Author Archives: mike@standardsmichigan.com
- Home
- Articles posted by mike@standardsmichigan.com (Page 3)

H.R. 5491 NCAA Accountability Act
Laken Riley Act passes 251-170, with 37 Democrats joining all Republicans in support
The murder of Laken Riley occurred on February 22, 2024, in Athens, Georgia. Laken Riley, a 22-year-old nursing student at Augusta University, disappeared when she was jogging at the University of Georgia (UGA). Her body was found near a lake of a wooded area at UGA; her death was caused by blunt force trauma. The police described Riley’s killing as a “crime of opportunity”, and that no murder had been committed at UGA in almost 30 years; a gap filled by the open border policy of Democrat President Joseph Biden, Homeland Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas and chain of Democrat District Attorney’s who let the perpetrator run free.
The murder has international news, generating extensive media attention — though not nearly as much as the George Floyd tragedy and the Black Lives Matter zietgeist — sparking debate over illegal immigration in United States after U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) confirmed that Ibarra is a Venezuelan illegal immigrant who is not a U.S. citizen and was caught crossing the border but released back into the United States
Jose Antonio Ibarra, a 26-year-old Venezuelan citizen who entered the US illegally, was arrested by UGA police and has been charged with felony murder, false imprisonment, and kidnapping.[4] Ibarra lived about 1 mile (1.6 km) from the area where Riley’s body was found..
European leaders are indifferent to the rape and murder of their young women by migrant men also:
It happened again. Another European girl was killed at the hands of a migrant in Vienna and she wasn’t the first one this week. And tomorrow it will happen again, because white lives don’t matter to our globalist leaders.
But they matter to me, so I’m making you a promise. 👇🏻 pic.twitter.com/fAS93ux8CQ
— Eva Vlaardingerbroek (@EvaVlaar) March 6, 2024
“But what is government itself but the greatest of all reflections on human nature? If men were angels, no government would be necessary. If angels were to govern men, neither external nor internal controls on government would be necessary. In framing a government which is to be administered by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: you must first enable the government to control control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to control itself.” — James Madison, Federalist 51
Relevant Federal Executive & Legislative Committees
House of Representatives: Committee on Education & the Workforce
Senate: Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions
SCOTUS: West Virginia, et al. v. Environmental Protection Agency
H.R. 221: Expand Pell Grant eligibility to certain trade schools
H.R. 193: Teach Relevant Apprenticeships to Drive Economic Success Act
H.R. 302: Energy Cybersecurity University Leadership Act of 2023
The University Campus As A Designed Work and an Artefact of Cultural Heritage
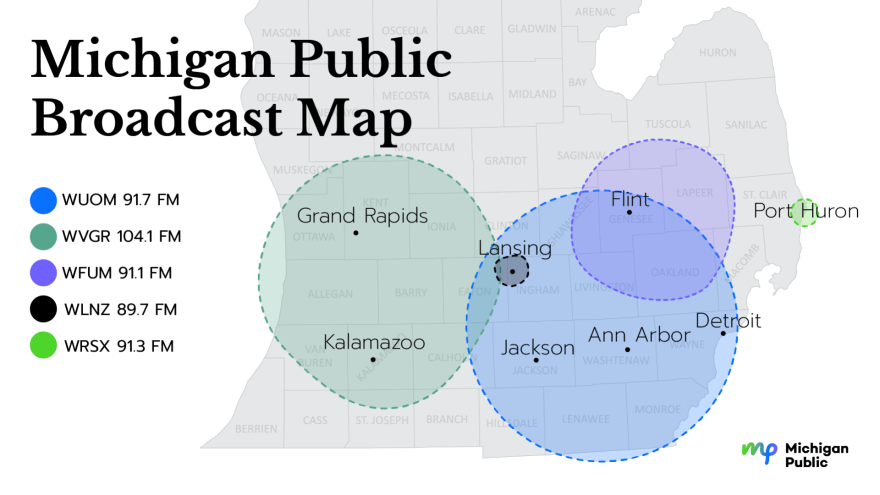
Radio Transmission Power & Frequency Allocation
Why are there at least 10 publicly funded radio stations receivable in a 75 mile radius (back and forth, up and down) the I-94/I-75 corridor of Michigan — all of them domiciled in public universities? These stations also receive revenue from other non-profit organizations, unending funding drives and private advertising from multinational financing organizations such as Schwab, Fidelity and other for-profit corporations. Most of them purchase their “content” from the same source; reflecting the same large government bias seen across the entire nation; concentrated in college towns with spotty intellectual history.
Within an approximate 50 mile radius of the University of Michigan, five national public radio stations are receivable:
WUOM University of Michigan Ann Arbor
WEMU Eastern Michigan University
WDET Wayne State University
WKAR Michigan State University
WGTE University of Toledo
Move 25 miles to the northwest and two more are receivable:
WLNZ Landing Community College
Move 25 miles northeast and three more are receivable
WFUM University of Michigan Flint
WMUK Western Michigan University
WAUS Andrews University
FCC ONLINE TABLE OF FREQUENCY ALLOCATIONS: 47 C.F.R. § 2.106
(Revised July 1, 2022)
Standards for radio broadcast coverage can vary depending on factors like location, broadcasting technology, and regulatory requirements. Here’s a general list covering various aspects:
- Technical Standards:
- Transmission Power and Frequency Allocation: Standards set by regulatory bodies like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States or Ofcom in the UK regulate the power levels and frequencies allocated to radio stations to prevent interference.
- Audio Quality: Standards for audio encoding and decoding, such as those defined by organizations like the European Broadcasting Union (EBU) or the Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) standards.
- Antenna Design and Installation: Standards for antenna design, placement, and maintenance to ensure efficient transmission and coverage.
- Content Standards:
- Language and Content Regulations: Regulations on language, decency, and content suitability enforced by regulatory bodies to ensure broadcasts adhere to community standards and do not contain offensive or harmful material.
- Advertising Standards: Guidelines on the content and placement of advertisements to prevent deceptive practices and ensure fairness and transparency.
- Copyright and Licensing: Regulations governing the use of copyrighted material and licensing agreements for broadcasting music, interviews, and other content.
- Emergency Broadcast Standards:
- Emergency Alert Systems (EAS): Standards for implementing emergency alert systems to disseminate important information to the public during emergencies or disasters.
- Public Safety Communications: Standards for communication protocols and procedures to coordinate with emergency services and agencies during crises.
- Accessibility Standards:
- Closed Captioning: Standards for providing closed captioning for the hearing impaired, ensuring accessibility to radio broadcasts.
- Descriptive Video Service (DVS): Standards for providing audio descriptions of visual content for the visually impaired.
- Ethical Standards:
- Journalistic Integrity: Guidelines for ethical reporting and journalism standards, including accuracy, fairness, and impartiality.
- Disclosure of Sponsored Content: Standards for disclosing sponsored or paid content to maintain transparency and trust with the audience.
- Conflict of Interest Policies: Standards for identifying and managing conflicts of interest in news reporting and programming.
- Health and Safety Standards:
- Electromagnetic Radiation Exposure Limits: Standards set by health organizations and regulatory bodies to limit human exposure to electromagnetic radiation emitted by radio transmitters.
- Workplace Safety: Standards for ensuring the safety of radio station personnel and compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
These standards are often enforced by governmental regulatory agencies, industry organizations, and professional associations to ensure the quality, integrity, and safety of radio broadcast coverage.
— NPR (@NPR) April 12, 2023
Fences
Colkett, Victoria Susanna; King’s College Chapel, Cambridge, as Seen from Clare Hall Piece and Crotches; National Trust, Anglesey Abbey;
Best practice discovery and promulgation for land use between colleges and universities and their host municipalities in the United States is hastened by a combination of codes, standards, and government regulations. Here are some key ones:
- Zoning Codes: Zoning ordinances dictate land use within municipalities, including where educational institutions can be located and what activities they can undertake.
- Building Codes: These are regulations that govern the construction and maintenance of buildings. Educational institutions must comply with these codes for the safety and welfare of their occupants.
- Fire Codes: Fire codes ensure that buildings meet safety standards regarding fire prevention, evacuation procedures, and firefighting equipment. Compliance is crucial for the safety of students and staff.
- Health Codes: Health codes set standards for sanitation, food safety, and other health-related matters. Colleges and universities, especially those with dining facilities and student housing, must adhere to these regulations.
- Environmental Regulations: These regulations govern environmental protection, waste management, and pollution control. Educational institutions may need to comply with federal, state, and local environmental laws.
- Parking and Transportation Regulations: Municipalities often have regulations concerning parking, traffic flow, and public transportation. Colleges and universities must consider these factors when planning campus infrastructure and events.
- Land Use Regulations: Beyond zoning codes, municipalities may have additional land use regulations that affect educational institutions, such as restrictions on expansion or development in certain areas.
- Permitting and Licensing Requirements: Colleges and universities may need permits or licenses for certain activities, such as hosting events, serving alcohol, or operating transportation services.
- Taxation Laws: While educational institutions often enjoy tax-exempt status, they may still be subject to certain taxes, such as property taxes on non-educational properties or sales taxes on commercial activities.
- Student Housing Regulations: Some municipalities have specific regulations governing student housing, including occupancy limits, safety standards, and rental property inspections.
- Noise Ordinances: Municipalities may have ordinances regulating noise levels, particularly in residential areas. Colleges and universities must consider these regulations when planning events or construction activities.
- Community Relations Agreements: In some cases, colleges and universities may enter into agreements with their host municipalities to address specific issues or concerns, such as traffic management, public safety, or community engagement initiatives.
During today’s colloquium we explore the catalogs of the dominant standards developments whose titles are most frequently incorporated by reference into local statues. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
Chesterton’s Fence is a simple rule of thumb that suggests you should never destroy a fence, change a rule, or alter a tradition if you do not understand why it was created in the first place. China’s Four Pests Campaign during the Great Leap Forward shows the tragic consequences of meddling with things we do not fully understand.
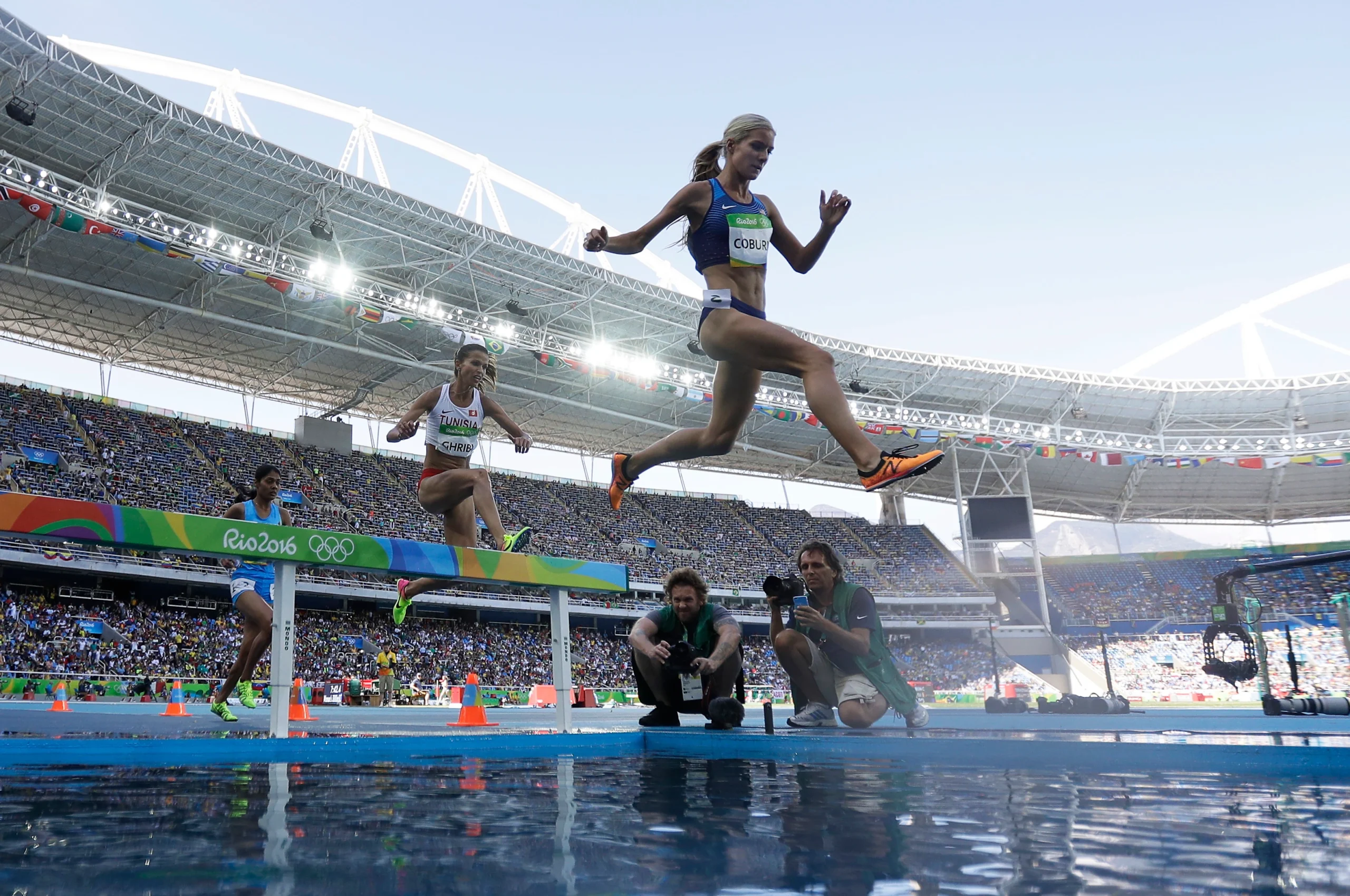
Steeplechase Water Jump
The steeplechase event requires a combination of speed, endurance, and jumping ability, as athletes must clear the barriers while maintaining their pace and negotiating the water jump. The rules and specifications for the steeplechase event are set by the International Association of Athletics Federations the governing body for the sport of athletics (track and field) worldwide; with minor adaptations by the NCAA for intercollegiate competition.
The steeplechase is a distance race with barriers and a water pit that athletes must clear during the race. According to the NCAA Track and Field and Cross Country rulebook, the standards for the steeplechase water jump are as follows:
- Length: The water pit must be at least 3.66 meters (12 feet) long.
- Width: The water pit must be at least 3.66 meters (12 feet) wide.
- Depth: The water pit must have a minimum depth of 0.7 meters (2 feet 4 inches) and a maximum depth of 0.9 meters (2 feet 11 inches).
- Slope: The slope of the water pit must not exceed 1:5, meaning that for every 5 meters in length, the water pit can rise by no more than 1 meter in height.
- Barrier: The water pit must be preceded by a solid barrier that is 91.4 cm (3 feet) high. Athletes are required to clear this barrier before landing in the water pit.
These standards may be subject to change and may vary depending on the specific NCAA division (Division I, Division II, or Division III) and other factors such as venue requirements. Therefore, it’s always best to refer to the official NCAA rules and regulations for the most up-to-date and accurate information on the steeplechase water jump standards in NCAA competitions.
ASTM F 2157-09 (2018) Standard Specification for Synthetic Surfaced Running Tracks
This specification establishes the minimum performance requirements and classification when tested in accordance with the procedures outlined within this specification. All documents referencing this specification must include classification required.
ASTM F 2569-11 Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Force Reduction Properties of Surfaces for Athletic Use
This test method covers the quantitative measurement and normalization of impact forces generated through a mechanical impact test on an athletic surface. The impact forces simulated in this test method are intended to represent those produced by lower extremities of an athlete during landing events on sport or athletic surfaces.
ASTM F 2949-12 Standard Specification for Pole Vault Box Collars
This specification covers minimum requirements of size, physical characteristics of materials, standard testing procedures, labeling and identification of pole vault box collars.
ASTM F 1162/F1162M-18 Standard Specification for Pole Vault Landing Systems
This specification covers minimum requirements of size, physical characteristics of materials, standard testing procedures, labeling and identification of pole vault landing systems.
ASTM F 2270-12 (2018) Standard Guide for Construction and Maintenance of Warning Track Areas on Sports Fields
This guide covers techniques that are appropriate for the construction and maintenance of warning track areas on sports fields. This guide provides guidance for the selection of materials, such as soil and sand for use in constructing or reconditioning warning track areas and for selection of management practices that will maintain a safe and functioning warning track.
ASTM F 2650-17e1 Standard Terminology Relating to Impact Testing of Sports Surfaces and Equipment
This terminology covers terms related to impact test methods and impact attenuation specifications of sports equipment and surfaces.
Voice Communications Devices for Use by Emergency Services
The frequency differences between public safety radio and public broadcasting radio are mainly due to their distinct purposes and requirements.
- Public safety radio operates on VHF and UHF bands for emergency services communication These radio systems are designed for robustness, reliability, and coverage over a specific geographic area. They prioritize clarity and reliability of communication over long distances and in challenging environments. Encryption may also be employed for secure communication.
- Public broadcasting radio operates on FM and AM bands for disseminating news, entertainment, and cultural content to the general public. These radio stations focus on providing a wide range of content, including news, talk shows, music, and cultural programming. They often cover broad geographic areas and aim for high-quality audio transmission for listener enjoyment. Unlike public safety radio, public broadcasting radio stations typically do not require encryption and prioritize accessibility to the general public.
NFPA 1930 is in a custom cycle due to the Emergency Response and Responder Safety Document Consolidation Plan (consolidation plan) as approved by the NFPA Standards Council. As part of the consolidation plan, NFPA 1930 is combining Standards NFPA 1801, NFPA 1802, NFPA 1932, NFPA 1937, and NFPA 1962.
Firefighter radio communication faces several special technical challenges due to the nature of the environment they operate in and the criticality of their tasks. Here are some of the key challenges:
- Interference and Signal Degradation: Buildings, debris, and firefighting equipment can obstruct radio signals, leading to interference and degradation of communication quality.
- Multipath Propagation: Radio signals can bounce off surfaces within buildings, causing multipath propagation, which results in signal fading and distortion.
- Limited Bandwidth: Firefighter radio systems often operate on limited bandwidths, which can restrict the amount of data that can be transmitted simultaneously, impacting the clarity and reliability of communication.
- Noise: The high noise levels present in firefighting environments, including sirens, machinery, and fire itself, can interfere with radio communication, making it difficult for firefighters to hear and understand each other.
- Line-of-Sight Limitations: Radio signals typically require a clear line of sight between the transmitter and receiver. However, in complex urban environments or within buildings, obstructions such as walls and floors can obstruct the line of sight, affecting signal strength and reliability.
- Equipment Durability: Firefighter radio equipment needs to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including high temperatures, smoke, water, and physical impacts. Ensuring the durability and reliability of equipment in such conditions is a significant challenge.
- Battery Life: Prolonged operations in emergency situations can drain radio batteries quickly. Firefighters need reliable battery life to ensure continuous communication throughout their mission.
- Interoperability: Different emergency response agencies may use different radio systems and frequencies, leading to interoperability issues. Ensuring seamless communication between various agencies involved in firefighting operations is crucial for effective coordination and response.
- Priority Access: During large-scale emergencies, such as natural disasters or terrorist attacks, communication networks may become congested, limiting access for emergency responders. Firefighters need priority access to communication networks to ensure they can effectively coordinate their efforts.
- Training and Familiarity: Operating radio equipment effectively under stress requires training and familiarity. Firefighters must be trained to use radio equipment efficiently and effectively, even in challenging conditions, to ensure clear and concise communication during emergencies.
National Institute of Standards & Technology
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670