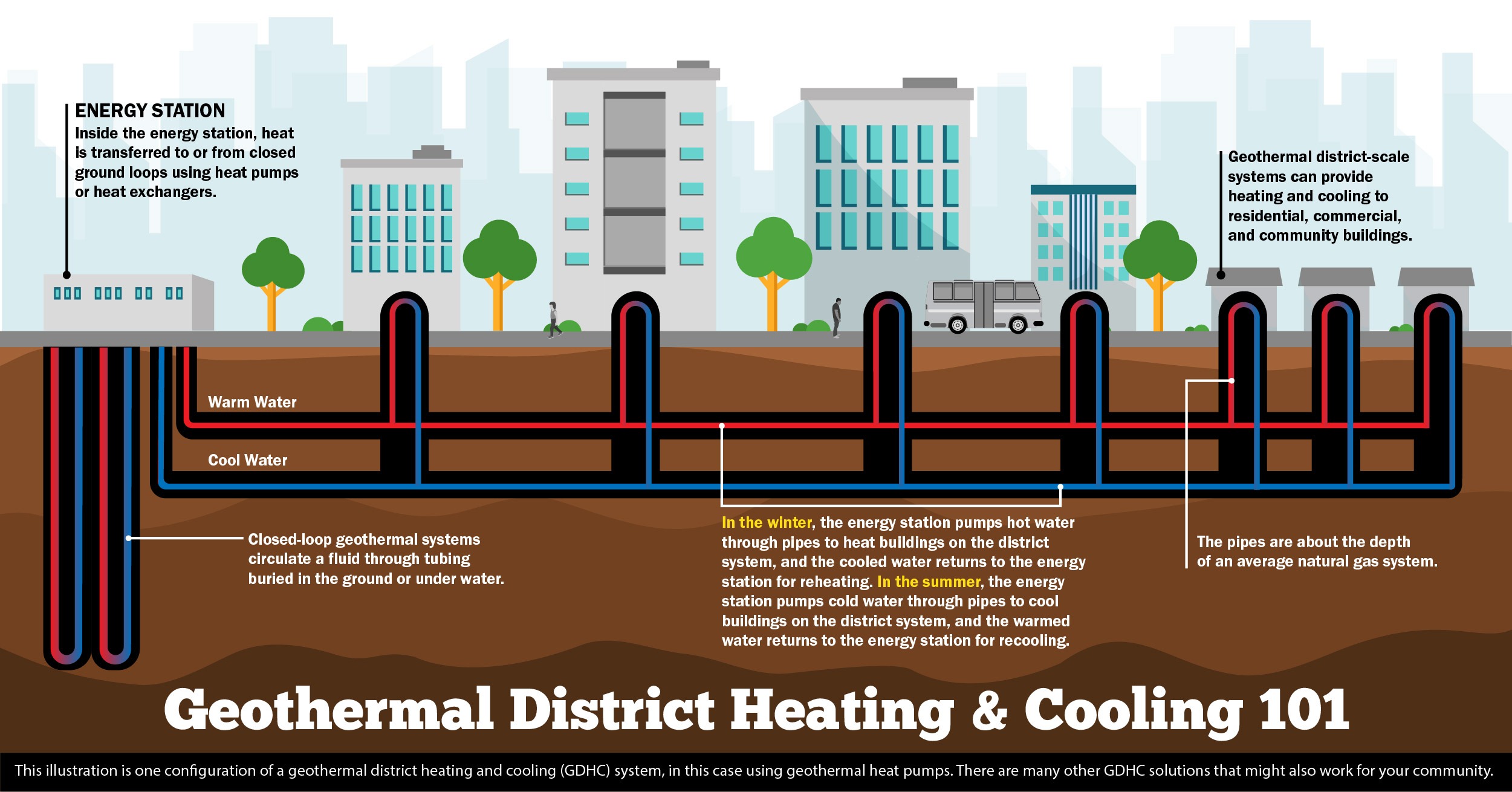
Geothermal systems cool buildings by leveraging the stable temperatures found beneath the Earth’s surface. A geothermal heat pump system consists of a ground loop, heat exchanger, and distribution system.
In cooling mode, the system extracts heat from the building and transfers it to the ground. The ground loop, typically composed of pipes buried horizontally or vertically, circulates a fluid that absorbs heat from the building’s interior. The fluid, warmed by this process, is then pumped through the ground loop where the Earth’s cooler temperatures absorb the heat, effectively dissipating it into the ground.
The cooled fluid returns to the heat pump, which distributes the now-cooler air throughout the building via the distribution system, such as ductwork. This process is highly efficient because the ground maintains a relatively constant temperature year-round, allowing the geothermal system to operate with less energy compared to traditional air-source cooling methods.
At the moment, though the technology has been made practical since Prince Piero Ginori Conti’s discovery in 1904, and has since tracked well in local building codes and environmental regulations, the bibliography for earth energy systems is nascent and relatively thin. One trade association is emerging from the gathering pace of applications and case studies: Closed-Loop/Geothermal Heat Pump Systems Design and Installation Standards

We maintain the IGSHPA catalog on the standing agenda of our Energy, Mechanical and Air Conditioning colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.

Partial Bibliography:
Handbook of Best Practices for Geothermal Drilling
Best Practices for Designing Geothermal Systems
Geothermal Direct Use Engineering and Design Guidebook
International Standards
ISO 13612-1:2014 – Heating and cooling systems in buildings — Method for calculation of the system performance and system design for heat pump systems — Part 1: Design and dimensioning.
-
- This standard covers the design and performance calculation of geothermal heat pump systems.
ISO 14823:2017 – Intelligent transport systems — Graphic data dictionary.
-
- While not specific to geothermal, this standard includes data relevant to various systems, including geothermal energy systems.
ISO 52000-1:2017 – Energy performance of buildings — Overarching EPB assessment — Part 1: General framework and procedures.
-
- This standard provides a general framework for assessing the energy performance of buildings, which includes geothermal systems.
IEC 61753-111-7:2014 – Fibre optic interconnecting devices and passive components – Performance standard – Part 111-7: Sealed closures for category S – Subterranean environments.
-
- Relevant for the installation of geothermal systems that include fiber optic components in subterranean environments.
North American Standards
CSA C448: Design and installation of earth energy systems.
ANSI/CSA C448 Series-16 – Design and Installation of Earth Energy Systems.
-
- This standard covers the design and installation of geothermal heat pump systems in the United States, providing guidelines on installation practices, materials, and system performance.
ASHRAE Standard 90.1 – Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings.
-
- This standard sets the minimum energy efficiency requirements for the design and construction of buildings, including the installation of geothermal systems.
IGSHPA Standards – International Ground Source Heat Pump Association (IGSHPA) Standards.
-
- The IGSHPA develops standards for the design and installation of geothermal heat pump systems, with a focus on closed-loop systems.
NFPA 54 – National Fuel Gas Code.
-
- Although primarily focused on fuel gas systems, this standard may intersect with geothermal systems when they involve hybrid solutions that include gas heating.
EPA Standards for Geothermal Energy (40 CFR Part 144) – Underground Injection Control (UIC) Program.
-
- This standard regulates the injection of fluids into underground wells, relevant for geothermal systems that involve deep wells for heat exchange.
UL 1995 – Heating and Cooling Equipment.
-
- This standard applies to the safety of heating and cooling equipment, including geothermal heat pumps.

“Neptune’s Horses” 1919 | Walter Crane





























