“In swimming, there are no referees, no foul lines,
no time-outs, and no substitutions.
It’s just you and the water.” – Unknown
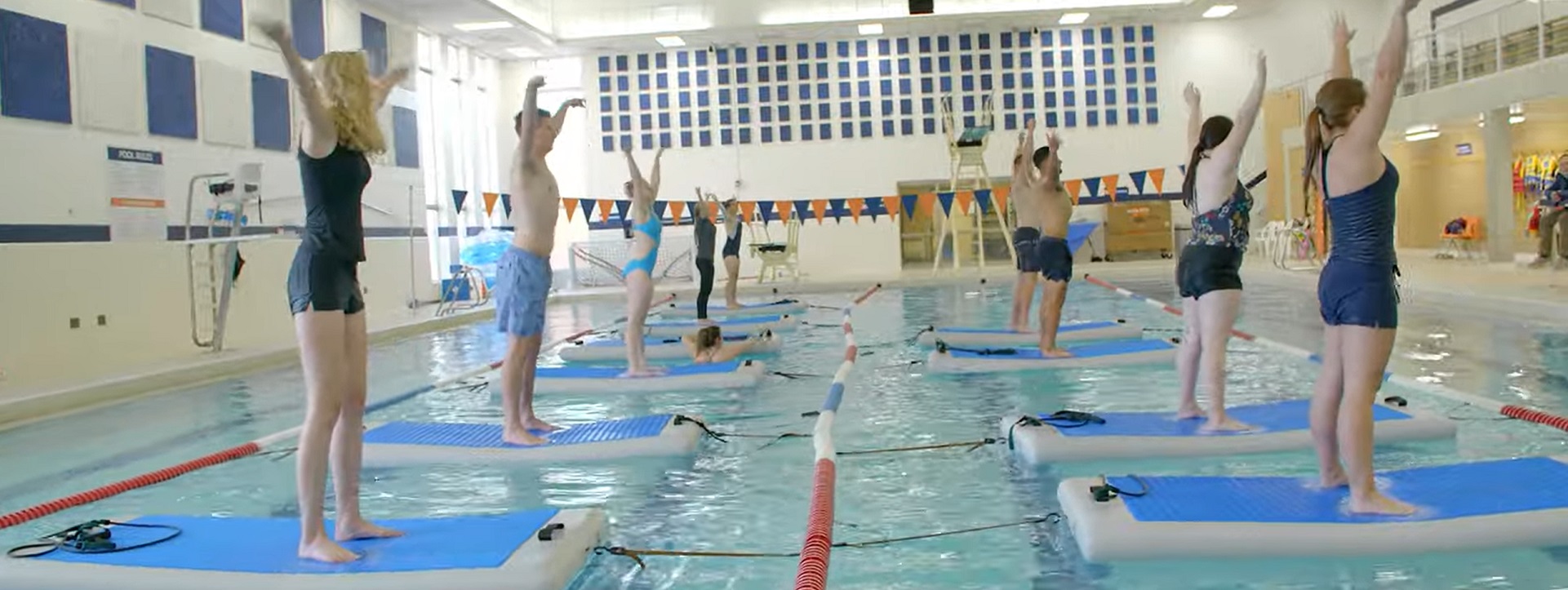
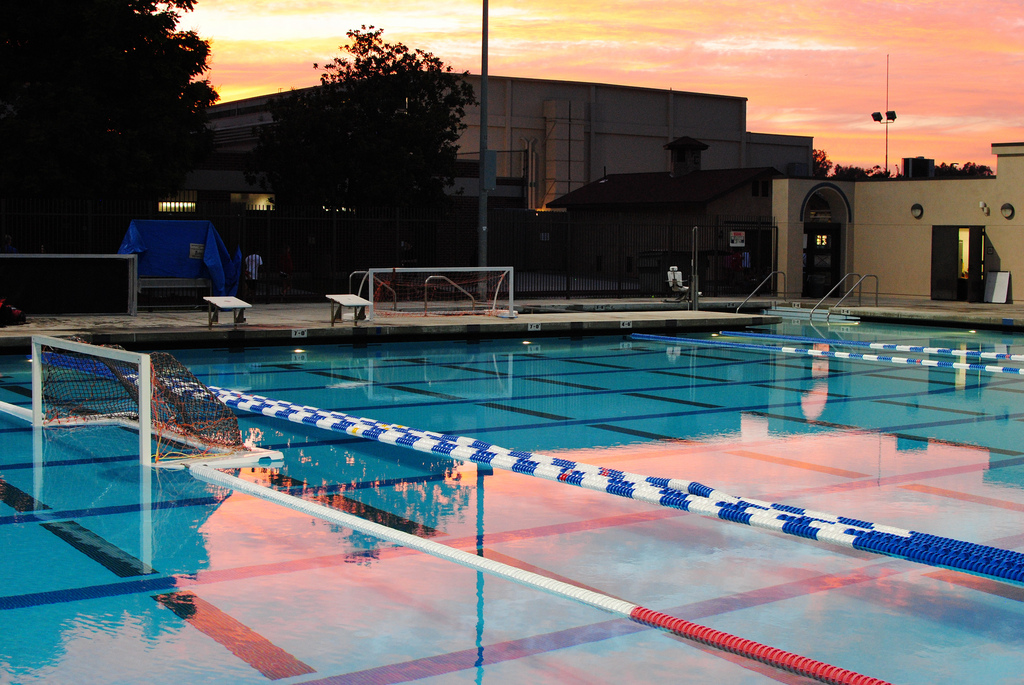
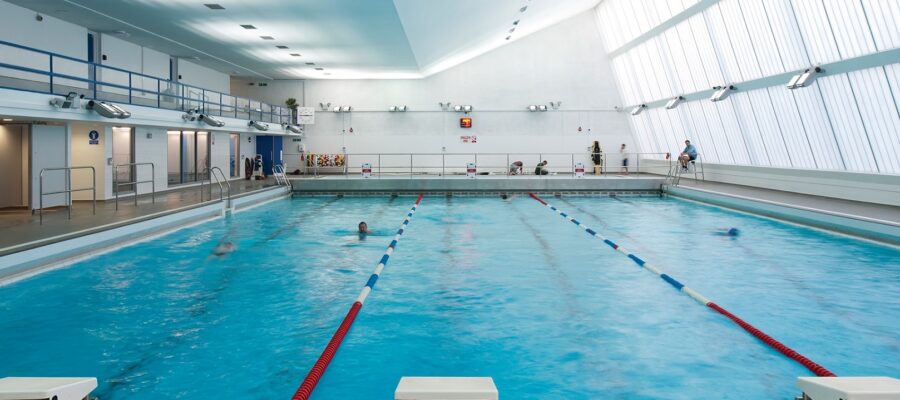
There are several specific problems that swimming pool overhead lighting aims to solve:
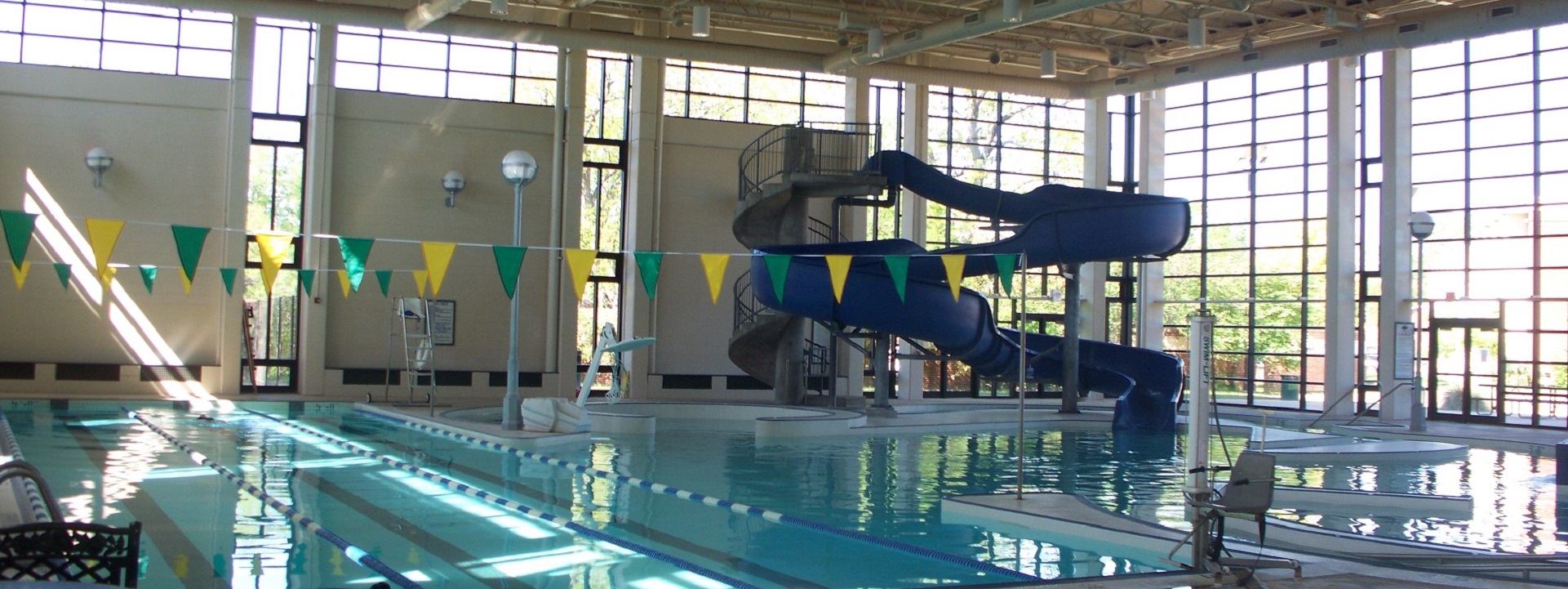
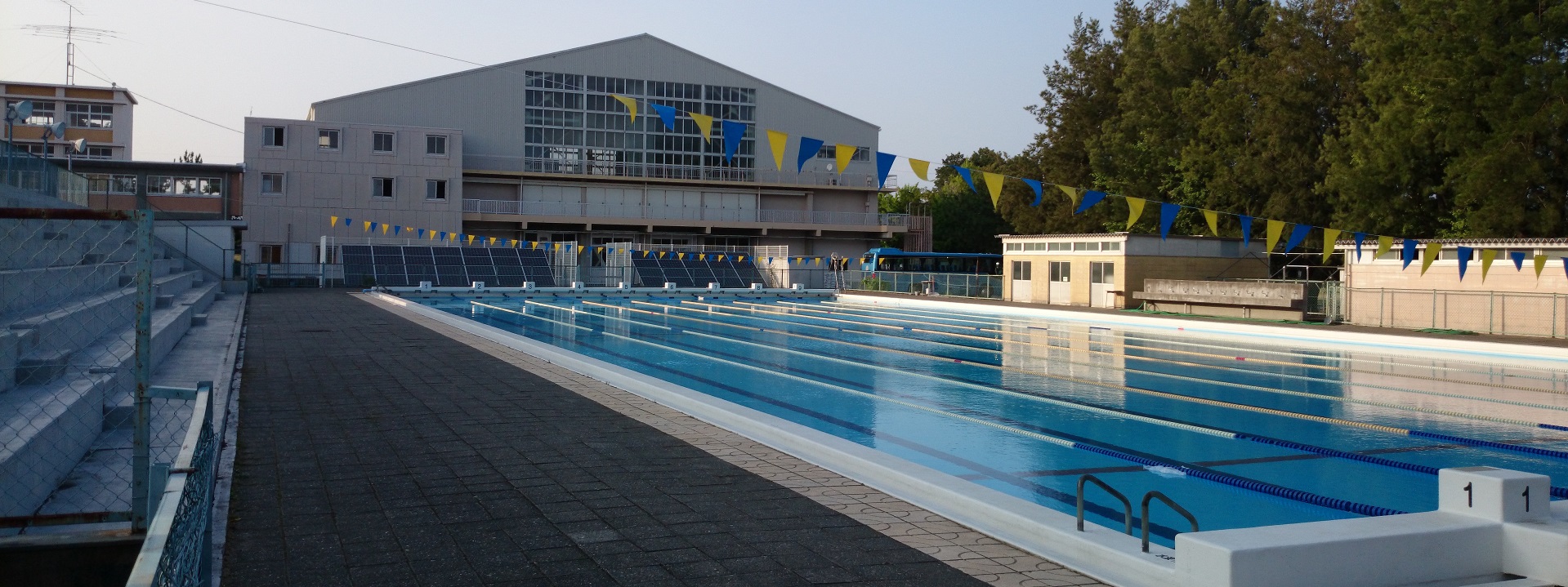
- Visibility: Swimming pool overhead lighting is designed to improve visibility in and around the pool. This is important for safety reasons, as it helps swimmers see where they are going and avoid obstacles or hazards.
- Aesthetics: Overhead lighting can enhance the appearance of the swimming pool by creating a visually appealing atmosphere. This is especially important for commercial pools where the aesthetics can be an important factor in attracting customers.
- Functionality: Overhead lighting can provide additional functionality by allowing the pool to be used during evening hours or in low light conditions. This can increase the usability of the pool and make it more appealing to users.
- Energy efficiency: Modern overhead pool lighting solutions are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing the overall energy consumption and operating costs of the pool.
- Longevity: Overhead pool lighting must be designed to withstand exposure to water, chlorine, and other harsh chemicals, as well as exposure to the elements. The lighting system must be durable and reliable to ensure longevity and prevent costly repairs or replacements.
Overall, swimming pool overhead lighting is an important component of a safe, functional, and visually appealing pool. It provides illumination for visibility, enhances aesthetics, and improves functionality, while also being energy-efficient and durable.
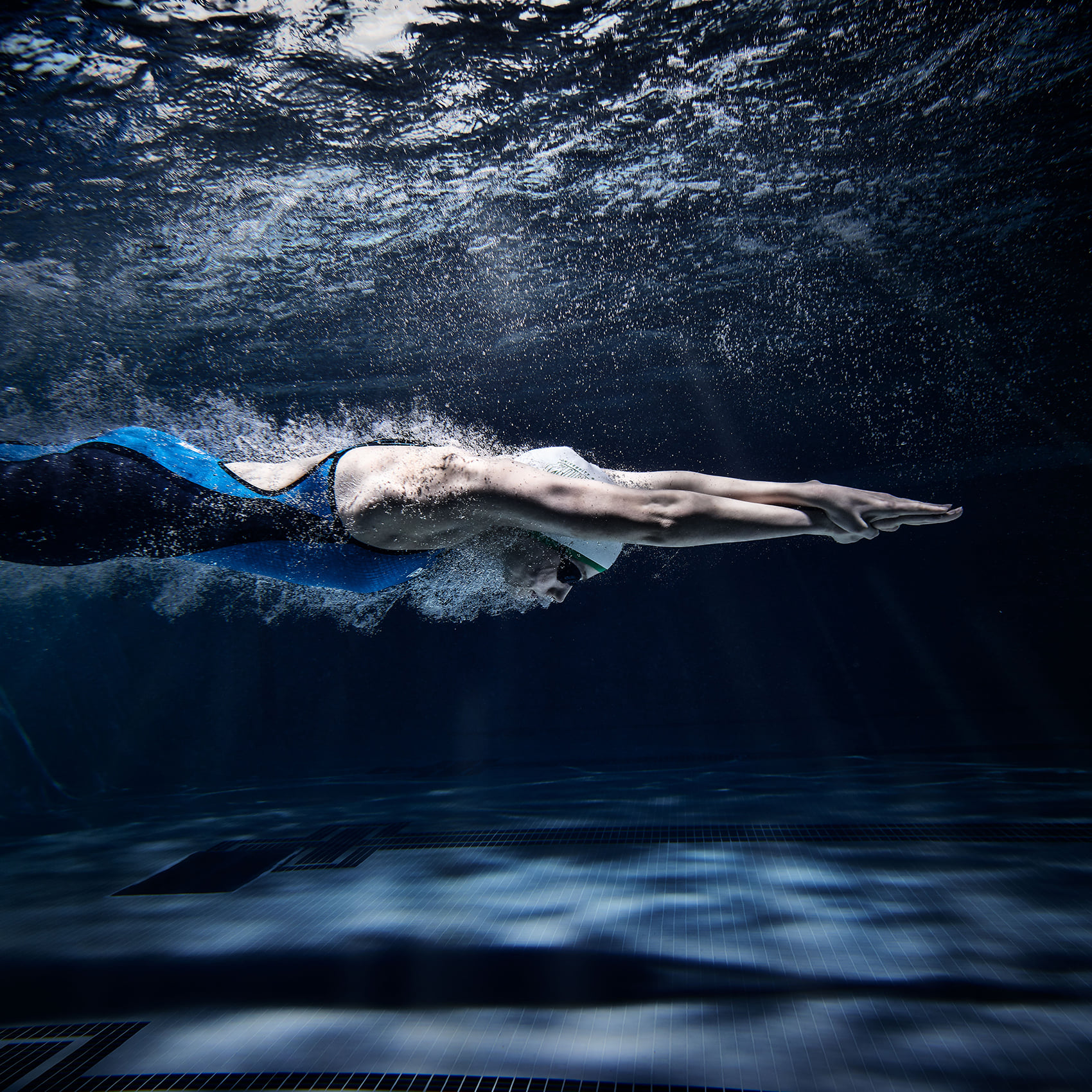

After athletic arena life safety obligations are met (governed legally by NFPA 70, NFPA 101, NFPA 110, the International Building Code and possibly other state adaptations of those consensus documents incorporated by reference into public safety law) business objective standards may come into play. For almost all athletic facilities, the consensus documents of the Illumination Engineering Society[1], the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers[2][3] provide the first principles for life safety. For business purposes, the documents distributed by the National Collegiate Athletic Association inform the standard of care for individual athletic arenas so that swiftly moving media production companies have some consistency in power sources and illumination as they move from site to site. Sometimes concepts to meet both life safety and business objectives merge.
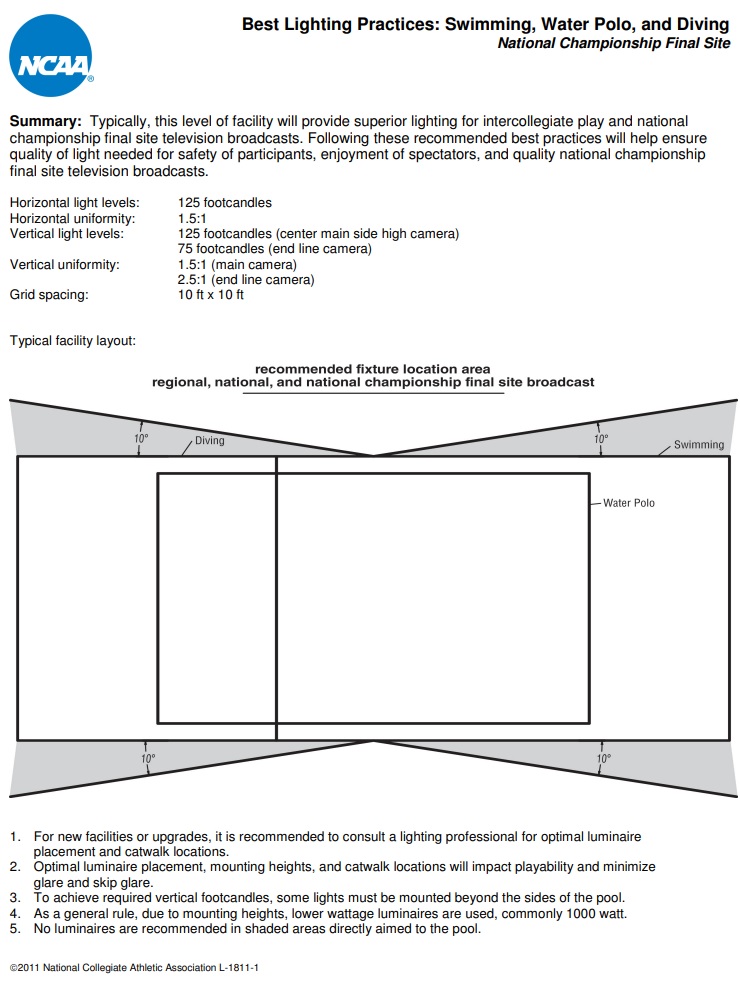
During water sport season the document linked below provides information to illumination designers and facility managers:
NCAA Best Lighting Practices
Athletic programs are a significant source of revenue and form a large part of the foundation of the brand identity of most educational institutions in the United States. We focus primarily upon the technology standards that govern the safety, performance and sustainability of these enterprises. We collaborate very closely with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee where subject matter experts in electrical power systems meet 4 times each month in the Americas and Europe.
See our CALENDAR for our next colloquium on Sport facility codes and standards. We typically walk through the safety and sustainability concepts in play; identify commenting opportunities; and find user-interest “champions” on the technical committees who have a similar goal in lowering #TotalCostofOwnership.

Issue: [15-138]*
Category: Electrical, Architectural, Arts & Entertainment Facilities, Athletics
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Jack Janveja, Jose Meijer, Scott Gibbs
More
Watersport Time Standards
Sport Lighting