Facilities Management Campus Planning | University of Colorado Net Position 2023: $9.661B
Tag Archives: Summer
- Home
- Posts tagged "Summer"

“Lisztomania” Brat Pack Mashup
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Morning Tea
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Campus Child Day Care
Today at the usual hour we review a selection of global building codes and standards that guide best practice for safety, accessibility, and functionality for day care facilities; with special interest in the possibilities for co-locating square footage into the (typically) lavish unused space in higher education facilities.
Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
International Building Code
-
- Governs overall building construction, fire safety, occupancy classification, and egress requirements for daycare centers.
International Fire Code
-
- Regulates fire prevention measures, emergency exits, fire alarms, sprinkler systems, and evacuation protocols for daycare centers.
National Fire Protection Association
-
- NFPA 101 – Life Safety Code: Addresses occupancy classification, means of egress, fire safety, and emergency planning.
- NFPA 5000 – Building Construction and Safety Code: Provides fire protection and structural safety guidelines.
Americans with Disabilities Act
-
- Requires daycare centers to be accessible for children and parents with disabilities, covering entrances, bathrooms, play areas, and signage.
European Norms – CEN Standards
-
- EN 1176 – Playground Equipment and Safety Requirements: Covers safety standards for daycare playgrounds and outdoor spaces.
- EN 16890 – Safety Requirements for Mattresses in Children’s Products.
British Standards (BS) for Early Years Facilities
-
- BS 8300: Accessibility requirements for childcare facilities.
- BS 9999: Fire safety guidance for daycare and educational buildings.
Australian Building Code & National Construction Code
-
- Covers fire safety, structural integrity, ventilation, and child safety measures for daycare centers.
ISO 45001 – Occupational Health and Safety Management
-
- Establishes safety requirements for employees working in daycare facilities, ensuring a safe environment for both children and staff.
Canadian Building Code & Fire Code (NBC & NFC)
-
- Provides structural, fire safety, and child safety guidelines for daycare centers in Canada.
“A Group of Children Playing the Game ‘Oranges and Lemons’ in a Domestic Interior”
Harry Brooker (1848-1940)https://t.co/YpxsSUf8nV pic.twitter.com/kjhgJvYxPs— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) February 24, 2025
Push-Cart Cold Brew
Standards Indiana | Indiana University Total Net Position: $5.223B
Evie Mendelsohn: Campus Symphony – The Art and Architecture of Indiana University
“Beau Soir” 1878 Claude Debussy
Abhik Mazuimder & Bryson Karrer
Indiana University @IUJSoM
print(“Evensong”)https://t.co/vgfbVyudWM pic.twitter.com/fznFUJZHMK— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) September 26, 2022
I taught these boys (grown men!) when they were just 6 and now they are graduating from college 😮 pic.twitter.com/eNmVf6HiXy
— Sarah Oberle (@S_Oberle) May 21, 2024
Rain & Lightning
The thunderbolt steers all things.
—Heraclitus, c. 500 BC

After the rain. Personal photograph taken by Mike Anthony biking with his niece in Wirdum, The Netherlands
Today at 15:00 UTC we examine the technical literature about rainwater management in schools, colleges and universities — underfoot and on the roof. Lightning protection standards will also be reviewed; given the exposure of outdoor athletic activity and exterior luminaires.
We draw from previous standardization work in titles involving water, roofing systems and flood management — i.e. a cross-cutting view of the relevant standard developer catalogs. Among them:
American Society of Civil Engineers
American Society of Plumbing Engineers
ASHRAE International
ASTM International
Construction Specifications Institute (Division 7 Thermal and Moisture Protection)
Environmental Protection Agency | Clean Water Act Section 402
Federal Emergency Management Agency
FM Global
Water Cycle Equation:
Precipitation = Runoff + Infiltration + Evapotranspiration + ΔStoragehttps://t.co/DdIA3UWUxy
Georgia Southern University Civil Engineering & Constructionhttps://t.co/rVhv4tyuBt@GeorgiaSouthern pic.twitter.com/9yo5NZrJQH— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) September 10, 2020
IAPMO Group (Mechanical and Plumbing codes)
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
Heat Tracing Standards
Notice of New Standard Product IEEE 1692-2023
IEEE Guide for the Protection of Communication Installations from Lightning Effectshttps://t.co/y8ZdmtBDRV pic.twitter.com/JG30sFEJlr
— IEEE Standards Association | IEEE SA (@IEEESA) September 2, 2024
International Code Council
Chapter 15 Roof Assemblies and Rooftop Structures
Why, When, What and Where Lightning Protection is Required
National Fire Protection Association
National Electrical Code: Article 250.16 Lightning Protection Systems
Lightning Protection
Underwriters Laboratories: Lightning Protection
Underground Stormwater Detention Vaults
United States Department of Agriculture: Storm Rainfall Depth and Distribution
Readings: The “30-30” Rule for Outdoor Athletic Events Lightning Hazard
As always, our daily colloquia are open to everyone. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
Enjoying Princeton, with its replica of Magdalen's Great Tower, and its authentically British-style rain pic.twitter.com/FqaQTIUFqc
— Dinah Rose (@DinahGLRoseKC) September 10, 2023
The “lightning effect” seen in carnival tricks typically relies on a scientific principle known as the Lichtenberg figure or Lichtenberg figure. This phenomenon occurs when a high-voltage electrical discharge passes through an insulating material, such as wood or acrylic, leaving behind branching patterns resembling lightning bolts.
The process involves the creation of a temporary electric field within the material, which polarizes its molecules. As the discharge propagates through the material, it causes localized breakdowns, creating branching paths along the way. These branching patterns are the characteristic Lichtenberg figures.
In the carnival trick, a high-voltage generator is used to create an electrical discharge on a piece of insulating material, such as acrylic. When a person touches the material or a conductive object placed on it, the discharge follows the path of least resistance, leaving behind the branching patterns. This effect is often used for entertainment purposes due to its visually striking appearance, resembling miniature lightning bolts frozen in the material. However, it’s crucial to handle such demonstrations with caution due to the potential hazards associated with high-voltage electricity.
How you know we haven’t had rain for awhile… pic.twitter.com/5zb84HeDUR
— Allison farms (@Allisonfarms) August 5, 2024
Lightning Protection Systems
2026 Public Input Report | 2026 Public Comment Report
FEMA National Risk Index: Lightning
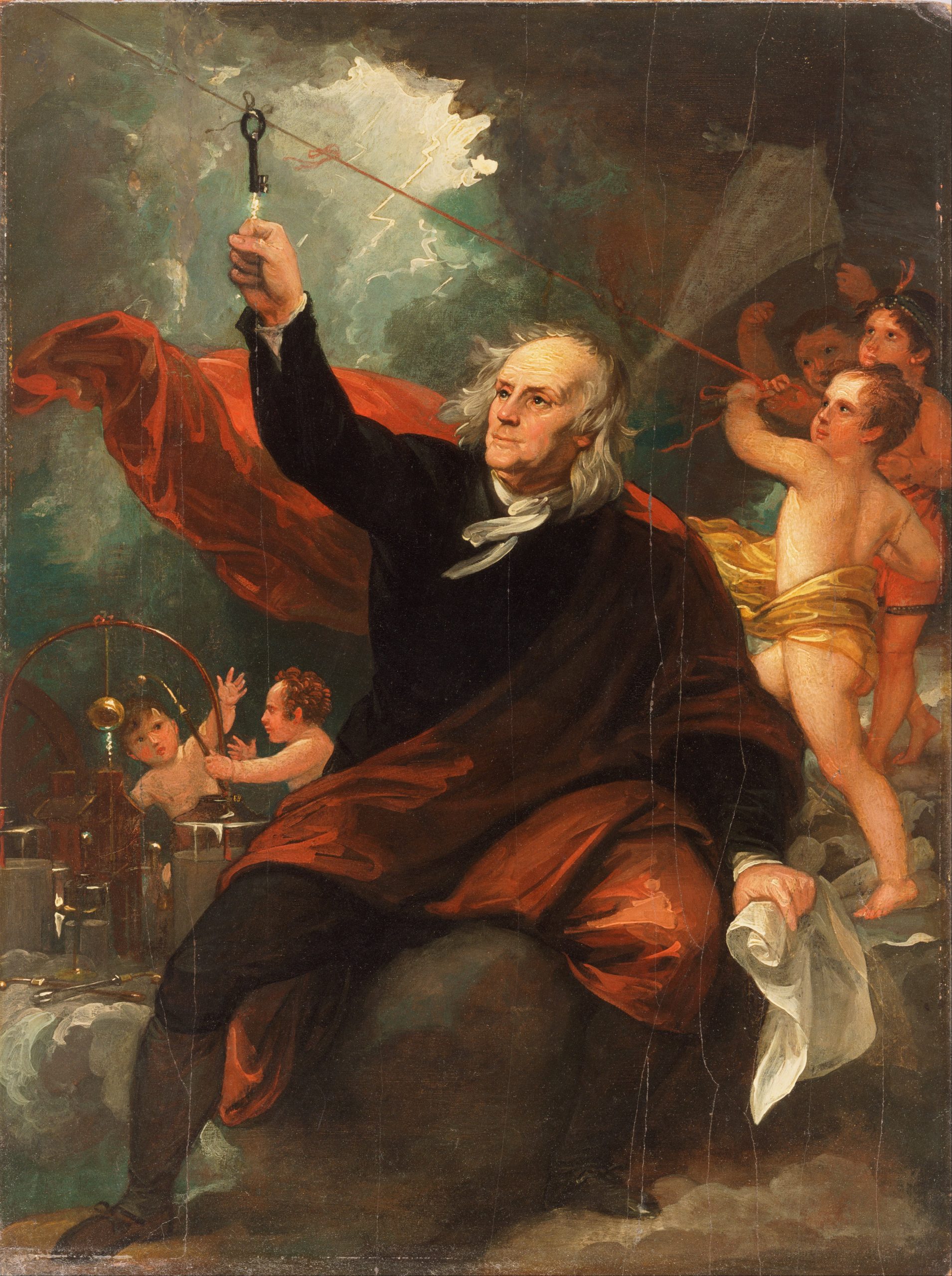
Benjamin Franklin conducted his famous experiment with lightning on June 10, 1752.
He used a kite and a key to demonstrate that lightning was a form of electricity.
This experiment marked an important milestone in understanding the nature of electricity
and laid the foundation for the development of lightning rods and other lightning protection systems.
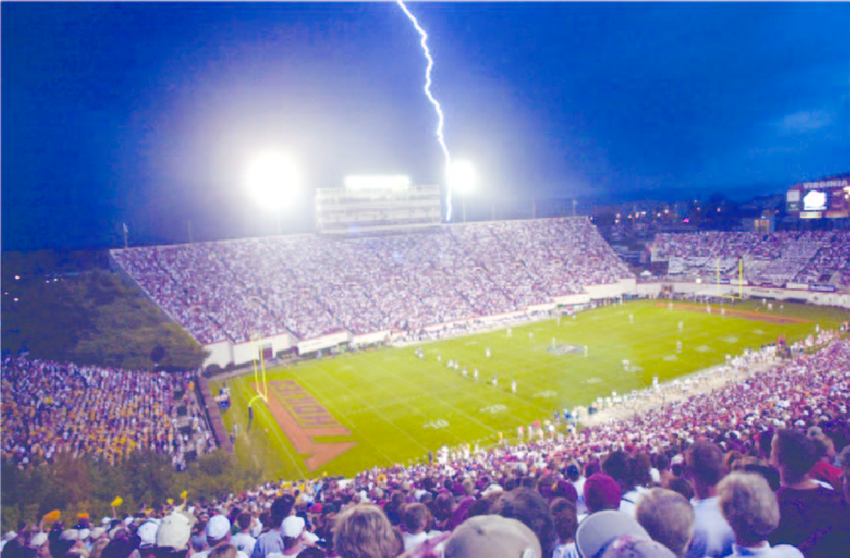
Seasonal extreme weather patterns in the United States, resulting in damages to education facilities and delays in outdoor athletic events — track meets; lacrosse games, swimming pool closures and the like — inspire a revisit of the relevant standards for the systems that contribute to safety from injury and physical damage to buildings: NFPA 780 Standard for the Installation of Lightning Protection Systems
To paraphrase the NFPA 780 prospectus:
- This document shall cover traditional lightning protection system installation requirements for the following:
(1) Ordinary structures
(2) Miscellaneous structures and special occupancies
(3) Heavy-duty stacks
(4) Structures containing flammable vapors, flammable gases, or liquids with flammable vapors
(5) Structures housing explosive materials
(6) Wind turbines
(7) Watercraft
(8) Airfield lighting circuits
(9) Solar arrays - This document shall address lightning protection of the structure but not the equipment or installation requirements for electric generating, transmission, and distribution systems except as given in Chapter 9 and Chapter 12.
(Electric generating facilities whose primary purpose is to generate electric power are excluded from this standard with regard to generation, transmission, and distribution of power. Most electrical utilities have standards covering the protection of their facilities and equipment. Installations not directly related to those areas and structures housing such installations can be protected against lightning by the provisions of this standard.)
- This document shall not cover lightning protection system installation requirements for early streamer emission systems or charge dissipation systems.
“Down conductors” must be at least #2 AWG copper (0 AWG aluminum) for Class I materials in structures less than 75-ft in height
“Down conductors: must be at least 00 AWG copper (0000 AWG aluminum) for Class II Materials in structures greater than 75-ft in height.
Related grounding and bonding requirements appears in Chapters 2 and Chapter 3 of NFPA 70 National Electrical Code. This standard does not establish evacuation criteria.
The current edition is dated 2023 and, from the transcripts, you can observe concern about solar power and early emission streamer technologies tracking through the committee decision making. Education communities have significant activity in wide-open spaces; hence our attention to technical specifics.
Public input on the 2026 revision is receivable until 1 June 2023.
We always encourage our colleagues to key in their own ideas into the NFPA public input facility (CLICK HERE). We maintain NFPA 780 on our Power colloquia which collaborates with IEEE four times monthly in European and American time zones. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
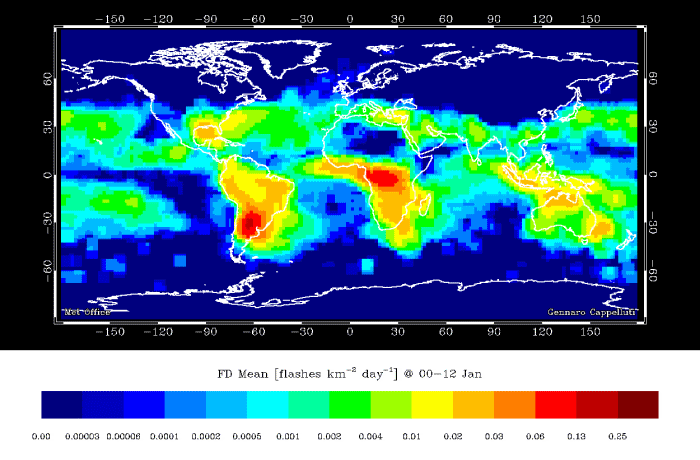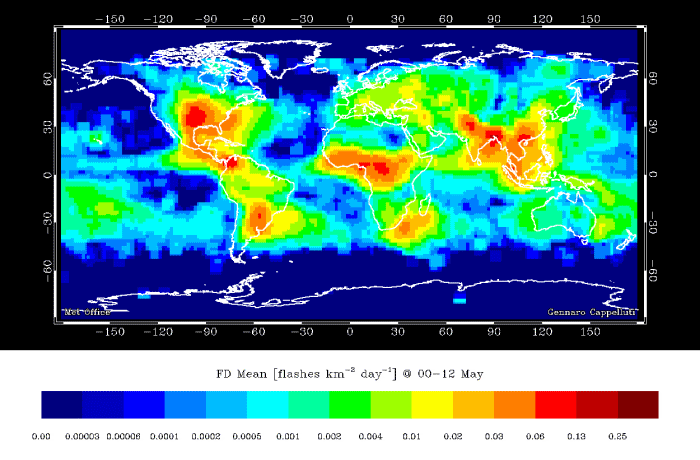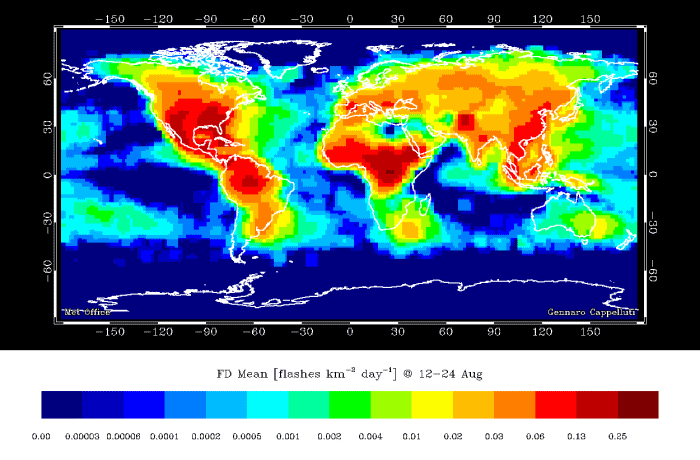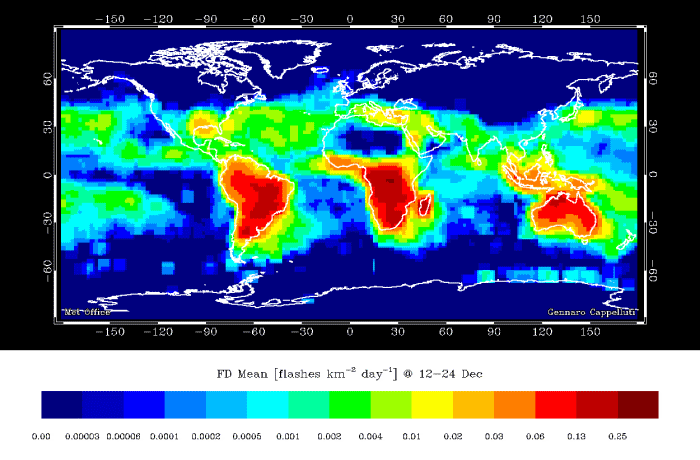
Lightning flash density – 12 hourly averages over the year (NASA OTD/LIS) This shows that lightning is much more frequent in summer than in winter, and from noon to midnight compared to midnight to noon.
Issue: [14-105]
Category: Electrical, Telecommunication, Public Safety, Risk Management
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Kane Howard
Didn't really plan for all possibilities, did they. 🤓
NC State's brand-new scoreboard shorts out due to lightning storms https://t.co/KWm78nrRau
— DJ (@DJ87112331) September 10, 2023
The "Top engineering school in the state" just built a $15 million scoreboard without a lightning rod.
Wasn't it just last year that their game got delayed because they couldn't turn the lights on? https://t.co/wWt9gSMYIv
— Steele (@0Gstank) September 9, 2023
More
Installing lightning protection system for your facility in 3 Steps (Surge Protection)
IEEE Education & Healthcare Facility Electrotechnology
Readings: The “30-30” Rule for Outdoor Athletic Events Lightning Hazard
Churches and chapels are more susceptible to lightning damage due to their height and design. Consider:
Height: Taller structures are more likely to be struck by lightning because they are closer to the cloud base where lightning originates.
Location: If a church or chapel is situated in an area with frequent thunderstorms, it will have a higher likelihood of being struck by lightning.
Construction Materials: The materials used in the construction of the building can affect its vulnerability. Metal structures, for instance, can conduct lightning strikes more readily than non-metallic materials.
Proximity to Other Structures: If the church or chapel is located near other taller structures like trees, utility poles, or buildings, it could increase the chances of lightning seeking a path through these objects before reaching the building.
Lightning Protection Systems: Installing lightning rods and other lightning protection systems can help to divert lightning strikes away from the structure, reducing the risk of damage.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of lightning protection systems is essential to ensure their effectiveness. Neglecting maintenance could result in increased susceptibility to lightning damage.
Historical Significance: Older buildings might lack modern lightning protection systems, making them more vulnerable to lightning strikes.
The risk can be mitigated by proper design, installation of lightning protection systems, and regular maintenance.
Storm Shelters
2024 GROUP A PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES
When is it ever NOT storm season somewhere in the United States; with several hundred schools, colleges and universities in the path of them? Hurricanes also spawn tornadoes. This title sets the standard of care for safety, resilience and recovery when education community structures are used for shelter and recovery. The most recently published edition of the joint work results of the International Code Council and the ASCE Structural Engineering Institute SEI-7 is linked below:
2020 ICC/NSSA 500 Standard for the Design and Construction of Storm Shelters.
Given the historic tornados in the American Midwest this weekend, its relevance is plain. From the project prospectus:
The objective of this Standard is to provide technical design and performance criteria that will facilitate and promote the design, construction, and installation of safe, reliable, and economical storm shelters to protect the public. It is intended that this Standard be used by design professionals; storm shelter designers, manufacturers, and constructors; building officials; and emergency management personnel and government officials to ensure that storm shelters provide a consistently high level of protection to the sheltered public.
This project runs roughly in tandem with the ASCE Structural Engineering Institute SEI-17 which has recently updated its content management system and presented challenges to anyone who attempts to find the content where it used to be before the website overhaul. In the intervening time, we direct stakeholders to the link to actual text (above) and remind education facility managers and their architectural/engineering consultants that the ICC Code Development process is open to everyone.
The ICC receives public response to proposed changes to titles in its catalog at the link below:
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
You are encouraged to communicate with Kimberly Paarlberg (kpaarlberg@iccsafe.org) for detailed, up to the moment information. When the content is curated by ICC staff it is made available at the link below:
We maintain this title on the agenda of our periodic Disaster colloquia which approach this title from the point of view of education community facility managers who collaborate with structual engineers, architects and emergency management functionaries.. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting, open to everyone. ![]()
Readings:
FEMA: Highlights of ICC 500-2020
ICC 500-2020 Standard and Commentary: ICC/NSSA Design and Construction of Storm Shelters
Students presenting posters on how to be prepared for natural disasters and emergencies #onedistrictoneteam #D59learns @CCSD59 @D59Byrd pic.twitter.com/NOsa3ekkTD
— Mrs. Darga (@MrsDarga) September 19, 2023
Chilled Banana Pudding Overnight Oats
2024 Net Position: $880,267,990 (Page 4) | Senior Administration Organization Chart
Banana Pudding Overnight Oats is a delicious and nutritious breakfast dish made by combining rolled oats, mashed bananas, milk, and other flavorings, and allowing them to sit and “soak” in the refrigerator overnight. This results in a creamy, flavorful, and satisfying bowl of oats that are ready to eat in the morning without any cooking required. It’s convenient make-ahead breakfast option that can be customized to suit individual tastes and dietary preferences. Here’s a simple recipe for Banana Pudding Overnight Oats:
Ingredients:
1 ripe banana, mashed
1/2 cup rolled oats
1/2 cup milk (any type of milk, such as dairy milk, almond milk, or coconut milk)
1 tablespoon chia seeds (optional)
1 teaspoon vanilla extract
1/2 teaspoon ground cinnamon
1/4 teaspoon salt
1 tablespoon sweetener of choice (such as honey, maple syrup, or agave nectar)
Additional banana slices, crushed cookies, or whipped cream for garnish (optional)
Instructions:
In a medium-sized bowl, mash the ripe banana with a fork until smooth. Add the rolled oats, milk, chia seeds (if using), vanilla extract, cinnamon, salt, and sweetener to the bowl with the mashed banana. Stir well to combine. Cover the bowl with plastic wrap or a lid and refrigerate overnight, or for at least 4-6 hours, to allow the oats to absorb the liquid and soften.
In the morning, give the oats a good stir and adjust the sweetness or consistency to taste by adding more sweetener or milk if desired. Serve the Banana Pudding Overnight Oats in bowls or jars, and garnish with additional banana slices, crushed cookies, or whipped cream if desired.
Enjoy your delicious and creamy Banana Pudding Overnight Oats for a nutritious and convenient breakfast!
vbvbvbvb
More:
Texas A&M University: Banana Nut Overnight Oats
Harvard University: Oats the Nutrition Source
Colorado University: Overnight Oats
US Food & Drug Administration: Gluten-Free Labeling of Foods
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670