“The wireless age has brought us closer together,
yet we must work to ensure that it does not divide us.”
— Guglielmo Marconi
When the electric grid and the internet are down and there is no cell service, radio can still work to help communities stabilize. Starting 2024 we will break down our coverage of the radio frequency technology standards used in educational settlements into into two categories:
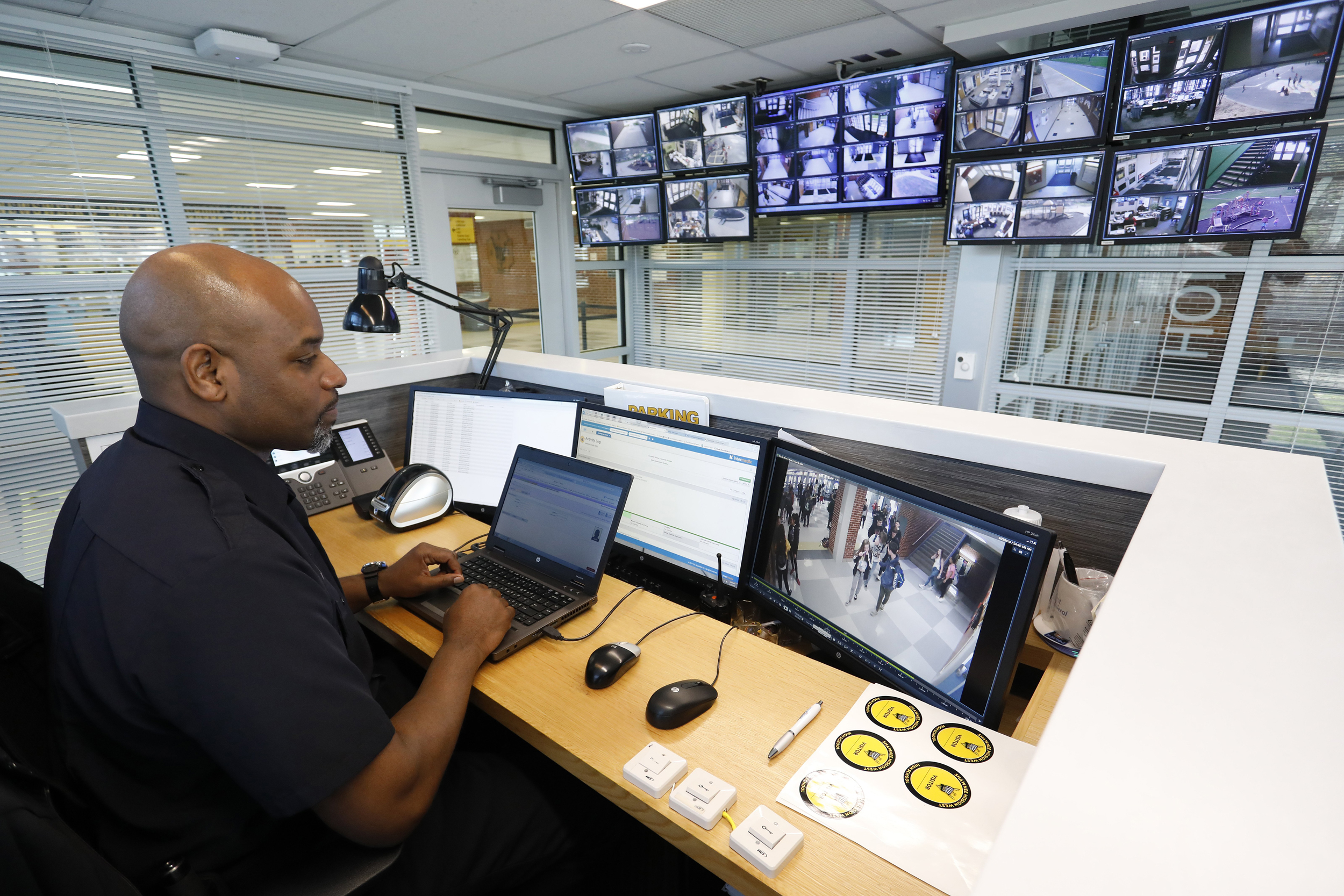
Radio 300: Security and maintenance radio. These usually use a single radio channel and operate in a half-duplex mode: only one user on the channel can transmit at a time, so users in a user group must take turns talking. The radio is normally in receive mode so the user can hear all other transmissions on the channel. When the user wants to talk he presses a “push-to-talk” button, which turns off the receiver and turns on the transmitter; when he releases the button the receiver is activated again. Multiple channels are provided so separate user groups can communicate in the same area without interfering with each other.
Note that a core title in this domain — NFPA 1802 Standard on Two-Way, Portable RF Voice Communications Devices for Use by Emergency Services Personnel in the Hazard Zone — is part of an NFPA catalog reorganization. Best practice content will be rolled into NFPA 1300 Standard on Fire and Emergency Service Use of Thermal Imagers, Two-Way Portable RF Voice Communication Devices, Ground Ladders, and Fire Hose, and Fire Hose Appliances.
As of this posting APCO International has no public consultations on any titles in its public safety radio standards catalog. (Association of Public Safety Communications Officials Standards Catalog)
The IT Law Wiki: Spectrum Allocation
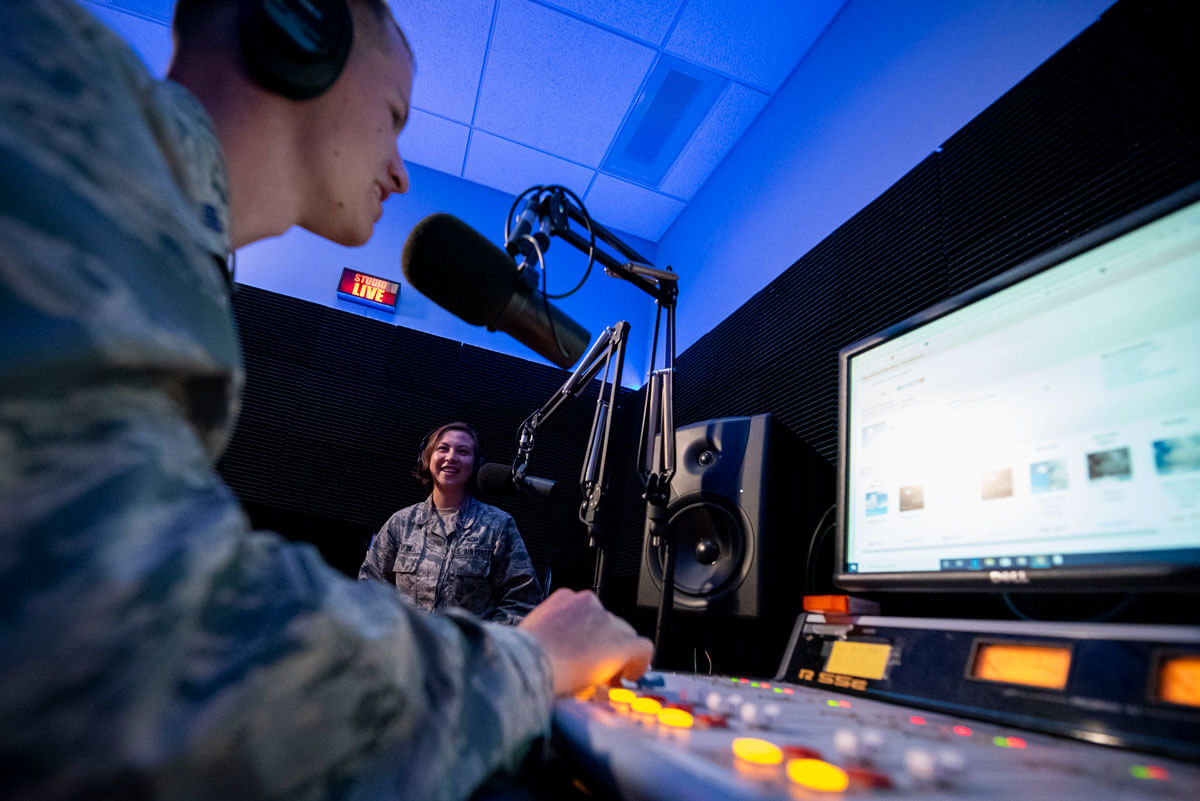
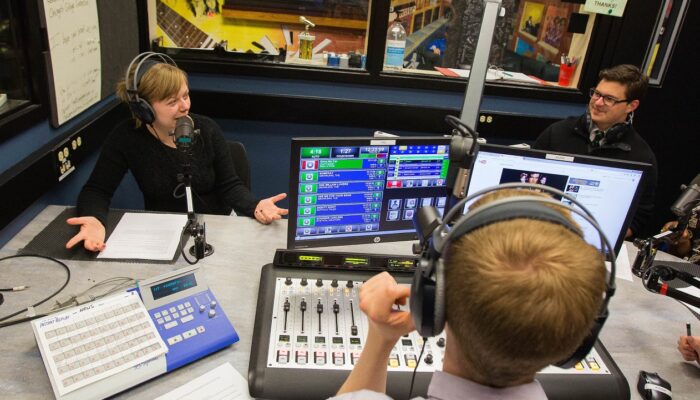
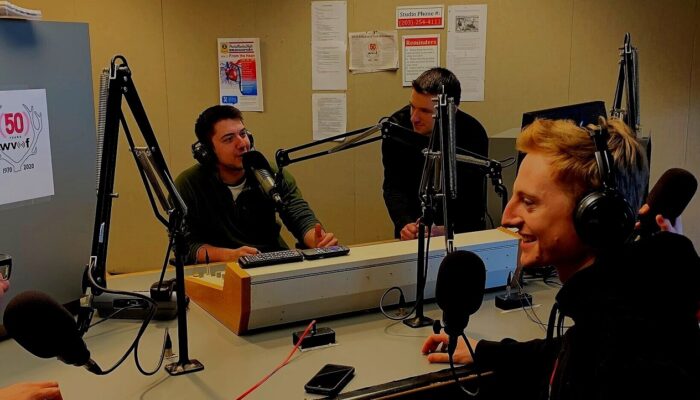
Radio 400: Student radio. College radio stations are typically considered to be public radio radio stations in the way that they are funded by donation and grants. The term “Public radio” generally refers to classical music, jazz, and news. A more accurate term is community radio, as most staff are volunteers, although many radio stations limit staff to current or recent students instead of anyone from the local community. There has been a fair amount of drama over student-run radio station history; a topic we steer away from.
The Low Power FM radio service was created by the Commission in January 2000. LPFM stations are authorized for noncommercial educational broadcasting only (no commercial operation) and operate with an effective radiated power (ERP) of 100 watts (0.1 kilowatts) or less, with maximum facilities of 100 watts ERP at 30 meters (100 feet) antenna height above average terrain. The approximate service range of a 100 watt LPFM station is 5.6 kilometers (3.5 miles radius). LPFM stations are not protected from interference that may be received from other classes of FM stations.
We follow — but do not respond — to consultations on titles covering the use of radio frequencies for the Internet of Things. At the moment, most of that evolution happens at the consumer product level; though it is wise to contemplate the use of the electromagnetic spectrum during widespread and extended loss of broadband services.

Maxwell equations: Four lines that provide a complete description of light, electricity and magnetism
We do not include policy specifics regarding the migration of National Public Radio beyond cultural content into political news; though we acknowledge that the growth of publicly financed radio domiciled in education communities is a consideration in the technology of content preparation informed by the Public Broadcasting Act of 1967.
We drill into technical specifics of the following:
- Radios used for campus public safety and campus maintenance
- Student-run campus radio stations licensed by the Federal Communications Commission as Low Power FM (LPFM)
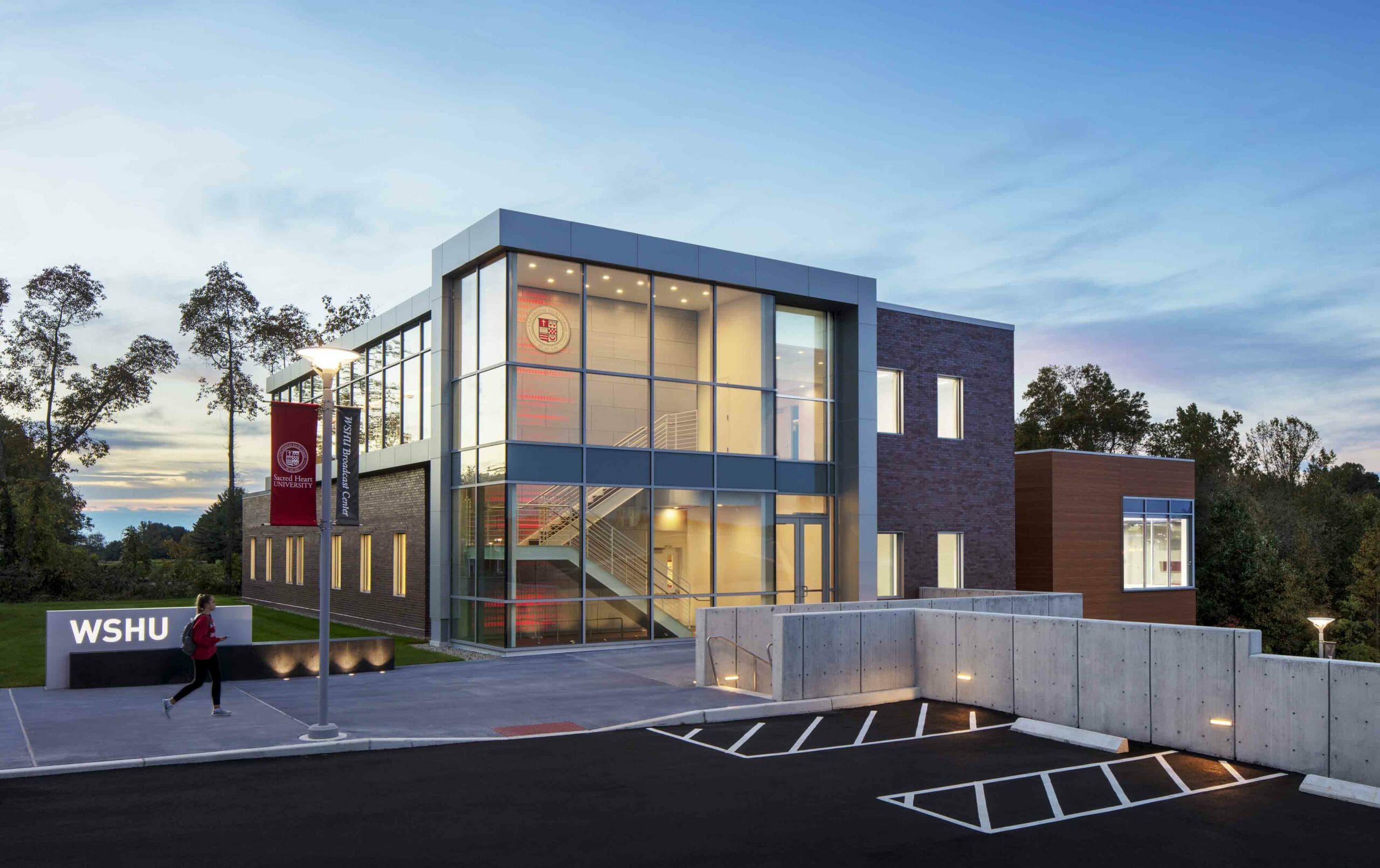
- Facilities for regional broadcast of National Public Radio operating from education communities
- Off-campus transmission facilities such as broadcast towers.
- Grounding, bonding, lightning protection of transmission and receiving equipment on buildings
- Broadcast studio electrotechnologies
Radio technology is regulated by the Federal Communications Commission with no ANSI-accredited standards setting organizations involved in leading practice discovery and promulgation. Again, we do not cover creative and content issues. Join us today at 11 AM/ET using the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
More
International Telecommunications Union: News Magazine No.1 2022
International Special Committee on Radio Interference
Campus Safety Radio JVCKENWOOD CAMPUS SAFETY 5 TIPS TO LOWER COSTS
Discussion: College Town Drive Time Radio OR “A Half Truth is a Full Lie”
Global Positioning System: A Generation of Service to the World