RELATED RESEARCH: NIST Technical Note 1779: General Guide on Emergency Communications Strategies for Buildings, February 2013
Tag Archives: D5
- Home
- Posts tagged "D5" (Page 2)

Farmer’s Dinner Theatre
This project was created a few years ago in Kentucky to bring awareness to farm safety through a dinner theatre is continuing to gain momentum in rural communities. The focus now is more on farm mental health and wellness.
Our Knott County Extension Office recently worked with UK student-athletes who conducted the Cats Holiday Toy Drive, spreading holiday cheer to children in Eastern KY 🎁
Read more >> https://t.co/NvscaMbIQZ pic.twitter.com/4fOtsRaLGl
— UK Extension (@UKExtension) December 22, 2022
This program has been adopted or implemented by extension services and related organizations in several other states. This initiative uses short plays performed during a community dinner to educate farmers and their families on health, safety, mental health, and farm-related issues in an engaging, non-traditional way:
- Nebraska — Cooperative Extension services have hosted events as part of the program’s expansion.
- North Carolina — The program is active through local extension efforts.
- Tennessee — Events have been held, often in collaboration with extension agents.
- Virginia — Particularly notable in the Shenandoah Valley, where Virginia Cooperative Extension offices (e.g., in Rockingham County) partnered with local groups like Valley Urgent Care and Future Farmers of America (FFA) chapters to organize Farm Safety Dinner Theaters, adapting the UK model for community-based participatory approaches.
The program is designed to be replicable nationwide. The University of Kentucky provides an online Farmers Dinner Theater Toolkit for any cooperative extension service, community group, or organization to stage their own events, customizing scripts to local needs. This has enabled wider adoption beyond the original sites. These efforts focus on helping farmers by addressing critical topics like injury prevention, hearing loss, skin cancer, stress, and suicide awareness in a social, farmer-friendly setting that encourages discussion and behavior change.
Entertainment Occupancies
2025 GROUP B PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES | Complete Monograph 2630 Pages
N.B.
G73-25 Section 410: Stages, Platforms and Technical Production Areas (Page 591-…) Submitted by the American Society of Theater Consultants
G77-25: Emergency ventilation (Pages 601-…)
G27-25: Type A and B stage definition (Page 490)
G78-25: Technical Production areas (Page 602)
American Society of Theater Consultants | Oberlin College
2024 GROUP A PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES | Complete Monograph 2658 Pages
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE

“View from the Ancient Theater in Taormina to Mount Etna” c. 1880 Carl Wuttke
Safety and sustainability for any facility begins with an understanding of who shall occupy it. University settings, with mixed-use phenomenon arising spontaneously and temporarily, present challenges and no less so in square-footage identified as performing arts facilities. Education communities present the largest installed base of mixed use and performing arts facilities. A distinction is made between supervised occupants that are in secondary schools (generally under age 18) and unsupervised occupants that are in university facilities (generally above age 18).
First principles regarding occupancy classifications for performing arts facilities appear in Section 303 of the International Building Code Assembly Group A-1. The public edition of the 2021 IBC is linked below:
2024 IBC Chapter 3: Occupancy Classification and Use
Each of the International Code Council code development groups A, B and C; fetch back to these classifications. You can sample the safety concepts in play with an examination of the document linked below:
2019 GROUP B PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE GROUP B I-CODES
2019 GROUP B PUBLIC COMMENT AGENDA
Each of the foregoing documents are lengthy so we recommend using search terms such as “school”, “college”, ‘”university”, “auditorium”, “theater”, “children”, “student” to hasten your cut through it.
We find continuation of lowering of the lighting power densities as noteworthy. Technical committees assembled and managed by the International Code Council, the American Society of Heating & Refrigeration Engineers and the Illumination Engineering Society are leaders in developing consensus products that drive the LED illumination transformation.
The revision schedule for the next tranche of ICC titles that are built upon the foundation of the IBC is linked below:
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
We encourage experts in education communities — facility managers, research and teaching staff, architectural and engineering students — to participate directly in the ICC Code Development process at the link below:
https://www.iccsafe.org/cdpaccess/









We reserve a place on the agenda of our standing Lively 200 colloquia on this topic. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [18-166]
Category: Architectural, Healthcare Facilities, Facility Asset Management
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Richard Robben
The International Code Council (ICC) develops its codes and standards through a consensus-driven process. The ICC Code Development Process follows these major stages:
Code Change Proposal Submission
Stakeholders (e.g., government officials, industry professionals, and the public) submit proposals to modify existing codes or introduce new provisions.
Committee Action Hearing (CAH)
Expert committees review and evaluate submitted proposals.
Public testimony is allowed, and committees vote on whether to approve, disapprove, or modify the proposals.
Public Comment Period
After the CAH, the public can submit comments or suggest modifications to the committee’s decisions.
These comments help refine the proposed changes before final voting.
Public Comment Hearing (PCH)
ICC members discuss and vote on public comments.
This step ensures that all voices are heard and debated before finalizing changes.
Online Governmental Consensus Vote (OGCV)
Governmental members vote on the final code changes electronically.
Only governmental voting members (e.g., code officials) participate in this stage to ensure the process remains unbiased.
Publication of New Code Edition
Approved code changes are incorporated into the next edition of the ICC codes.
The ICC updates its codes every three years (e.g., 2021, 2024, 2027 editions).
This structured process ensures that ICC codes remain comprehensive, up-to-date, and responsive to industry needs while maintaining safety and functionality.
Potato Latkes & Sufganiyot
Financial Position $1.417B (Page 16) | Campus Master Plan 2025-2035 | Revenue Bonds
Traditional Hanukkah foods (Spoon University) are often fried or cooked in oil, symbolizing the miracle of the oil that lasted eight days in the rededication of the Second Temple in Jerusalem.
Latkes (Potato Pancakes): Grated potatoes mixed with onions, eggs, and flour, then fried until crispy. They are often served with applesauce or sour cream.
Sufganiyot (Jelly-filled Doughnuts): Deep-fried doughnuts filled with jelly or custard and dusted with powdered sugar. They represent the oil that miraculously burned for eight days.
Brisket: Slow-cooked beef brisket is a popular main course for Hanukkah dinners.
Applesauce: Often served as a topping for latkes or as a side dish.
Matzo Ball Soup: While traditionally associated with Passover, some families also serve matzo ball soup during Hanukkah. It consists of light, fluffy dumplings made from matzo meal in a chicken broth.
Kugel: A baked casserole dish that can be sweet or savory, made with noodles, potatoes, or other ingredients.
Chocolate Gelt: Chocolate coins wrapped in gold or silver foil, often used in the game of dreidel.
Dreidel Cookies: Cookies shaped like the spinning top used in the traditional Hanukkah game of dreidel.
Cheese: In reference to the story of Judith, who is said to have fed cheese to an enemy general to make him thirsty and then gave him wine to make him drunk.
time to lock in, Knights 🔒
Good luck on finals! 🫶 pic.twitter.com/RdAT9Ug2e0
— UCF (@UCF) December 2, 2024
Fire Alarm & Signaling Code

“Prometheus Bound” | Thomas Cole (1847)
NFPA 72 National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code is one of the core National Fire Protection Association titles widely incorporated by reference into public safety legislation. NFPA 72 competes with titles of “similar” scope — International Fire Code — developed by the International Code Council. We place air quotes around the word similar because there are gaps and overlaps depending upon whether or not each is adopted partially or whole cloth by the tens of thousands of jurisdictions that need both.
Our contact with NFPA 72 dates back to the early 2000’s when the original University of Michigan advocacy enterprise began challenging the prescriptive requirements for inspection, testing and maintenance (IT&M) in Chapter 14. There are hundreds of fire alarm shops, and thousands of licensed fire alarm technicians in the education facility industry and the managers of this cadre of experts needed leadership in supporting their lower #TotalCostofOwnership agenda with “code-writing and vote-getting”. There was no education industry trade association that was even interested, much less effective, in this space so we had to do “code writing and vote getting” ourselves (See ABOUT).
Code writing and vote getting means that you gather data, develop relationships with like minded user-interests, find agreement where you can, then write proposals and defend them at NFPA 72 technical committee meetings for 3 to 6 years. Prevailing in the Sturm und Drang of code development for 3 to 6 years should be within the means of business units of colleges and universities that have been in existence for 100’s of years. The real assets under the stewardship of these business units are among the most valuable real assets on earth.
Consider the standard of care for inspection, testing and maintenance. Our cross-cutting experience in over 100 standards suites allows us to say with some authority that, at best the IT&M tables of NFPA 72 Chapter 14 present easily enforceable criteria for IT&M of fire alarm and signaling systems. At worst, Chapter 14 is a solid example of market-making by incumbent interests as the US standards system allows. Many of the IT&M requirements can be modified for a reliability, or risk-informed centered maintenance program but fire and security shops in the education industry are afraid to apply performance standards because of risk exposure. This condition is made more difficult in large universities that have their own maintenance and enforcement staff. The technicians see opportunities to reduce IT&M frequencies — thereby saving costs for the academic unit facility managers — the enforcement/compliance/conformity/risk management professionals prohibit the application of performance standards. They want prescriptive standards for bright line criteria to make their work easier to measure.
While we have historically focused on Chapter 14 we have since expanded our interest into communication technologies within buildings since technicians and public safety personnel depend upon them. Content in Annex G — Guidelines for Emergency Communication Strategies for Buildings and Campuses — is a solid starting point and reflects of our presence when the guidance first appeared in the 2016 Edition. We shall start with a review of the most recent transcript of the NFPA Technical Committee on Testing and Maintenance of Fire Alarm and Signaling Systems
NFPA 72 First Draft Meeting (A2024)
Public Emergency Reporting Systems (SIG-PRS) First Draft
Public comment of the First Draft of the 2025 Edition is receivable until May 31, 2023. As always, we encourage direct participation in the NFPA process by workpoint experts with experience, data and even strong opinions about shortcomings and waste in this discipline. You may key in your proposals on the NFPA public input facility linked below:
You will need to set up a (free) NFPA TerraView account. Alternatively, you may join us any day at 11 AM US Eastern time or during our Prometheus or Radio colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the online meeting.
Issue: [15-213]
Category: Fire Safety & Security, #SmartCampus, Informatics
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Joe DeRosier, Josh Elvove, Jim Harvey, Marcelo Hirschler
More
2013 NFPA 72 National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code (357 pages)
TIA-222 Standard For Towers And Antenna Supporting Structures
Bleachers, Folding Seating & Grandstands
Play is the making of civilization—how one plays the game
more to the point than whether the game is won or lost.
We follow development of best practice literature for spectator seating structures produced by the International Code Council, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA 102), the American Society of Civil Engineers Structural Engineering Institute (ASCE SEI-7). There are also federal regulations promulgated by the Consumer Product Safety Commission. (Note that some of the regulations were inspired by the several regional building code non-profits before the International Code Council was formed in year ~ 2000)
The parent standard from the International Code Council is linked below:
ICC 300 Standard on Bleachers, Folding and Telescopic Seating, and Grandstands
The development of this standard is coordinated with the ICC Group A Codes. We have tracked concepts in it previous revisions; available in the link below.
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
As always, we encourage our colleagues with workpoint experience to participate directly in the ICC Code Development process. CLICK HERE to get started.








Category: Athletics & Recreation, Architectural, Public Safety
Contact: Mike Anthony, Jack Janveja, Richard Robben
Virtual reality technology in evacuation simulation of sport stadiums
LEARN MORE:
Radio Transmission Power & Frequency Allocation
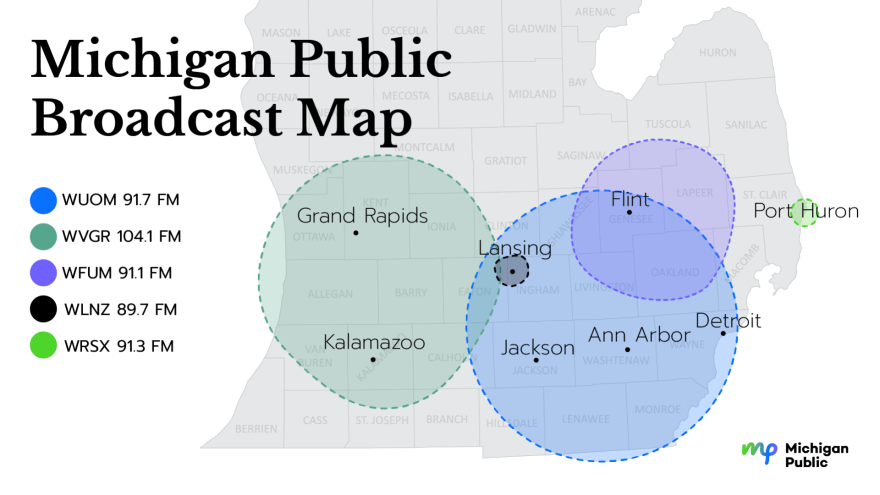
Why are there at least 10 publicly funded radio stations receivable in a 75 mile radius (back and forth, up and down) the I-94/I-75 corridor of Michigan — all of them domiciled in public universities? These stations also receive revenue from other non-profit organizations, unending funding drives and private advertising from multinational financing organizations such as Schwab, Fidelity and other for-profit corporations. Most of them purchase their “content” from the same source; reflecting the same large government bias seen across the entire nation; concentrated in college towns with spotty intellectual history.
Within an approximate 50 mile radius of the University of Michigan, five national public radio stations are receivable:
WUOM University of Michigan Ann Arbor
WEMU Eastern Michigan University
WDET Wayne State University
WKAR Michigan State University
WGTE University of Toledo
Move 25 miles to the northwest and two more are receivable:
WLNZ Landing Community College
Move 25 miles northeast and three more are receivable
WFUM University of Michigan Flint
WMUK Western Michigan University
WAUS Andrews University
FCC ONLINE TABLE OF FREQUENCY ALLOCATIONS: 47 C.F.R. § 2.106
(Revised July 1, 2022)
Standards for radio broadcast coverage can vary depending on factors like location, broadcasting technology, and regulatory requirements. Here’s a general list covering various aspects:
- Technical Standards:
- Transmission Power and Frequency Allocation: Standards set by regulatory bodies like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States or Ofcom in the UK regulate the power levels and frequencies allocated to radio stations to prevent interference.
- Audio Quality: Standards for audio encoding and decoding, such as those defined by organizations like the European Broadcasting Union (EBU) or the Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) standards.
- Antenna Design and Installation: Standards for antenna design, placement, and maintenance to ensure efficient transmission and coverage.
- Content Standards:
- Language and Content Regulations: Regulations on language, decency, and content suitability enforced by regulatory bodies to ensure broadcasts adhere to community standards and do not contain offensive or harmful material.
- Advertising Standards: Guidelines on the content and placement of advertisements to prevent deceptive practices and ensure fairness and transparency.
- Copyright and Licensing: Regulations governing the use of copyrighted material and licensing agreements for broadcasting music, interviews, and other content.
- Emergency Broadcast Standards:
- Emergency Alert Systems (EAS): Standards for implementing emergency alert systems to disseminate important information to the public during emergencies or disasters.
- Public Safety Communications: Standards for communication protocols and procedures to coordinate with emergency services and agencies during crises.
- Accessibility Standards:
- Closed Captioning: Standards for providing closed captioning for the hearing impaired, ensuring accessibility to radio broadcasts.
- Descriptive Video Service (DVS): Standards for providing audio descriptions of visual content for the visually impaired.
- Ethical Standards:
- Journalistic Integrity: Guidelines for ethical reporting and journalism standards, including accuracy, fairness, and impartiality.
- Disclosure of Sponsored Content: Standards for disclosing sponsored or paid content to maintain transparency and trust with the audience.
- Conflict of Interest Policies: Standards for identifying and managing conflicts of interest in news reporting and programming.
- Health and Safety Standards:
- Electromagnetic Radiation Exposure Limits: Standards set by health organizations and regulatory bodies to limit human exposure to electromagnetic radiation emitted by radio transmitters.
- Workplace Safety: Standards for ensuring the safety of radio station personnel and compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
These standards are often enforced by governmental regulatory agencies, industry organizations, and professional associations to ensure the quality, integrity, and safety of radio broadcast coverage.
National Public Radio is the soundtrack of American academia and American academia has always been partial to large government:
“It was always the woman, and above all the young ones who where the most bigoted adherents to the party” — (George Orwell, ‘1984’)
— NPR (@NPR) April 12, 2023
National Center for Spectator Sports Safety and Security
The legacy of Merry Old England lives on in the American South. pic.twitter.com/ujnDUIz3Q3
— 𝒩𝒶𝓉𝒶𝓁𝒾𝒶 (@classicspilled) October 3, 2025
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670