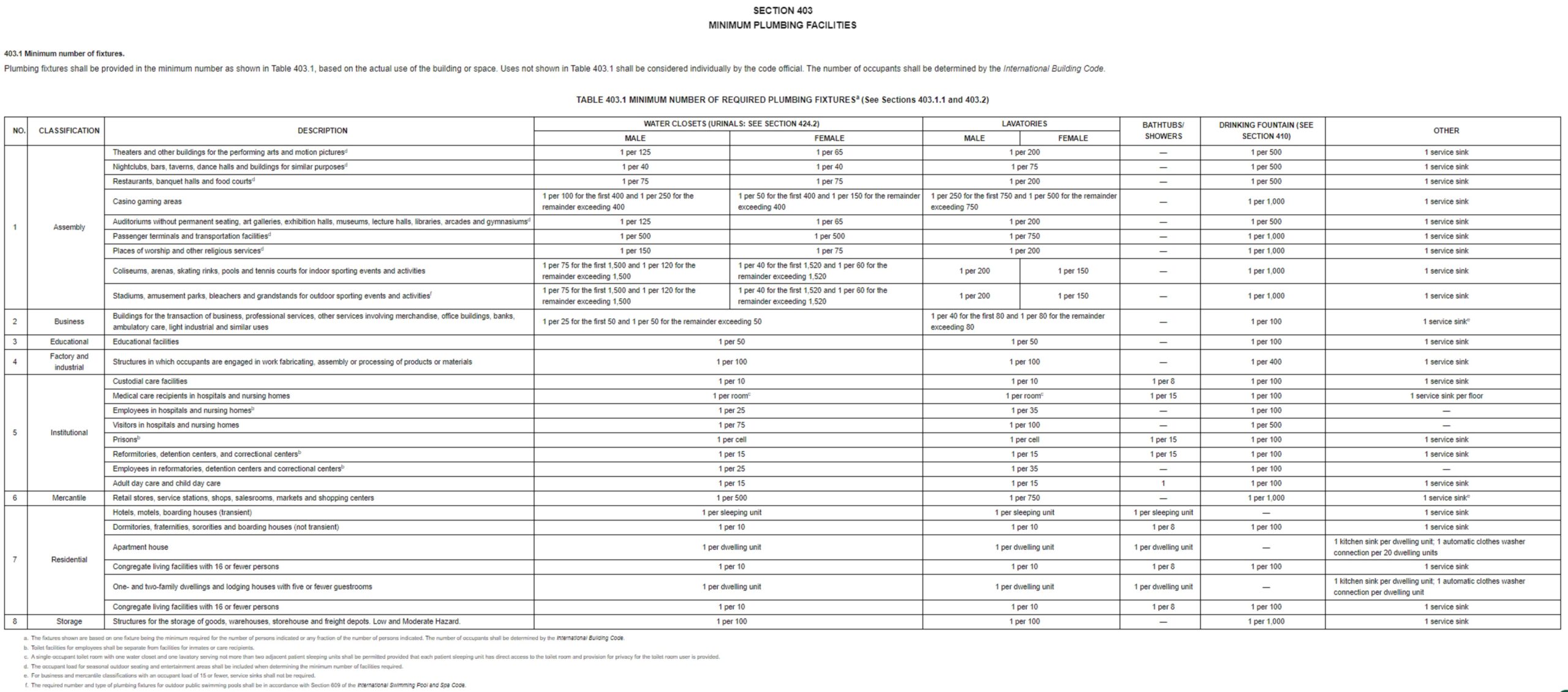
GROUP A MODEL BUILDING CODES: Comments on Committee Actions will be received until July 8th
International Building Code Chapter 4, Section 406.2.7

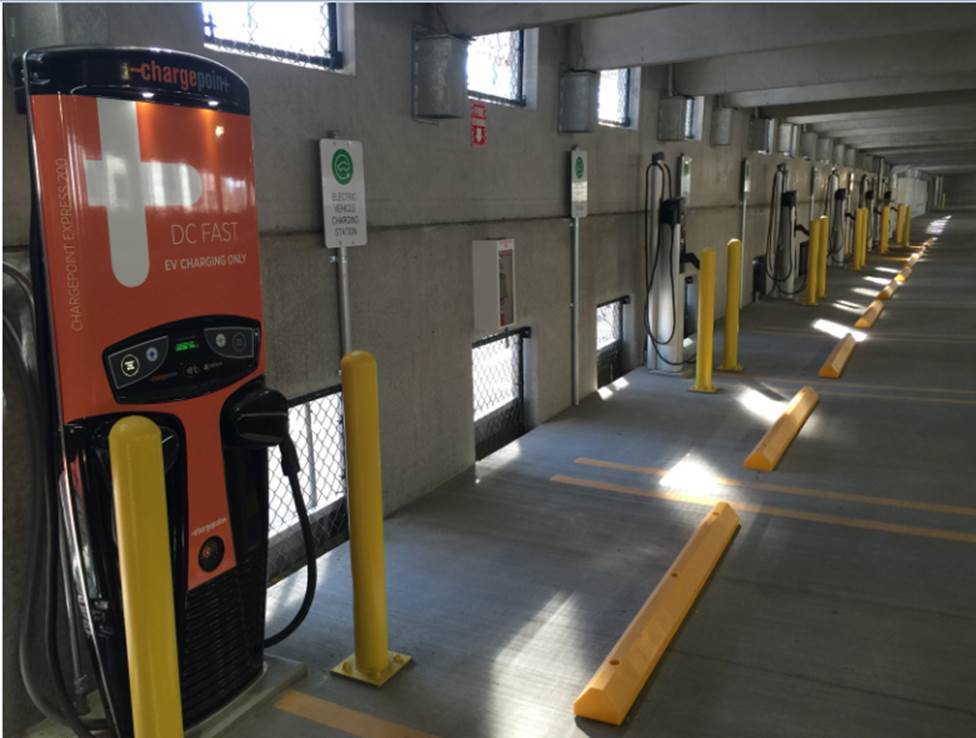
Edison electric vehicle | National Park Service, US Department of the Interior
Free public access to the 2021 edition of the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) is linked below:
2021 International Energy Conservation Code
Electric vehicle charging stations are addressed in the 2024 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) within two specific appendices:
Appendix RE: This appendix provides detailed requirements for electric vehicle charging infrastructure, focusing on both residential and commercial buildings. It includes definitions and infrastructure standards to ensure that new constructions are equipped to support electric vehicle charging
Appendix CG: This appendix offers guidance on electric vehicle power transfer and charging infrastructure, emphasizing the integration of EV-ready requirements into building designs. It outlines the necessary provisions for installing and managing EV charging stations, ensuring compliance with energy conservation standards
.These appendices are part of the broader efforts to incorporate EV infrastructure into building codes, promoting energy efficiency and supporting the transition to electric vehicles.
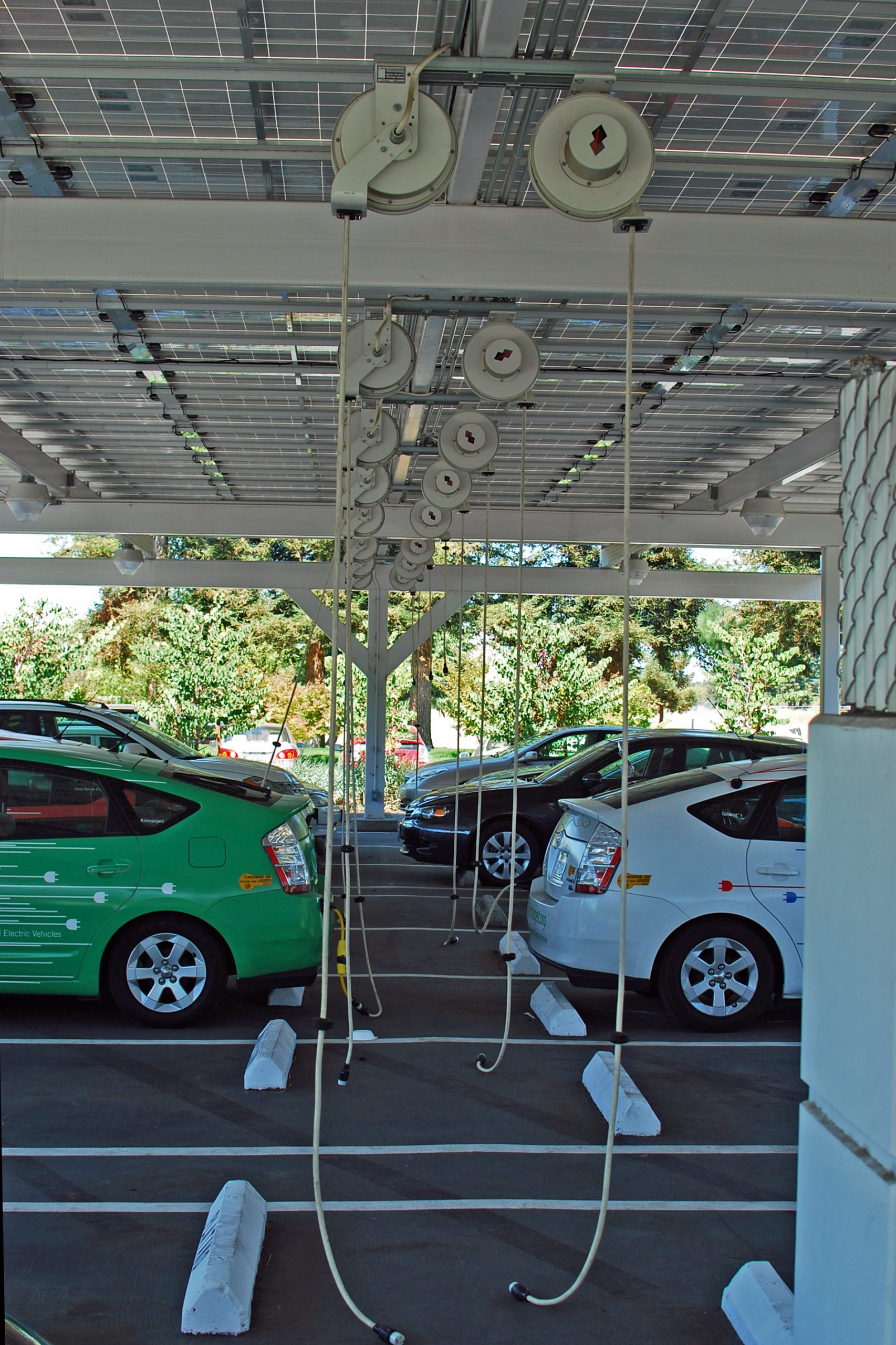

Recharging infrastructure at at Google’s Mountain View (California) campus | Pretty ugly, eh?

“Gas” 1940 Edward Hopper
This standard will be updated within a reconfigured code development cycle linked below:
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
Keep in mind that many electric vehicle safety and sustainability concepts will track in other titles in the ICC catalog. It is enlightening to see other energy related proposals tracking in the most recent Group A code revision cycle
The following proposals discussed during the Group A Hearings ended earlier this month are noteworthy:
IBC § 202 (NEW) | G66-21 | Electrical mobility definitions
IBC § 1107.2, et al | E124-21 & E125-21 & E126-21 | Electrical vehicle charging stations for R-2 occupancies.
From the Group B revision cycle — COMPLETE MONOGRAPH:
R309.6 Electric vehicle charging stations and systems. Where provided, electric vehicle charging systems shall be installed in accordance with NFPA 70. Electric vehicle charging system equipment shall be listed and labeled in accordance with UL 2202. Electric vehicle supply equipment shall be listed and labeled in accordance with UL 2594.
IBC 406.2.7 Electric vehicle charging stations and systems. Where provided, electric vehicle charging systems shall be installed in accordance with NFPA 70. Electric vehicle charging system equipment shall be listed and labeled in accordance with UL 2202. Electric vehicle supply equipment shall be listed and labeled in accordance with UL 2594. Accessibility to electric vehicle charging stations shall be provided in accordance with Section 1108.
TABLE R328.5 MAXIMUM AGGREGATE RATINGS OF ESS (Energy Storage Systems) – PDF Page 1476
Incumbents are socking in EV concepts all across the ICC catalog. We refer them to experts in the Industrial Applications Society IEEE E&H Committee.


One of the more spirited debates in recent revision cycles is the following:
Who shall pay for electrical vehicle charging infrastructure?
The underlying assumption is that the electrification of the global transportation grid has a net benefit. We remain mute on that question; the question of net gain.
Of course, many proposals pointed the finger at the stakeholder with the deepest pockets. Accordingly, new commercial building owners will be required to install charging stations for new buildings. During 2018 and 2019 we tracked the action in the workspace below so that we could collaborate with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee:
2021 Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
Given that most higher education facilities are classified as commercial, the cost of charging stations will be conveyed into the new building construction budget unless the unit takes an exception. Generally speaking, most colleges and universities like to display their electric vehicle credentials, even if the use of such charging stations remains sparse.

Cornell University

Issue: [11-40]
Category: Electrical, #SmartCampus
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey
* The education industry has significant square footage this is classified as residential; particularly on the periphery of large research campuses.
LEARN MORE:
ICC 2021/2022 Code Development Cycle
The Top 5 Energy Efficiency Proposals for the 2021 IECC
Archive / IECC Electric Vehicle Charging