2026 NEC CMP-18 Public Input Report
Modular furniture systems with integral power and telecommunication fittings require attention to power and digital pathways. “Modular systems furniture” is a generic term for bundles of panels, worksurfaces, shelves, and other items sold by a single manufacturer as a package for furnishing offices. The modular furniture system environment is characterized by close proximity to electrical energy. Where there is electrical energy there are concerns for shock and fire safety.
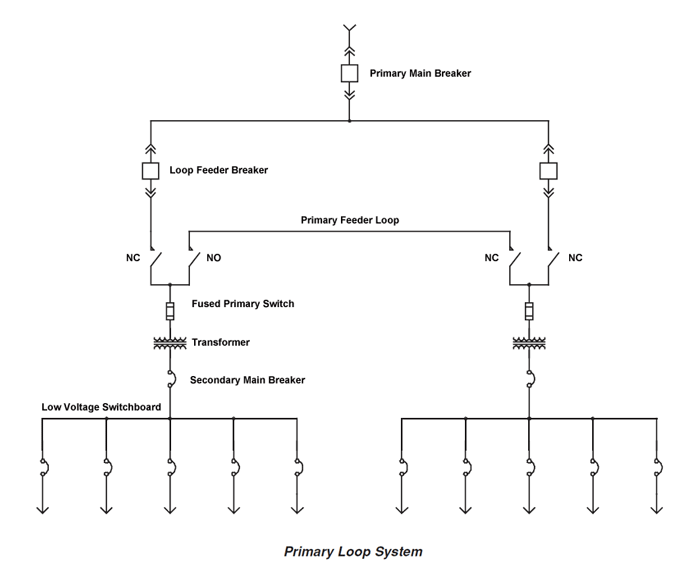
Fire safety considerations appear in NFPA 70 National Electrical Code (NEC)– generally in Articles 210 (Branch Circuits), Article 220 (Branch Circuit, Feeder and Service Load Calculations) — and with more specific safety considerations appearing in Articles 604 (Manufactured Wiring Systems) and Article 605 (Office Furnishings). The current edition of the National Electrical Code is linked below:
Public Access 2023 National Electrical Code
Over the past 30-odd years modular furniture manufacturers have worked out a lot of the bugs in products; making it easier for furniture contractors to deliver a safer and more effective installation. What remains are site-specific conditions — such as lighting load, current draw of space heaters and personal air conditioners through the furniture power pathway — that must be reckoned with. A sample of other considerations:
- Harmonic heating of the furniture pathway caused by non-linear, harmonic load
- The risk of double-phasing when circuit breakers are joined with handle ties back at the panelboard and share a neutral
- Any lighting equipment used with the partitions must have of properly sized cord no more than 9 ft long
- Modularity in power tap cords (“whips’) between furniture raceways and the first gathering point
There are other safety and sustainability issues related to USB outlets, and data/voice outlets[2] that we will cover in another post and in our collaborations with IEEE SCC-18 and the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee (IEEE E&H).
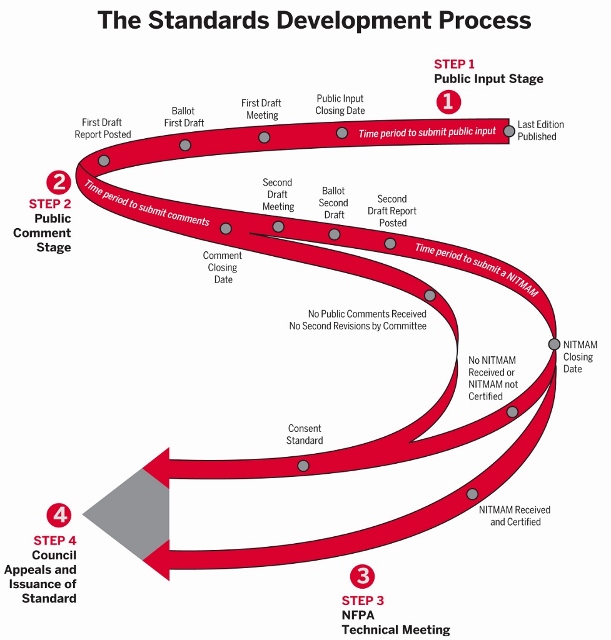
We find office wiring a relatively lively “promontary” in safety and sustainability circles. The transcript of debate among interior wiring experts is always a good place to listen in on the technical discussion; linked below:
Public Input Report – 2023 National Electrical Code Panel 7
Public Input Report – 2023 National Electrical Code Panel 18
We find manufactured wiring concepts tracking that effects office occupancies for all industries. Market incumbents continue advocacy for more ground fault and tamper-resistant receptacles in day care and gymnasium.
A more significant debate tracks in Chapter 2 — related to office modular furniture wiring because electrical load calculations determine how designers specify branch circuits for all occupancy classifications present in education communities (which is nearly every occupancy type defined in the International Building Code):
Public Input Report – 2023 National Electrical Code Panel 2
,Standards Michigan, beginning with its inspiration in the original University of Michigan standards advocacy enterprises, has a long and storied engagement with Chapter 2 of the NEC covered here and also academic literature and also in research sponsored by NFPA’s Fire Protection Research Foundation.
We always encourage our workpoint experts in the thousands of electrical and telecommunication units in the education and healthcare facilities industry to participate directly in the NFPA Code Development process (CLICK HERE to join a committee).
Since both the National Electrical Code and the National Electrical Safety Code revision cycles are roughly coincident in 2021 we working on electrical power issues every day, collaborating with the IEEE E&H Committee. Online meetings are open to everyone.
Issue: [16-102]
Category: Electrical, Interior Furnishings, Telecommunications
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Massimo Mitolo
[1] Rightsizing electrical power systems in large commercial facilities
[2] Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard
More