The literature for designing, building and maintaining sport and recreation related spaces in education settlements cuts across so many safety and sustainability risk aggregations that, starting 2024, we begin breaking up the topic according to four seasons; mindful that not all seasons are present in all settlements at all times of the year and in different age groups.
Volleyball at the high school level in the USA is a winter sport but a fall sport at the collegiate level. Rifle and Fencing is only a collegiate sport. Swimming “short course” (25 meter) competition is a winter sport depending upon regional facilities. (e.g. University of Southern California, University of North Carolina Wilmington, University of Michigan)
Join us today when we sort through the literature and any live public consultations on proposed changes to the most frequently referenced titles.
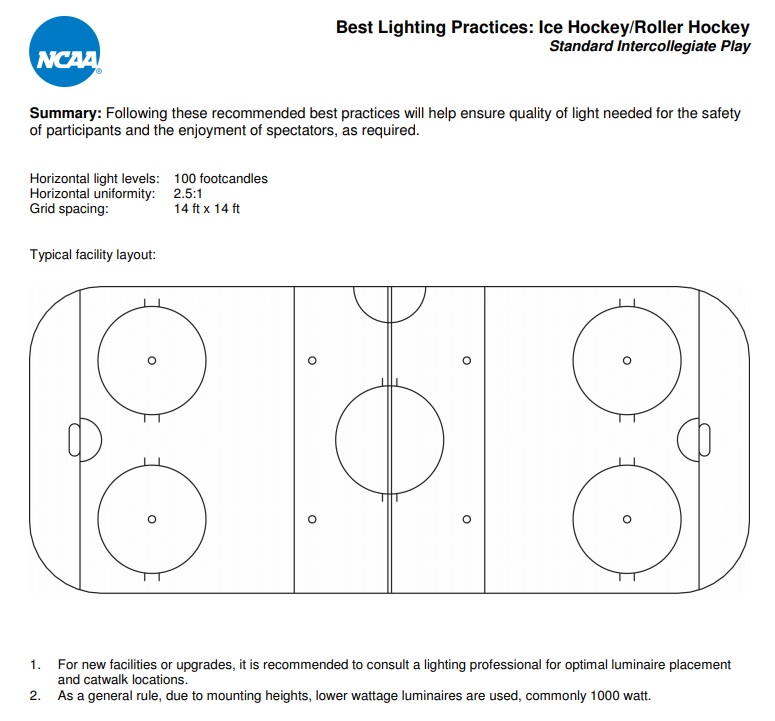
Hockey
Figure Skating
Rifle
Recreation
Swimming
Related:
Virtual reality technology in evacuation simulation of sport stadiums