ASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide, Second Edition
Classification of Laboratory Ventilation Design Levels
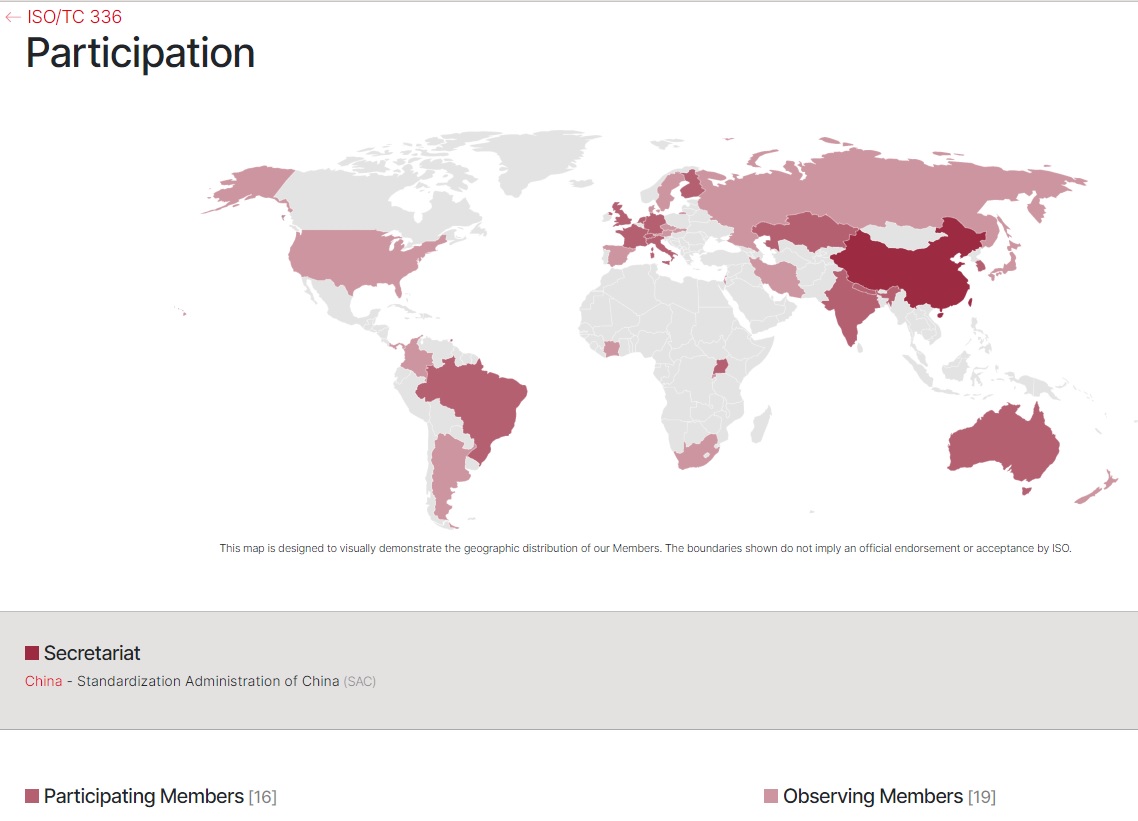
ISO/DIS 22544Laboratory design — Vocabulary (Under Development)
The Haldane Principle § “On Being the Right Size” J.B.S Haldane
We break down our coverage of laboratory safety and sustainability standards thus:
Laboratories 100 covers a broad overview of the safety and sustainability standards setting catalogs; emphasis on titles incorporated by reference into public safety laws.
Laboratories 200 covers laboratory occupancies primarily for teaching
Laboratories 300 covers laboratories in healthcare clinical delivery.
Laboratories 400 covers laboratories for scientific research; long since creating the field of environmental health and safety in higher education and a language (and acronyms of its own: CSHEMA)
In the most recent fiscal year, the National Institutes of Health had a budget of approximately $47.7 billion. A substantial portion of this budget is allocated to research at colleges and universities. Specifically, about 83% of NIH’s funding, which translates to roughly $39.6 billion, is awarded for extramural research. This funding is distributed through nearly 50,000 competitive grants to more than 2,500 universities, medical schools, and other research institutions across the United States
The cost to build a “standard” classroom runs about $150 to $400 per square foot; a scientific research laboratory about $400 to $1200 per square foot.
Laboratories 500 is broken out as a separate but related topic and will cover conformity and case studies that resulted in litigation. Both Laboratories 200 and 400 will refer to the cases but not given a separate colloquium unless needed.
At the usual time. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
February 27, 2023
Research findings related to laboratory safety:
- Identifying and Evaluation Hazards in Research Laboratories
- “Evaluating the Efficacy of Laboratory Hazard Assessment Tools for Risk Management in Academic Research Laboratories” – This study from 2021 evaluated the effectiveness of various laboratory hazard assessment tools in academic research laboratories, and found that a combination of tools and approaches may be most effective for managing risks.
- “A Framework for Assessing Laboratory Safety Culture in Academic Research Institutions” – This 2020 study developed a framework for assessing laboratory safety culture in academic research institutions, which can help identify areas for improvement and promote a culture of safety.
- “Enhancing Laboratory Safety Culture Through Peer-to-Peer Feedback and Coaching” – This 2020 study found that peer-to-peer feedback and coaching can be an effective way to enhance laboratory safety culture, as it encourages open communication and feedback among colleagues.
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Laboratory Safety Training Programs for Graduate Students” – This 2019 study evaluated the effectiveness of laboratory safety training programs for graduate students, and found that interactive and hands-on training was more effective than traditional lecture-based training.
- “Improving Laboratory Safety Through the Use of Safety Climate Surveys” – This 2018 study found that safety climate surveys can be an effective way to improve laboratory safety, as they provide insight into employee perceptions of safety culture and identify areas for improvement.
- Chemistry laboratory safety climate survey (CLASS): A tool for measuring students’ perceptions of safety
These recent research findings suggest that laboratory safety culture can be improved through a variety of approaches, including hazard assessment tools, peer-to-peer feedback and coaching, interactive training, and safety climate surveys. Some of these findings will likely set the standard of care we will see in safety standards incorporated by reference into public safety regulations.
Related:
November 29, 2021
Today we break down the literature setting the standard of care for the safety and sustainability of instruction and research laboratories in the United States specifically; and with sensitivity to similar enterprises in research universities elsewhere in the world. We will drill into the International Code Council Group A titles which are receiving public input until January 10, 2022.
Join us by clicking the Daily Colloquia link at the upper right of our home page.
The original University of Michigan Workspace for [Issue 13-28] in which we advocate for risk-informed eyewash and emergency shower testing intervals has been upgraded to the new Google Sites platform: CLICK HERE
Related:
September 20, 2021
Today we break down the literature setting the standard of care for the safety and sustainability of instruction and research laboratories in the United States specifically; and with sensitivity to similar enterprises in research universities elsewhere in the world.
Classification of Laboratory Ventilation Design Levels – ASHRAE
ASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide
Join us by clicking the Daily Colloquia link at the upper right of our home page.
May 10, 2021
Today we will poke through a few proposals for the 2021/222 revision of the International Code Council’s Group A Codes. For example:
IFC § 202 et. al | F175-21| Healthcare Laboratory Definition
IBC § 202 et. al | E7-21| Collaboration Room
IBC § 1110.3 et. al | E143-21| Medical scrub sinks, art sinks, laboratory sinks
. . .
IFGC § 403, etl al| G1-21| Accessibility of fuel gas shut off valves
IBC § 307 Tables | G36-21| For hazardous materials in Group B higher education laboratory occupancies
IBC § 302.1 et. al | G121-21| Separation from other nonlaboratory areas for higher education laboratories
And about 20 others we discussed during the Group A Hearings ended last week. We will have until July 2nd to respond. The electrotechnology proposals will be referred to the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee which is now preparing responses to this compilation by Kimberly Paarlberg.
March 15, 2021
Today we break down action in the literature governing the safety and sustainability of instruction and research laboratories in the United States specifically; but also with sensitivity to similar enterprises in research universities elsewhere in the world. “Everyone” has an iron in this fire:
International Building Code Chapter 38: Higher Education Laboratories
ASCE Structural Engineering Institute (so that the foundations and “bone structure” of laboratories survive earthquakes, floods and other Force majeure mayhem)
National Electrical Code Chapter 5: Special Occupancies
ASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide
NFPA 45 Standard on Fire Protection for Laboratories Using Chemicals
IEEE Electrical Safety in Academic Laboratories
…and ISEA, AWWA, AIHA, BIFMA, CLSI, LIA, IAPMO, NSF, UL etc. among ANSI accredited standards developing organizations…
..and addition to NIST, Federal code of Regulations Title 29, NIH, CDC, FEMA, OSHA etc
…and state level public health regulations; some of them adapted from OSHA safety plans
Classroom and offices are far simpler. Laboratories are technically complicated and sensitive area of concern for education communities not only responsible for the safety of instructional laboratories but also global communities with faculty and staff that must simultaneously collaborate and compete. We have been tip-toeing through the technical and political minefields for nearly 20 years now and have had some modest success that contributes to higher safety and lower costs for the US education community.
Colloquium open to everyone. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
More
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
National Institutes of Health
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
NFPA Fire Code requirements for laboratories at colleges and universities
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
National Conference of Standards Laboratories
National Institute of Standards and Technology/Information Technology Laboratory