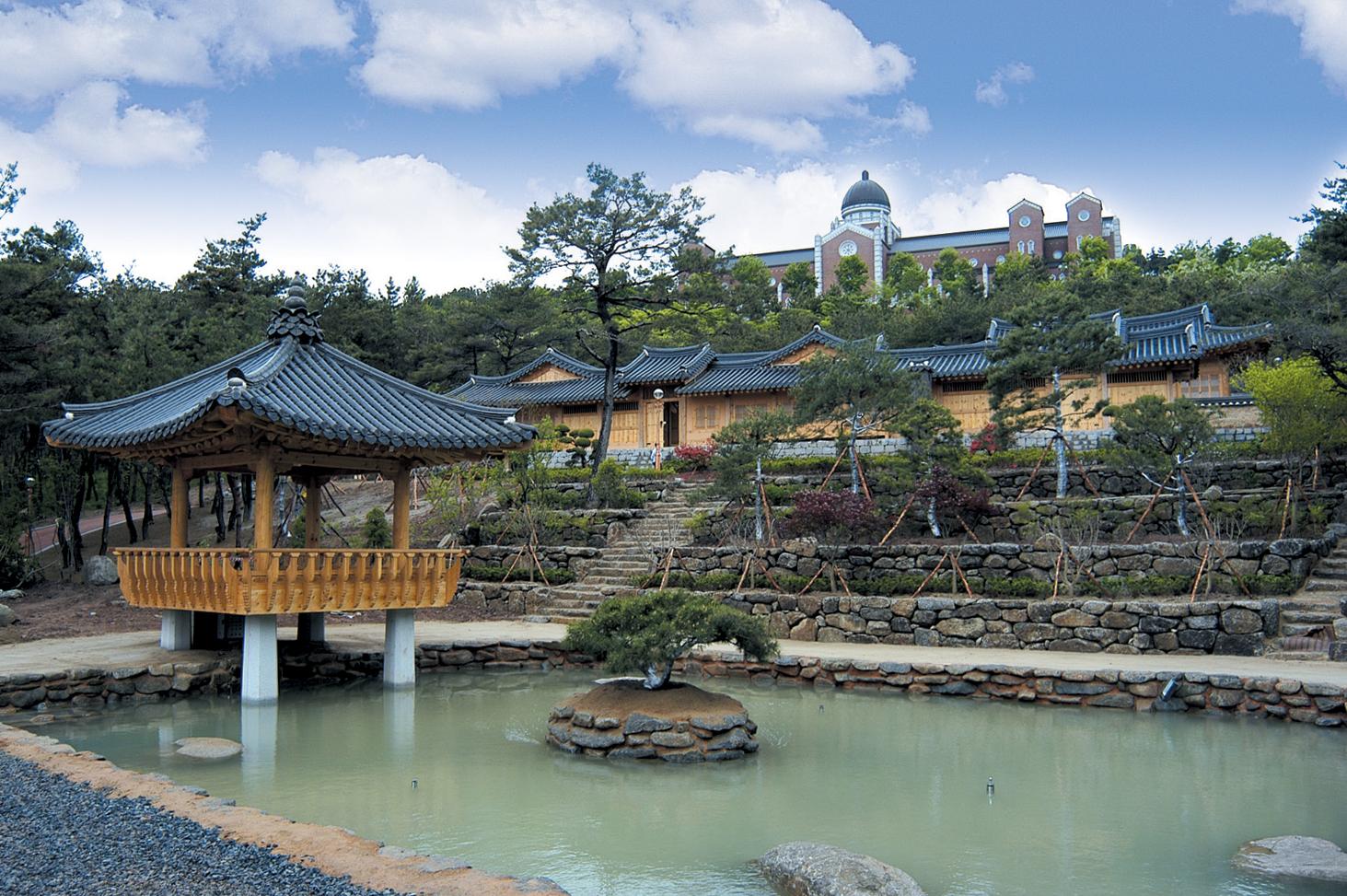
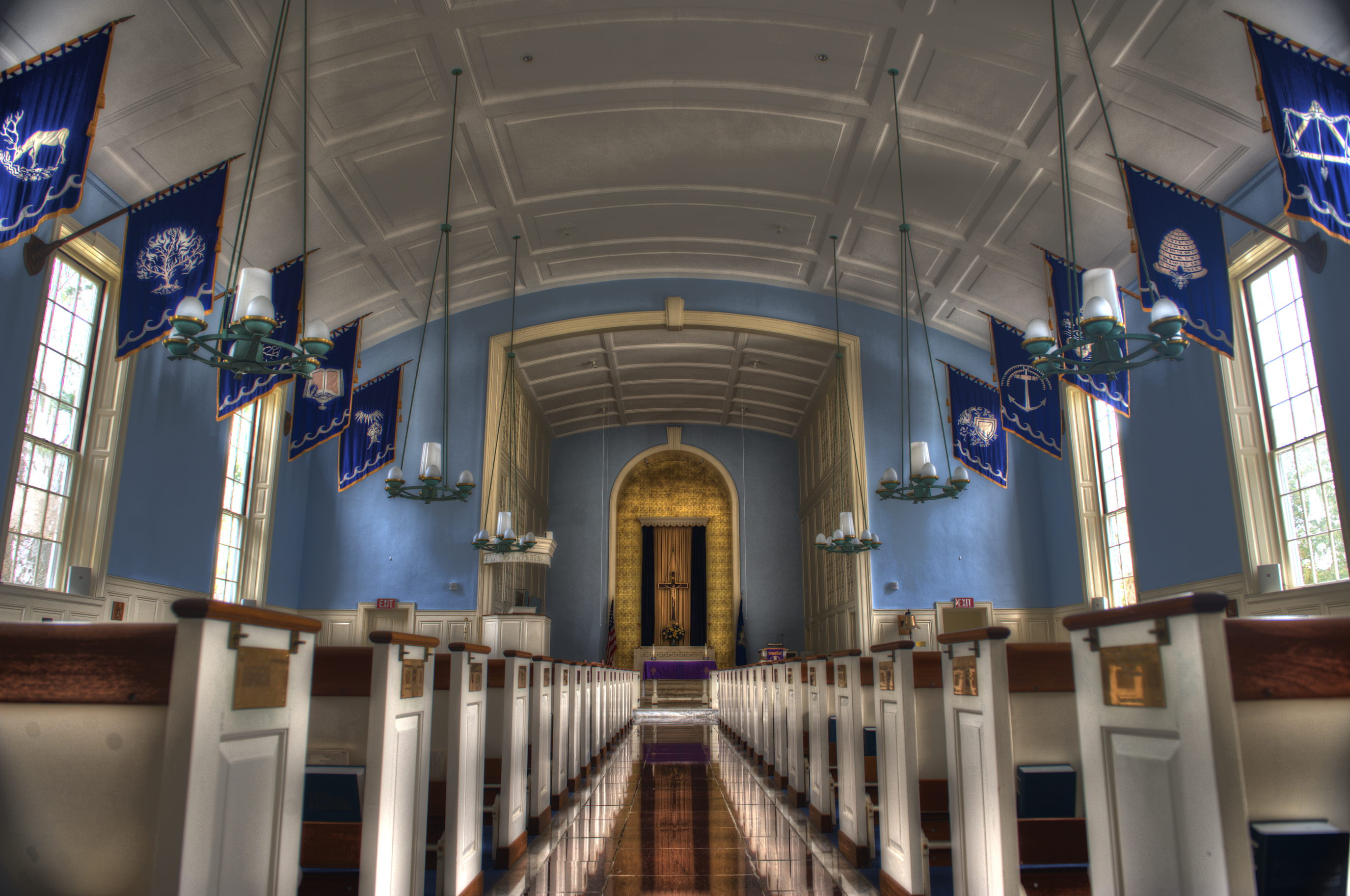
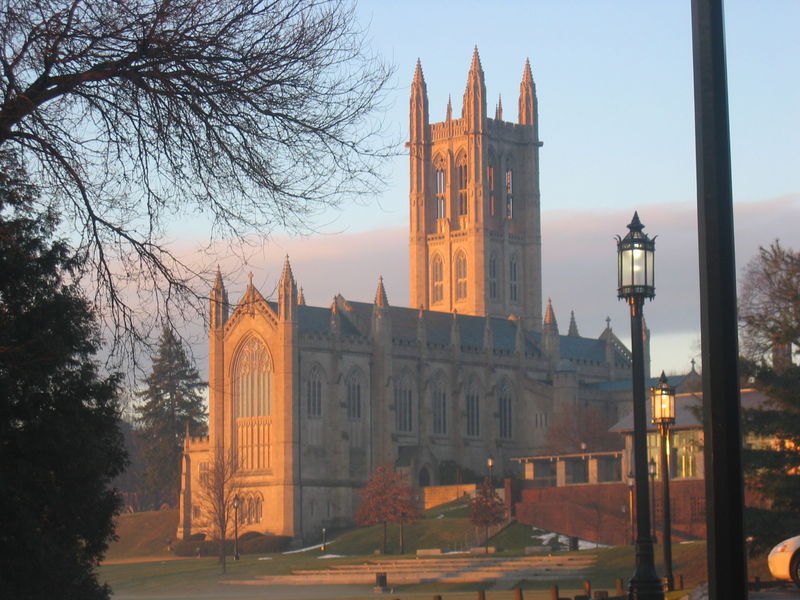
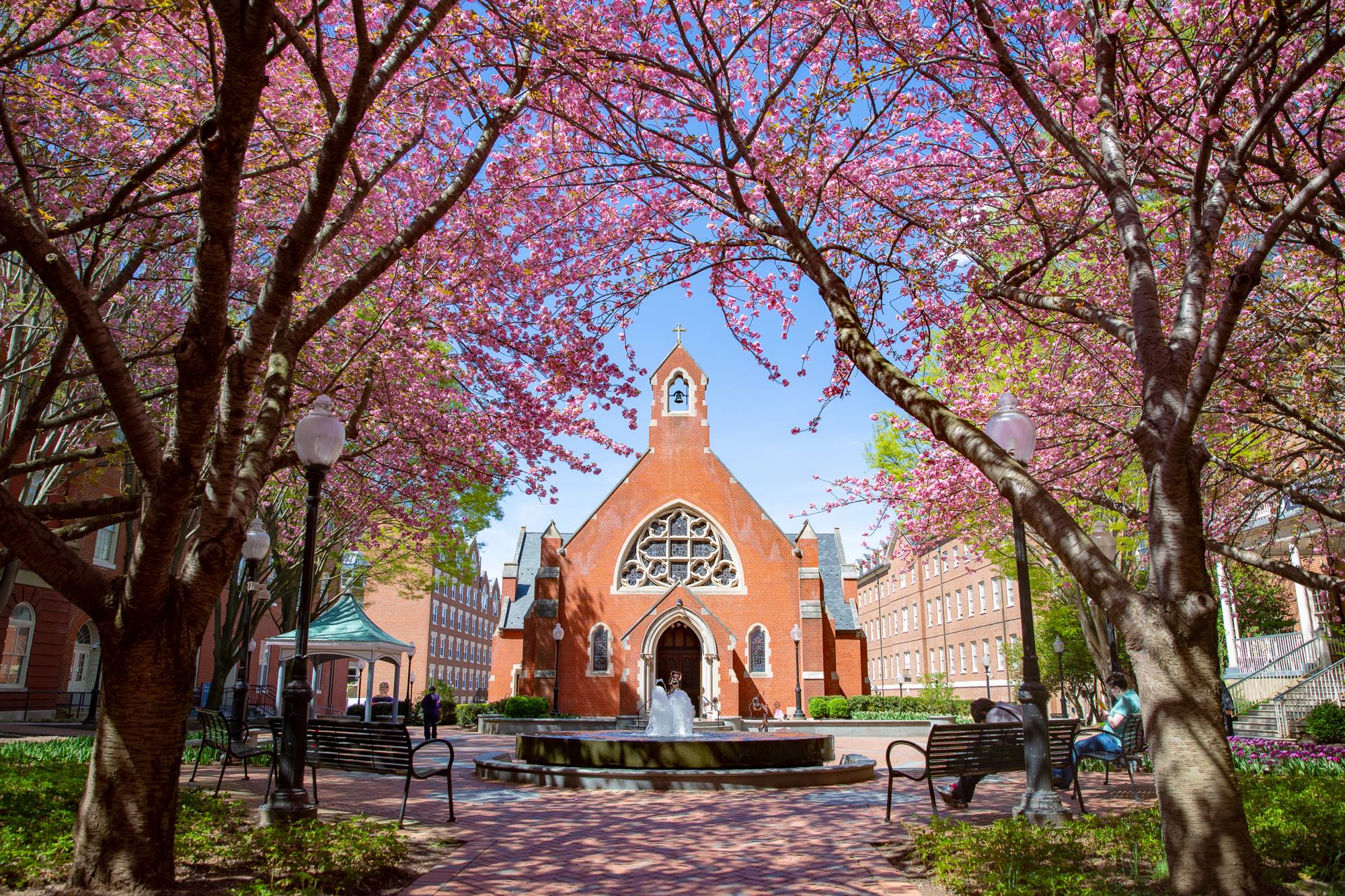
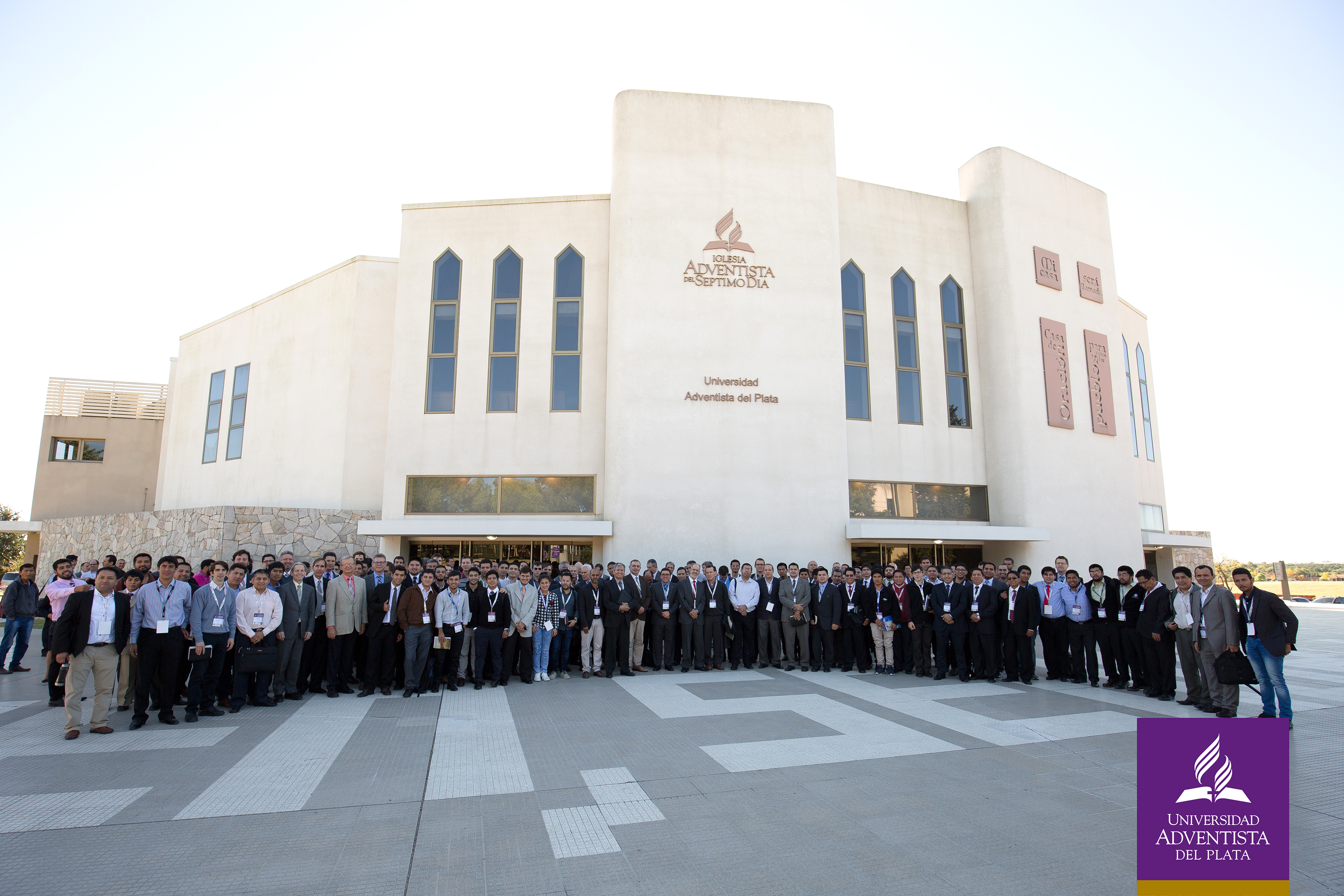
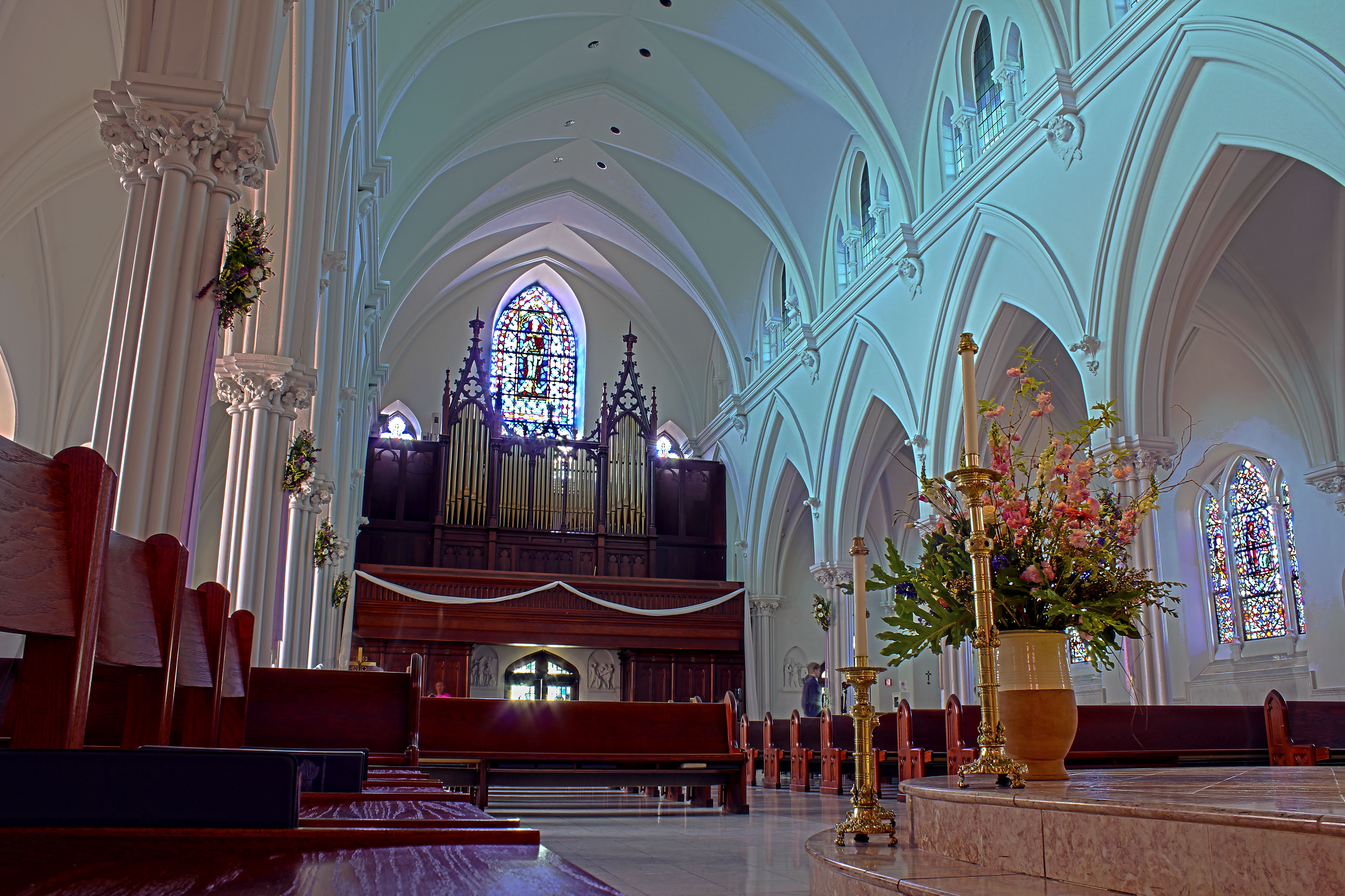
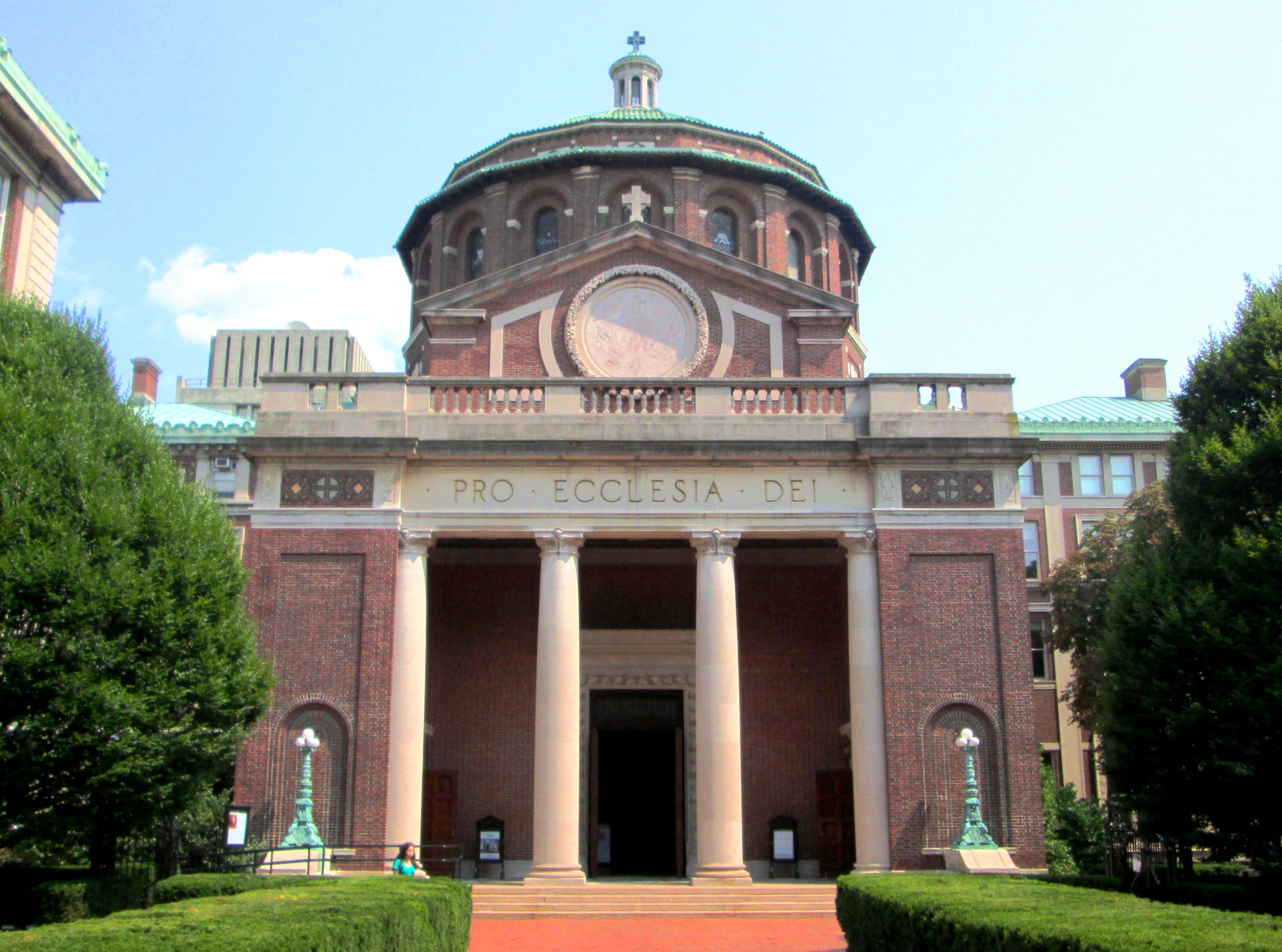
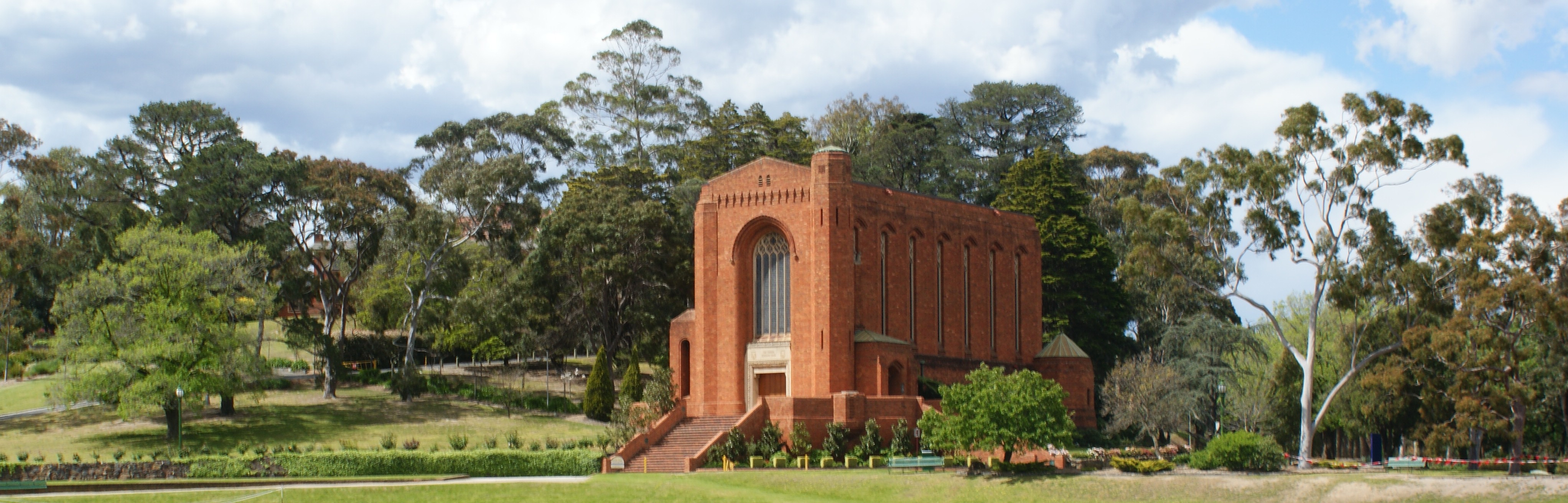
Facilities Management Campus Planning | University of Colorado Net Position 2023: $9.661B
Author Archives: mike@standardsmichigan.com
- Home
- Articles posted by mike@standardsmichigan.com (Page 3)

High Tea Wichita
🌻 Standards Kansas 🌻
Newman University hosts its Heritage Month in February to celebrates the English heritage of the university’s namesake, St. John Henry Newman. It typically takes place in the Dugan-Gorges Conference Center following the St. Newman Mass and features meticulously prepared finger foods, English breakfast or Earl Grey tea, and elegant tea sets, fostering a sense of community among students, alumni, faculty, and staff.
Thank you to our amazing chorale and troubadours for last night’s Pilgrims of Hope fall concert! 🎹 It was a beauty to behold.#NUExcellence #NewmanU #fall #concert pic.twitter.com/ij1GkQkYli
— Newman University (@NewmanU) November 24, 2025
Why and How High Tea Originated as a Working-Class Custom: High tea, despite its modern association with elegance and afternoon tea, began as a practical, working-class custom in 19th-century Britain. Its origins lie in the Industrial Revolution, when factory workers, miners, and laborers, typically from the lower classes, returned home after long, physically demanding shifts. Unlike the leisurely afternoon tea enjoyed by the upper classes, high tea was a hearty, substantial meal served around 5–7 p.m., designed to sustain workers after a grueling day.
Why It Was Working-Class:Timing and Necessity: Workers couldn’t afford mid-afternoon breaks for tea, as their schedules revolved around factory or manual labor. High tea was served after work hours, replacing or supplementing dinner with affordable, filling foods like meat pies, bread, cheese, and tea, which provided energy and comfort.
Economic Constraints: The working class lacked the resources for the delicate sandwiches and pastries of upper-class afternoon tea. High tea used simple, inexpensive ingredients, reflecting the economic realities of laborers.
Cultural Context: Tea was a cheap, widely available beverage by the 19th century, thanks to Britain’s colonial trade. It became a staple for workers, offering warmth and stimulation, while the meal addressed their hunger.
How It Developed: High tea was served at a high dining table (unlike the low tables of aristocratic tea settings), where families gathered for a practical meal. The term “high” referred to the table height, distinguishing it from the refined “low tea” of the elite.
Food and Function:
The meal included robust dishes like stews, cold meats, or potatoes, paired with strong tea. It was less about social ritual and more about nourishment, often the main meal of the day for working families.
Social Evolution:
As tea became a British cultural staple, high tea spread across classes, but its working-class roots remained evident in its heartier fare and evening timing, contrasting with the lighter, earlier afternoon tea of the wealthy.
By the late 19th century, high tea’s association with the working class faded as middle and upper classes adopted and refined it, leading to its modern, more elegant connotations.
Afternoon tea this weekend pic.twitter.com/2UAZkGUXOj
— kat-astrophe! (@omwtfybkat) November 3, 2025
Campus Center Cafe
Net Position 2024: $3.918B | Facilities Management | Library Renovation Bonds
Smith College Campus Center | Weiss Manfredi
A few moments from Baccalaureate and the Senior Celebration Barbecue. #Smith2023 Jim Gipe for Smith College. https://t.co/vu5yM5AIoR pic.twitter.com/2vqRj5tU5n
— Smith College (@smithcollege) May 19, 2023
Warrior Coffee Project
Financial Statement 2023 | Next Phase Campus Master Plan
The Fall 2021 magazine is now available! In this issue, we highlight @LycoCEAE & how the program creates a smooth transition from backpack to briefcase for our students, including how Lycoming alumni contribute to that successful journey. Read it here: https://t.co/wclDIMUFui pic.twitter.com/UVqApHZeOx
— Lycoming College (@LycomingCollege) December 14, 2021
Willa Cather: “Pennsylvania is a beautiful state, filled with history and the evidence of hard work.”
Harper Lee: “In Pennsylvania, there’s a sense of history that’s palpable. You can feel it in the air.”
John Updike: “Pennsylvania is old and it’s new, it’s modern and it’s historical; a place where the past meets the present.”
James A. Michener: “Pennsylvania is a land of deep rivers and tall mountains, fertile valleys and ancient forests.”
H.G. Wells: “Pennsylvania has always been a dream to me, a place where hard work and determination lead to success.”
Tennessee Williams: “There’s a depth of character in the people of Pennsylvania, a resilience that comes from their history.”
David McCullough: “Pennsylvania is a cradle of American history, a place where the very fabric of our nation was woven.”
Louisa May Alcott: “The rolling hills of Pennsylvania are a testament to the enduring spirit of the American people.”
Annie Dillard: “Pennsylvania is a state of great beauty, with a landscape that inspires and a history that humbles.”
John Steinbeck: “The people of Pennsylvania have always struck me as the backbone of America, hardworking and proud.”
Edgar Allan Poe: “The streets of Pennsylvania cities hold many secrets, whispers of the past in every cobblestone.”
Mark Twain: “Pennsylvania is a state that embodies the very essence of the American spirit.”
F. Scott Fitzgerald: “There’s a timelessness to Pennsylvania, a sense of enduring strength and quiet beauty.”
Henry David Thoreau: “In Pennsylvania, nature and civilization coexist in a way that’s rare and beautiful.”
William Faulkner: “Pennsylvania’s history is written in its landscapes, its cities, and its people.”
Sylvia Plath: “The beauty of Pennsylvania’s seasons is a metaphor for the resilience of its people.”
Emily Dickinson: “Pennsylvania’s hills and valleys sing a song of history and hope.”
I don’t see a single blue state.
Just blue cities trying to tell us all how to live. pic.twitter.com/PoibseWRxP
— Shannon Hill (@ShannonMFHill) February 1, 2026
Ghana’s Rabbit Industry
Like many folk traditions of saying “Rabbit, rabbit” to your colleagues on the first day of the month has an unclear origin and has several variations and interpretations. We use it a reason to explore university research into food sources; the proper business of education communities everywhere. In one version of the tradition, saying “Rabbit, rabbit” or “White rabbit” as the first words upon waking on the first day of the month is believed to bring good luck for the rest of that month. It is thought to ensure good fortune, happiness, and general positivity throughout the coming weeks.
The specific origins and reasons behind this tradition are difficult to trace, as superstitions often evolve and are passed down through generations. It’s worth noting that this practice is not universally known or followed, and its popularity may vary among different regions and communities. Ultimately, the saying “Rabbit, rabbit” on the first day of the month is an example of a charming and whimsical superstition that some individuals enjoy participating in as a fun way to start the month on a positive note.
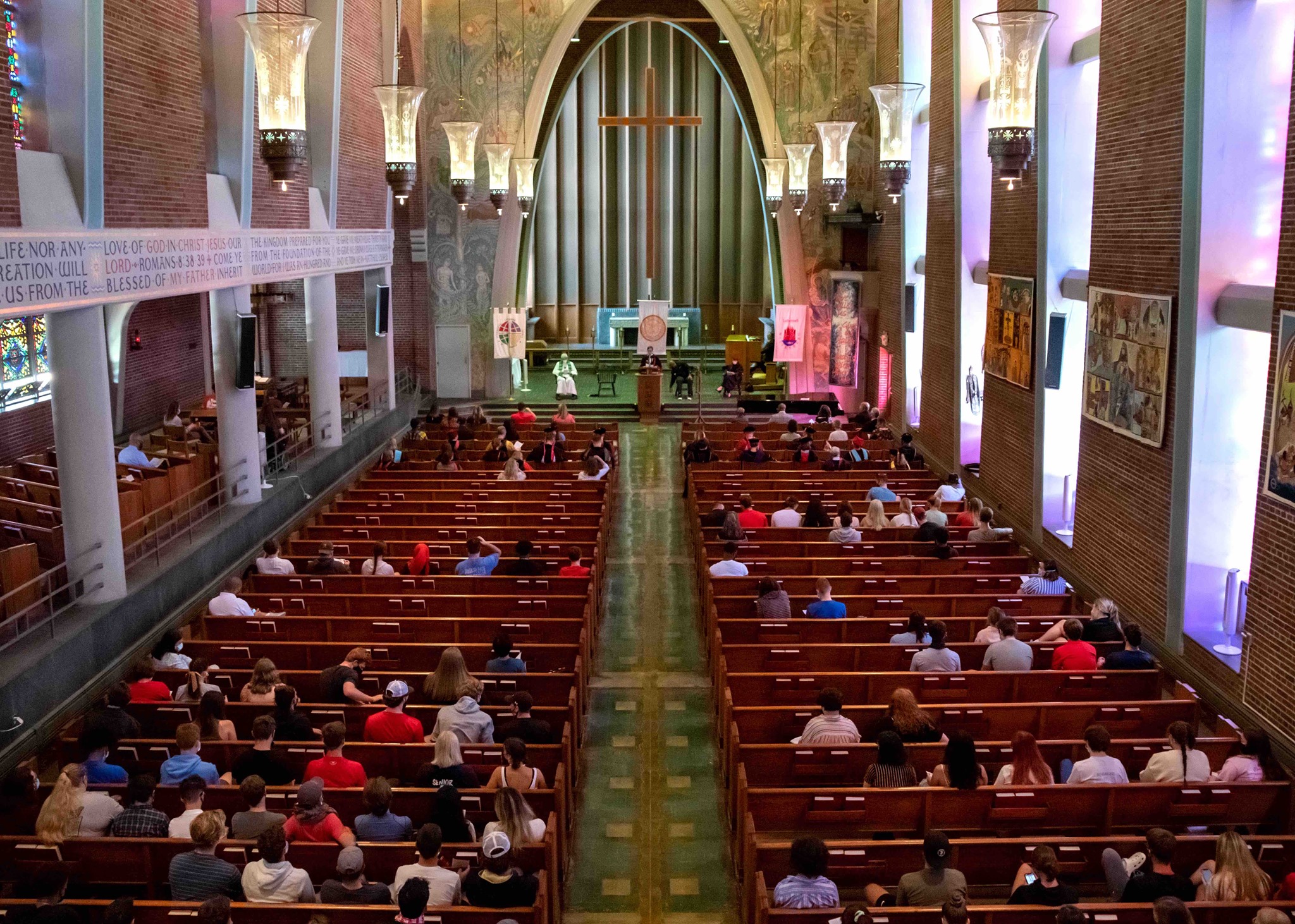
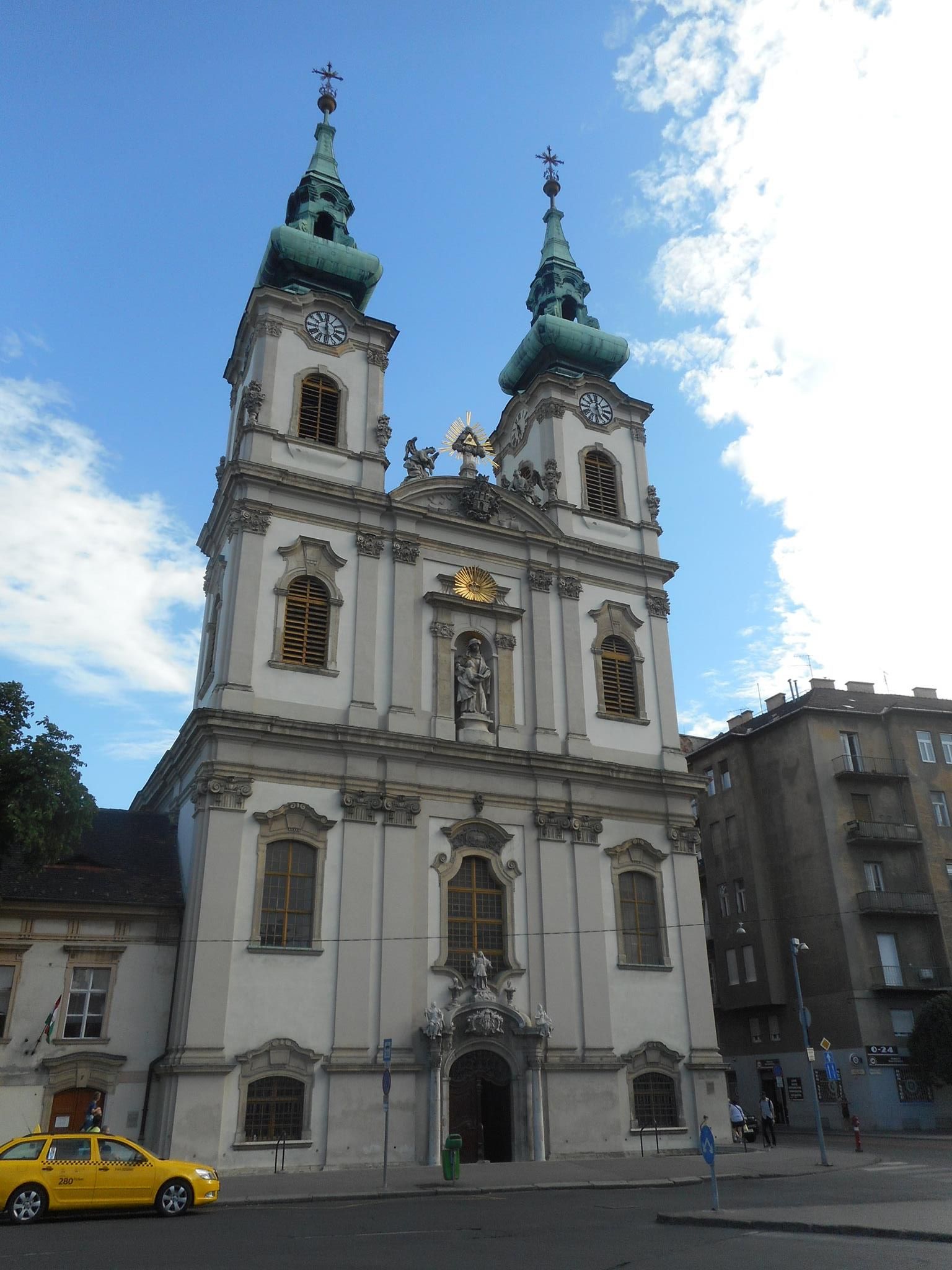
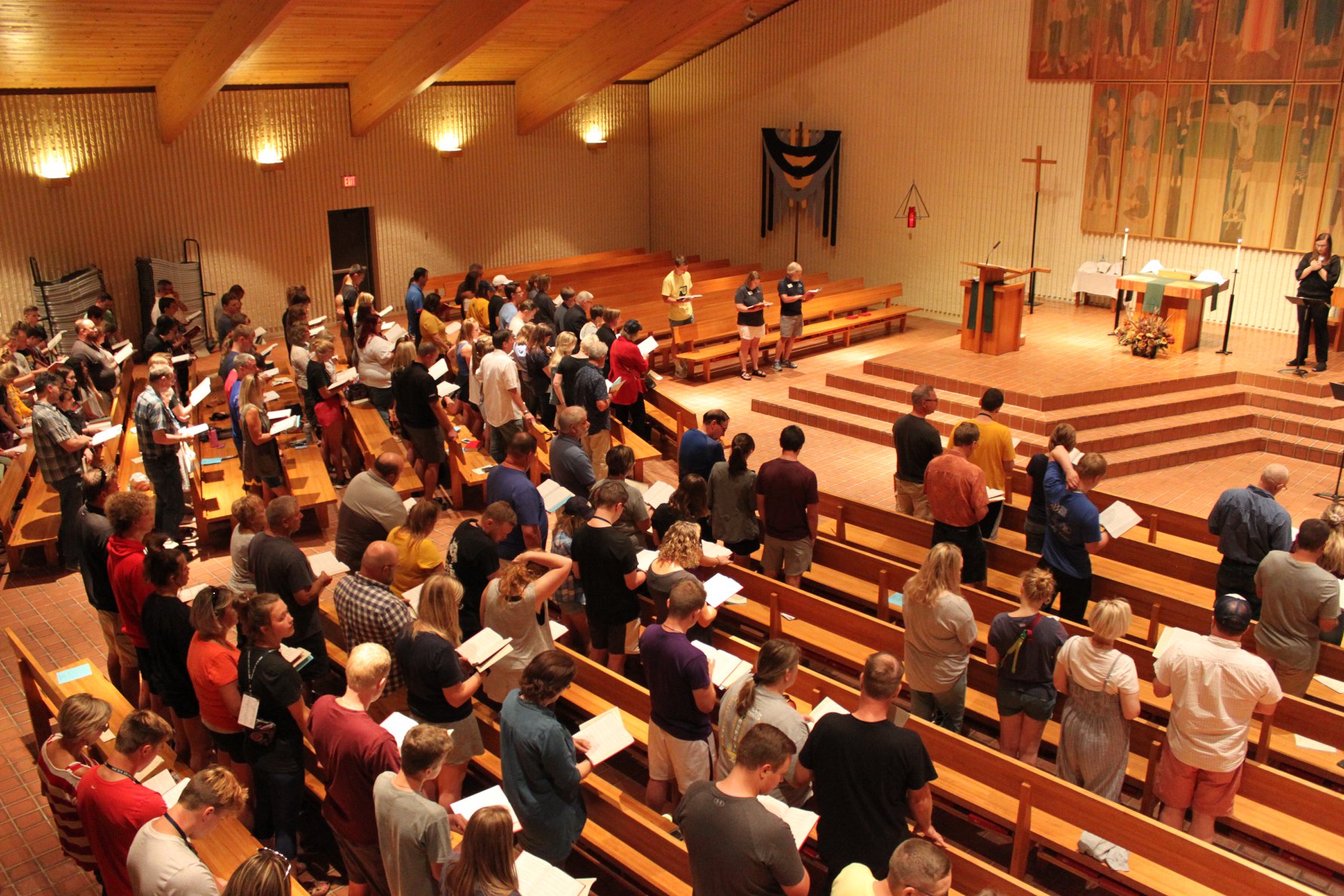
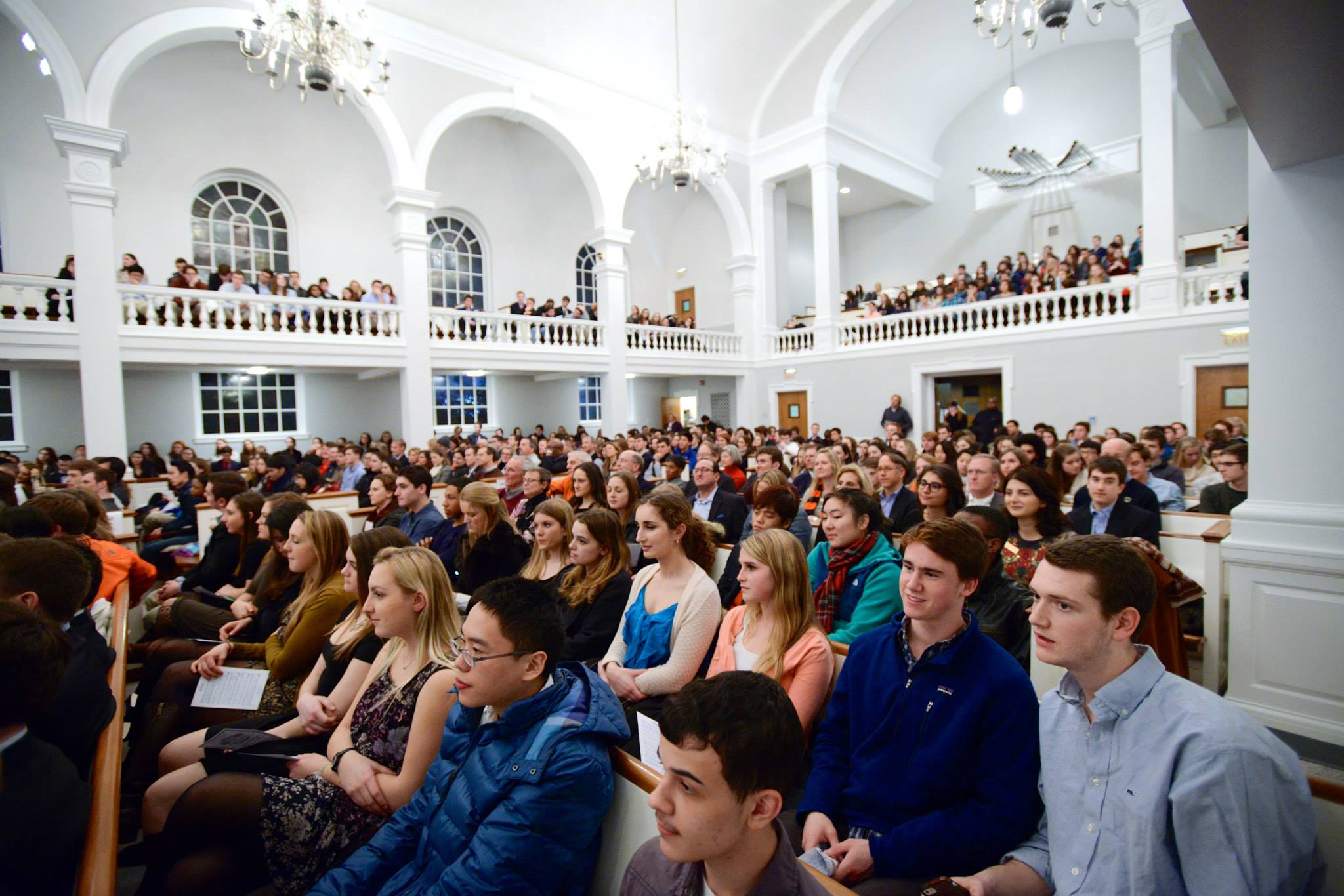
Sacred Spaces
“We need the sense of the sacred, and the sense that things transcend our grasp.
We need to know that we are dependent on others,
and that the condition of our existence is the existence of others.”
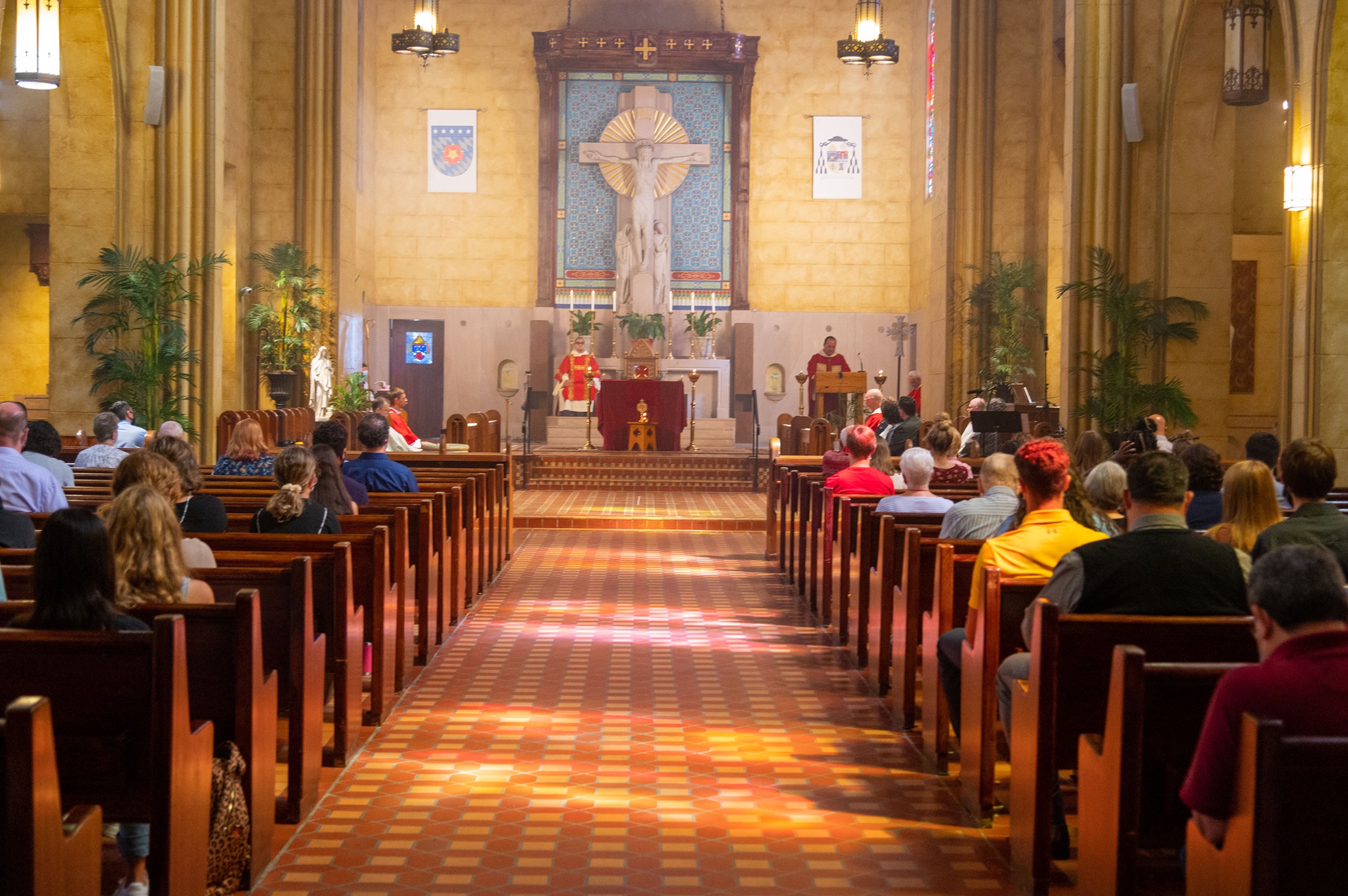
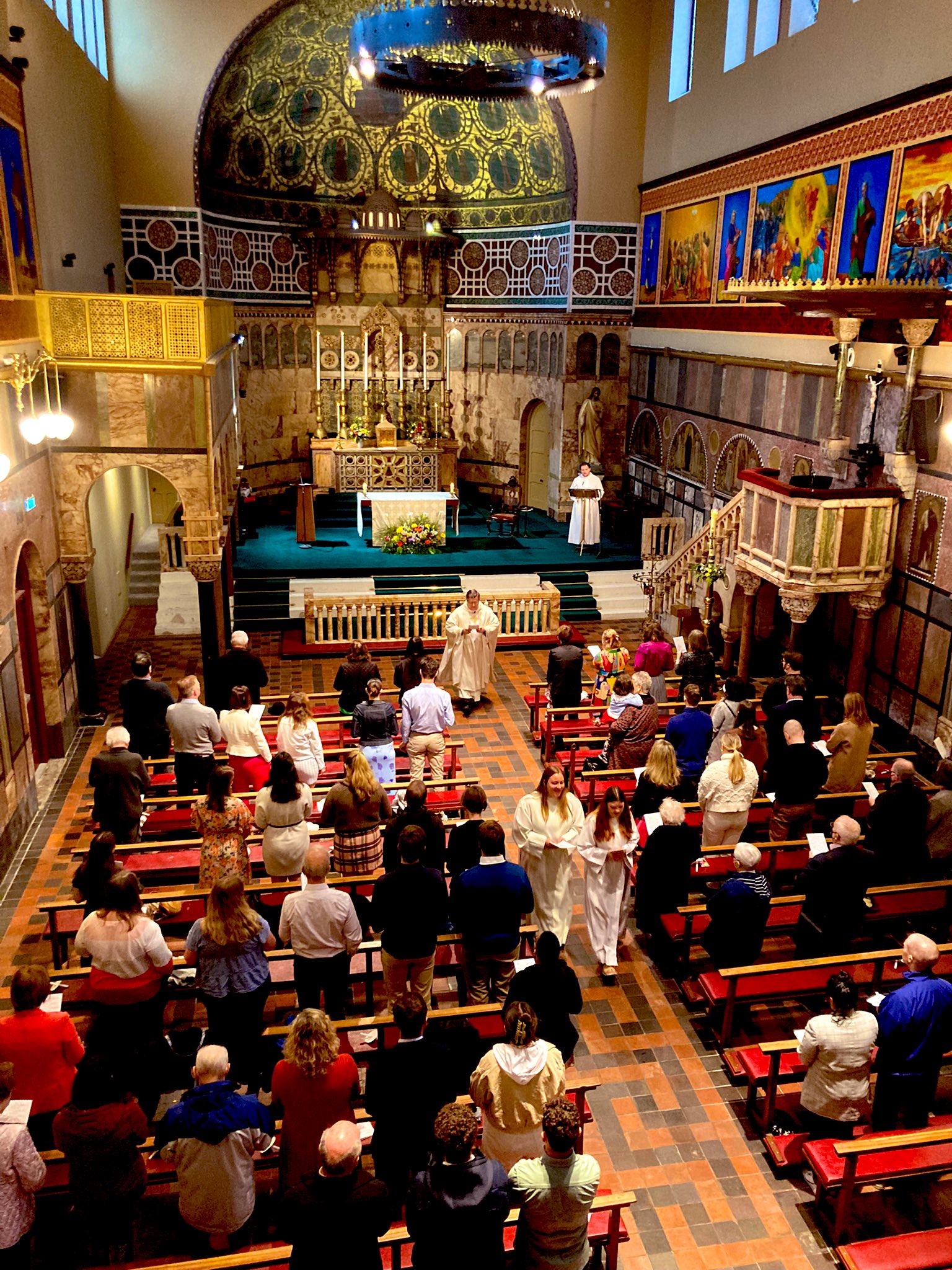
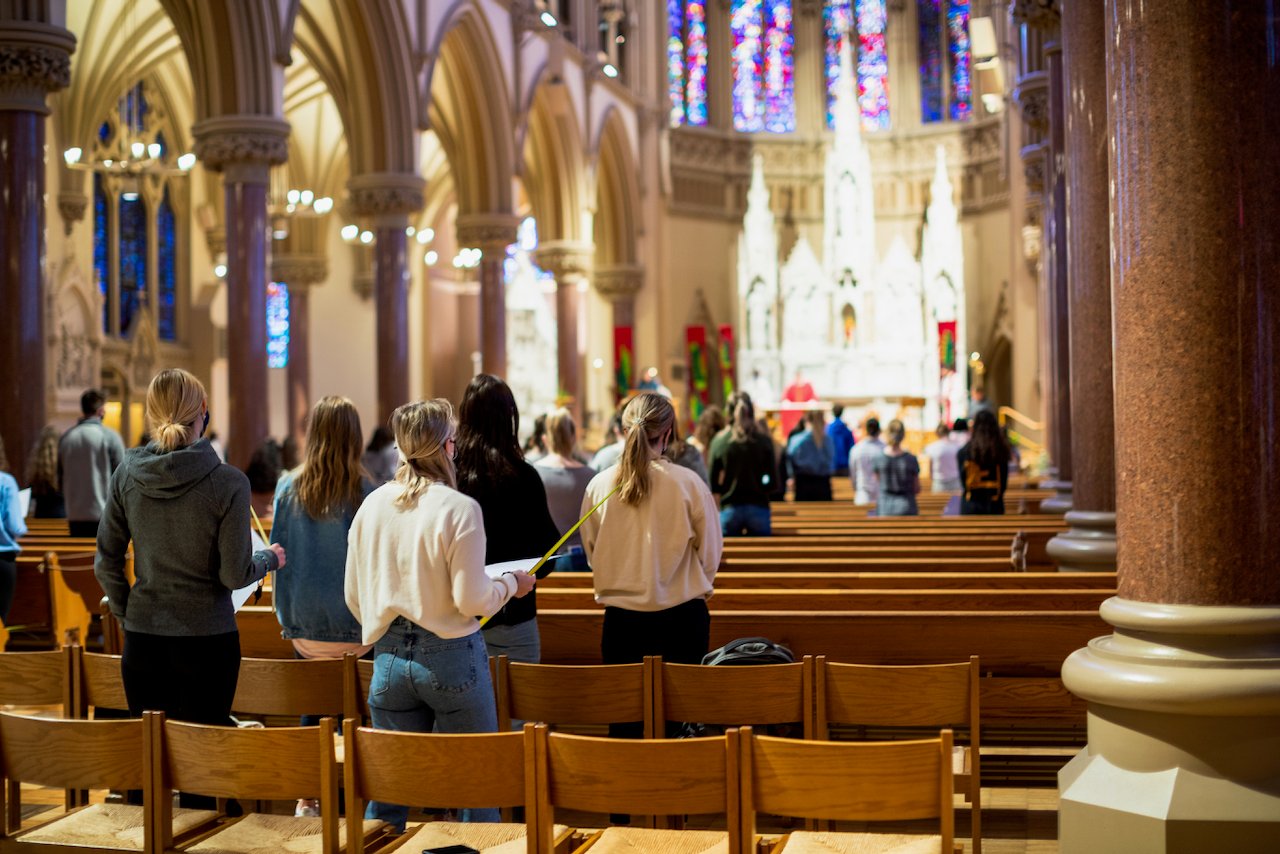
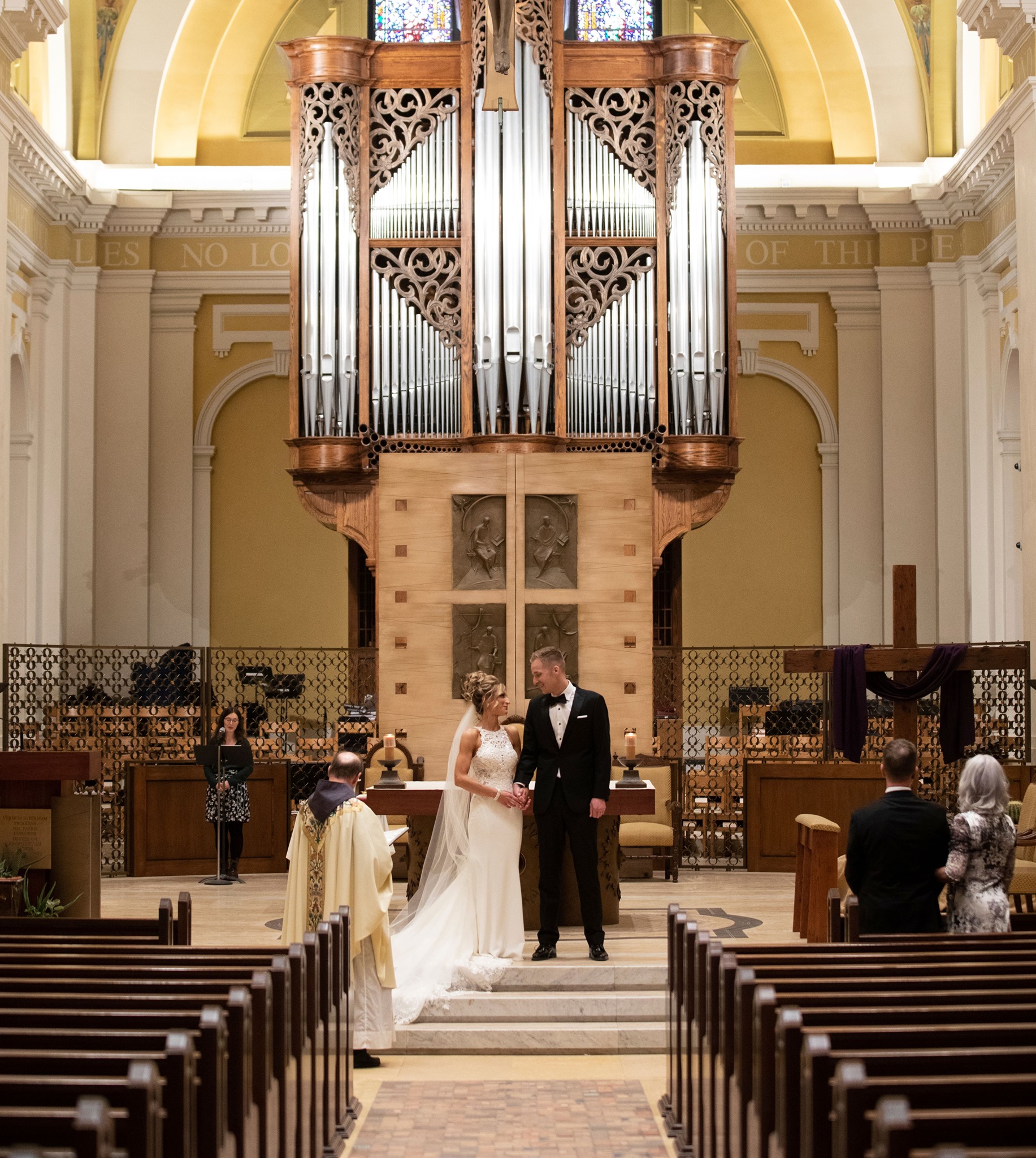
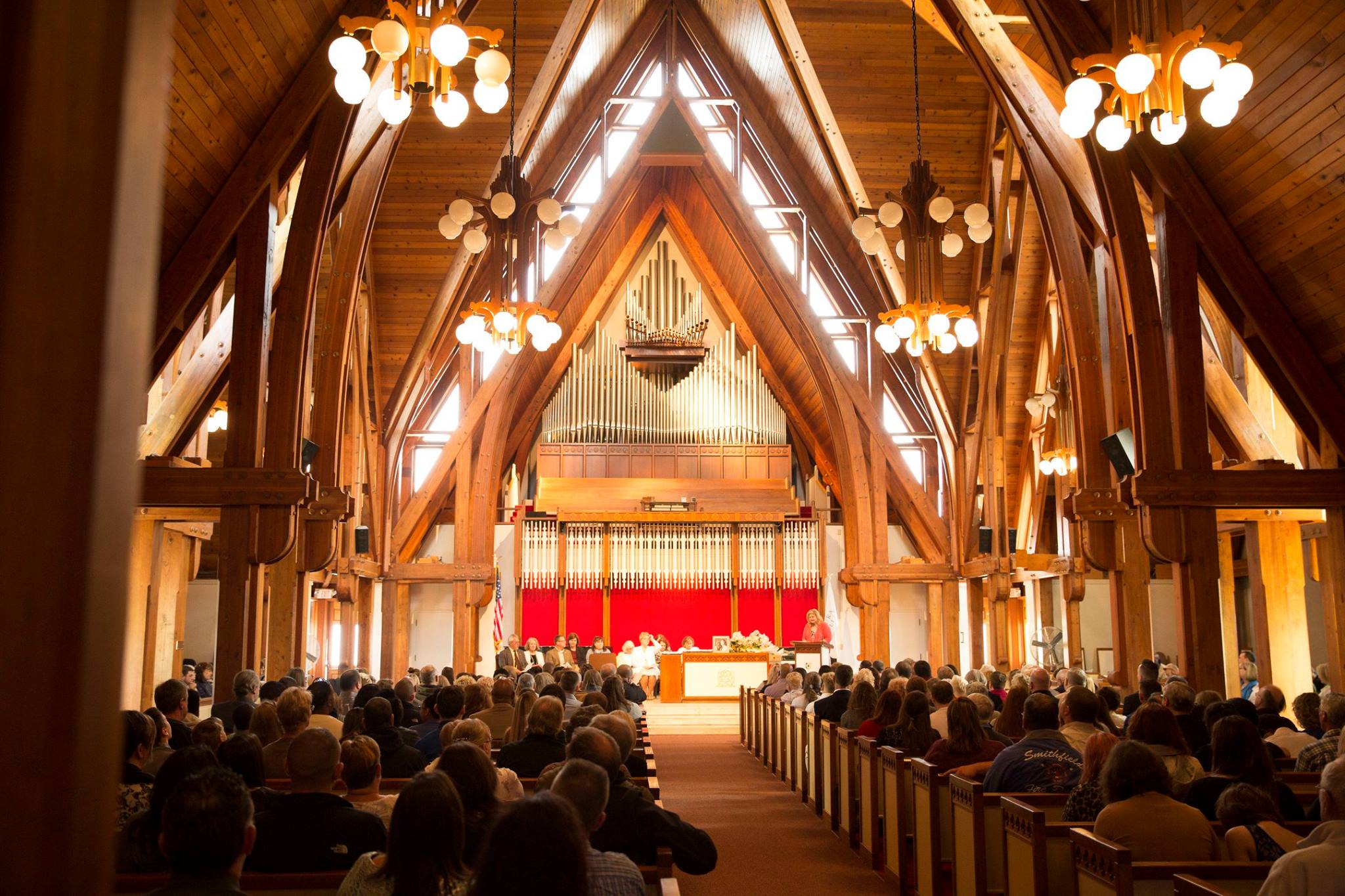
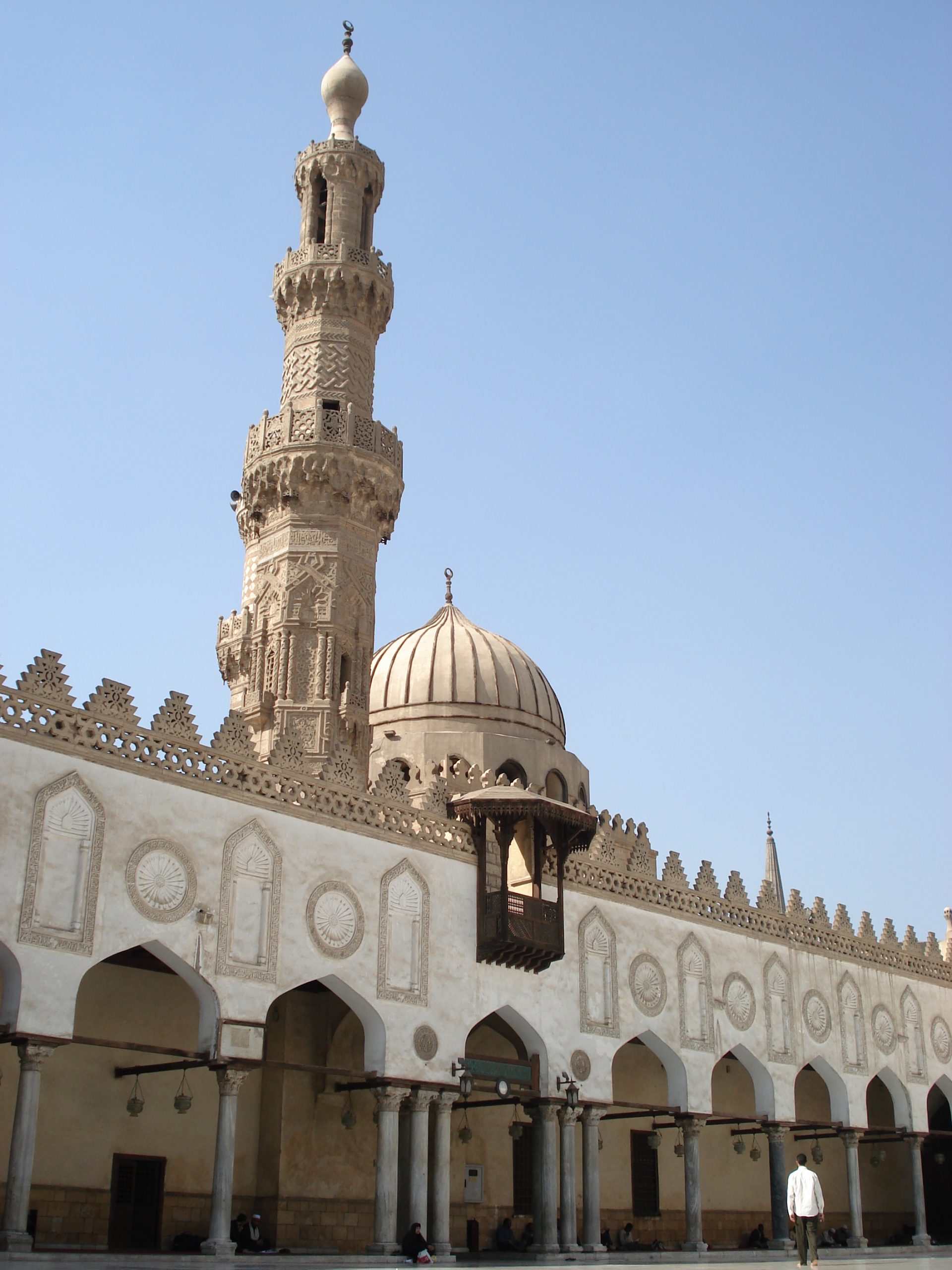
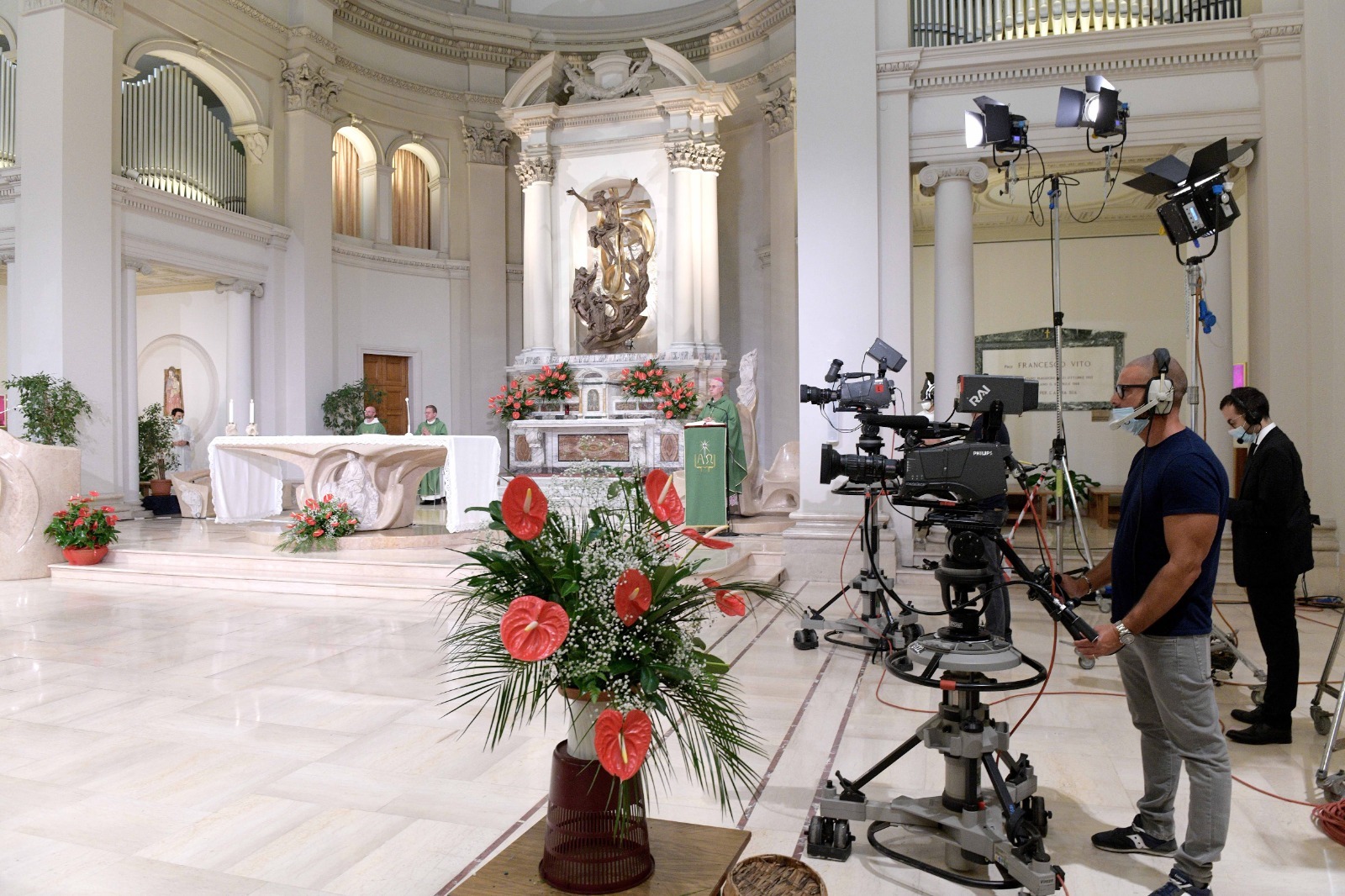
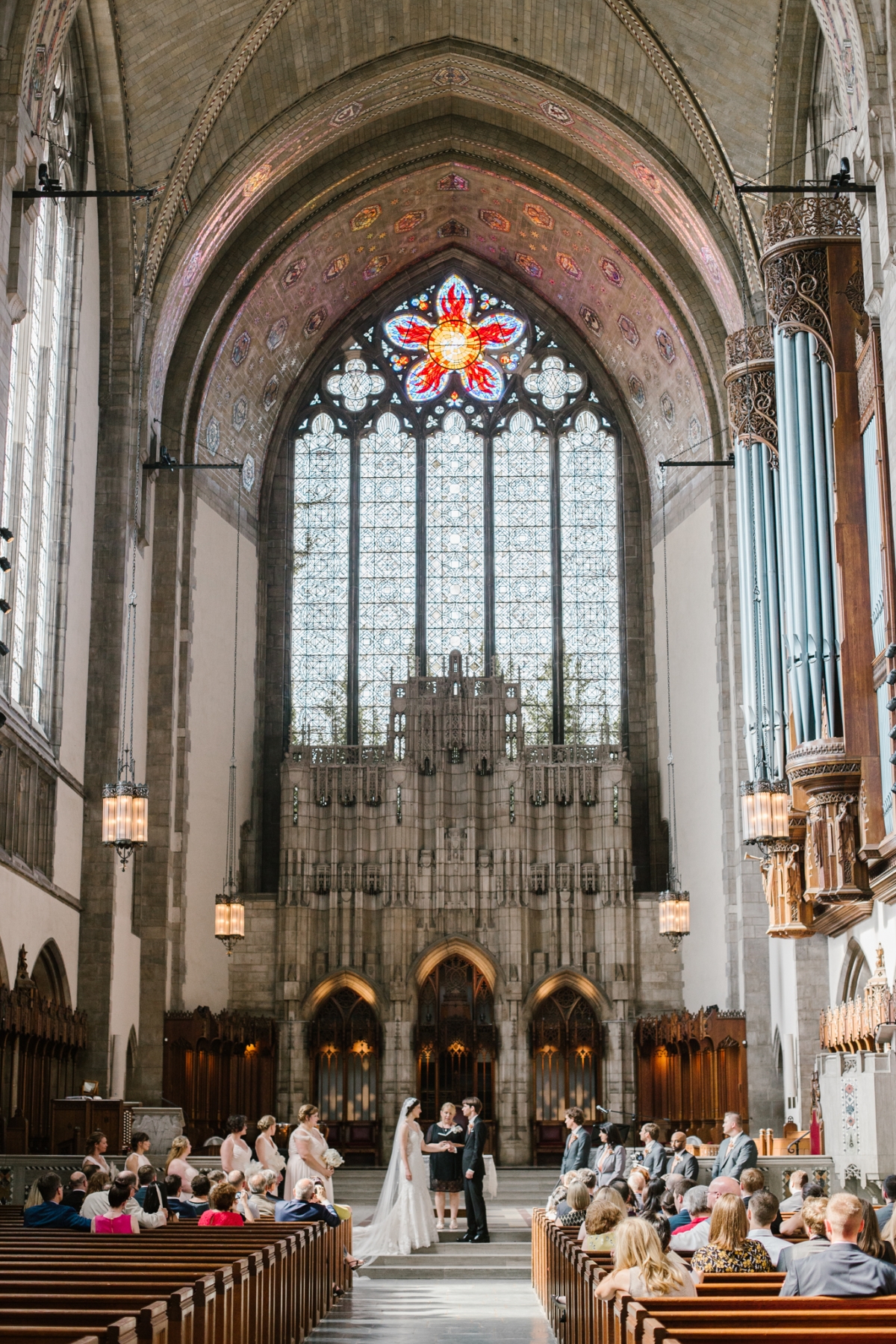
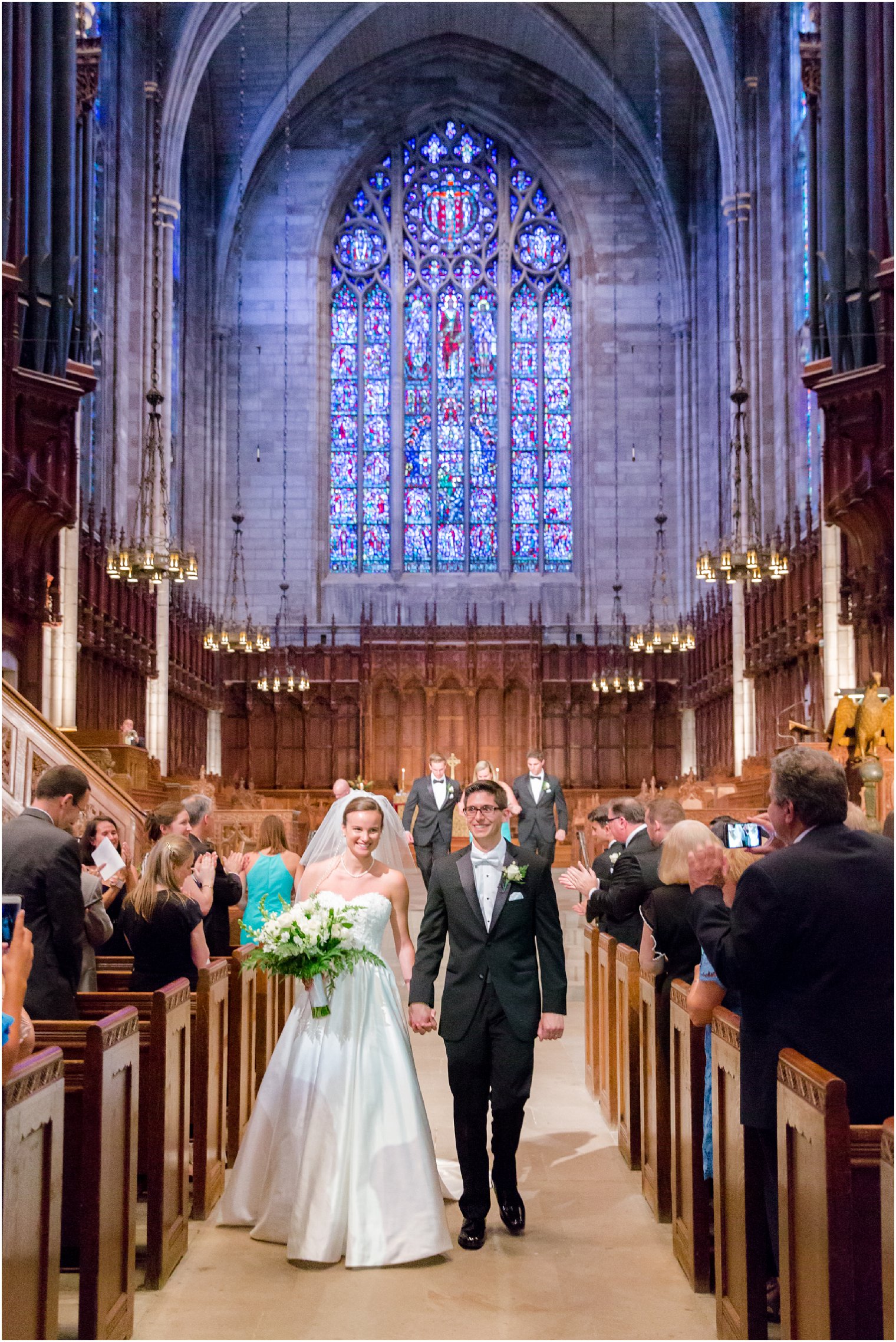
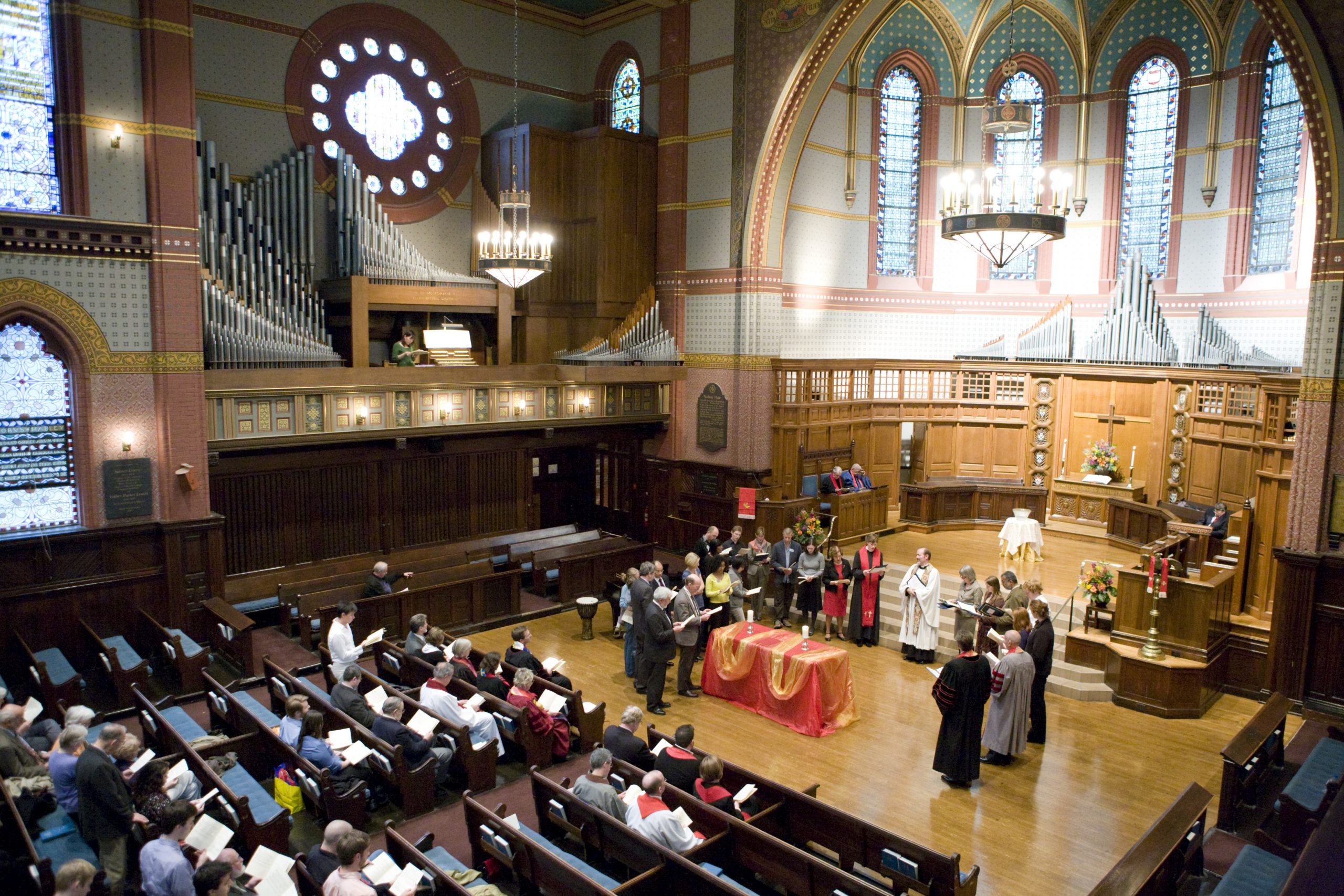
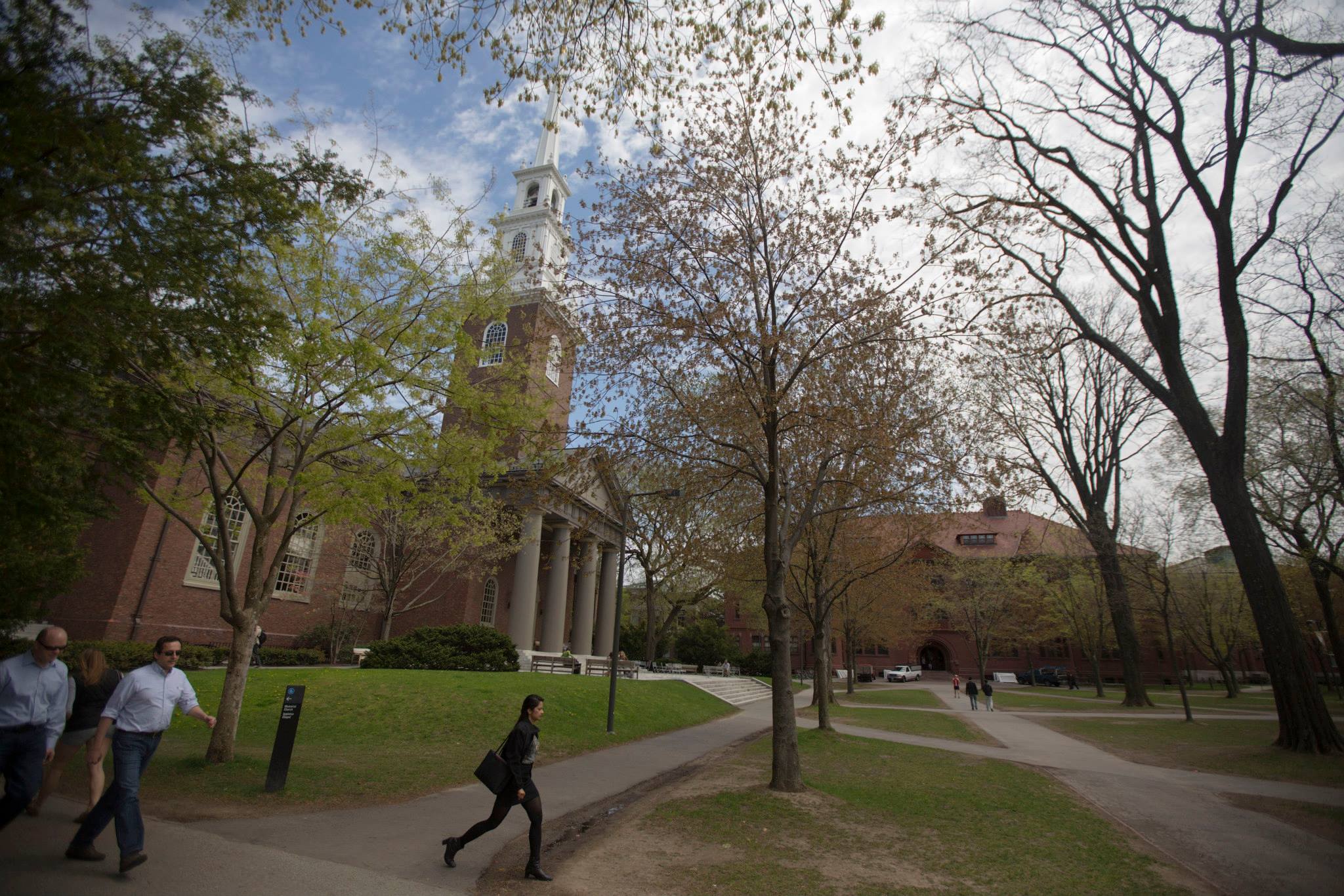
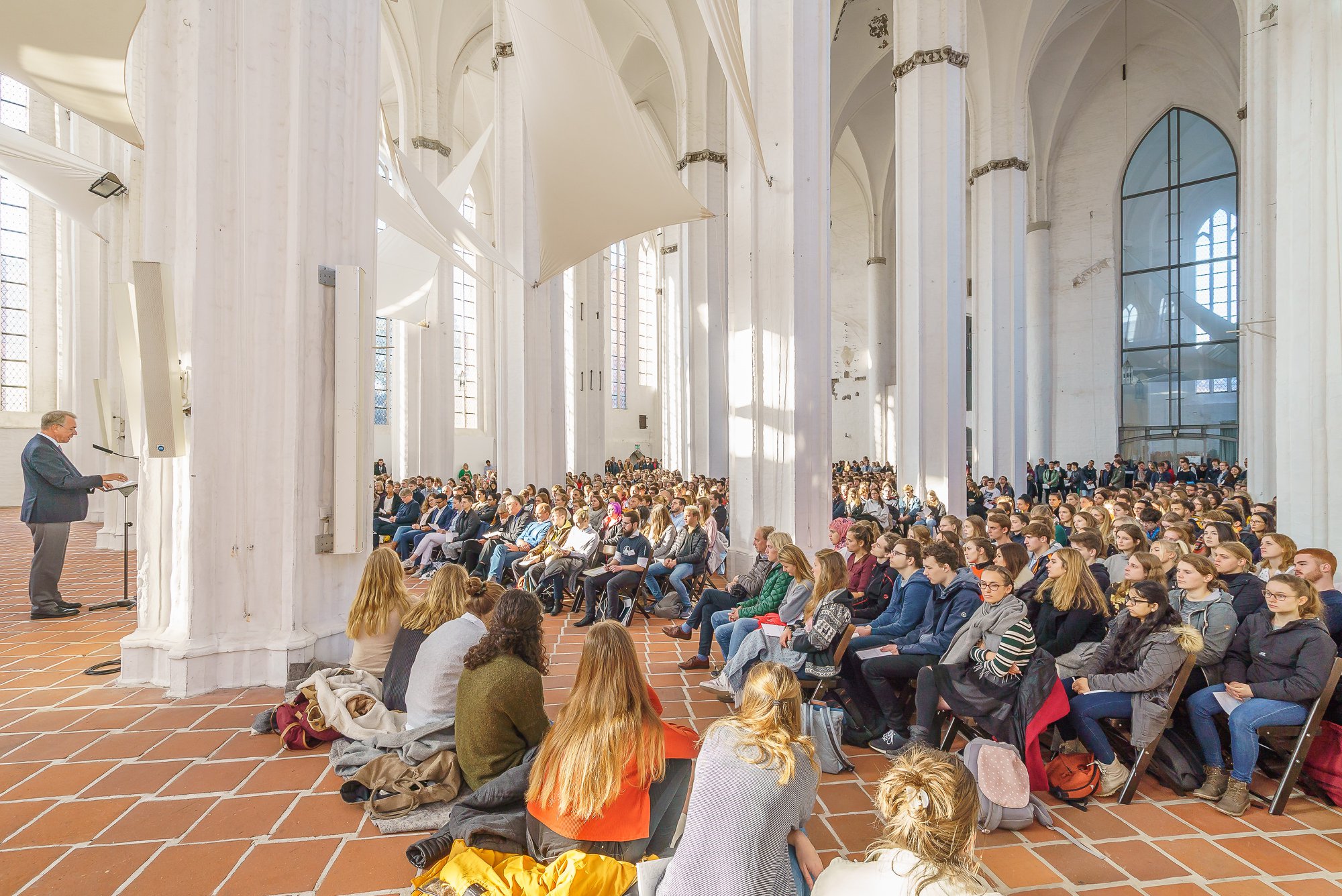
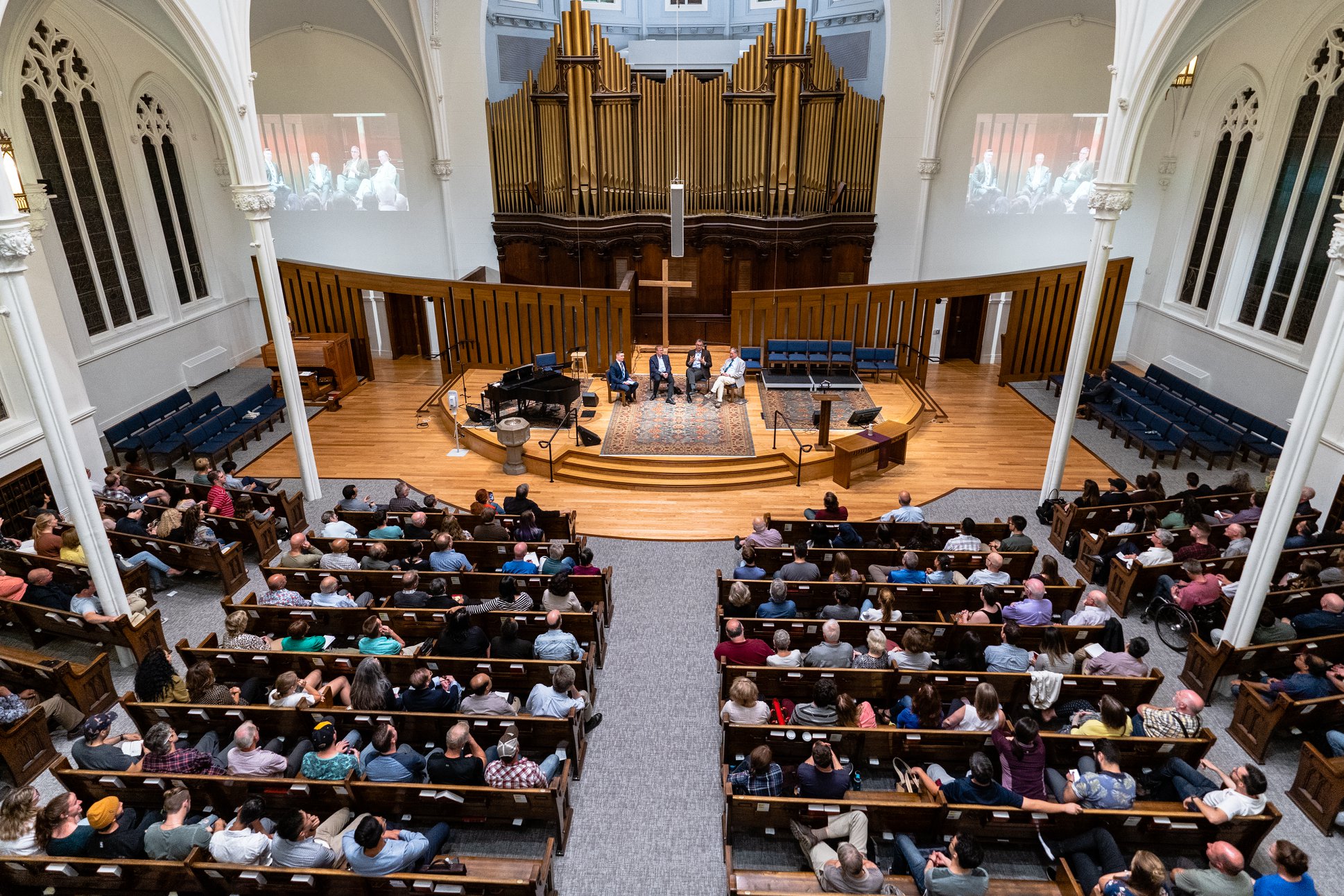
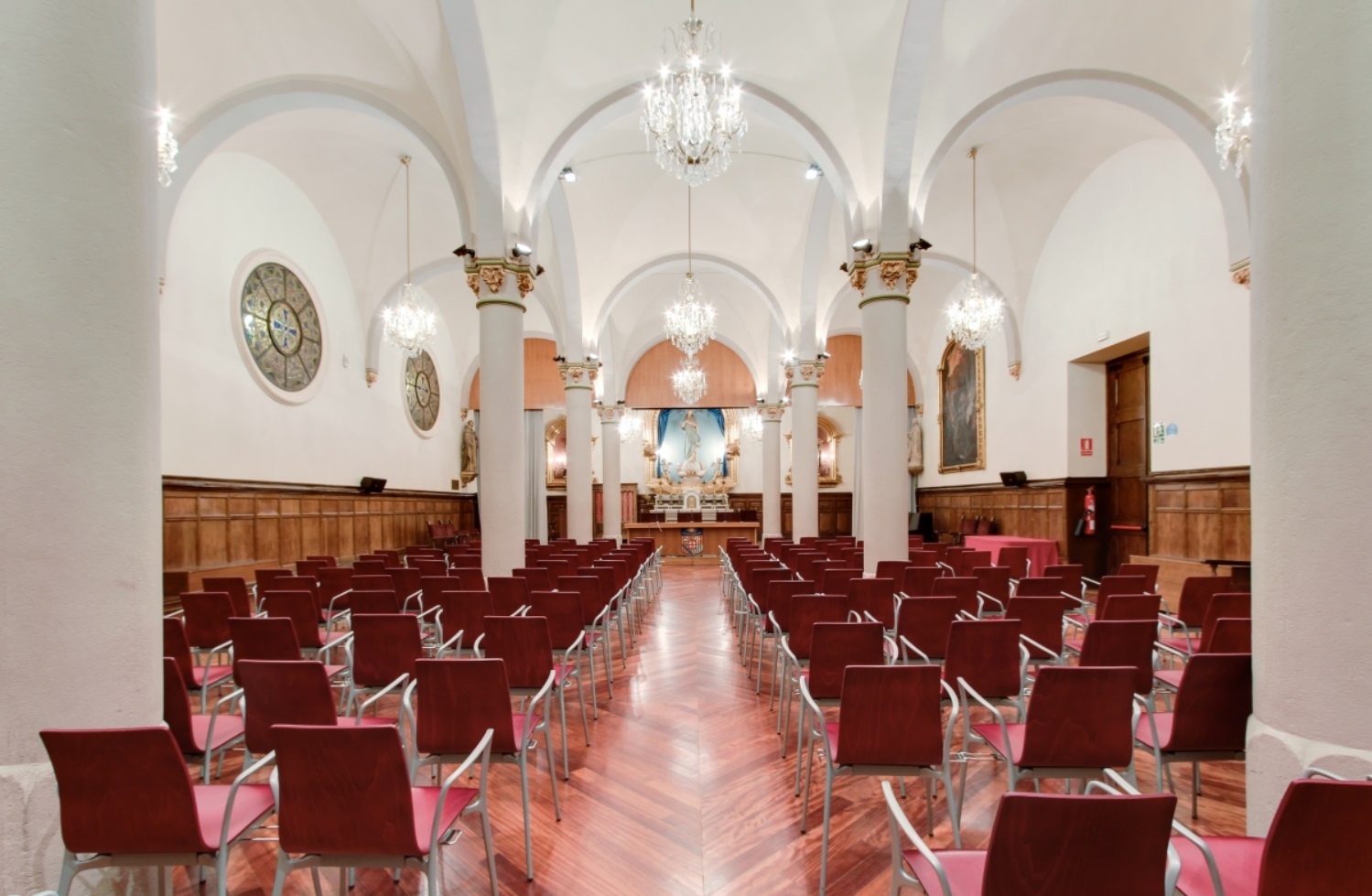
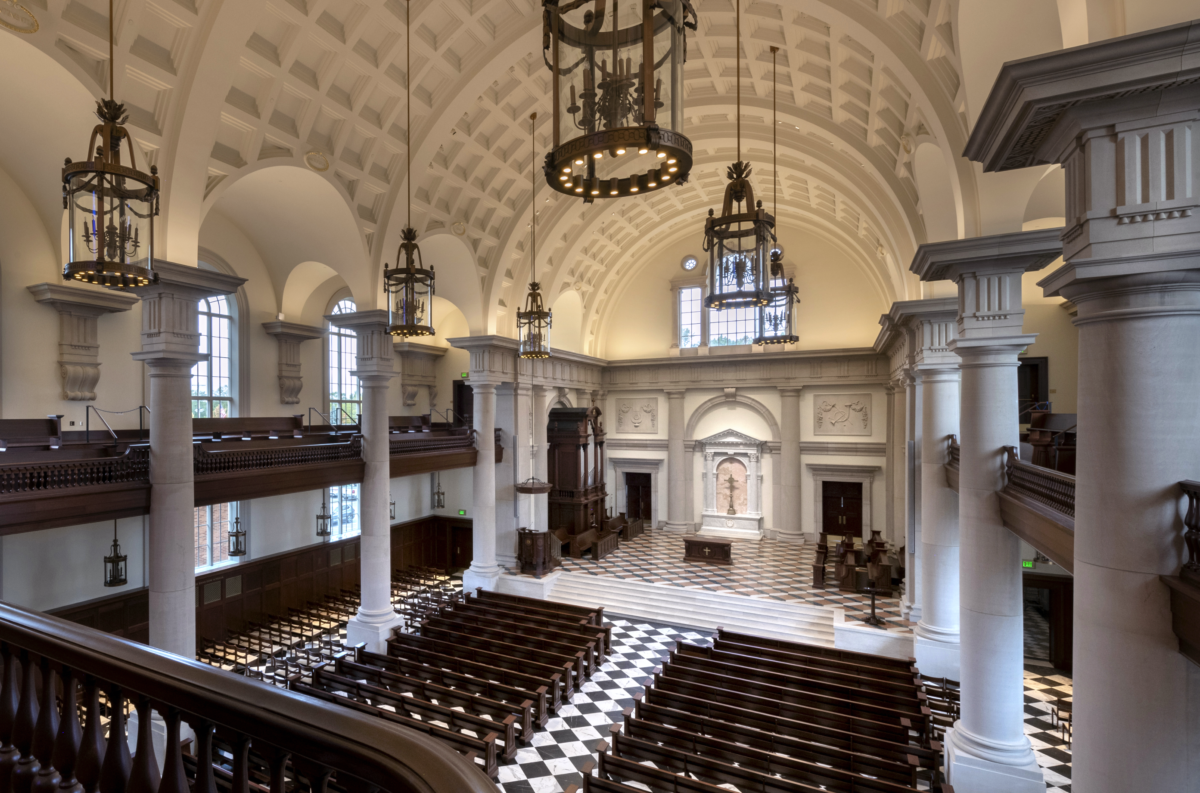
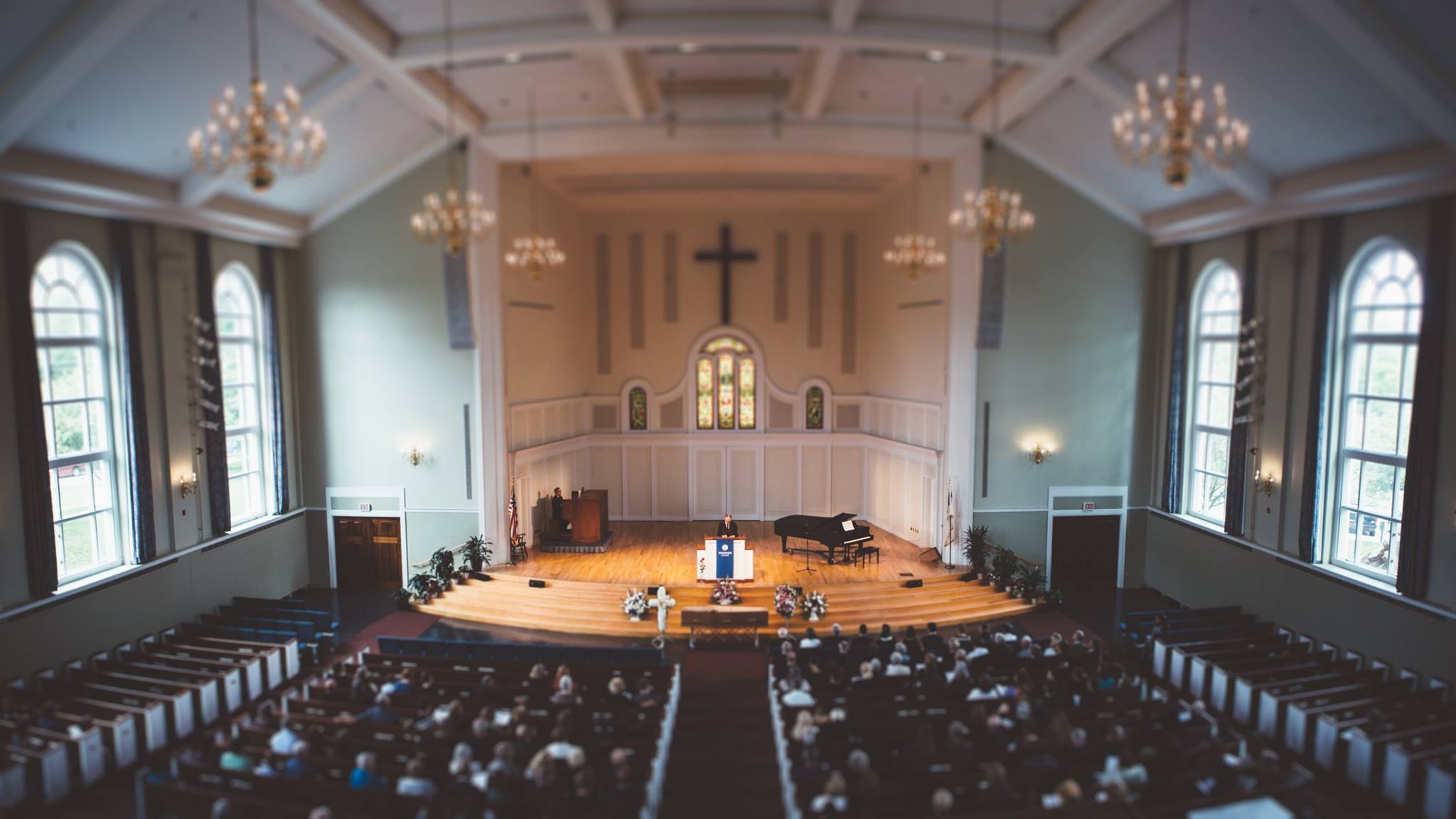
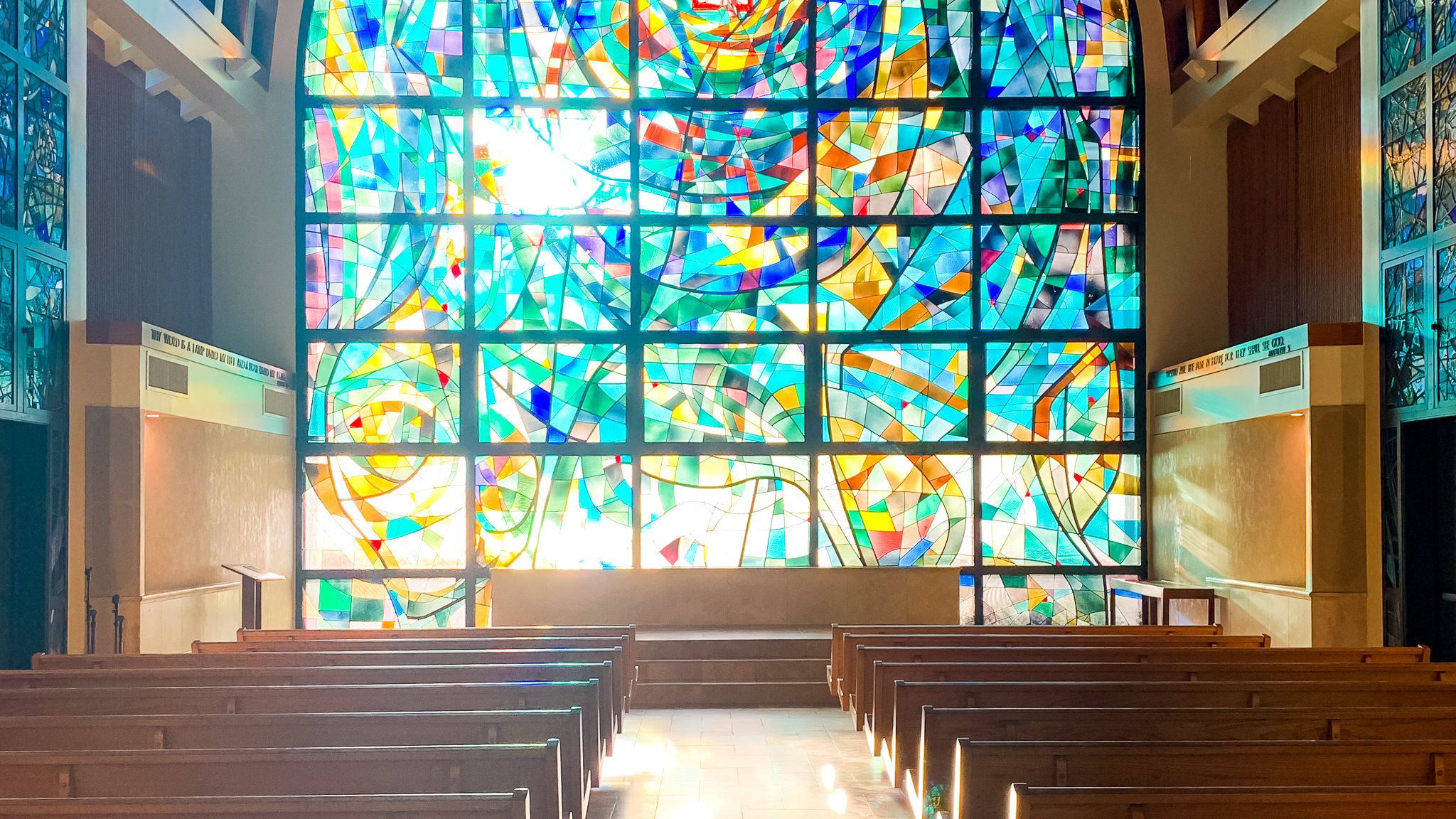
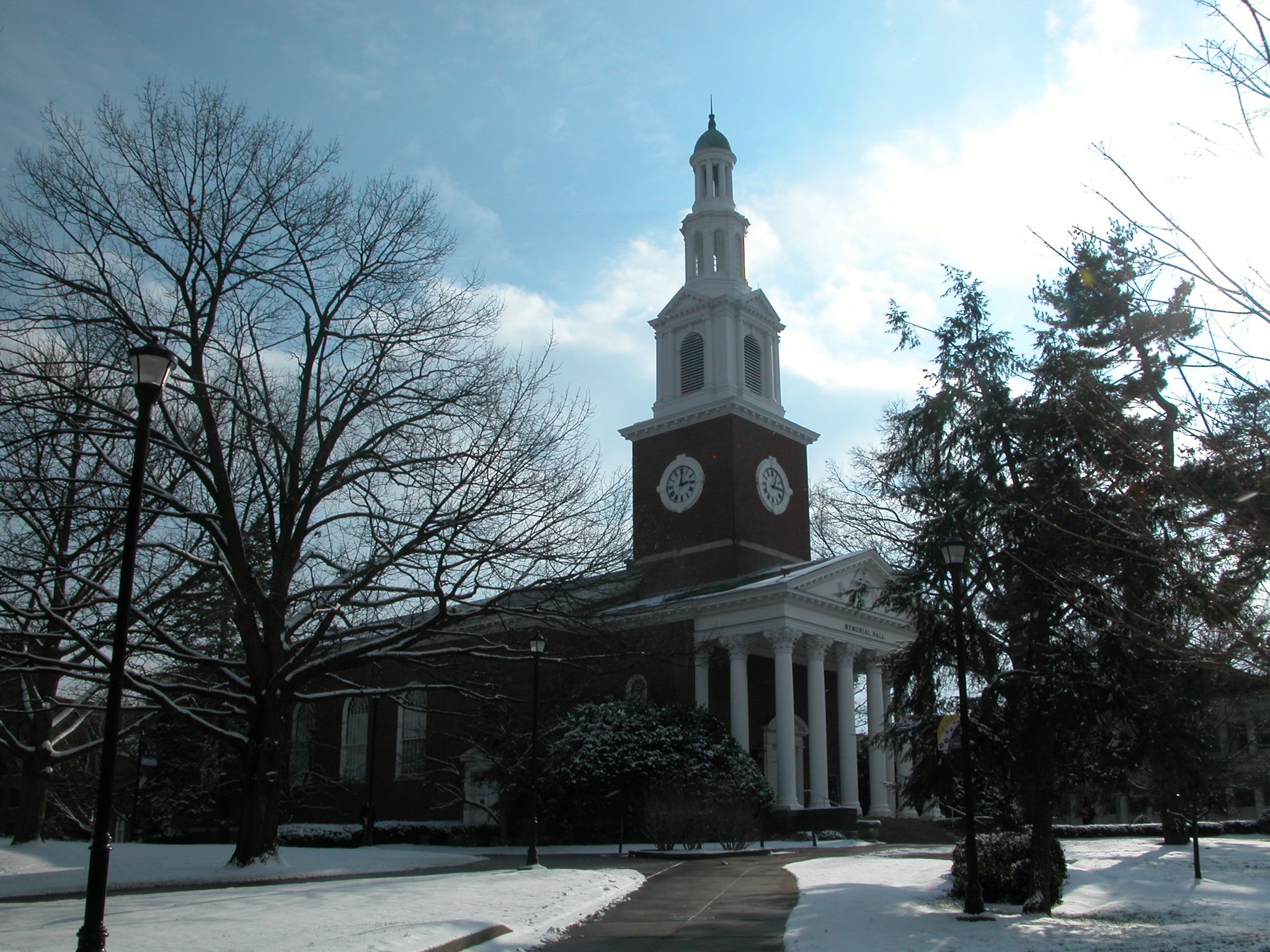
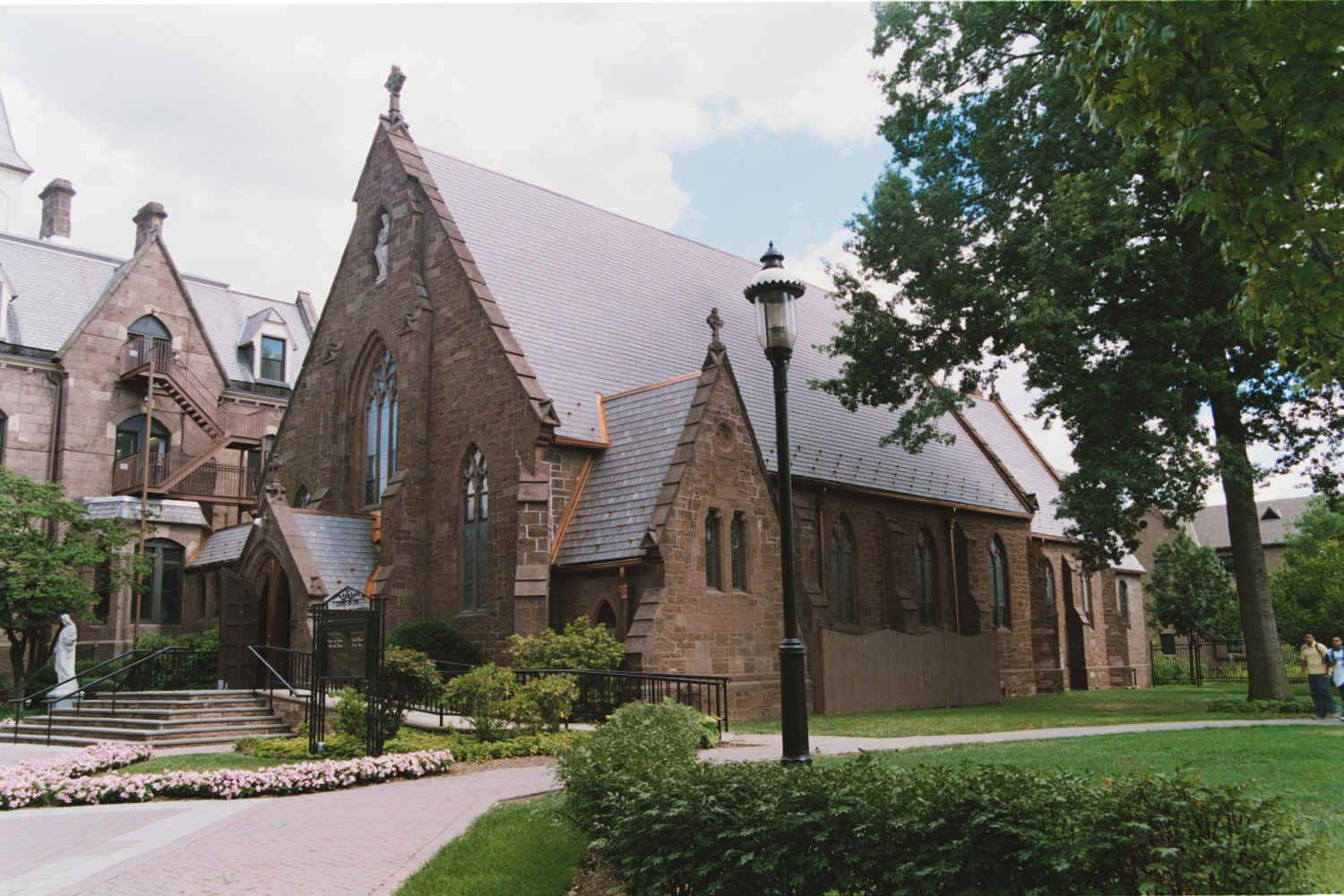
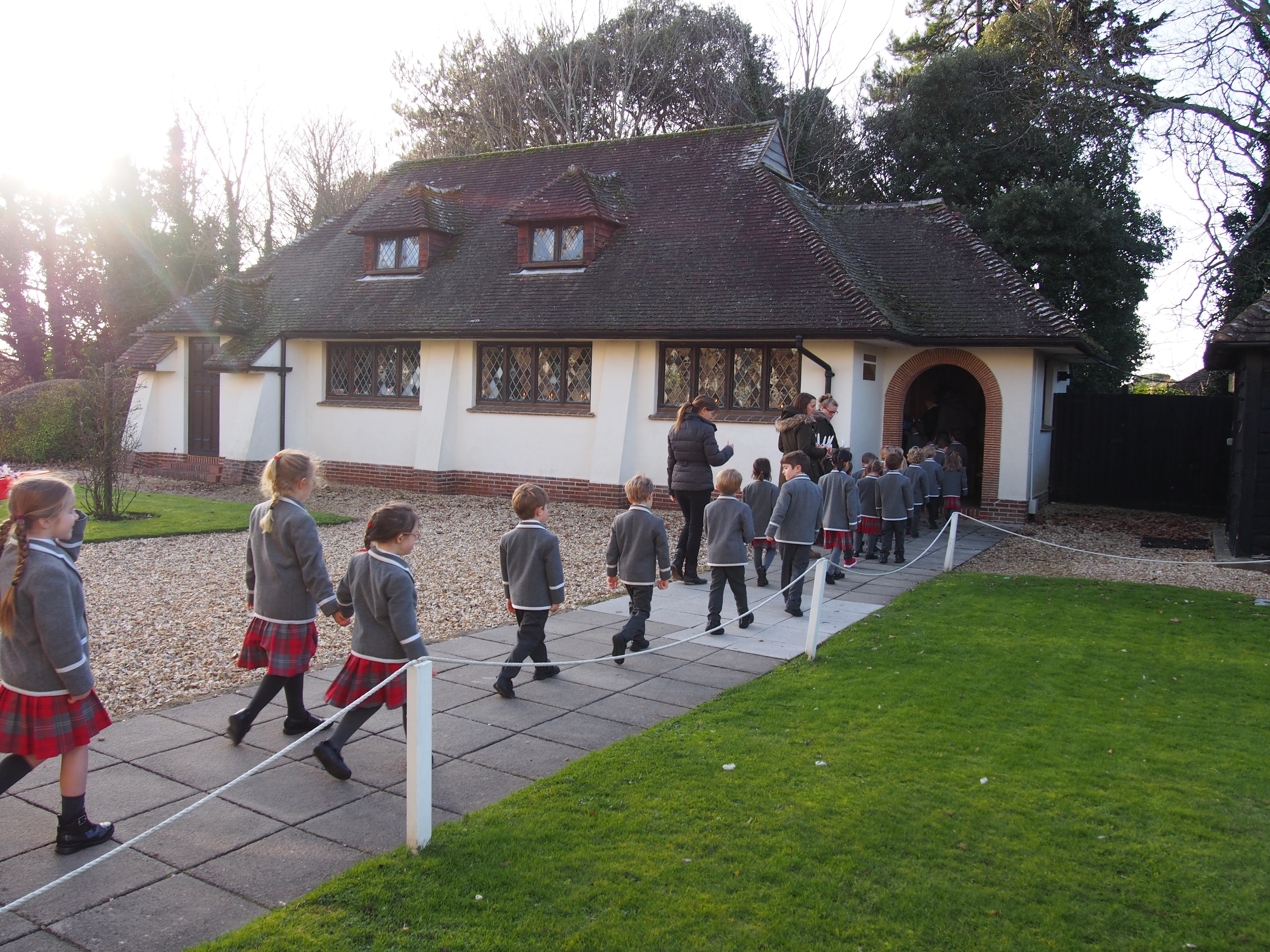
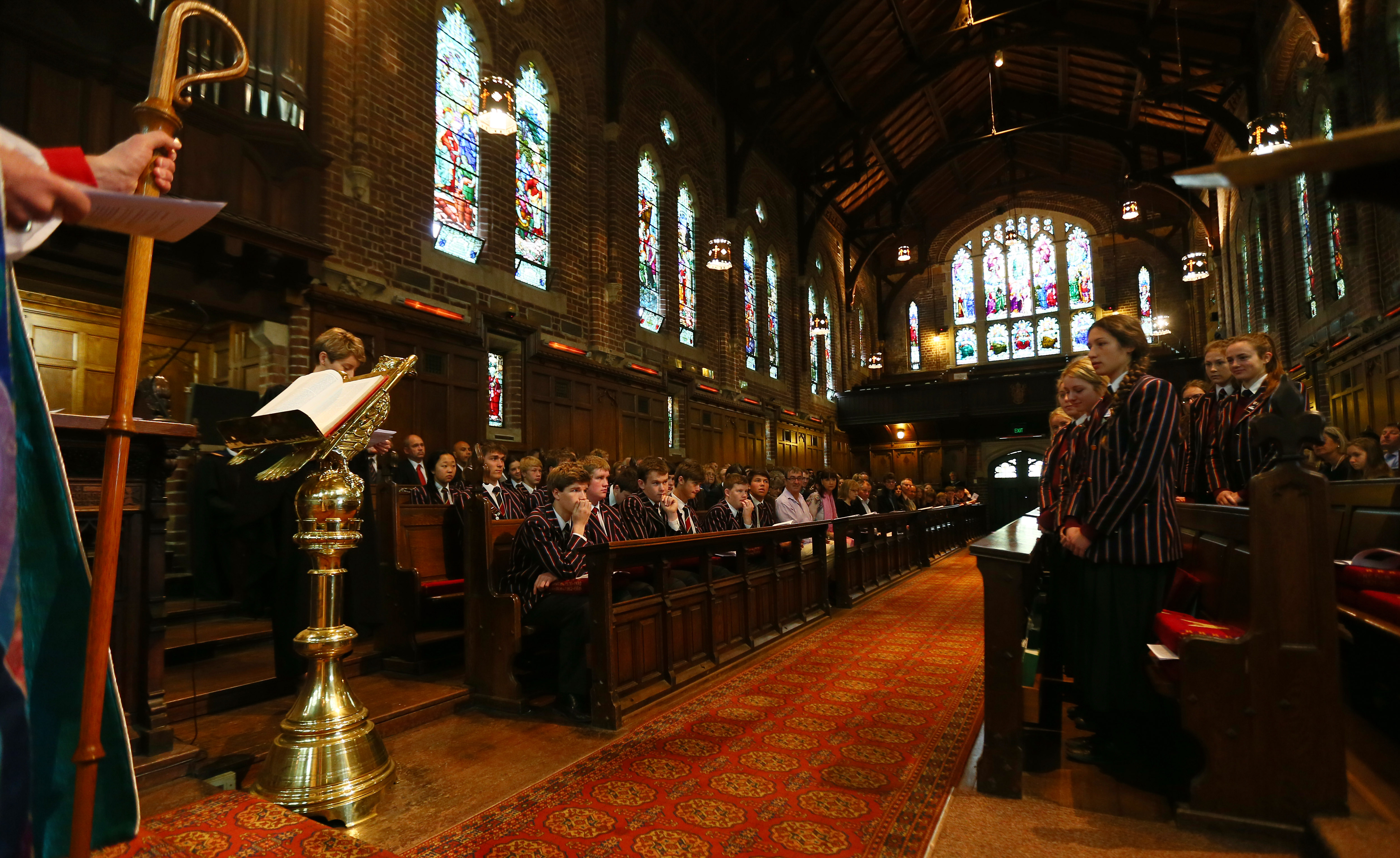
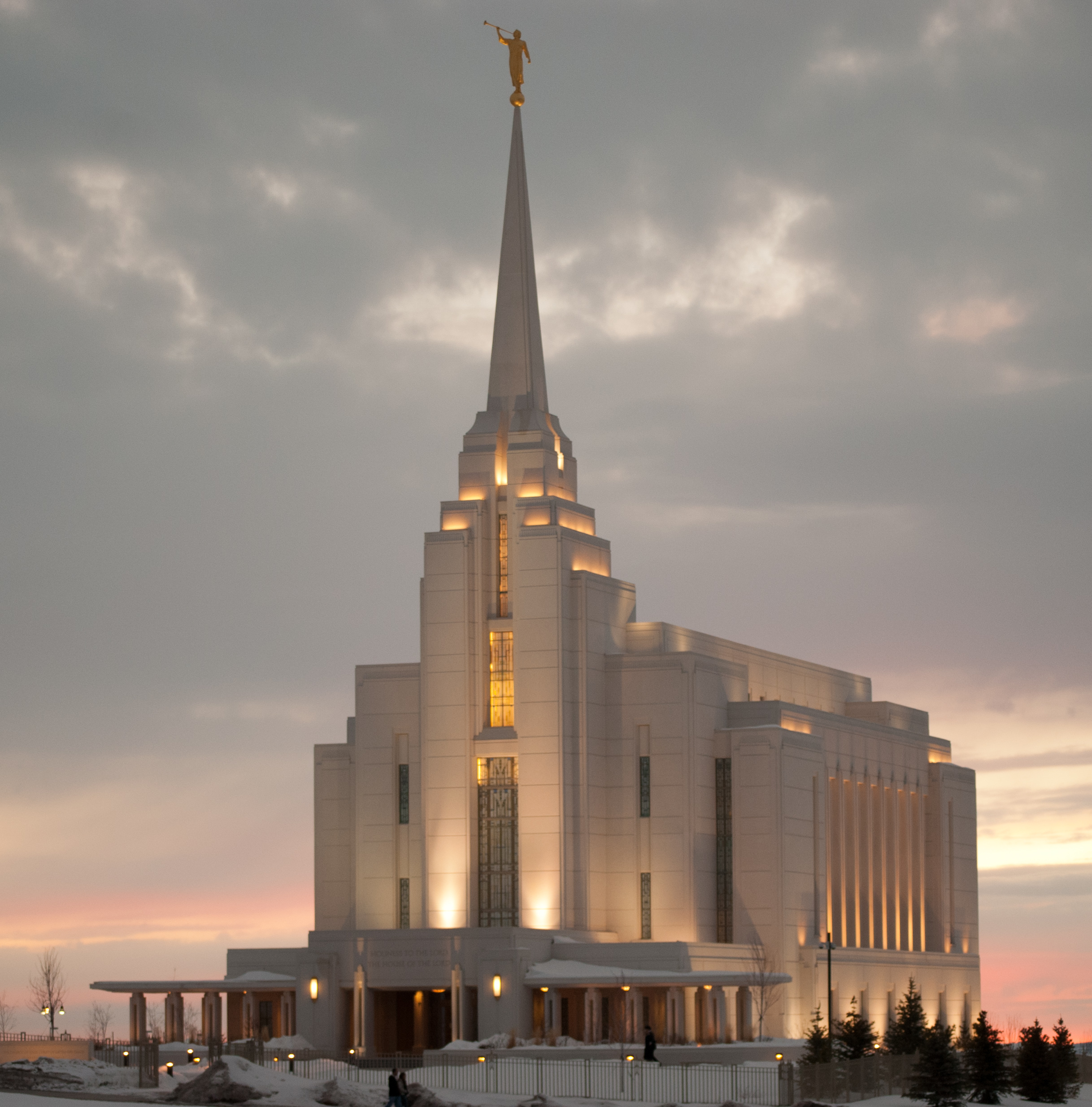
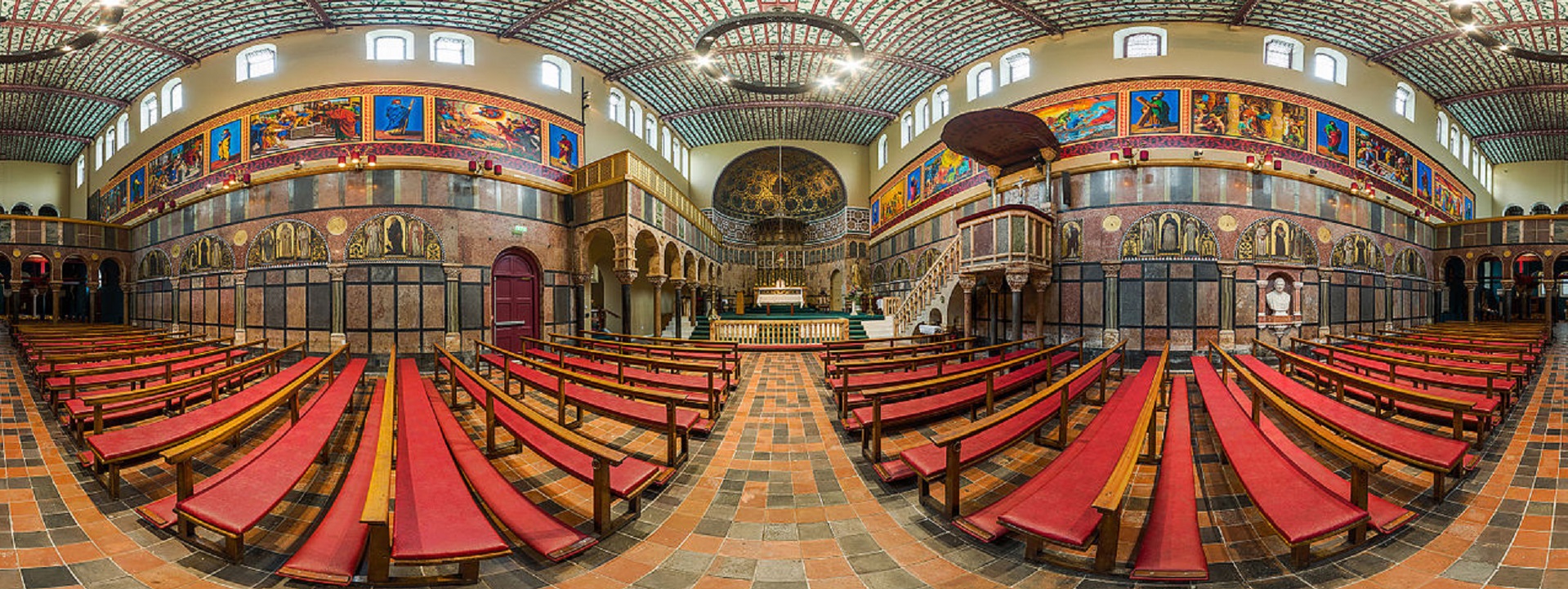
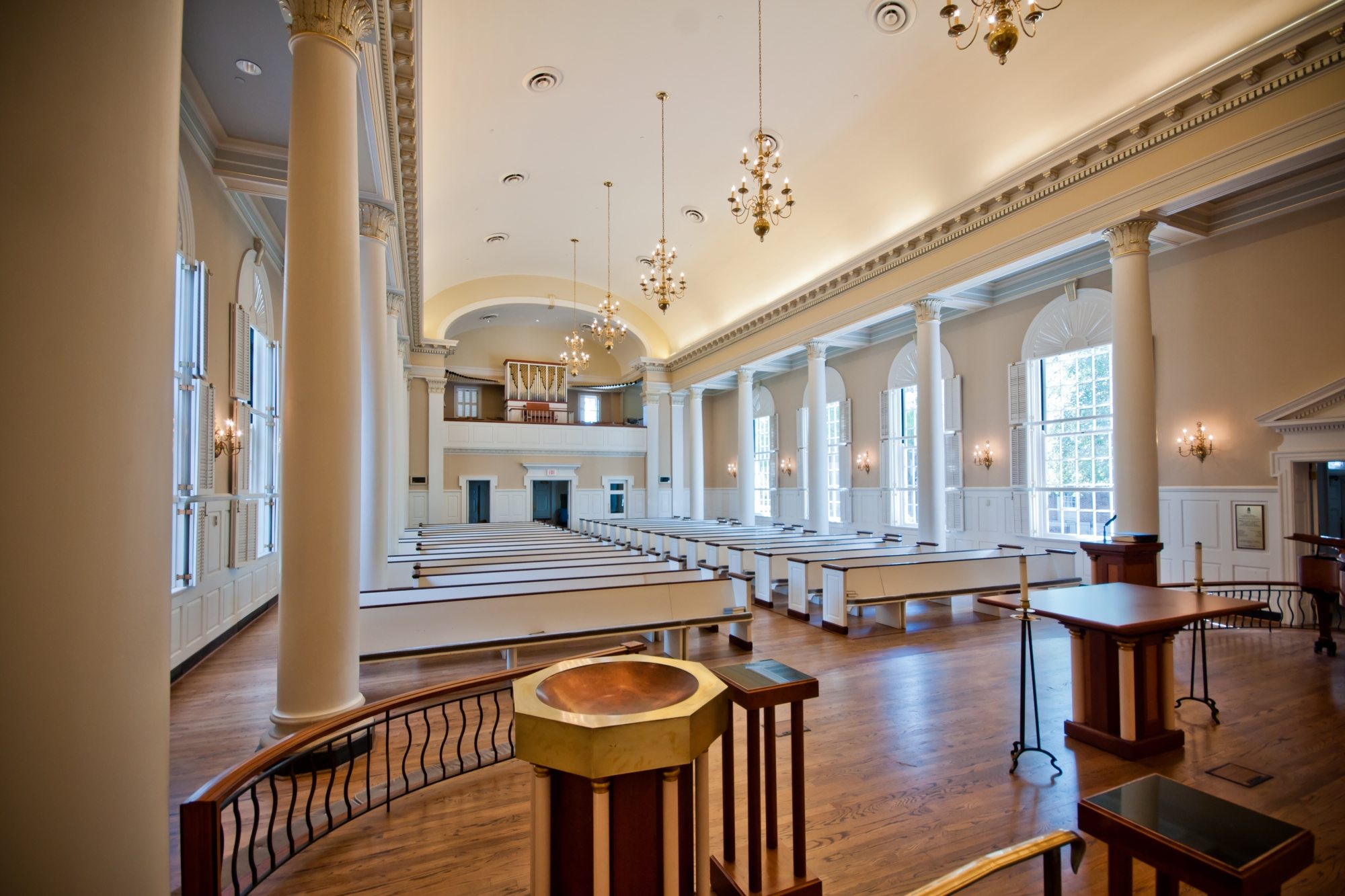
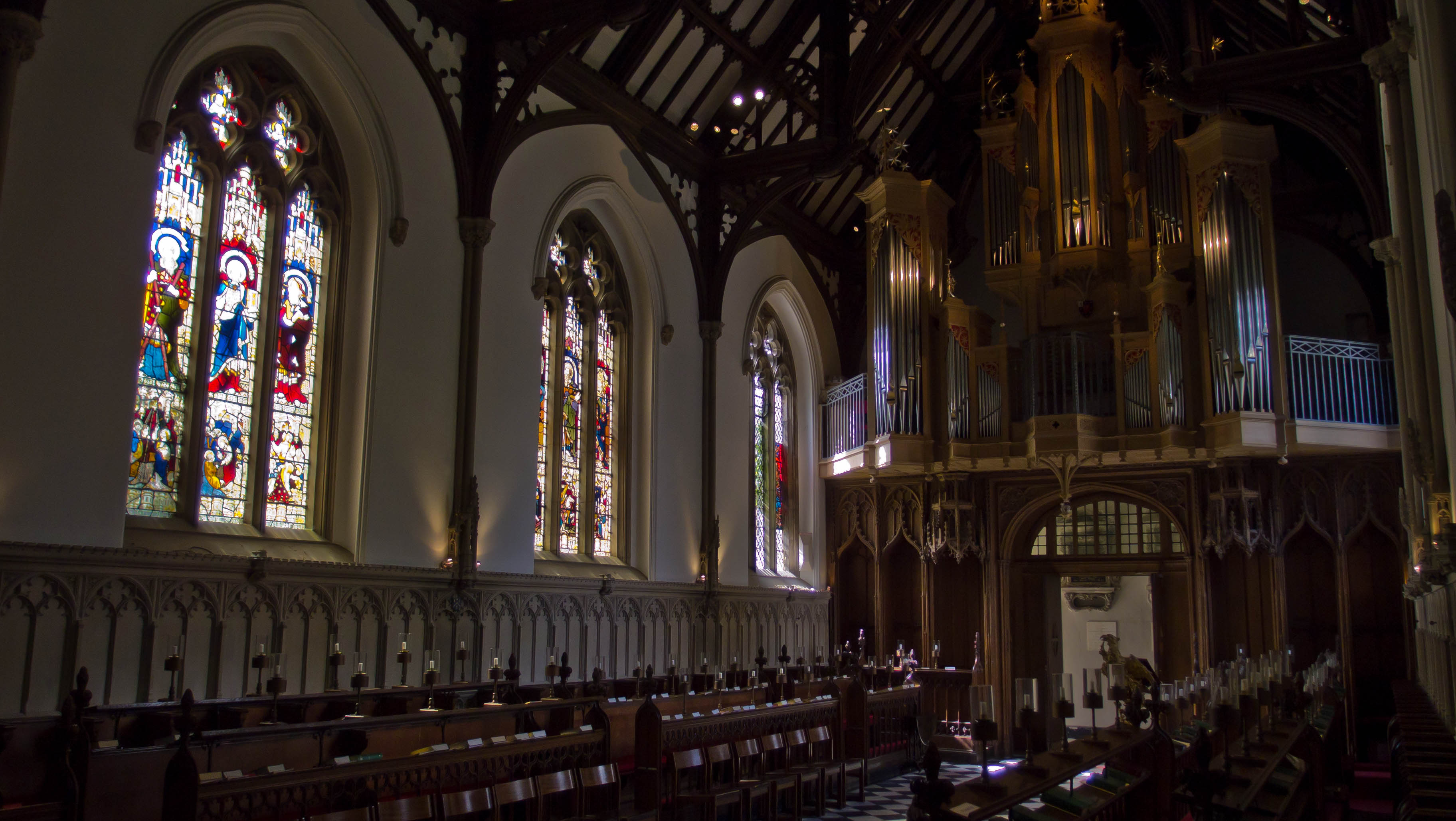
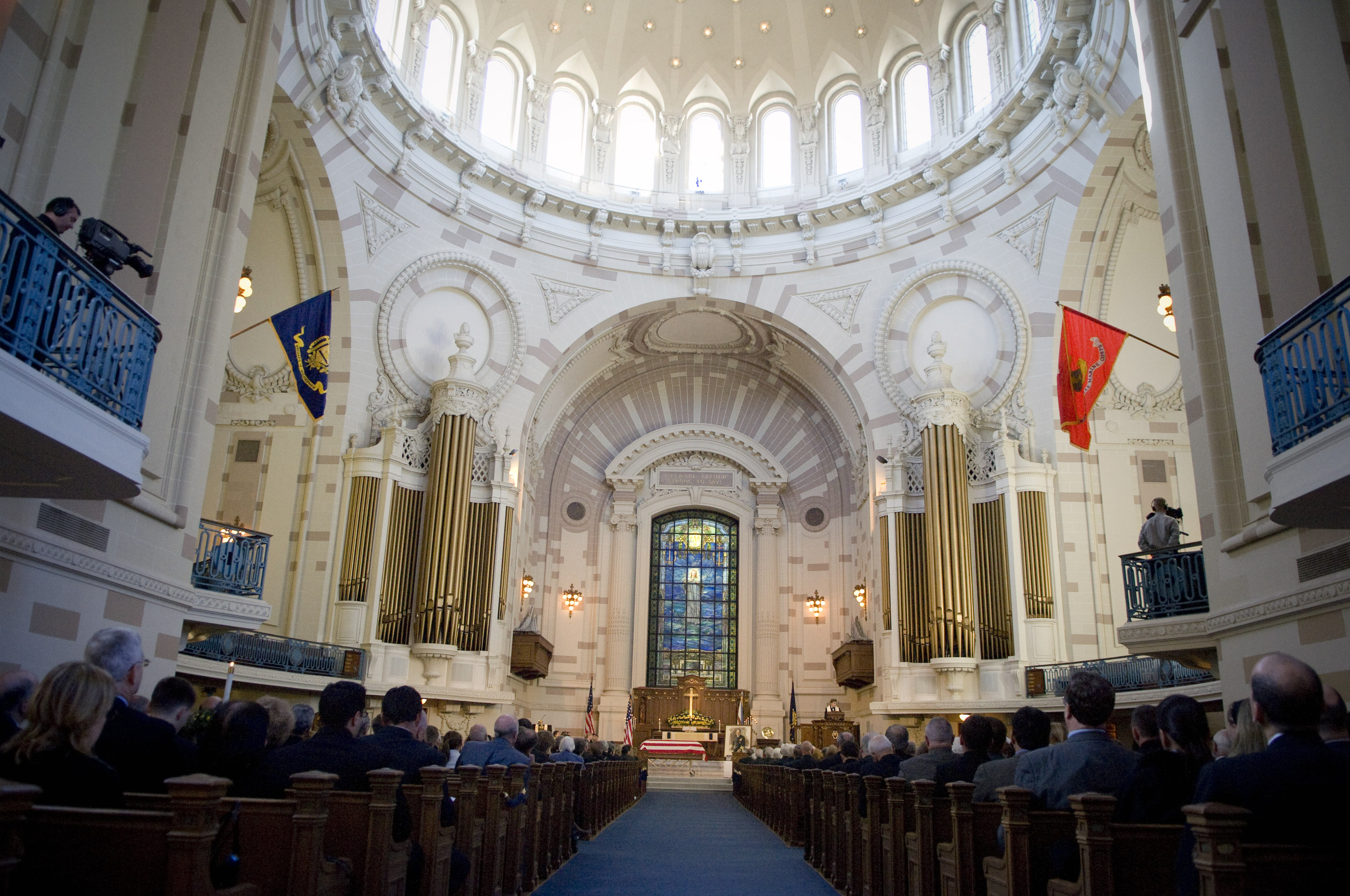
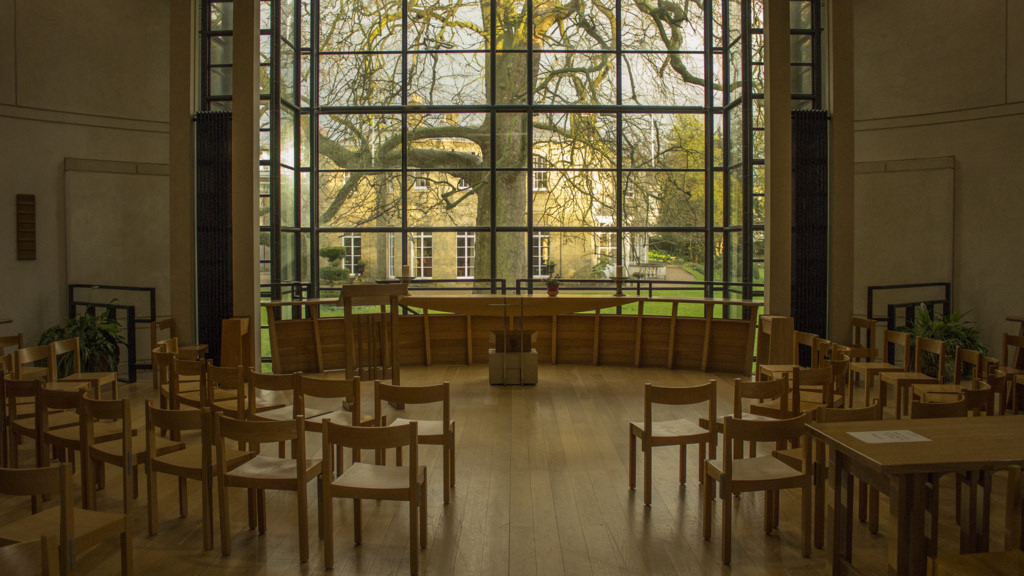
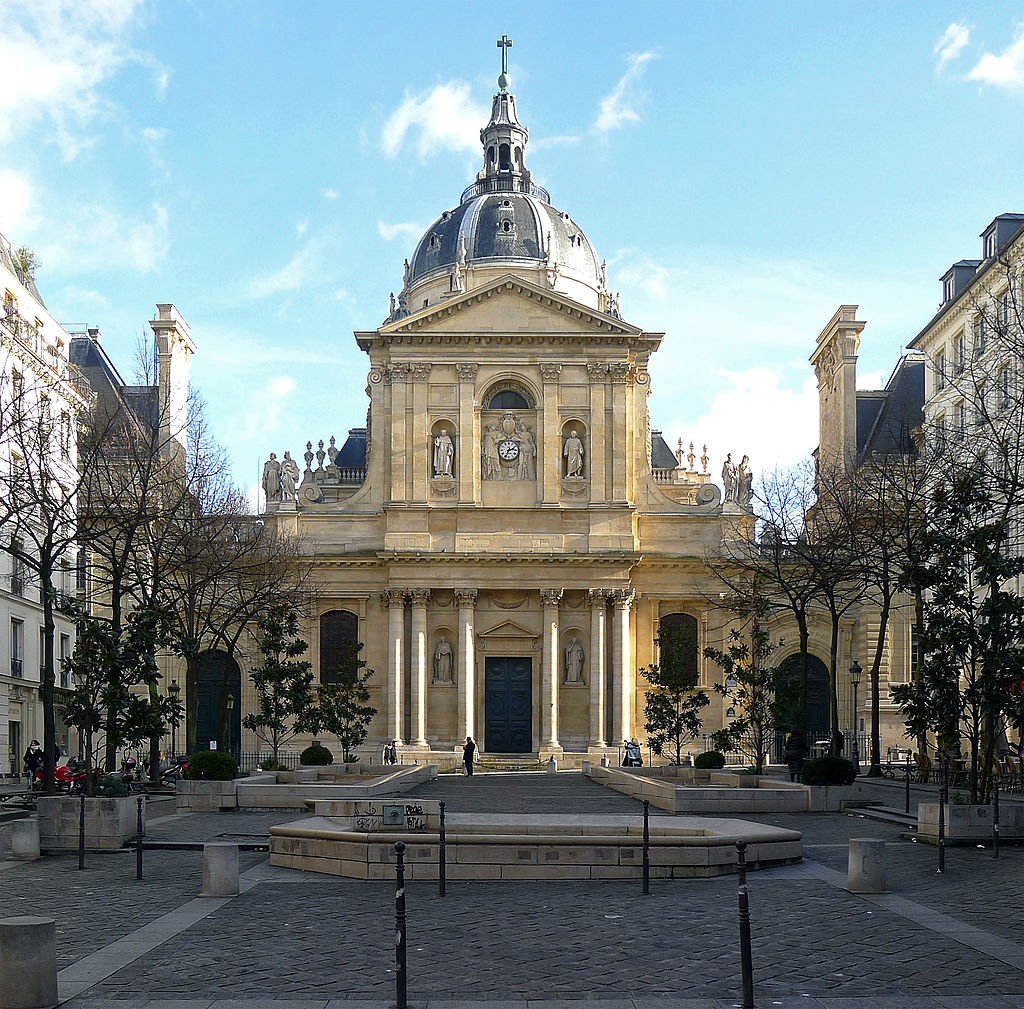
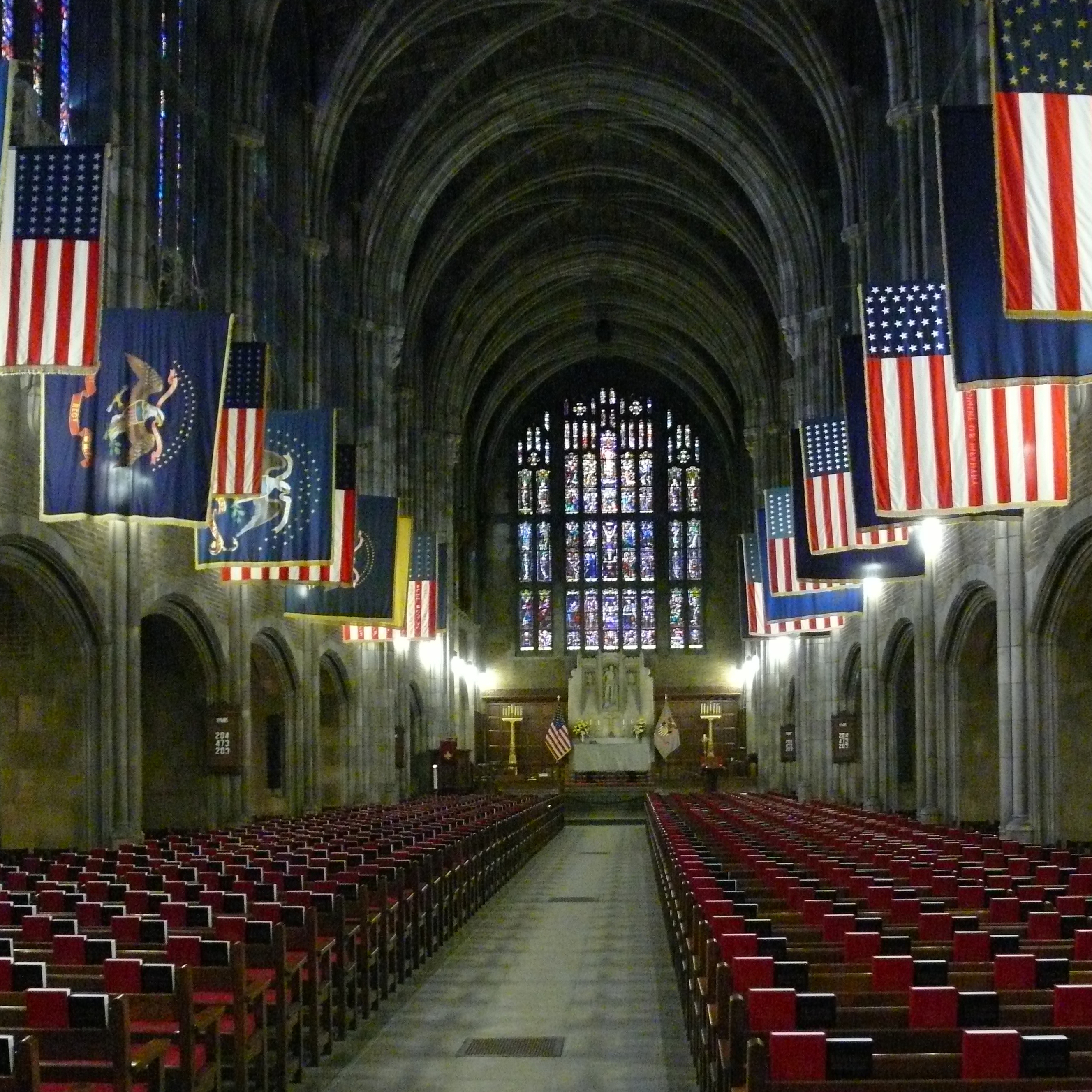
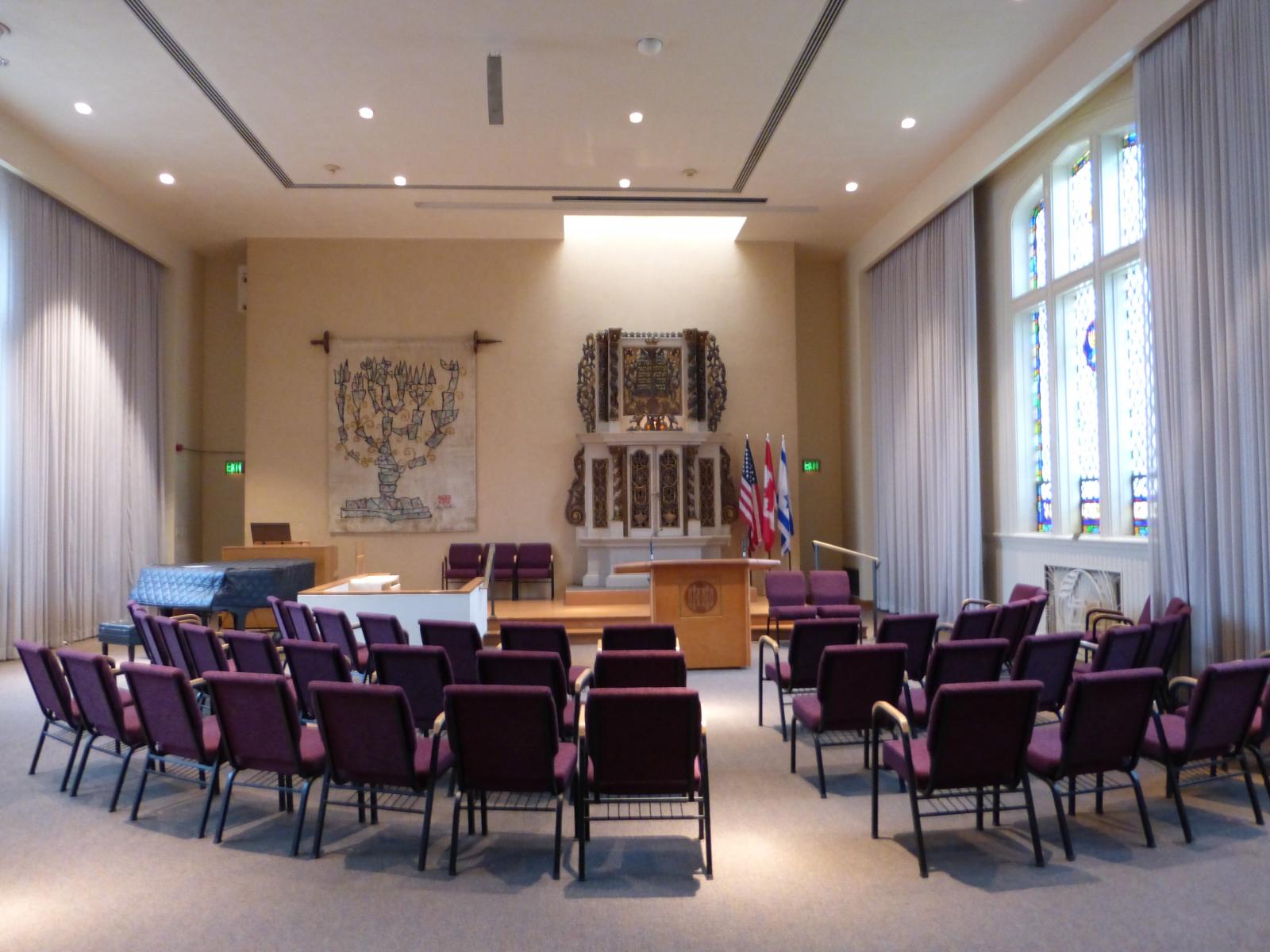
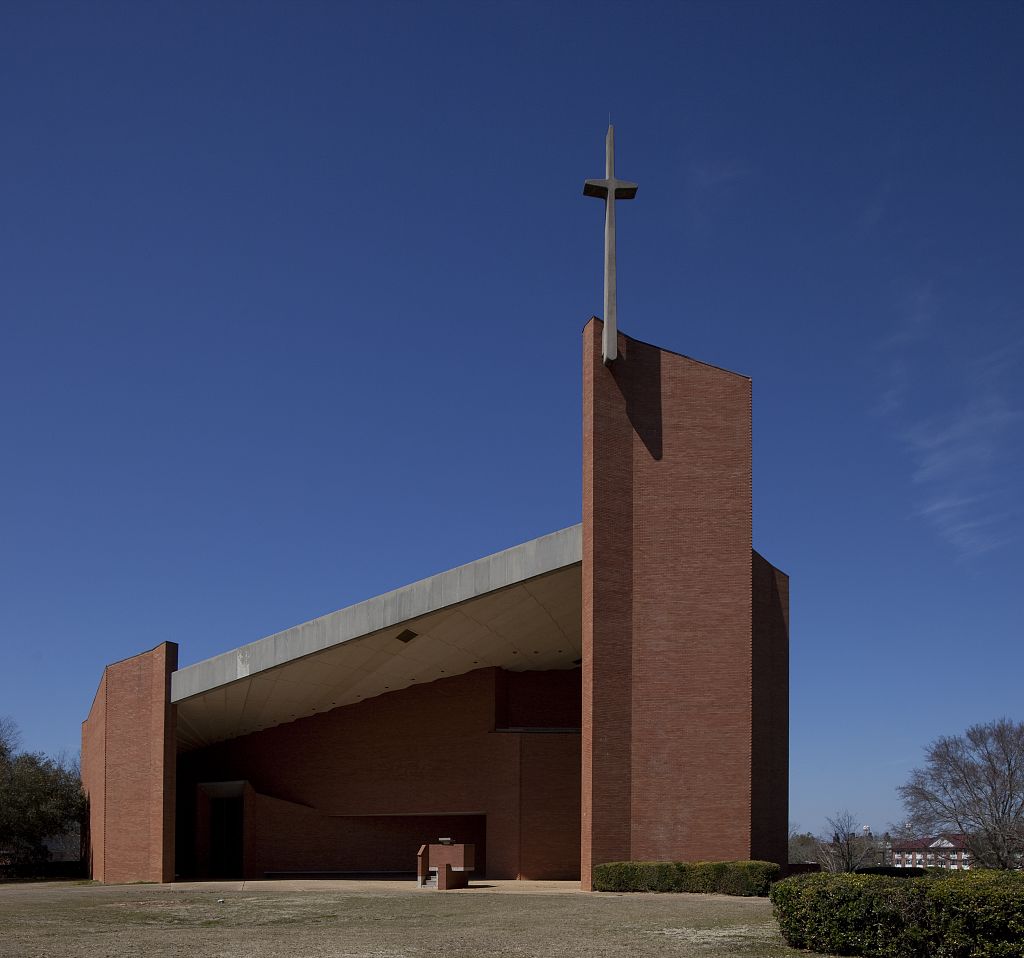
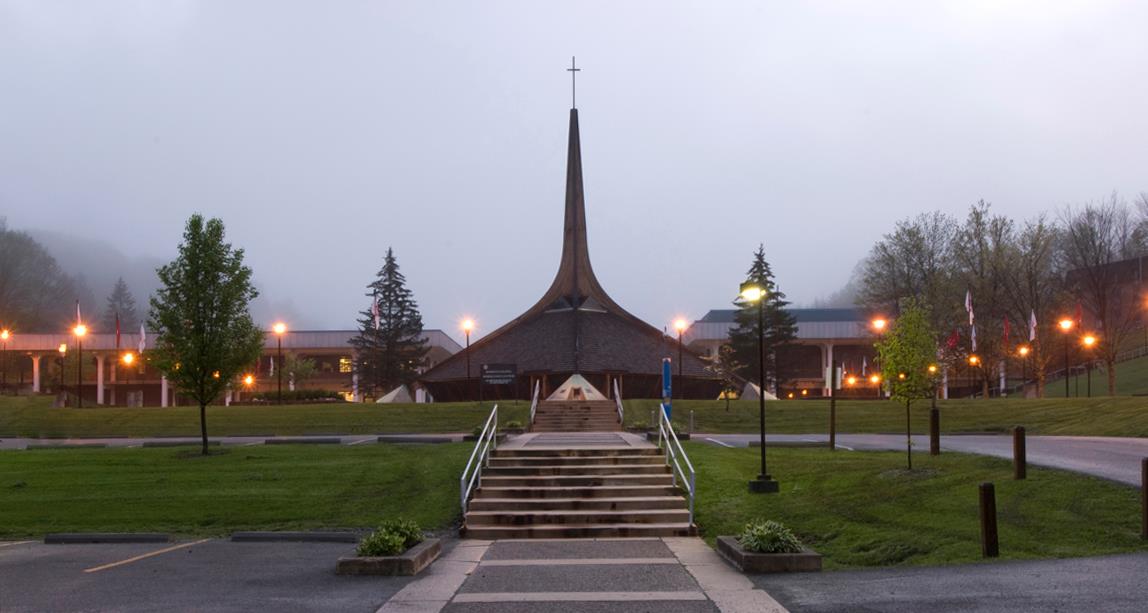
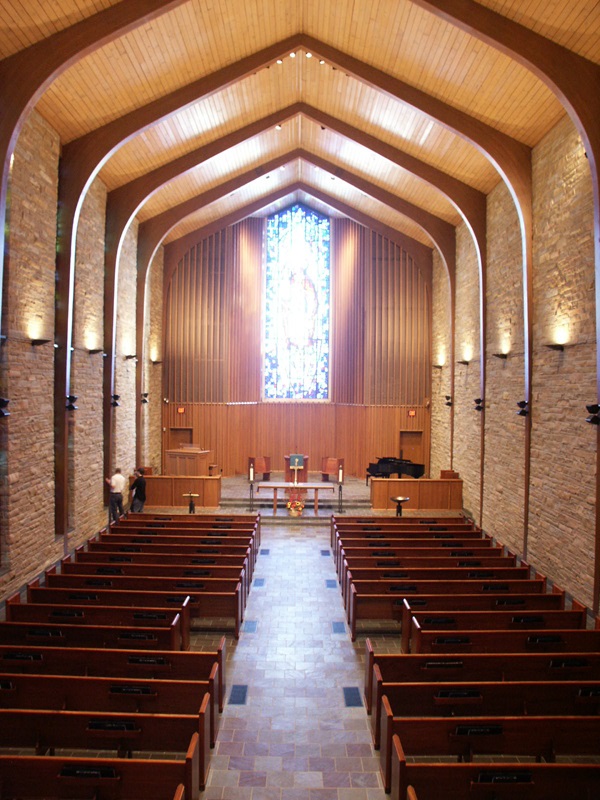
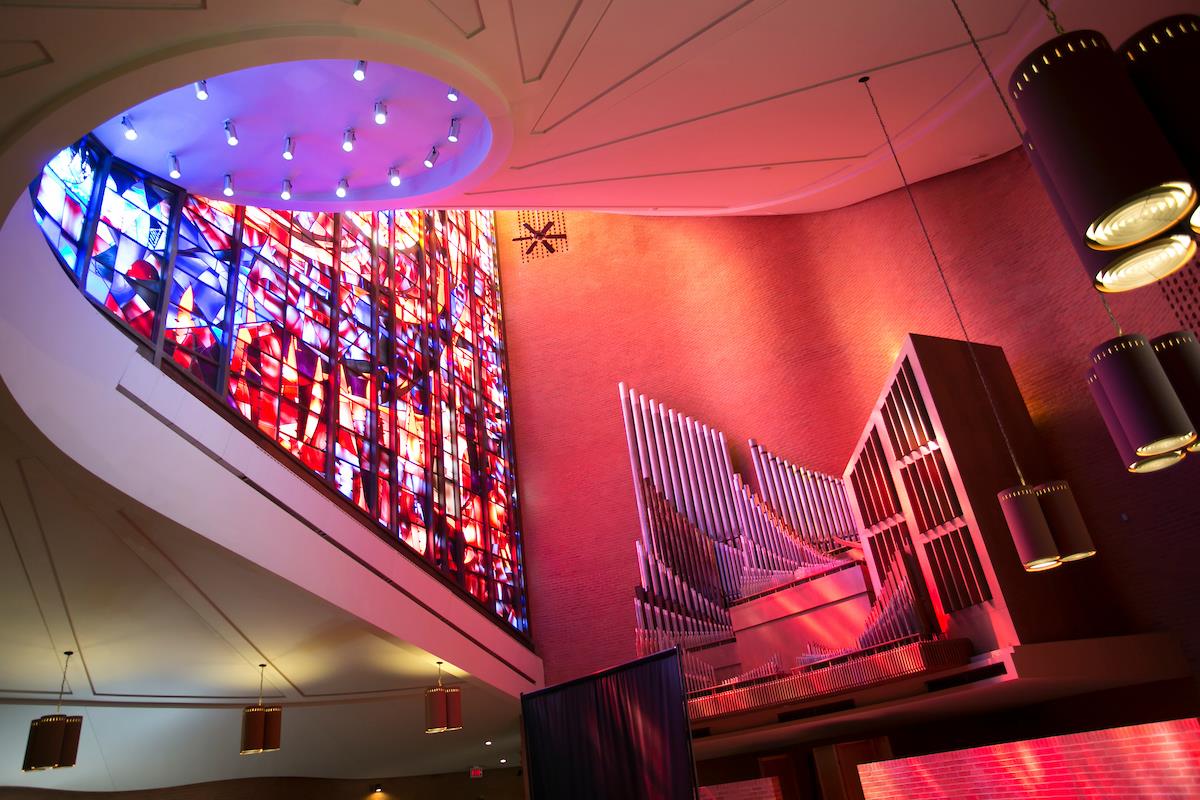
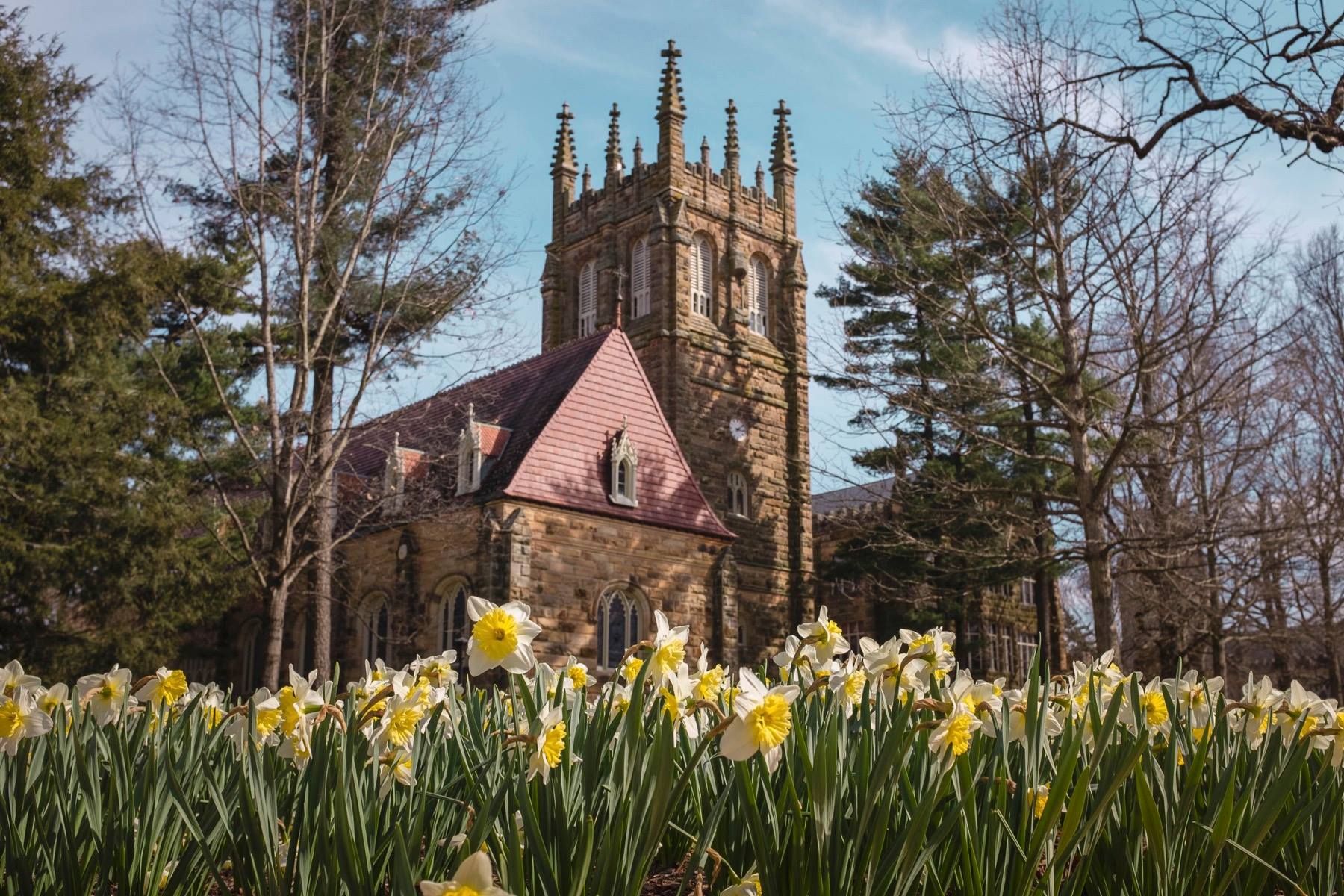
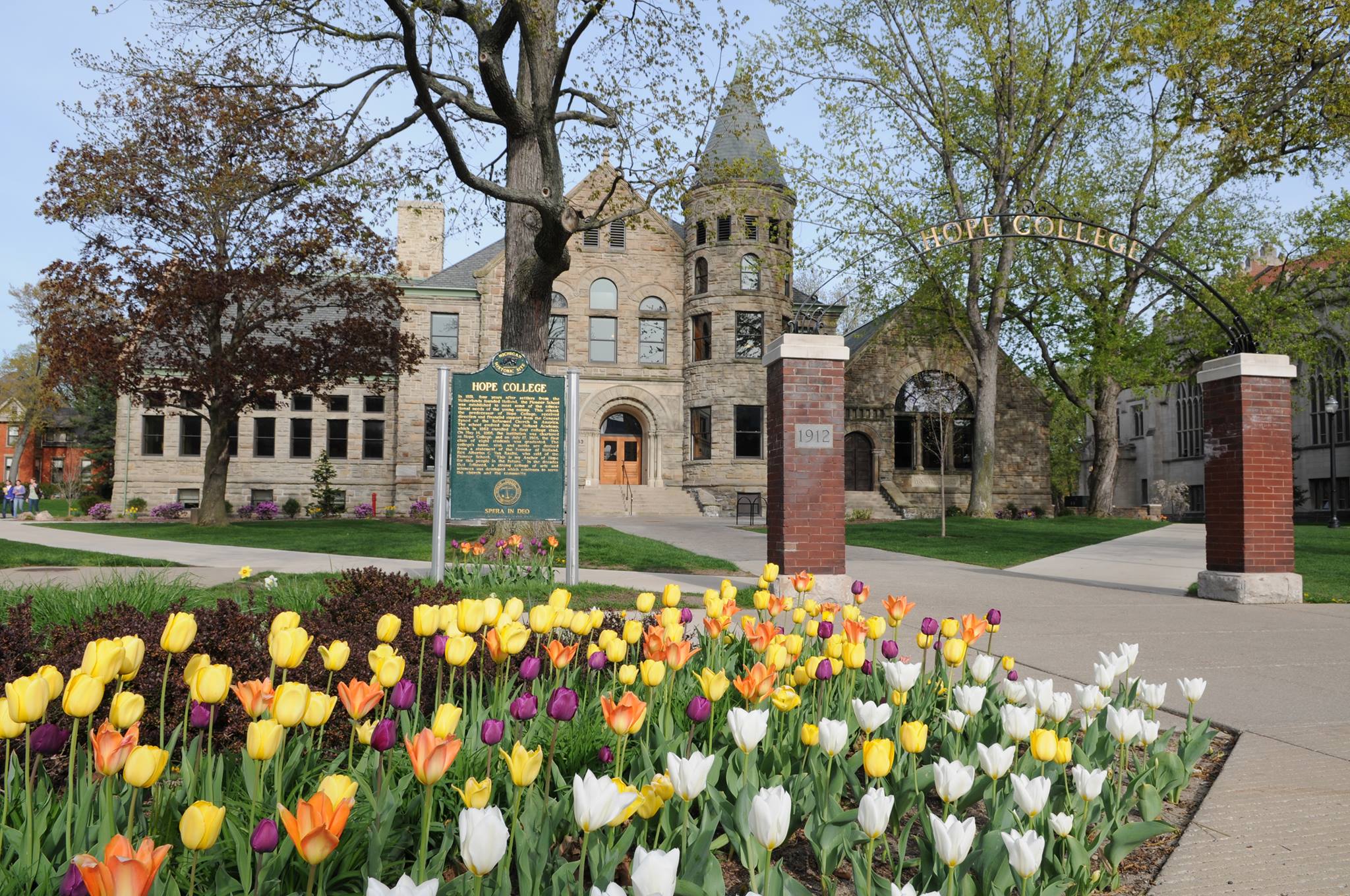
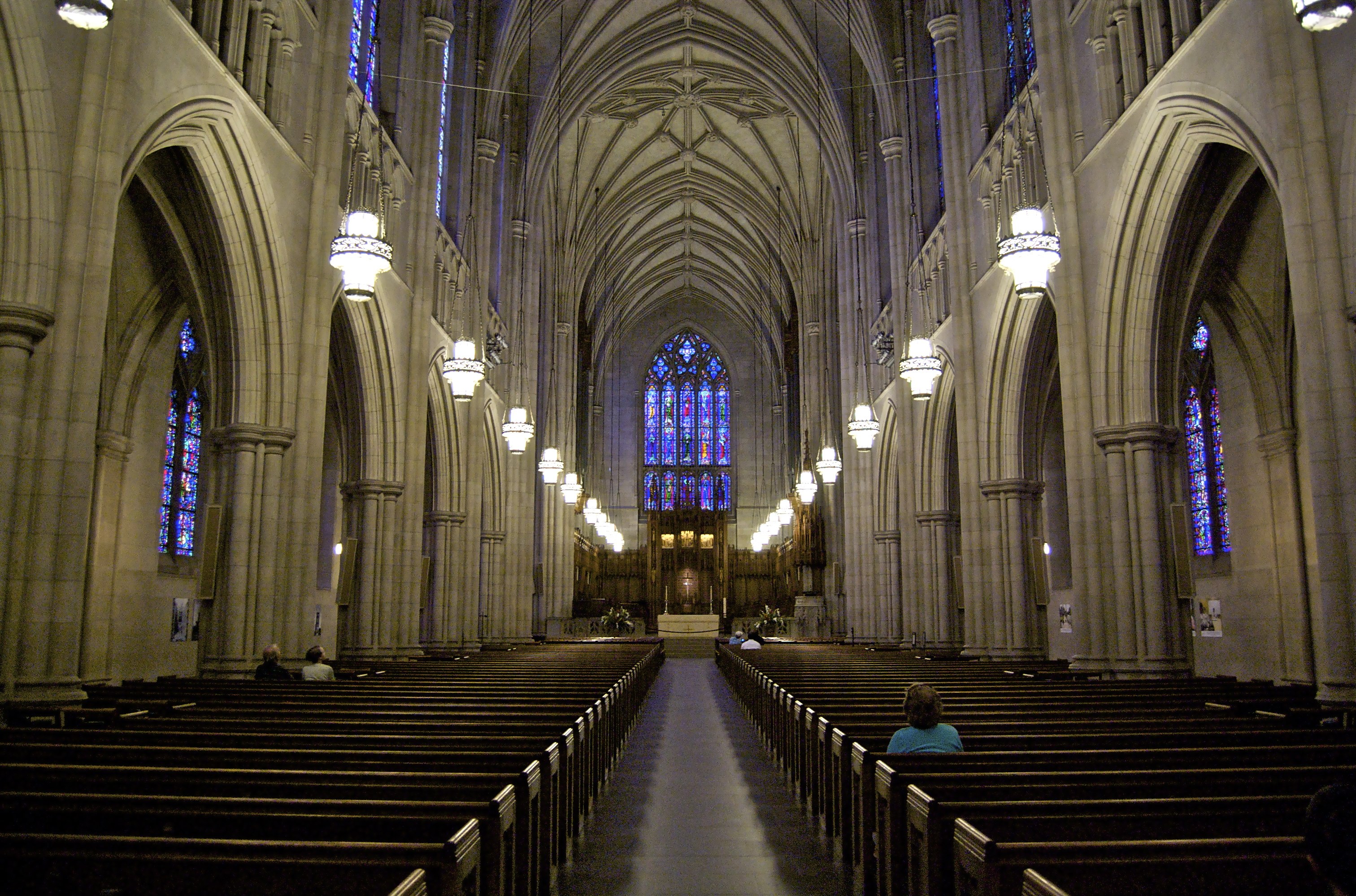
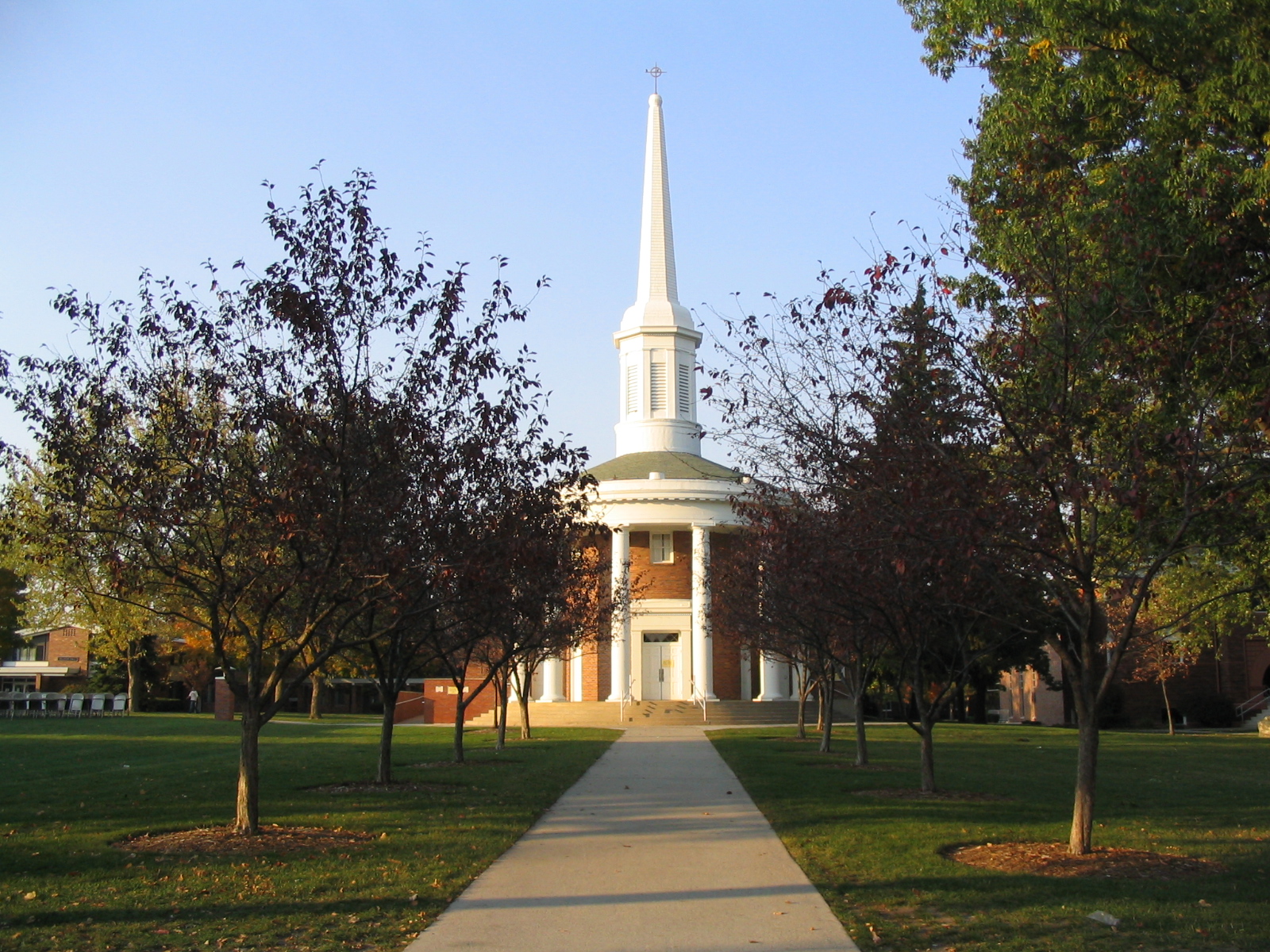
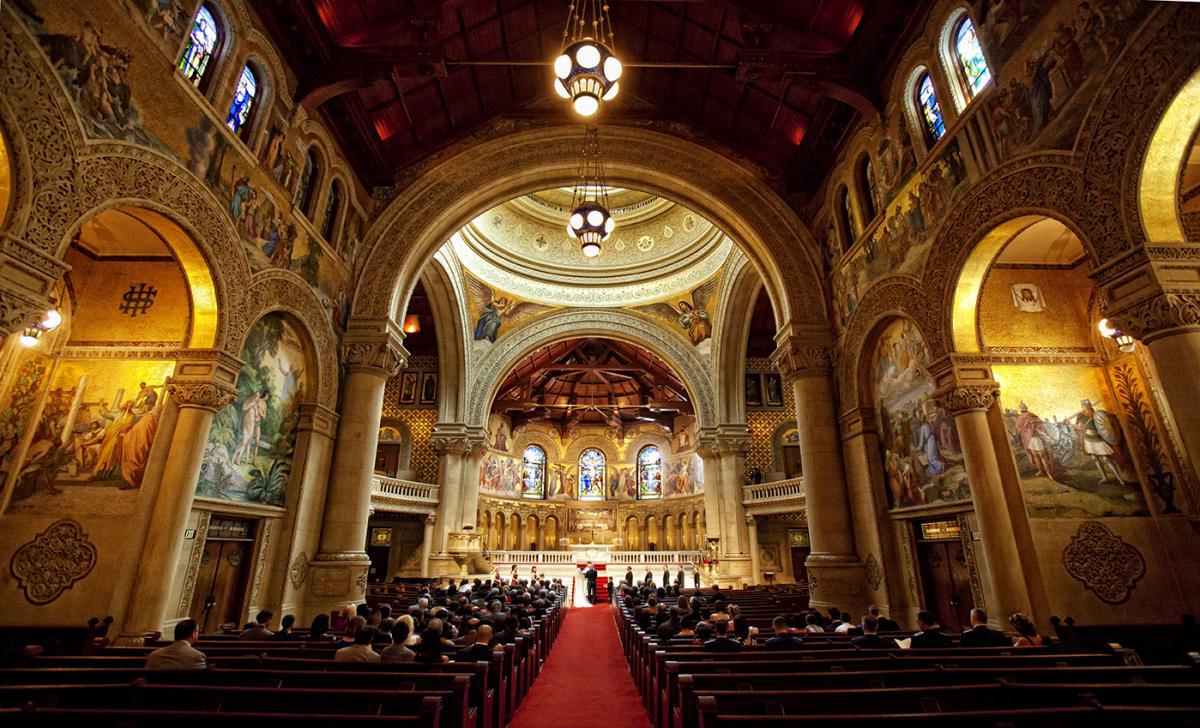
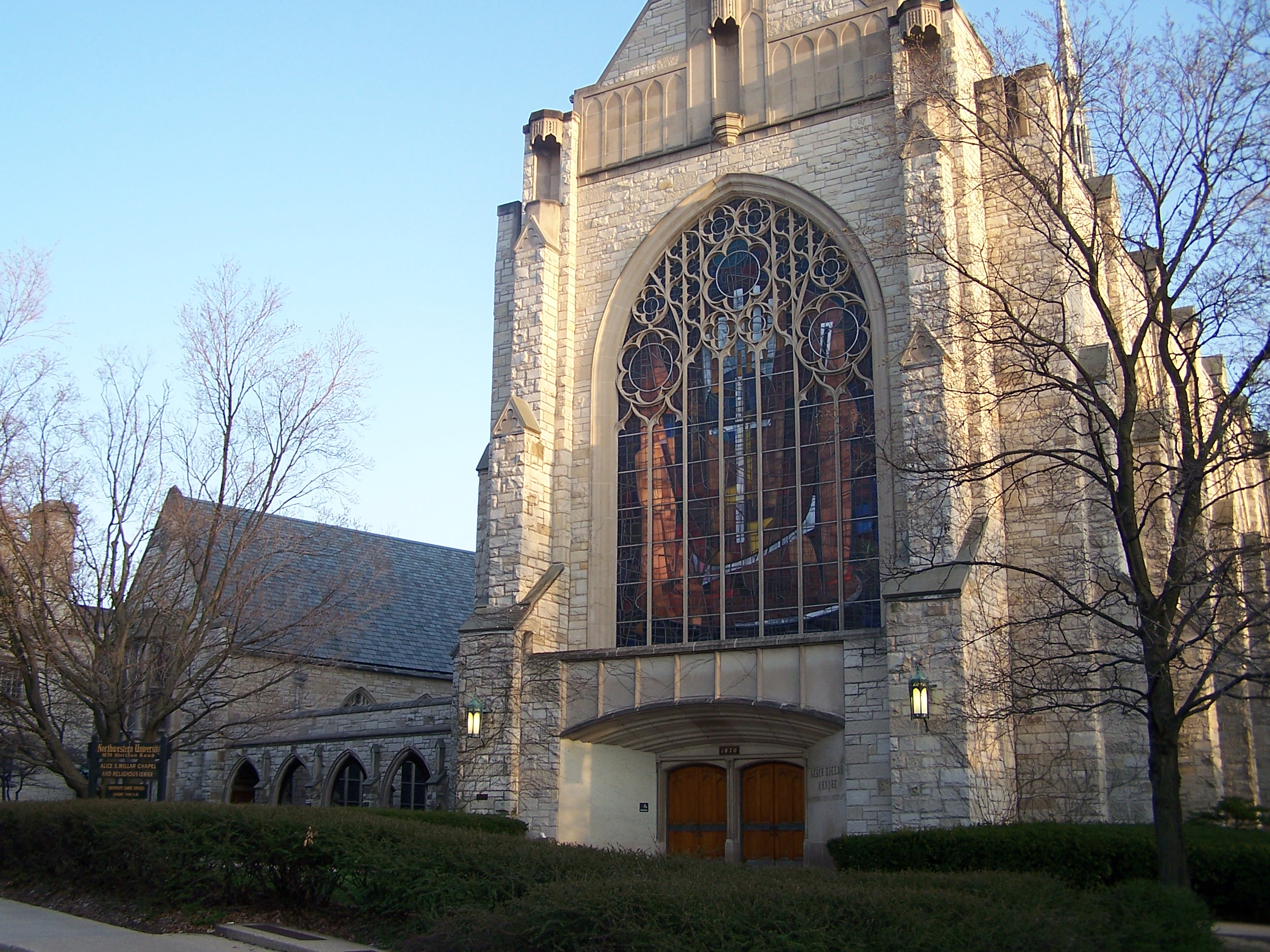
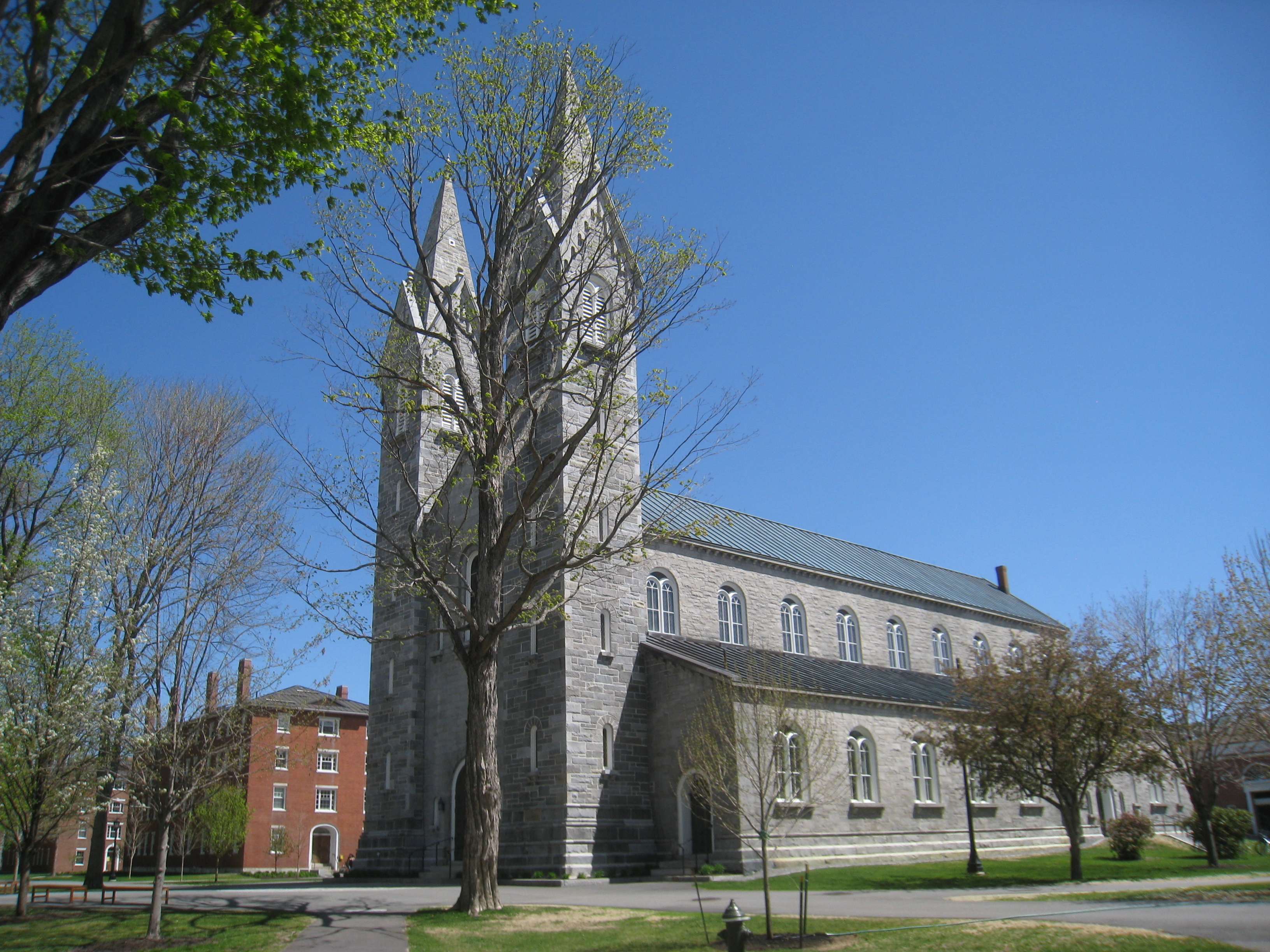
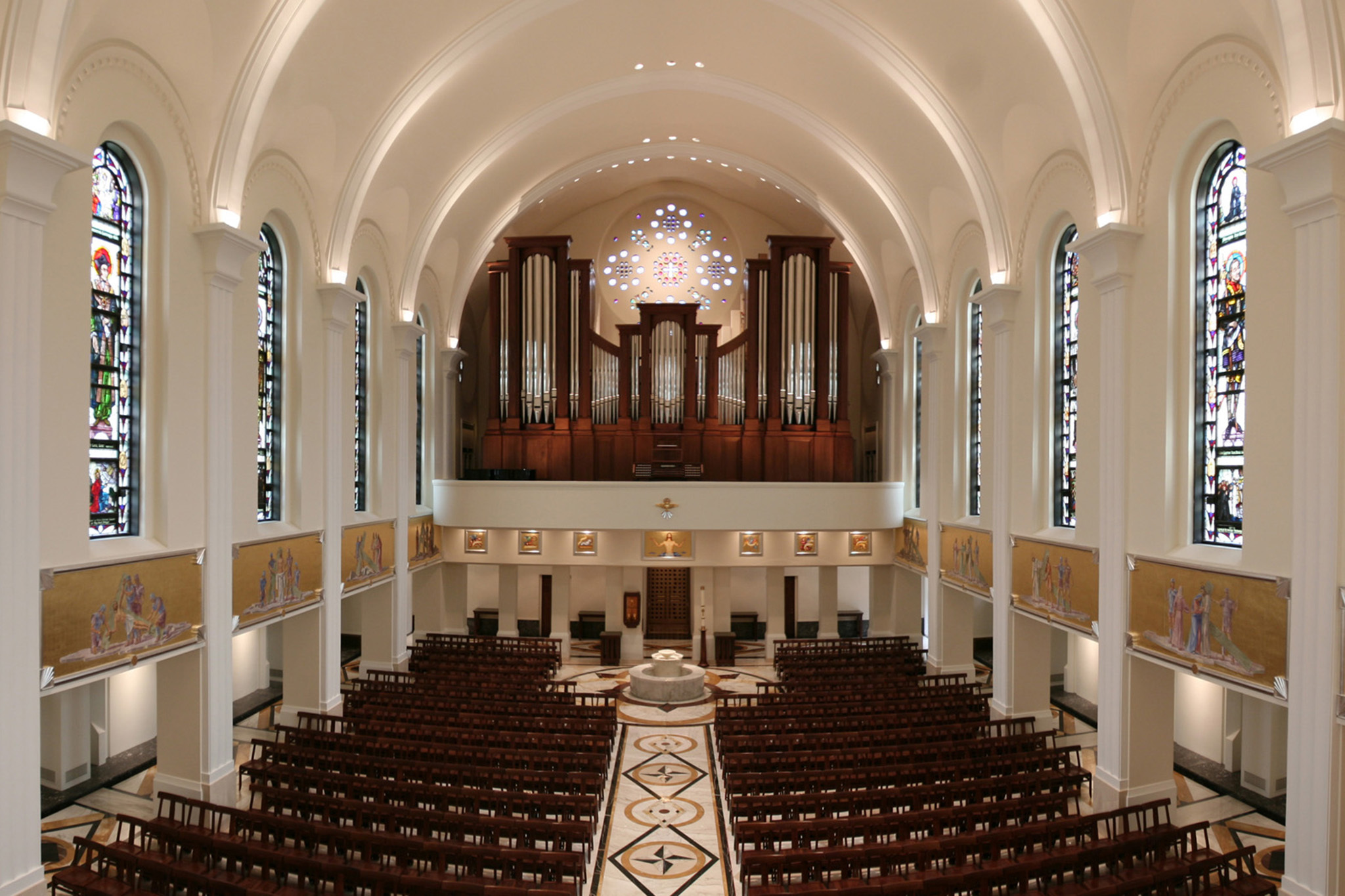
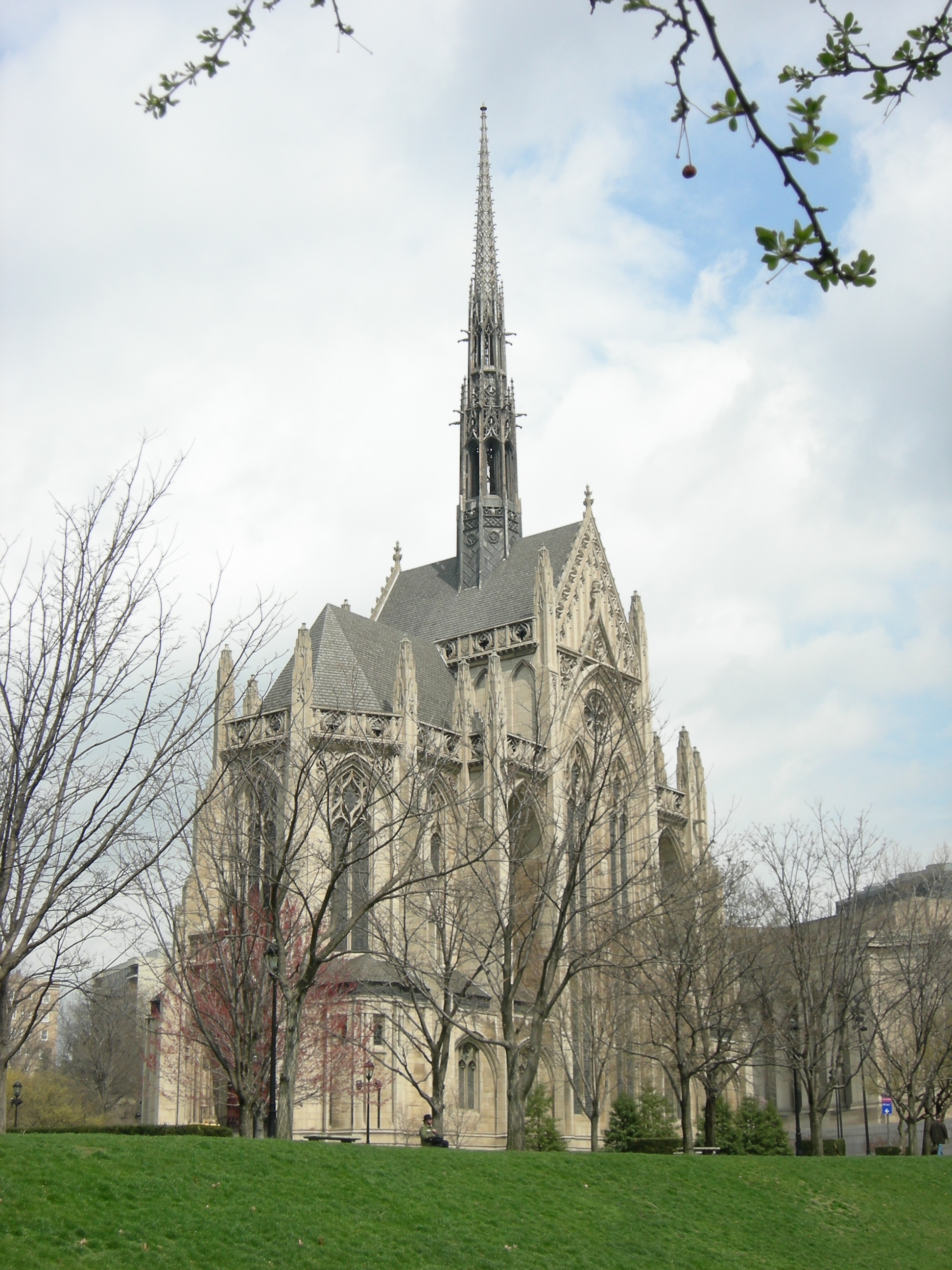
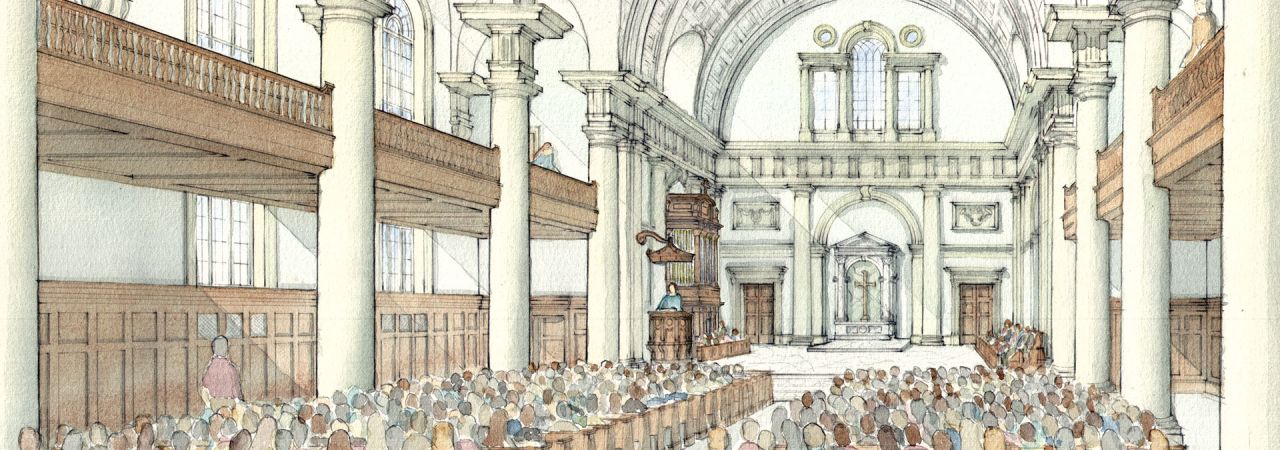
The founding of many education communities is inspired by faith communities. In many of them the place of worship was the very first building. College and university chapels are central places of worship for students, staff and faculty, and provide a space for solitude and reflection. A place for feeling at home in the world.
International Building Code | Section 303.4 Assembly Group A-3
There are several hundred technical standards, or parts of standards, that govern how churches and chapels are made safe and sustainable. Owing to innovations in construction, operation and management methods, those standards move, ever so slightly, on a near-daily basis. They are highly interdependent; confounded by county-level adaptations; and impossible to harmonize by adoption cycle. That movement tracked here as best we can within the limit of our resources and priorities. That’s why it’s best to simply click into our daily colloquia if you have a question or need guidance.
Lights are on in the little Baptist parsonage tonight. pic.twitter.com/RK4W6kjug5
— NYFarmer (@NYFarmer) June 7, 2025
Today is the Feast of Corpus Christi.
The 13th century Eucharistic chant of Ave verum corpus was set to music by Mozart in 1791 to be sung especially to celebrate the feast day.
Here I sing it in the historic chapel of Launde Abbey. #History pic.twitter.com/frkUFkPHVj
— Katie Marshall (@KatieHistory) June 11, 2023
Maps of Meaning: The Architecture of Belief | Jordan Peterson, Douglas Murray, Sam Harris
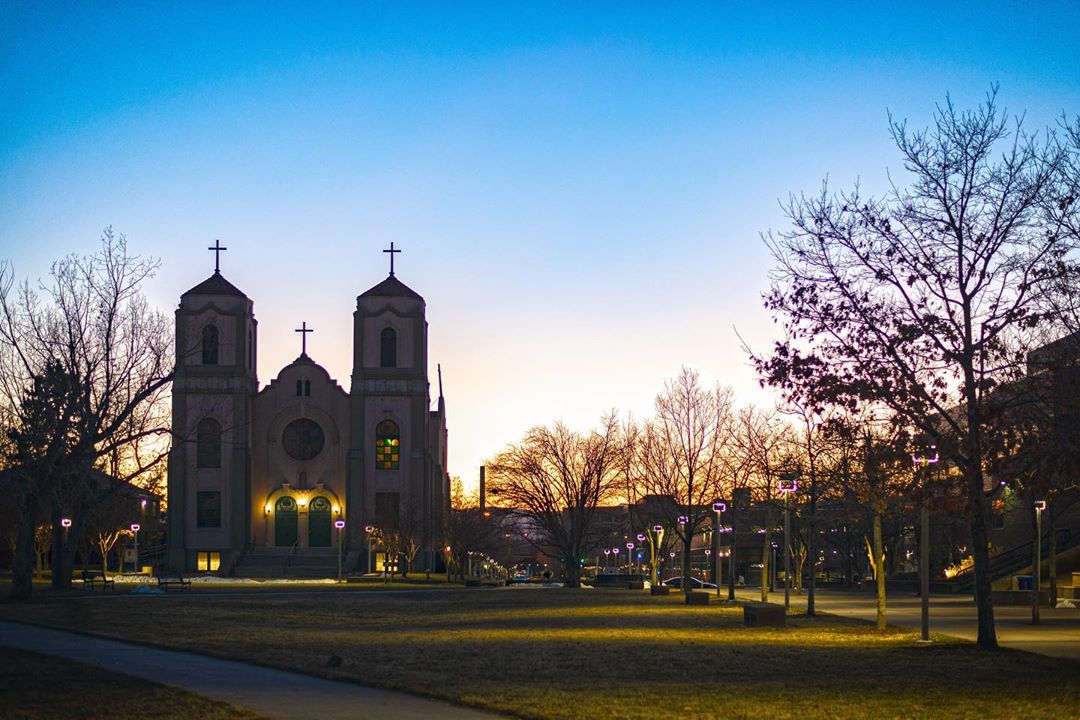
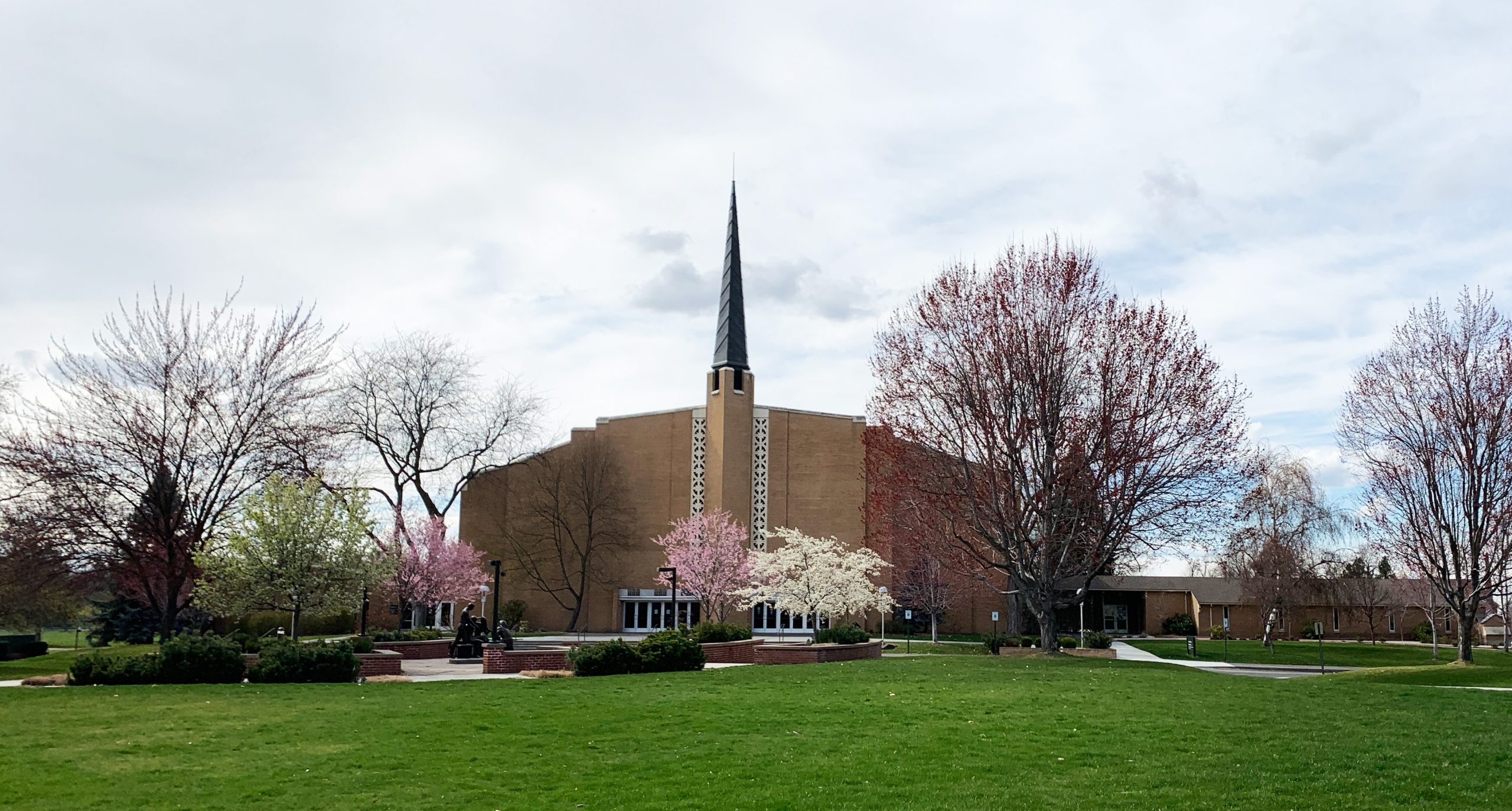
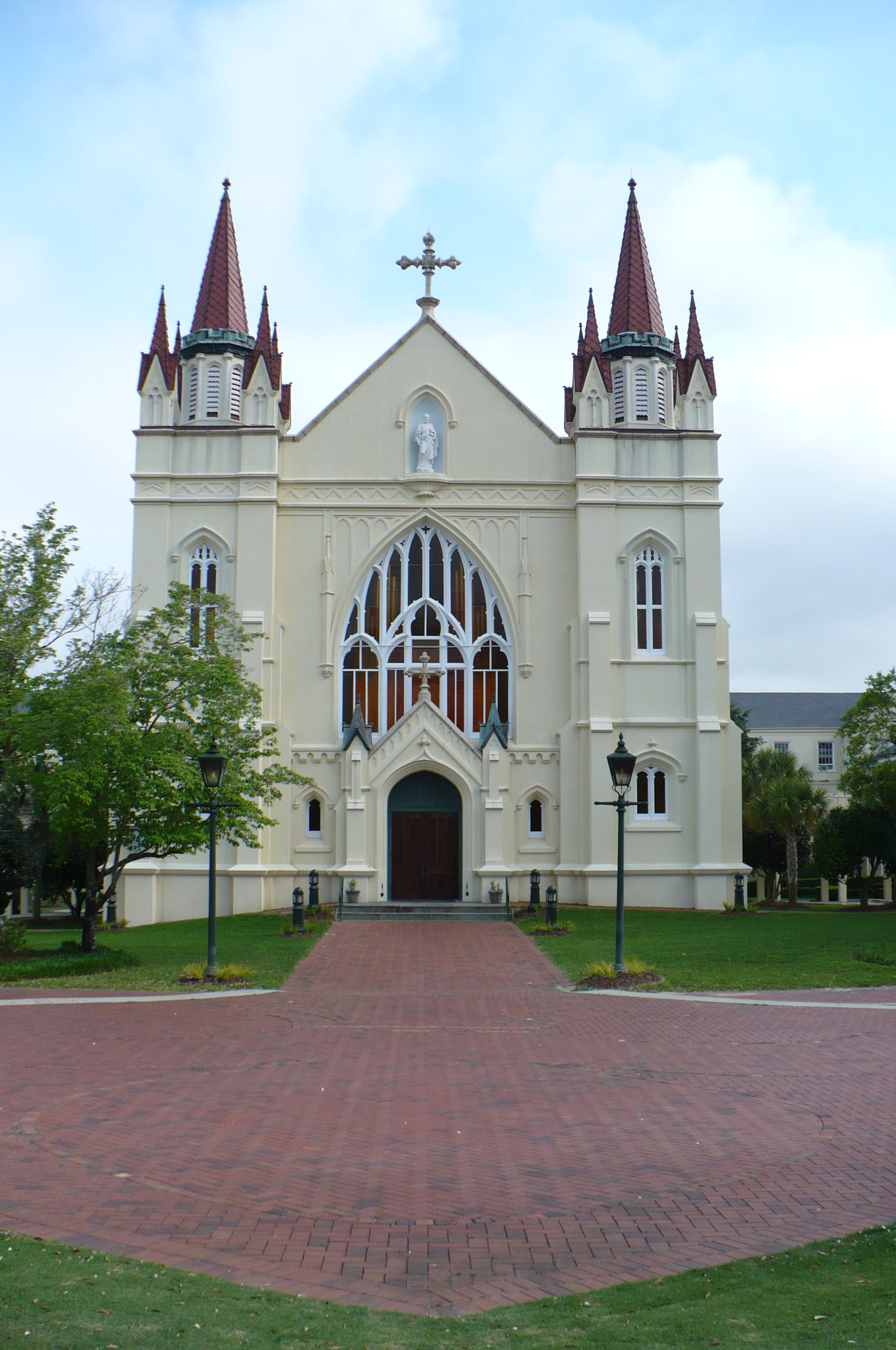
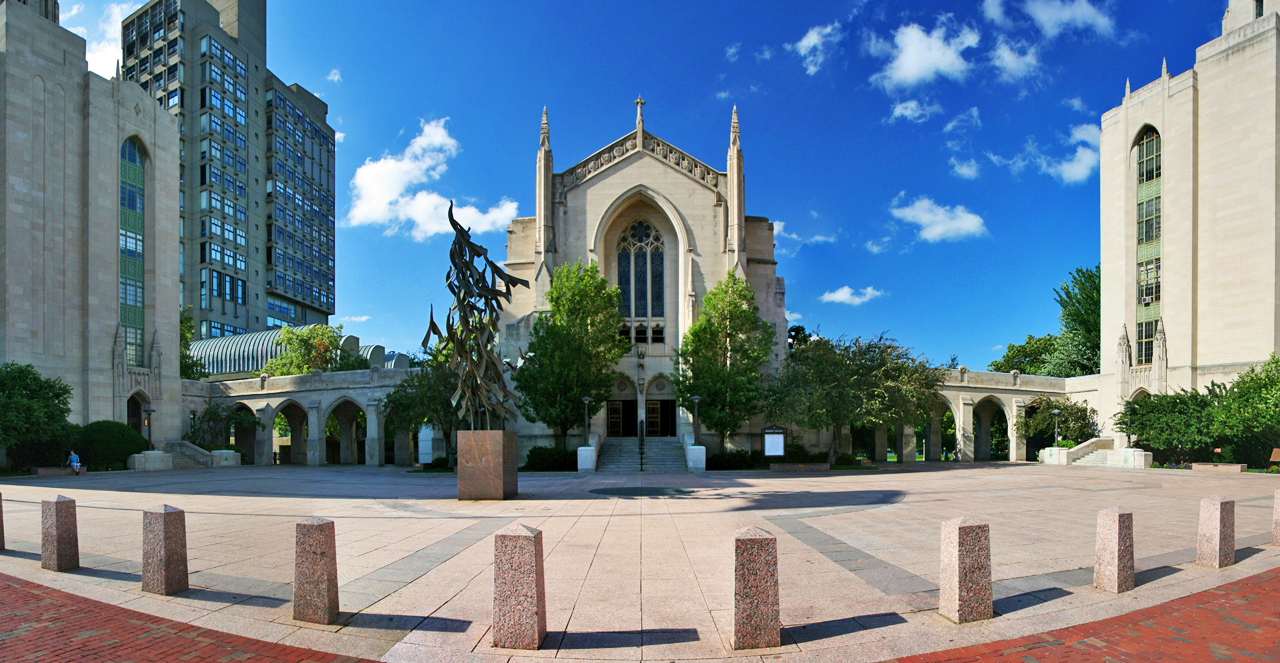
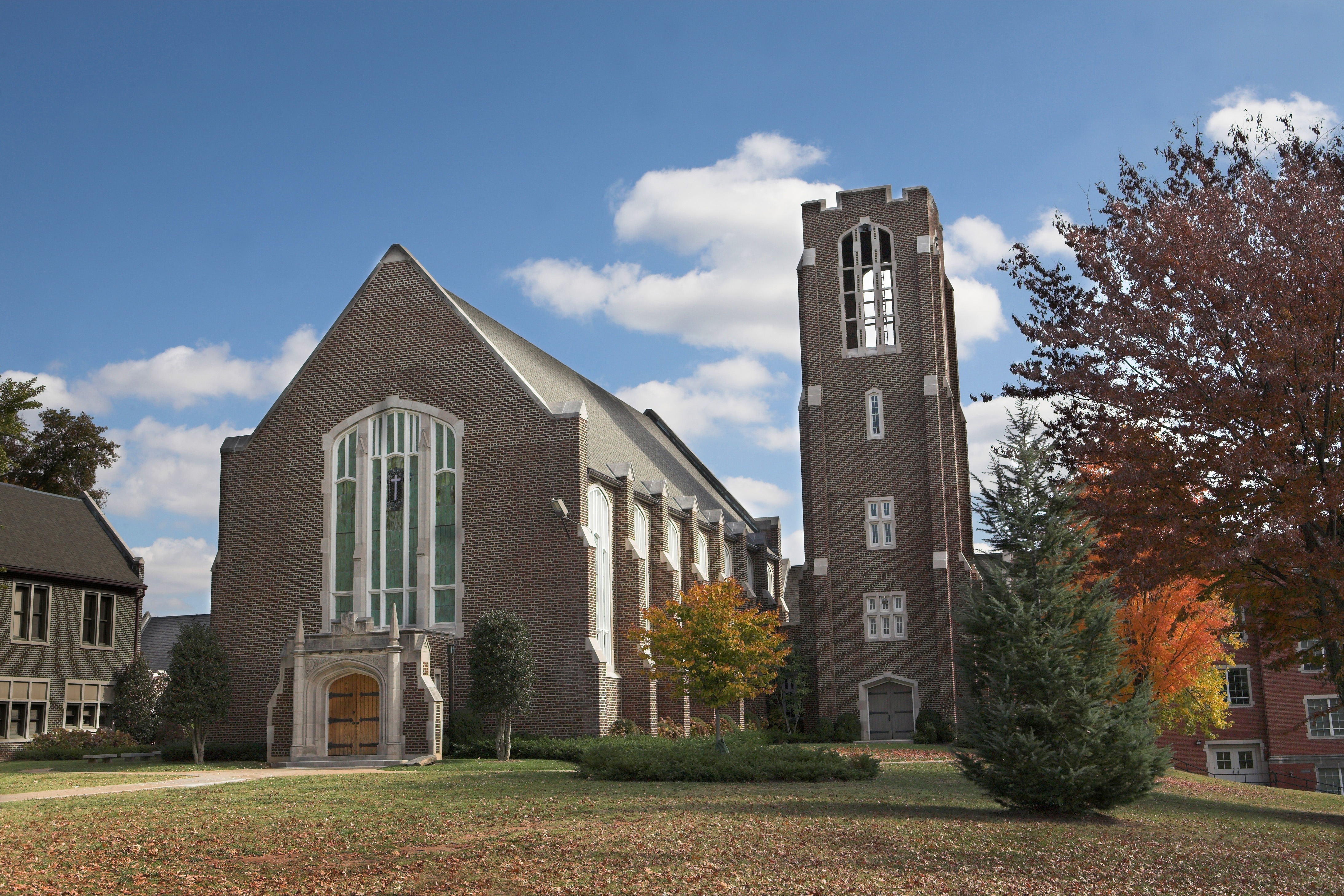
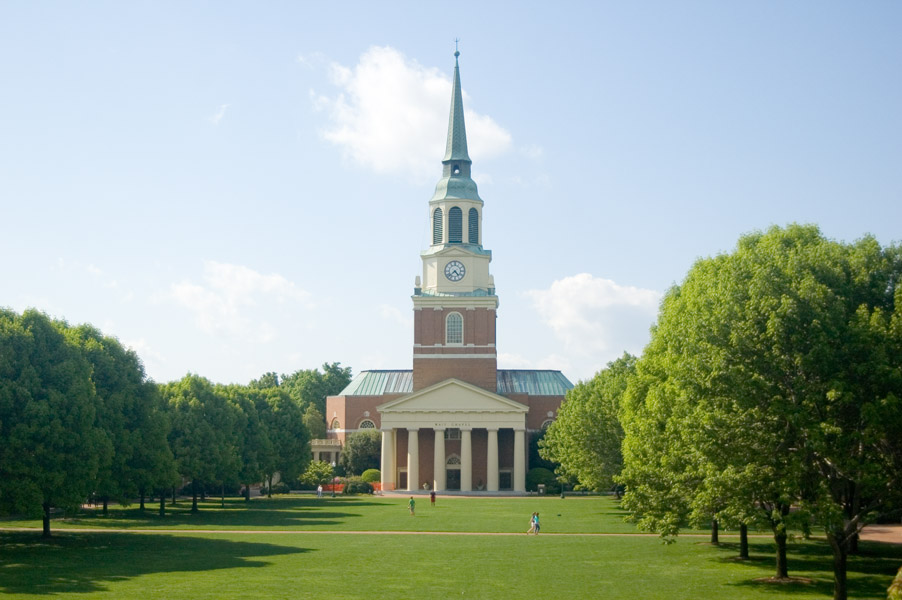
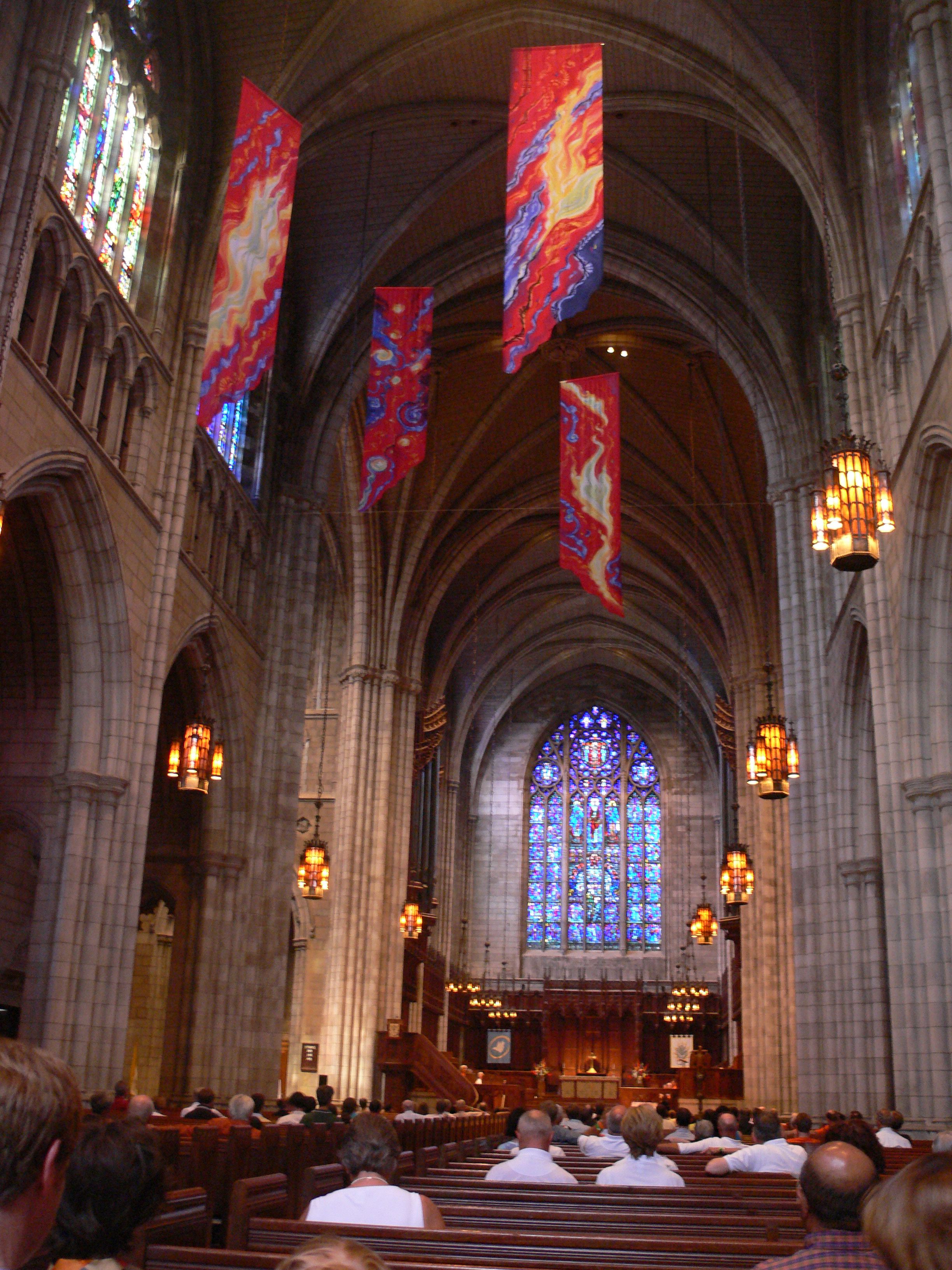
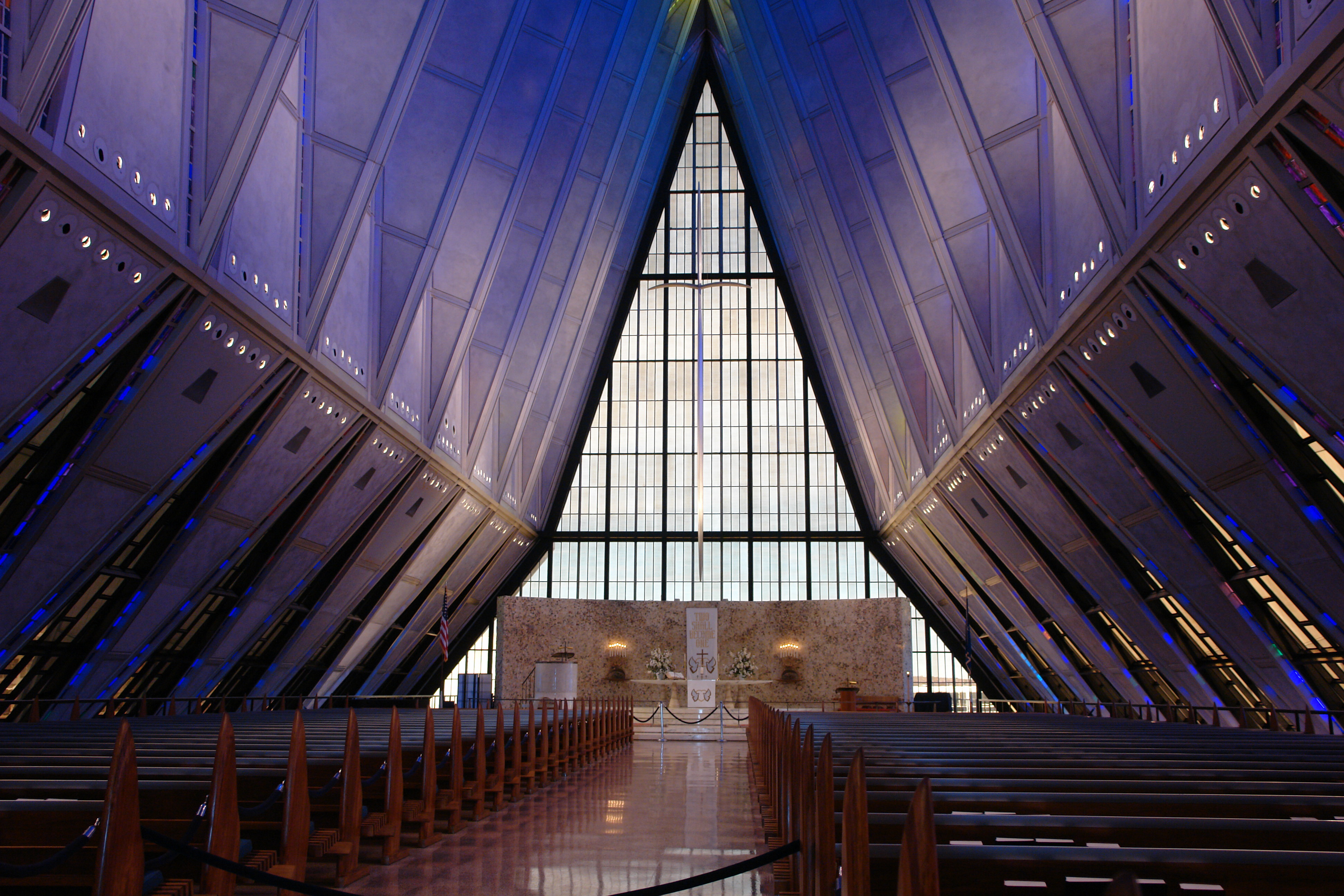
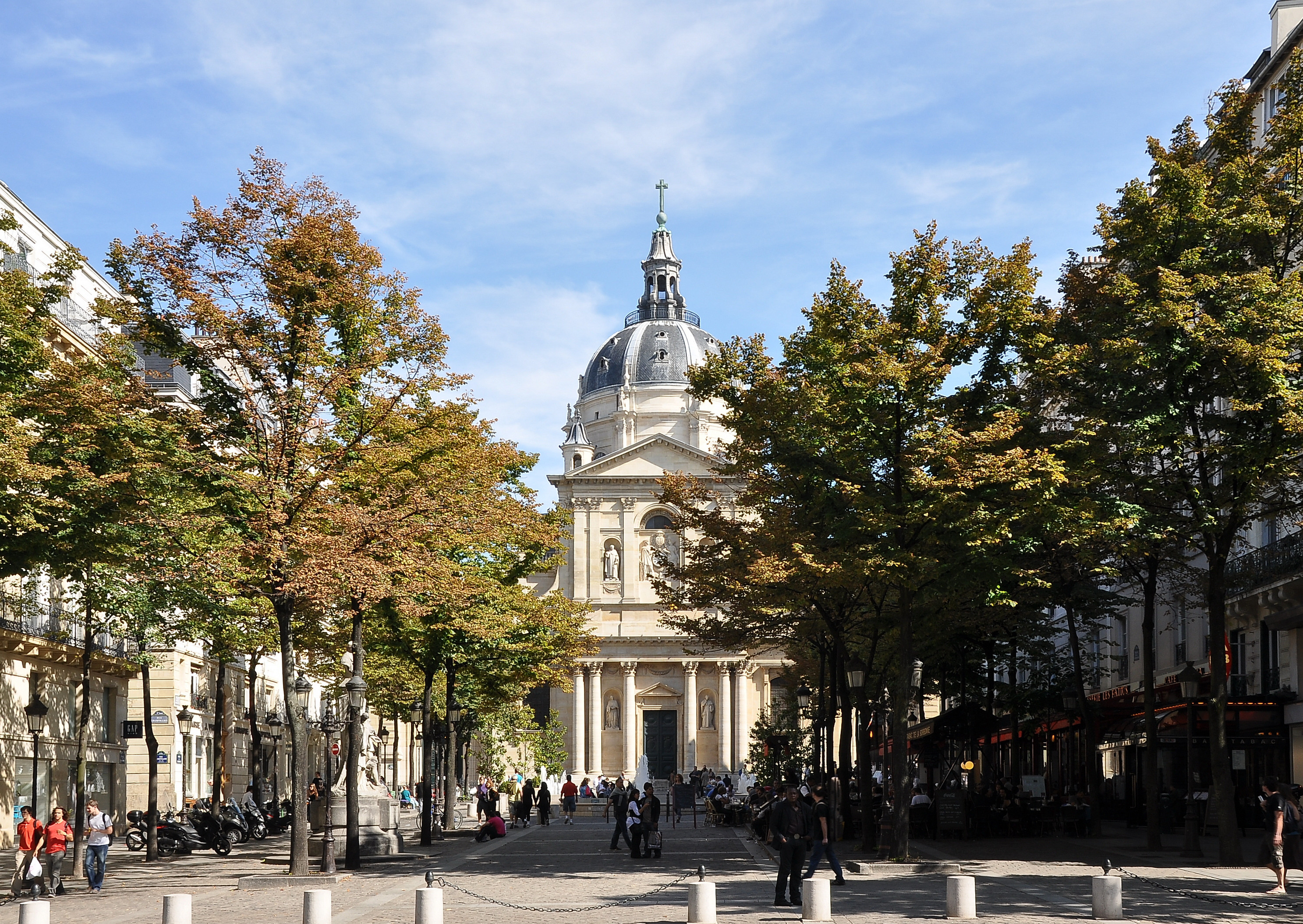
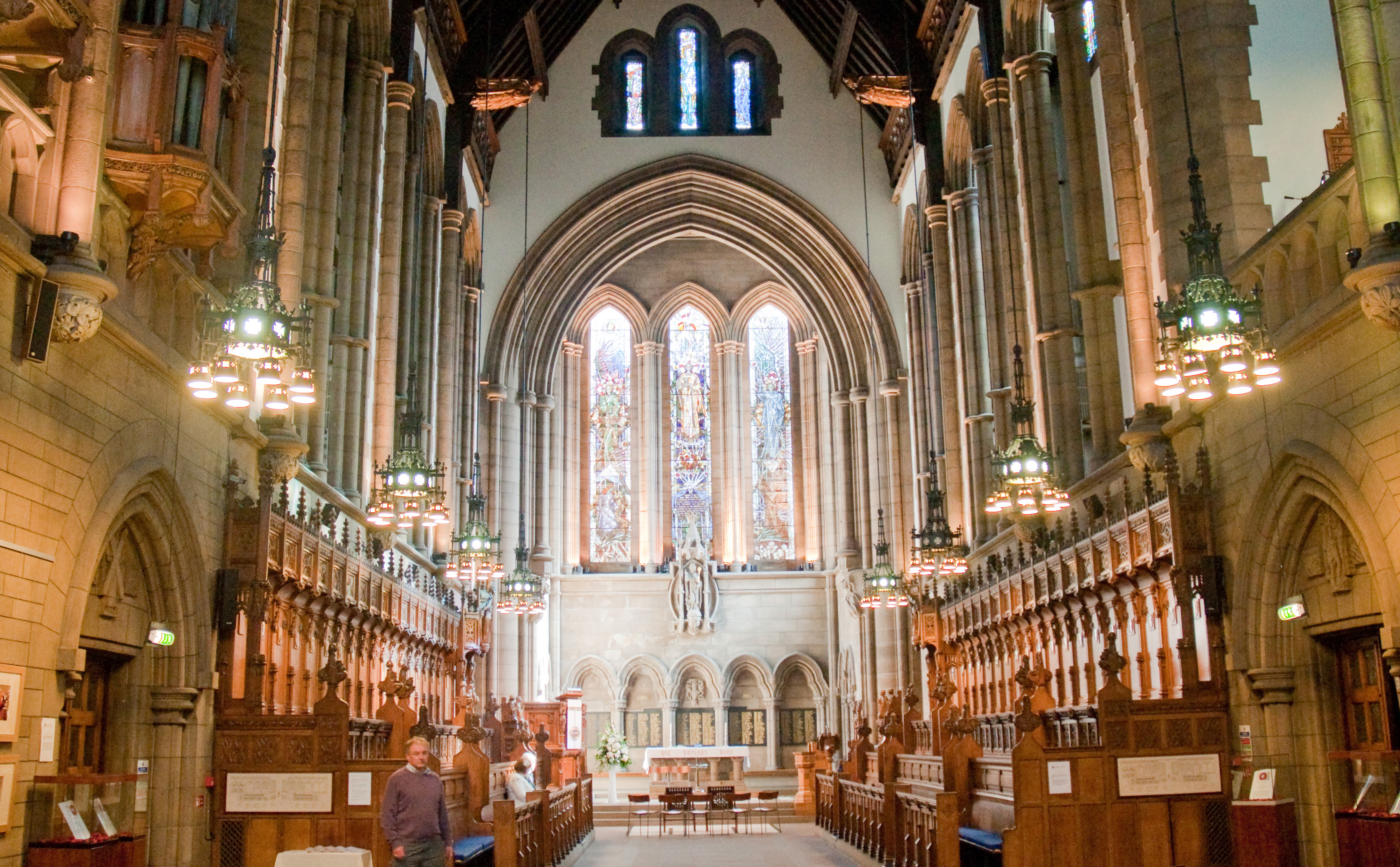
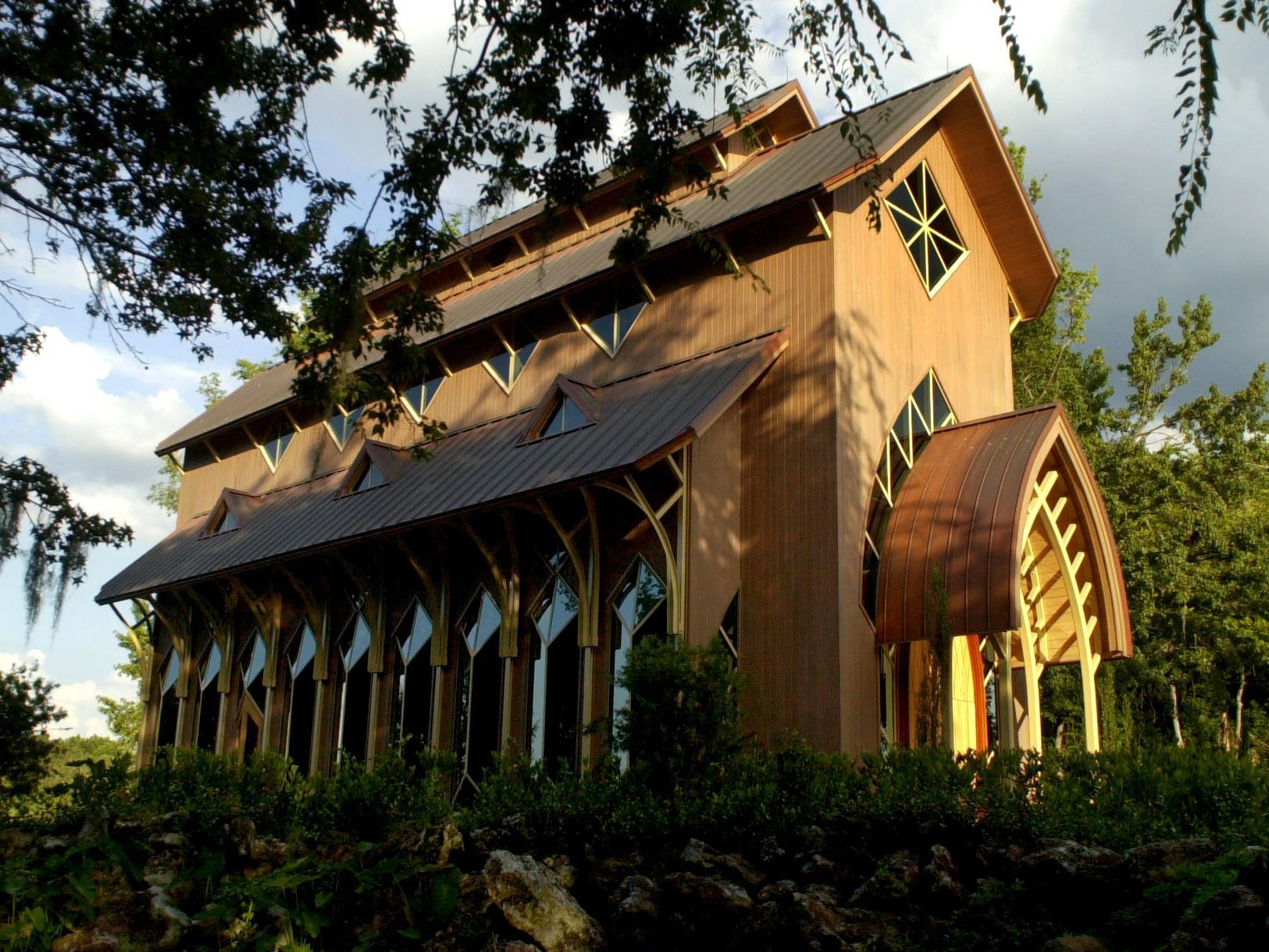
The image criteria of our WordPress theme does not permit many images of college and university chapels to be shown fully-dimensioned on sliders or widget galleries. We reproduce a few of the outsized images here and leave the complexities of financing, designing, building and maintaining of them in a safe and sustainable manner for another day. CLICK HERE for the links to our Sacred Space Standards workspace.
Click on any image for author attribution, photo credit or other information*.
In the sun-dappled chapel, all 155 new families were welcomed to the start of their Denstone journey. #ItStartsHere pic.twitter.com/veefqSVBGG
— Head | Denstone College (@DenstoneHead) September 3, 2023
I believe in Christianity as I believe that the sun has risen:
not only because I see it, but because by it I see everything else.
— C.S. Lewis
The “Dark Ages” produced the most divine vessels of light ever built.
Sainte-Chapelle:pic.twitter.com/B2lPLtWEVx
— Culture Critic (@Culture_Crit) February 12, 2024
Sainte-Chapelle:pic.twitter.com/B2lPLtWEVx
— Culture Critic (@Culture_Crit) February 12, 2024

Loyola Marymount University / Los Angeles, California

Luther College at the University of Regina / Saskatchewan, Canada
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Christ’s Chapel | Hillsdale College, Michigan![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
St. Ignatius Church | University of San Francisco![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
More coming.
*404 ERRORS and Page Not Found messages are common as webmasters move content.
More
CLICK HERE for bibliography
Collier County Florida
Interactive Campus Map | The Institute for Sacred Architecture: Everglade Oratory
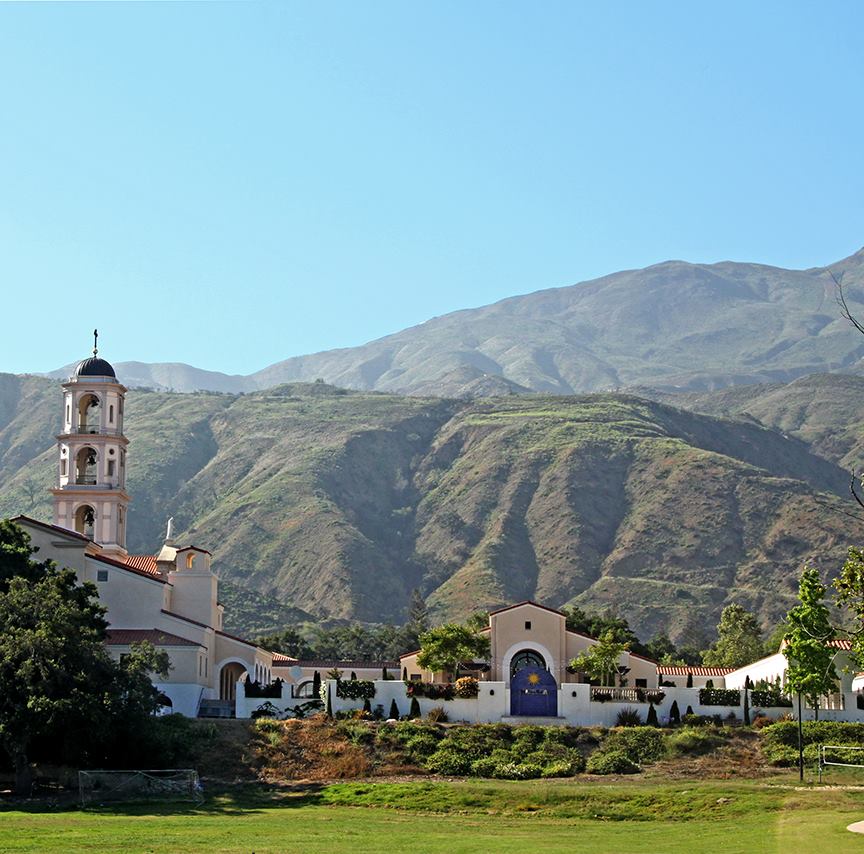
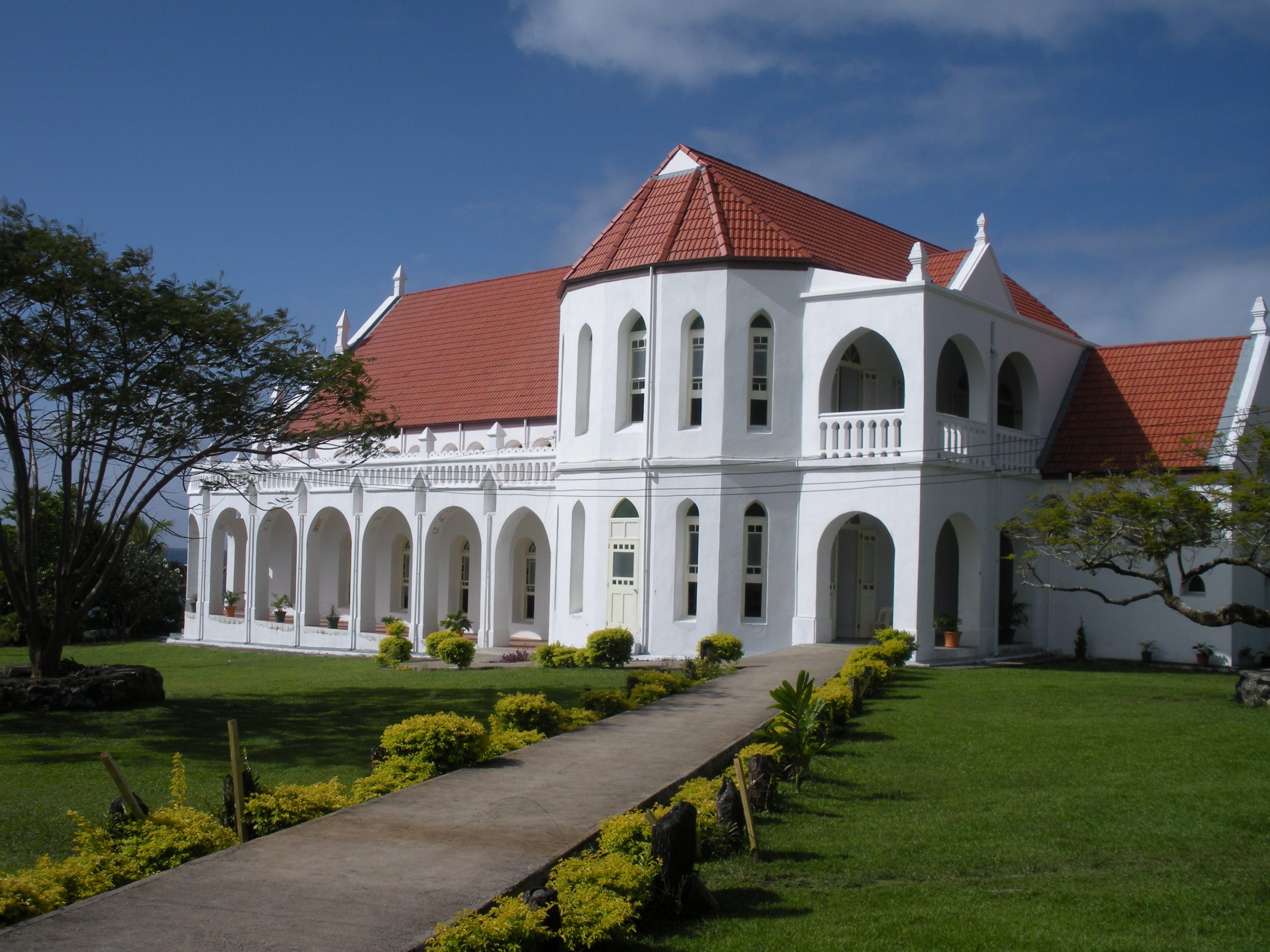
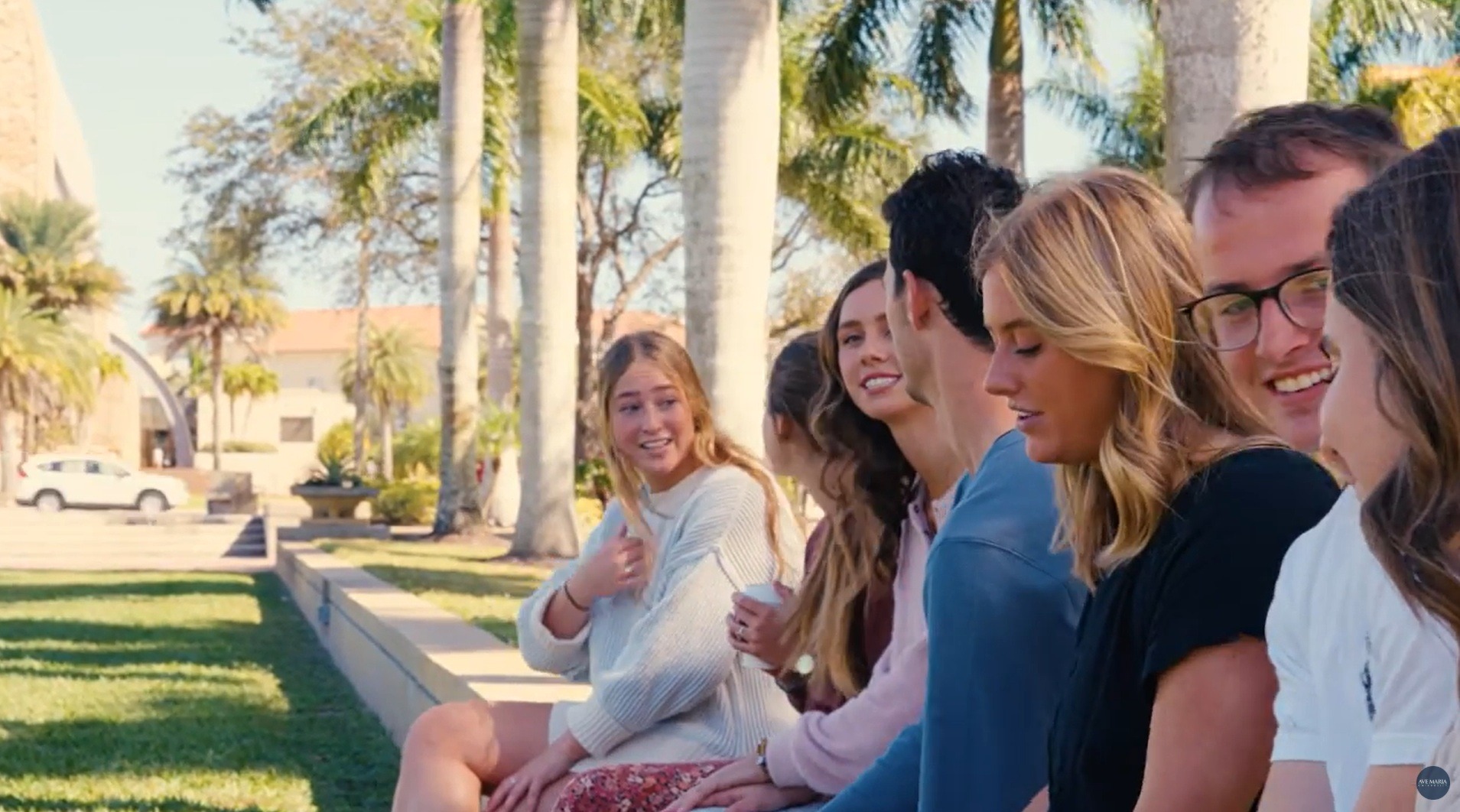
Ave Maria University was founded by Tom Monaghan, the founder of Michigan-based Domino’s Pizza, whose Catholic faith—rooted in his orphanage upbringing under nurturing nuns—drove a vision to renew faithful Catholic higher education amid secular trends and doctrinal challenges in existing institutions.
After selling Domino’s in 1998, Monaghan founded Ave Maria Institute (later College) in Ypsilanti, Michigan, that year, committing hundreds of millions to create an authentically Catholic liberal arts university loyal to the Church’s magisterium.Development accelerated in 2003 with a move to an interim Florida campus, followed by the permanent site in Ave Maria Town (2007), built on donated land from the Barron Collier family and Monaghan’s initial $250 million+ investment.
The university emphasizes faith-integrated academics to form ethical leaders. Under Monaghan’s ongoing stewardship as founder and chancellor, he has guided its growth, emphasizing Catholic identity, leadership formation, and cultural renewal, while transitioning day-to-day operations to presidents while remaining actively involved in its mission.
This is your moment: bring it to the world! Registration is OPEN for Ave Maria University’s Summer Leadership Conference. Join high school juniors and seniors from across the country for a week of formation, community, and unforgettable joy. Rising high school juniors and… pic.twitter.com/IE9PKGmmlu
— Ave Maria University (@avemariauniv) January 8, 2026
Sport News
Charlie Stramel sealed the game for @MSU_Hockey with his third of the game in OT 💥 pic.twitter.com/gwOUobsi10
— Big Ten Hockey (@B1GHockey) January 31, 2026
Danya Spoor – Clemson Track and Field pic.twitter.com/uAK3Hjx1ca
— World Athletes (@world_athelete) January 31, 2026
I’m not even an Indiana fan, but I never get tired of watching this. It’s one of the best things I’ve ever seen in football.
I hope somebody makes a movie out of it with Jerry Goldsmith writing the score.
— Denny Burk (@DennyBurk) January 23, 2026
Rocky Mountain Intercollegiate Skiing Association
RMISA Announces 2026 Alpine Schedule Changes https://t.co/sWwus8EY74
— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) January 11, 2026
Raw emotion from freshman Abbey Hayes following Creighton’s loss to Kentucky in the Elite Eight.
You can tell how badly she wanted this one for her older teammates. 💙@KETV | #GoJays pic.twitter.com/GqSh5qKtHK
— Matt Sottile (@MSottileTV) December 13, 2025
JUST IN: Indiana quarterback Fernando Mendoza honors his mother during his speech after winning the Heisman Trophy.
Mendoza’s mother suffers from Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
“Mom, this is your trophy as much as it is mine. You’ve always been my biggest fan … Your sacrifices,… pic.twitter.com/wYC8qZJHFj
— Collin Rugg (@CollinRugg) December 14, 2025
19.72M FOR AXELINA. 🤯
COLLEGIATE RECORD.
SWEDISH NATIONAL RECORD.
SCHOOL RECORD. pic.twitter.com/wxuCayNG0M— Nebraska Track & Field/Cross Country (@HuskerTFXC) December 12, 2025
Fernando Mendoza’s post game interview after winning the Big Ten
byu/justletmeregisteryou insports
JANE. HEDENGREN. 🤯
✅ SCHOOL RECORD
✅ NCAA RECORD (by 8 seconds btw)
✅ 10TH FASTEST 5000M BY AN AMERICAN
✅ 11TH INDOOR 5000M TIME IN THE WORLD
✅ FIRST COLLEGIATE WOMAN TO RUN SUB 14:50 (indoor AND outdoor)ARE. YOU. KIDDING???!!! pic.twitter.com/pKDqexpUkH
— BYU Track & Field/Cross Country (@BYUTFXC) December 6, 2025
Ending the fall season with a dub 🎯 pic.twitter.com/tmjIff6hIx
— Ole Miss Rifle (@OleMissRifle) November 23, 2025
Best thing about being 12-0… pic.twitter.com/jfGpEnTXVu
— Ohio State Football (@OhioStateFB) December 1, 2025
The highest single-season hit percentage in @b1gvolleyball history. ✍️@aandijackson has capped B1G play with a .559 hit%! pic.twitter.com/9tqusyW28J
— Nebraska Volleyball (@HuskerVB) December 1, 2025
@UNC_BearsVB @BigSkyConf Champions! Go Bears! pic.twitter.com/oNCWBGY2RH
— Andy Feinstein (@PresFeinstein) November 27, 2025
CHASE DOWN❗️ Şilan Ayyildiz finishes 9th individually at the cross country national championship to lead the Ducks to a 3rd place finish. Ayyildiz went from 18th to 9th place over the final K 😮💨 #GoDucks pic.twitter.com/spP7A0UEmo
— oregontf (@OregonTF) November 23, 2025
Dominic Zvada postgame walk off celebration 〽️#GoBlue pic.twitter.com/uTpJWX0l8n
— Michigan Football on UMGoBlue (@UMGoBlog) November 15, 2025
The future of college cross country is no longer about coaching but about recruiting.
Foreigners are recruited to take American scholarships. Many of the runners are older than your typical college age athlete.
Then they are called American Champions. Shame. pic.twitter.com/x8uEahTOX6
— Maggs (@aspen_lindsay) November 23, 2025
History was made at the Yale Bowl.
Yale topped previously undefeated Harvard in the 141st playing of The Game, earning a share of the Ivy League title and the league’s first-ever automatic bid to the NCAA FCS playoffs.
Highlights from @YaleAthletics: https://t.co/yzDxolHzpB pic.twitter.com/EvueCJDcej
— Yale University (@Yale) November 23, 2025
Rachel Forsyth’s season isn’t done yet! She will compete in her second-straight NCAA Championship! 🟢⚪ pic.twitter.com/Vz9sMgFdSH
— MSU Track & Field/Cross Country (@MSU_TFXC) November 15, 2025
Great chemistry between these dancers! Excellent.💃🕺❤️ pic.twitter.com/YNWsVt1PrB
— Love Music (@khnh80044) November 15, 2025
❤️🔥 Jason Colacino and Katie Boyle – Honky Tonk Now THAT’S what I call pure elegance, charm, and undeniable heat!! 🔥💖 pic.twitter.com/AgxGaFELpL
— Love Music (@khnh80044) November 14, 2025
BYU’s Jane Hedengren just beat the defending 5K and 10K national champion by 42 seconds head-to-head at regionals. FORTY-TWO SECONDS! We are witnessing greatness. 🏃♀️ pic.twitter.com/6ELw3anmhL
— BoozeCougs (@BoozeCougs) November 14, 2025
LEm’s absolute banger of a nanny, all in the latest 🙌🙌 pic.twitter.com/W7HH63mEZo
— Fishing Niche (@FishingNiche) November 16, 2025
A moment @sacredheartwsoc will remember for a lifetime 🏆❄️☃️
And those snow angels and penguin slides?? 10/10 way to celebrate punching your second @NCAA Tournament ticket in program history‼️#NCAASoccer x 🎥 @MAACSports pic.twitter.com/KM17KIH2Rv
— NCAA Soccer (@NCAASoccer) November 9, 2025
— MythoAmerica 🌲 (@MythoAmerica) August 31, 2024
It was a great day at Forest Akers East hosting our first Big Ten Cross Country Championship since 2012! pic.twitter.com/hYEyyaeUyD
— MSU Track & Field/Cross Country (@MSU_TFXC) November 1, 2025
The Best Thing You’ll See Today@umichfootball & @Coach_SMoore made dreams come true yesterday for our guy Luke 💙💛@Dream_On_3 pic.twitter.com/drZoFXWFwp
— Blue By 90 (@bluebyninety) November 1, 2025
Another milestone in our College history reached – we’re proud to present our first ever official College golf team! pic.twitter.com/4hCTJVZhPA
— Bishop’s Stortford College (@BSCollege) October 17, 2025
The beats that get us dialed in 🎧🔥 pic.twitter.com/VvHFDurett
— Ole Miss Rifle (@OleMissRifle) October 15, 2025
Led by senior Chad Perrine and junior Luke Skuratowicz, three Hope College men’s cross country runners finished in the Top 30 of the 167-runner field at the Muskegon Community College Jayhawk Invitational on Saturday. Read the meet recap on the Hope Athletics website. #d3xc pic.twitter.com/Dynob8mVrX
— Hope College Athletics (@HopeAthletics) October 11, 2025
Freshmen check. Call your parents, kids! pic.twitter.com/oMTRgFlRmk
— Bobby Guntoro (@bobbygunt) September 27, 2025
Another Top 🔟 on Tour ⭐️
You’ve made the Auburn Family incredibly proud. #WarEagle | #AuburnBeingAuburn pic.twitter.com/fPYfM5FULq
— Auburn Men’s Golf (@AuburnMGolf) September 15, 2025
OQXC Girls @ Troy XC Invitational! #sd113a pic.twitter.com/5VLmByUE3z
— Ms. McCormick (@MsMcCormickOQMS) September 20, 2025
Seeing a game at Oklahoma is awesome (outside of the outcome)
An A+ experience and awesome fans…
Apples to apples it’s light years better than a Texas home game
Great parking, great tailgating, street of bars a block from stadium
Awesome. Would highly recommend pic.twitter.com/i6NB7SvMPW
— James T. Yoder (@JamesYoder) September 7, 2025
Sebastian Moniz connects on this corner kick recently propelling our boys’ soccer team. Great stuff! #BPSoccer ⚽️⚽️🥅⚽️⚽️ @BayPathSuper pic.twitter.com/M3bRFHQXS2
— BPPrincipalVT Co-Moderator @UnlockTheMiddle (@BPPrincipalVT) September 6, 2025
These are the male cheerleaders America wants.pic.twitter.com/lfA5Pn6BpG
— Bill Mitchell (@mitchellvii) August 30, 2025
Ryker Comstock is your Student Athlete of the Week!
🌟 Great news, @CCHS_Gladiators fans! Your amazing support has helped us win the @TMobile #FN5GL $5K Fridays #sweepstakes 🙌 We’re so proud of our @clarkecentral spirit! pic.twitter.com/HJosLUtXtL
— CCHS Athletics (@CCHS_Gladiators) August 31, 2025
WORLD. CHAMPION. 🥇🤩
Luca Urlando grabs the 200 fly world title and becomes the SECOND AMERICAN EVER to go 1:51. Unreal swim. #AQUASingapore2025 pic.twitter.com/LHoq7vZTxQ
— USA Swimming (@USASwimming) July 30, 2025
Michigan Girl, Our Michigan Girl….
Hail the victor 〽️🇨🇦
Savannah Sutherland captures the women’s 400m crown at Canadian Champs in 5️⃣1️⃣.5️⃣1️⃣ seconds.
📸: Sean Burges/Mundo Sports Image pic.twitter.com/62fOGNFQL4
— DyeStat (@DyeStat) August 1, 2025
🚨 NEW WORLD RECORD 🚨
TEAM USA JUST SMASHED THE MIXED 400 FREESTYLE RELAY WORLD RECORD!!!
Jack Alexy – 46.91 👀
Patrick Sammon – 46.70 👀
Kate Douglass – 52.43
Torri Huske – 52.44 pic.twitter.com/5VZcPu50KM— Kyle Sockwell (@kylesockwell) August 2, 2025
WHAT. A WAY. TO CLOSE.
The U.S. grabs gold AND a world record in the last event of #AQUASingapore2025 to end the meet ON TOP of the gold and total medal table 🔥🔥 pic.twitter.com/mdaooxhGY2
— USA Swimming (@USASwimming) August 3, 2025
Northwest High School junior Cooper Lutkenhaus has run the fastest 800-meter race in the world for any athlete younger than 18! Cooper set the new U18 world best at the USA Track & Field Outdoor Championships by running a time of 1:42.27 to earn silver. pic.twitter.com/5imZ9yZHLN
— Northwest ISD (@NorthwestISD) August 3, 2025
🏅History made.
The U.S. men’s four won gold for the first time at the U23 World Championships. Ryan Martin, Wilson Morton, Sam Sullivan, and Lyle Donovan are victorious in the A Final, winning by 2.25 seconds. pic.twitter.com/2fAtSEwewA
— USRowing (@usrowing) July 26, 2025
Kate Douglass just threw down a 52.04 split on the 4×100 free relay 🥶
The U.S. will be top seed tonight after the group’s 3:33.57 in prelims.#AQUASingapore2025 pic.twitter.com/H4Mke7NpZN
— USA Swimming (@USASwimming) July 27, 2025
Over the weekend, Anhelina Khmil earned a second place finish at the CEV Nations Cup Final in Portugal as part of the Ukrainian team! pic.twitter.com/2zuEa9wk9c
— TCU Beach Volleyball (@TCUBeachVB) July 20, 2025
The bottom of the ground was nothing for Emily Beisel! She moves into the Top 4 of her set by almost two tenths of a second to lock in her place at the Cheyenne Frontier Days Semifinals. pic.twitter.com/1uDeztOlZM
— The Cowboy Channel (@Cowboy_Channel) July 20, 2025
He swims like the art of poetry. pic.twitter.com/rrhMP83DQD
— The Figen (@TheFigen_) July 12, 2025
Catherine giving trophies to Amanda, who is the runner-up and Iga the ladies single winner! pic.twitter.com/rZSntPOGig
— Sabirah Lohn 💕🦕🦖 (@SabirahLohn) July 12, 2025
While other kids are learning TikTok dances, she just set a record tying a goat in 7 seconds flat. pic.twitter.com/ZPELIagdxv
— Desiree (@DesireeAmerica4) July 13, 2025
THE TIGERS ARE NATIONAL CHAMPIONS pic.twitter.com/0sk6iV8gRc
— LSU Baseball (@LSUbaseball) June 22, 2025
Savannah Sutherland d capped an incredible career at Michigan with her second NCAA title and has been named the 2024-25 Female Michigan Athlete of the Year! 〽️ #LeadersAndBest
THE TIGERS ARE NATIONAL CHAMPIONS pic.twitter.com/0sk6iV8gRc
— LSU Baseball (@LSUbaseball) June 22, 2025
INFO » https://t.co/Caza1OyrCy | #GoBlue pic.twitter.com/YD6HTdYd0p— Michigan Track & Field / Cross Country (@UMichTrack) June 23, 2025
𝐀𝐔𝐁𝐔𝐑𝐍 𝐁𝐄𝐈𝐍𝐆 𝐀𝐔𝐁𝐔𝐑𝐍
Our list of Fences Riders of the Year is getting long…
✔️ 2025: Avery Glynn (SEC & NCEA ROTY); Kate Hagerty (SEC Freshman ROTY)
✔️ 7-straight SEC ROTY awards
✔️ 4 of the last 7 NCEA ROTY honors
✔️ 7 SEC Freshman ROTY awards#WarEagle pic.twitter.com/1bRaWk4ytY— Auburn Equestrian (@AuburnEQ) June 23, 2025
When you realize you’re the national champion AND you set the collegiate record 🥹 pic.twitter.com/BPUEuZmZMP
— Michigan Track & Field / Cross Country (@UMichTrack) June 15, 2025
Last practice before Eugene. #NCAATF x 🎥 @BYUTFXC
pic.twitter.com/3kNxStxS9Z— NCAA Track & Field (@NCAATrackField) June 6, 2025
Feelin’ Super 🦸♂️
🖥️ https://t.co/vUbrNtVRPX
🎟️ https://t.co/i73Q25MuVk
📲 https://t.co/D9Ga3efNbI#RoadToOmaha pic.twitter.com/1dpxaU8SEG— NCAA Baseball (@NCAABaseball) June 3, 2025
Kate Douglass and Shaine Casas are your #ToyotaNationals high point winners! 🙌 pic.twitter.com/bA9JJSWxEP
— USA Swimming (@USASwimming) June 8, 2025
💨💨💨
Savannah Sutherland sets the Hodges Stadium facility record and for the second straight year she sets the NCAA East First Round record in the 400H! pic.twitter.com/u48jsKv3Zm
— Michigan Track & Field / Cross Country (@UMichTrack) June 1, 2025
Meanwhile at the airport.. 😂 pic.twitter.com/BKRrslNY7x
— Buitengebieden (@buitengebieden) May 29, 2025
Kävin varastamassa rikkailta rahat ja nyt jakelen ne köyhille. Kenelle laitetaan ja paljonko? pic.twitter.com/AFUva64UPN
— Päivi Ekdahl 🇫🇮🇺🇦 (@EkdahlPaivi) May 31, 2025
Our medalist boats!!! 🥉🥉🥉🥉 #RowBlue pic.twitter.com/5qcjoirtmj
— Michigan Rowing (@umichrowing) May 18, 2025
Michigan just won the men’s gymnastics National Championship. pic.twitter.com/FYCWB4a9eK
— Scott Bell (@sbell021) April 20, 2025
Iconic.
Michigan ties its uneven bars record with a 49.725 in the first rotation of the evening.#GoBlue pic.twitter.com/6V5UKAkRDj
— Michigan Women’s Gymnastics (@UMichWGym) March 18, 2023
This Sunday, watch live on the BBC on in-person in our free Fan Parks.
Raw, unscripted live sport. This is The Boat Race. pic.twitter.com/foS7NqdOYL
— The Boat Race (@theboatrace) April 6, 2025
Ivan Puskovitch is a NATIONAL CHAMPION 🏆
He captures a start-to-finish victory in the #OWNats 5K! pic.twitter.com/LS3wRPGeqw
— USA Swimming (@USASwimming) April 6, 2025
— Navy Athletics (@NavyAthletics) March 29, 2025
Oh the beauty of @MorayGC & the @ScotStuSport Golf Championships. The perfect fit! pic.twitter.com/RQ7fX3Wsvx
— College Links Golf (@CLG_Scotland) March 29, 2025
The men got next 👊👊
Tune in to ESPN+ from March 26-29 to catch the men’s @NCAA Division I Swimming & Diving Championships. pic.twitter.com/JytMBGFJHS
— USA Swimming (@USASwimming) March 26, 2025
Our special guest for puck drop, @taylorheise9 🏒#WFrozenFour pic.twitter.com/re7L1gpRGU
— NCAA Ice Hockey (@NCAAIceHockey) March 23, 2025
The Broncos take the Last Call in Saint Paul and #FrozenFaceoff title in double OT! 🙌#NCHChockey // #BroncosReign pic.twitter.com/Nki7IvKLPr
— The NCHC (@TheNCHC) March 23, 2025
Sliding into the weekend like…🛷❄️ pic.twitter.com/GoSpxcuAcj
— AccuWeather (@accuweather) March 21, 2025
Your Duke family is proud of you guys! Dom and Gavin both fared well in the state tournament!! Dom went 2-2, and Gavin went 7-1! Gavin finished 3rd overall in his weight class!! Congratulations to both boys!! @WEVSD_sports @whsladydukes @AndyPeltz pic.twitter.com/5yEMNYkU7Q
— Robert Figuly (@RobertFiguly) March 23, 2025
Another @MSU_Hockey BIG10 Championship! What an exciting night at Munn Arena for our Spartan players, coaches, students and fans. Go Green!! pic.twitter.com/u9ZWUTeBVc
— Kevin Guskiewicz (@KevinGuskiewicz) March 23, 2025
Molly Miller making sure plenty of Lopes are involved when she cuts down the nets. @MollyMiller33 @GCU_WBB pic.twitter.com/2BhbuCDe48
— Jordan Hamm (@JordyHamm) March 15, 2025
Damn. Big Ten tournament champion in his first year as head coach. Let the dancing begin! #GoBlue pic.twitter.com/Zd57LBUwJF
— Santa Ono (@SantaJOno) March 16, 2025
Men’s 400m Champion
🥇 Will Floyd (@UGATrack)
📊 45.43#NCAATF x 🎥 ESPN+ pic.twitter.com/lcIb0zTYMX— NCAA Track & Field (@NCAATrackField) March 15, 2025
Every Thursday, coach Brandon runs men’s IM threshold practice and Coach Sarah & I run the women’s IM group. It’s one of those “all hands on deck” type of day. Last night, in the 400 IM the men went 1-2-3-5-10-11 and the women went 2-3-4-5-6-10-17-22. pic.twitter.com/pCfhLWSvoA
— Bobby Guntoro (@bobbygunt) March 1, 2025
TRE HOLLOMAN FOR THE WIN!!!!!
What a shot at the buzzer! Michigan State pulls off the win at Maryland, 58-55. #Spartans have won four games in a row, including three straight against ranked opponents.pic.twitter.com/1NMM6xdH46
— Hobie Artigue (@HeyItsMeHobie) February 27, 2025
Amanda Moll just broke the @NCAATrackField Pole Vault record with a height of 16-1.25 (4.91-meters)🤯#B1GTF x @UWTrack pic.twitter.com/5OUCmOS2QW
— Big Ten Network (@BigTenNetwork) March 1, 2025
Recapping Day ✌ of #MWITF https://t.co/7jbGnmF65r
— Air Force Track & Field/XC (@AF_TFXC) March 1, 2025
EASTON TALT 😱#NCAABaseball x 📹 FloBaseball / @BeaverBaseball pic.twitter.com/RUsWYVFOxi
— NCAA Baseball (@NCAABaseball) March 1, 2025
Great day in the weight room at Weatherford High School! We have football, basketball, girls and boys track programs working hard. We are blessed with the best facilities in the state! pic.twitter.com/gvH85GZmoM
— Rick Weaver (@rickweaver98) February 21, 2025
Peak German engineering pic.twitter.com/BxyzCVFSdU
— miss white (@cinecitta2030) February 22, 2025
The Revere Varsity Competition Squad traveled to Big Walnut High School today to compete in the OASSA State of Ohio Cheerleading Championships! They finished in fourth place, D3 Non Build Division!!! We are so proud of you ladies! @RevereLocal pic.twitter.com/evF06thfAD
— Doug Faris (@DougFaris) February 23, 2025
Wow! What an amazing couple of weeks for ‘OE’ Justin Davies. He broke the Welsh indoor 800m record at the Keely Klassic and then went on to become the British champion at the UK Indoor Championships! #uptherose 🌟🏅 pic.twitter.com/fgFq5AOX09
— Sport & PE | King Edward’s School (@KESBathSport) February 24, 2025
My girl shot her first ever perfect 5 bullseyes at her county tournament today
Great job girl! pic.twitter.com/Xhyl1bEK0R— kelli chalfant (@cf_farms7) February 22, 2025
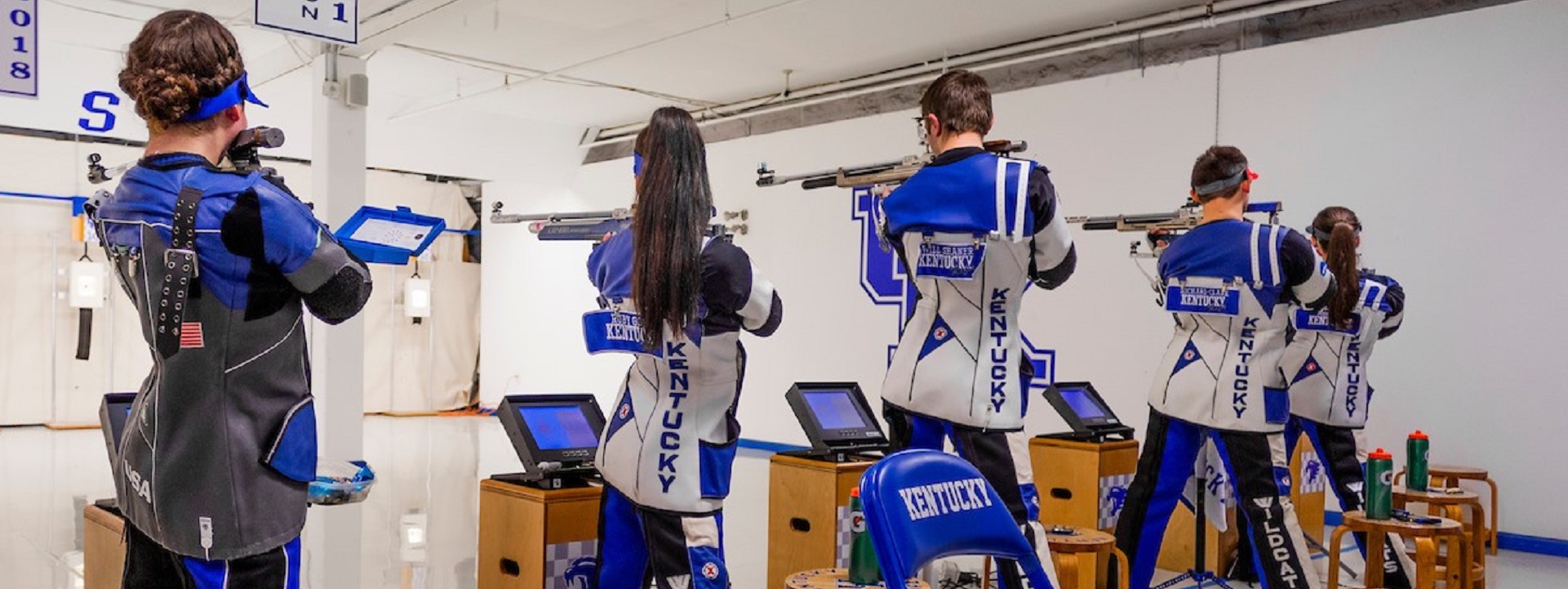
NCAA Rifle 🤝 Historic Memorial Coliseum
Rifle National Championships
📅 March 14-15
🏟️ Historic Memorial Coliseum
🎟️ https://t.co/MgMeX9j7ER #T37 #WeAreUK pic.twitter.com/mDooaFpvfu— UK Rifle (@UKRifle) February 14, 2025
A new ASTM standard addresses safety elements of #PoleVaulting areas. It establishes safety, performance, and maintenance recommendations for indoor/outdoor, and private-use pole vault facilities. https://t.co/pq1pCCQZRE pic.twitter.com/oz08sWDt4l
— ASTM International (@ASTMIntl) February 13, 2025
“With this executive order, THE WAR ON WOMEN’S SPORTS IS OVER.” –President Donald J. Trump 🇺🇸 pic.twitter.com/g97jV4eEPW
— The White House (@WhiteHouse) February 6, 2025
“We’re putting every school receiving taxpayer dollars on notice that if you let men take over women’s sports teams or invade your locker rooms, you will be investigated for violations of Title IX and risk your federal funding.” –President Donald J. Trump 🇺🇸 pic.twitter.com/MUd6FAetWr
— President Donald J. Trump (@POTUS) February 6, 2025
Draw two is in the books at the #OUA Men’s Curling Championship! 🥌
The @queensgaels got the better of the @LUVoyageurs 6-3, scoring 3 in the first end to take an early lead, while the @tmubold scored early and often to beat the @OT_Ridgebacks 10-1.
The @brockbadgers took down… pic.twitter.com/mc6CndjeZ9
— Ontario University Athletics (@OUAsport) February 7, 2025
👟 Our Gryphon Track and Field team heads to the state of the New York for today’s meet in the Cornell Upstate Challenge!
📅 Sat. Jan 17
📍 @CornellSports (Ithaca, NY)#GryphonPride pic.twitter.com/ahH5AuzEZE— Guelph Gryphons (@guelph_gryphons) January 18, 2025
Sunrise swim with @uncwswimdive on Saturday morning! pic.twitter.com/q7PExy1pWe
— Bobby Guntoro (@bobbygunt) January 11, 2025
Remember when it was so cold the rivers and lakes iced over? Our college wild swimmers certainly do – they took the plunge (without wetsuit insulation) and lived to report back! 🥶 pic.twitter.com/CKyLK0ySMu
— Trinity College (@TrinityOxford) January 17, 2025
“We’re feeling confident in our performance so far. We’re being challenged, but so far have managed to stay sharp.” – Catherine Clifford, third
This quote sums up the Canadian women’s performance thus far at the World University Games, as they remain undefeated after two wins on… pic.twitter.com/jetQK1TtbH
— Curling Canada (@CurlingCanada) January 18, 2025
A B1G @HuskerWBB WIN ‼️#B1GWBBall on @BigTenNetwork 📺 pic.twitter.com/1sjIY2H4Ri
— Big Ten Women’s Basketball (@B1Gwbball) January 17, 2025
Track and Field Collects Seven Wins at SVSU Classic https://t.co/UpoAphESGe
— svsuathletics (@svsuathletics) January 18, 2025
“Rowing is more poetry than sport.” — George Pocock (‘Boys in the Boat’ 2024), a British-born boat builder, rowing coach, and influential figure in American rowing, best known for his craftsmanship of racing shells and his philosophical approach to the sport.
“There is no greater glory for a man than that which he wins with his own hands and feet.” (Homer, Iliad c. 8th Century BCE)
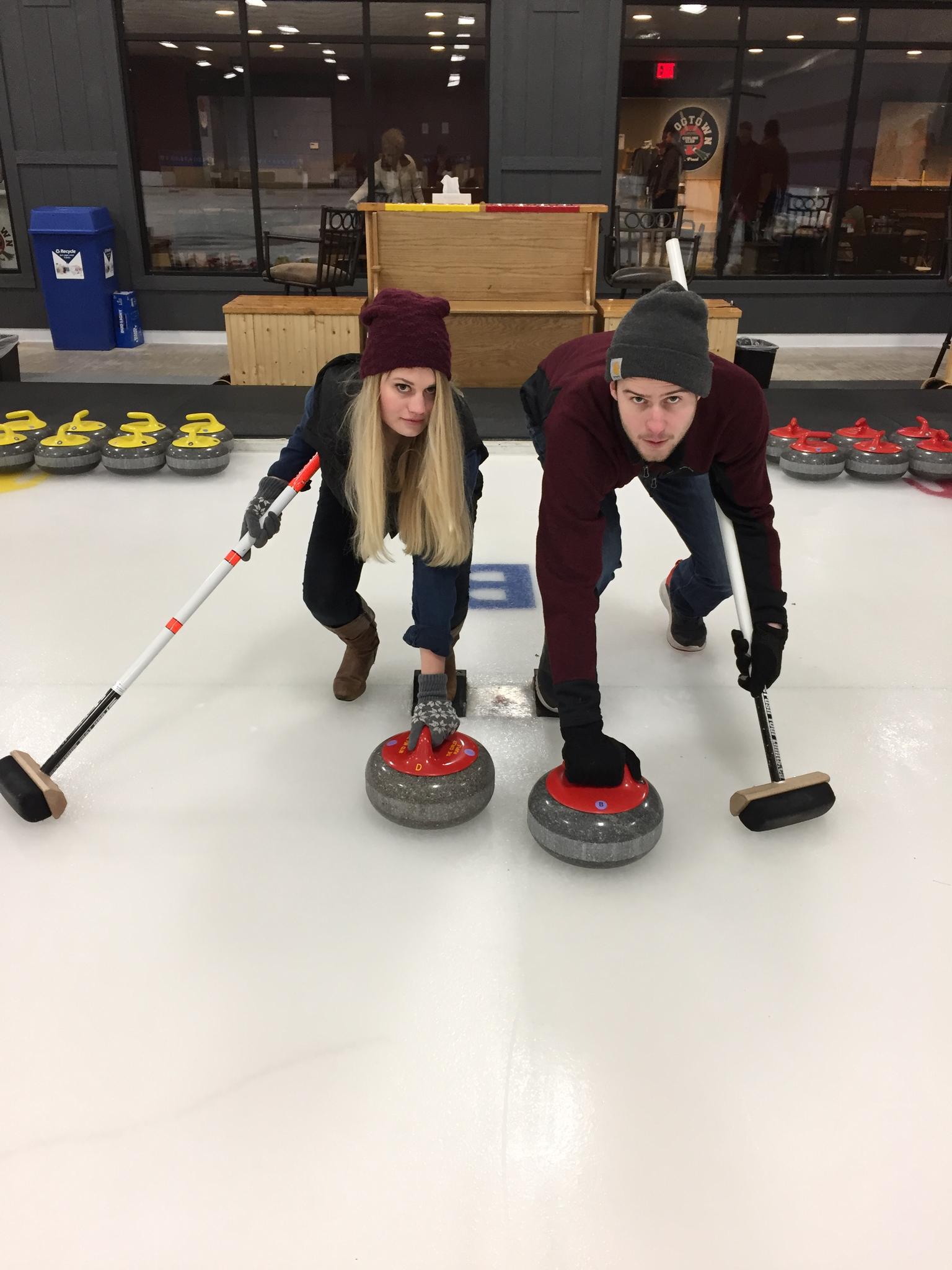
Curlin’
Sport and Wellbeing | Standards Scotland
The term “curling” is thought to derive from the way the stone moves and “curls” as it travels over the ice. The key feature of curling that sets it apart from other ice sports is the deliberate rotation, or “curl,” applied to the stones as players release them. This rotation causes the stone to curve or “curl” on its path down the ice, adding an element of strategy to the game.
The precise origin of the term is not definitively known, but it likely emerged organically as people described the action of the stones on the ice. The word “curling” has been associated with the sport for centuries, and as the game evolved and gained popularity, the term became firmly established.
The concept of curling is integral to the sport’s strategy, as players use the curl to navigate the stones around guards and other stones strategically placed on the ice. The unique way in which the stones move and interact with the playing surface is one of the defining characteristics of curling, and the name captures this distinctive feature
World Curling Mixed Championship 2024
Scientific American: Why Do Curling Stones Curl?
A curling facility typically consists of several key components to support the sport and provide a suitable environment for players and spectators:
- Flooding equipment, refrigeration for 3 degrees C, fine mist sprayers, ice planer, infrared thermometers.
- The playing surface is called a “sheet,” and it is a rectangular area of ice where the game is played. Each sheet is divided into several sections called “curling houses,” which are the target circles.
- Curling stones are made of granite and weigh around 38 to 44 pounds. Each team has eight stones, and players take turns sliding them down the ice towards the target area, known as the House.
- The house is the target area with concentric circles marked on the ice. The center of the house is the “button,” and the circles are used for scoring points.
- The hacks are footholds on either end of the sheet where players push off to slide the stones. The player in control of the stone uses the hack as a starting point for their delivery.
- Brooms, also known as brushes, are used by players to sweep the ice in front of the sliding stone. Sweeping can affect the stone’s trajectory and speed.
- A scoreboard is essential for keeping track of the score in a curling game. It typically displays the current score, the end in progress, and other relevant information.
- Players use locker rooms for changing into their curling attire and storing their personal belongings.
- A designated area where players can warm up before a game. It may include stretching space and possibly a small practice sheet.
- A facility usually has a clubhouse or main building that includes amenities such as viewing areas, meeting rooms, a bar, and possibly a restaurant. In the case of the Windsor Curling Club: Scotch Whiskey
- Equipment like ice resurfacers or Zambonis are used to maintain the quality of the ice surface between games.
The origin of curling is sketchy but this much is agreed upon: Curling is thought to have originated in Scotland, and its roots can be traced back to medieval times. The first written record of curling dates back to 1541 in the records of the Scottish city of Paisley, where a challenge was issued for a contest on the ice between two rival churches.
The early form of the game involved players sliding stones across frozen ponds and lochs, attempting to reach a target. Over time, the sport evolved, and rules were established. Early versions of curling stones were likely rudimentary compared to the polished granite stones used today.
Curling gradually gained popularity in Scotland and spread to other parts of the world, especially among Scottish immigrants. The sport found a home in Canada in the 18th century, where it has become particularly popular. The first curling club in North America, the Montreal Curling Club, was established in 1807. The Detroit Curling Club was established in 1840; one of the oldest curling clubs in the United States, owing much to its across the river relationship with Windsor Canada.
Rifle
Thanks for the memories, 2025!
2️⃣0️⃣2️⃣6️⃣🔜#T38 #WeAreUK pic.twitter.com/UfxJJquQKa
— UK Rifle (@UKRifle) December 31, 2025
Ending the fall season with a dub 🎯 pic.twitter.com/tmjIff6hIx
— Ole Miss Rifle (@OleMissRifle) November 23, 2025
Mountaineers set for home opener against Mount Aloysius
📰 https://t.co/sASRu72etD#HailWV pic.twitter.com/FmLUP0ZlxQ
— WVU Rifle (@WVURifle) October 30, 2025
Bringing home some hardware.
The Nanooks claim third at the 2025 NCAA Rifle Championships with an aggregate score of 4726!
SB – 2355
AR – 2371Thank you, #NanookNation pic.twitter.com/WZqqLCFMN8
— Alaska Rifle (@NanooksRifle) March 15, 2025
NCAA Rifle Competition began in 1980 and features both men’s and women’s teams competing together. The competition includes smallbore and air rifle events, with each athlete shooting in both disciplines.
The two primary events are smallbore rifle (also known as .22 caliber) and air rifle (using a .177 caliber air gun). Competitions typically involve both individual and team scoring, with athletes shooting a series of targets from different distances and positions.
Several U.S. colleges and universities have competitive rifle teams that participate in NCAA rifle competitions. Some of the notable institutions include:
- University of Alaska Fairbanks
- West Virginia University
- University of Kentucky
- Texas Christian University (TCU)
- University of Nebraska-Lincoln
- Murray State University
- Ohio State University
- University of Akron
- United States Military Academy (Army)
- University of Memphis
- North Carolina State University
- Jacksonville State University
- Morehead State University
- University of Mississippi (Ole Miss)
- U.S. Naval Academy (Navy)
The NCAA rifle competition serves as a pipeline for athletes aiming to compete in international events, including the Olympics where it was part of the inaugural modern Olympics in 1896. Rifle events scheduled for the 2024 Olympics include:
- 10m Air Rifle (Men and Women): Athletes will shoot from a standing position using a .177 caliber air rifle at a distance of 10 meters.
- 50m Rifle Three Positions (Men and Women): Competitors will shoot from kneeling, prone, and standing positions using a .22 caliber smallbore rifle at a distance of 50 meters.
- Mixed Team 10m Air Rifle: Teams composed of one male and one female shooter will compete together in the 10m air rifle event.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670