm
Sunday – 2:00pm#Lifeatmary pic.twitter.com/5w5MnEWk4K— University of Mary (@umary) March 21, 2025
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670