ISO/DIS 22544Laboratory design — Vocabulary (Under Development)
International Building Code Chapter 38: Higher Education Laboratories
Update: 6 June 2024
Update: 28 September 2023
Update: 10 May 2023
Update: 27 February 2023
Updated: September 20, 2021
Original Post: May 25, 2019
Colleagues in the US education facility industry who collaborated with the original University of Michigan codes and standards advocacy enterprise ahead of the launch of ISO TC 276 Biotechnology standard in 2015 may recall how the University of Michigan recommended that ANSI request removal of “facilities” from the scope of the proposed biotechnology standard; administered by the Deutsches Institut für Normung committee.
Our recommendation was accepted; thereby partitioning the science of biotechnology from the facilities that supported that activity as much as possible. Back in the early 2000’s we found the US research community in higher education was indifferent to participation in international standards of any kind; despite the concentration of chemical, energy, environmental air, electrical and fire safety risk aggregations.
Now the scope of this standard appears to recover some of the facility scope in another title; a few of the key details linked here.
Since the beginning of the original University of Michigan standards advocacy enterprise described in our ABOUT we found the US research community indifferent to participation in standards development of any kind; much less international standards. To a large degree it remains so. Perhaps in the fullness of time, respected voices will join ours.
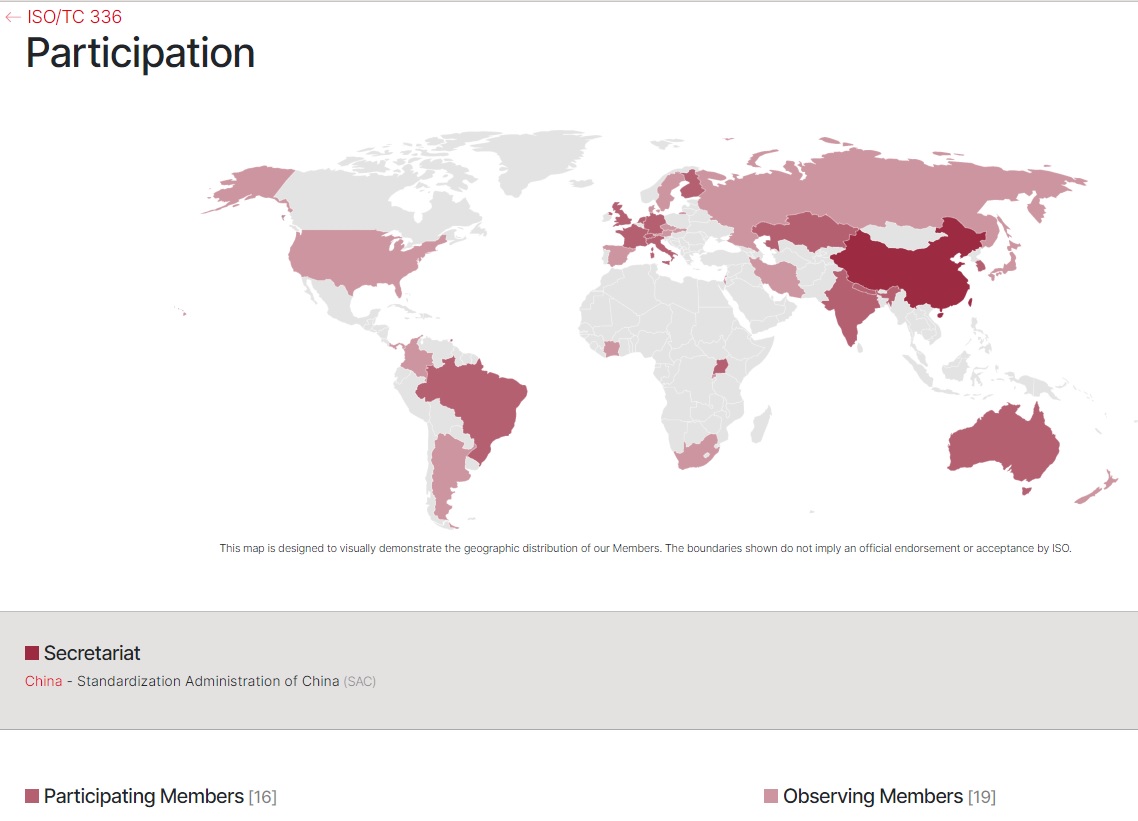
The Standards Administration of China is the Global Secretariat. The American National Standards Institute participates as an Observer. The business plan posted in 2019 is linked below:
ISO TC 336 Laboratory Design 22 March 2023 336 L
ISO TSP 290 (Laboratory Design) | 2019 (Shown for reference only)
You may communicate directly with Steve Cornish: scornish@ansi.org on any matter regarding this project.
Starting 2023 we are breaking up our coverage of laboratory-related best practice titles accordingly:
Laboratories 100 will cover all relevant standardization catalogs with special attention to titles that are incorporated by reference into public safety and sustainability laws.
Laboratories 200 will cover laboratory occupancies primarily for teaching and healthcare clinical delivery.
Laboratories 400 will cover laboratories for scientific research including medical research.
Laboratories 500 is broken out as a separate but related topic and will cover conformity and case studies that resulted in litigation. Both Laboratories 200 and 400 will refer to the cases but not given a separate colloquium unless needed.
We maintain titles from the project on the standing agendas of our periodic Global and Laboratories conversations open to everyone. Always at 15:00 UTC.
Issue: [19-134]
Category: Academic, International
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Christine Fischer, Jack Janveja, Richard Robben, Markus Scheufele, Larry Spielvogel
Source: ANSI Standards Action | Page 33
ANSI-Accredited U.S. Technical Advisory Groups (TAGS) to ISO
LINK TO ORIGINAL UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN ISO STANDARDS WORKSPACE
Reposted by ANSI July 13, 2020
Last week the American National Standards Institute notified stakeholders that the Standardization Administration of China (SAC) — the ISO member body for China — has submitted a proposal for a new field of ISO technical activity on “Laboratory Design”. The proposal bears resemblance to a notice of public consultation that was posted last year; now linked below:
ISO TSP 290 (Laboratory Design)
Comments on the (apparently revised) proposal are due at ANSI offices on August 3rd.
We refer you to Steve Cornish (scornish@ansi.org) and/or Henry Cheung (HCheung@ansi.org) at the American National Standards Institute.
We maintain consensus products of this nature on our Global and Laboratory teleconferences; open to everyone. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
Originally posted May 25, 2019
“Science, my boy, is made up of mistakes,
but they are mistakes which it is useful to make,
because they lead little by little to the truth.”
― Journey to the Center of the Earth
The Standardization Administration of China (SAC) — the ISO member body for China — has submitted a proposal for a new field of ISO technical activity on “Laboratory Design” with the following scope statement:
“…Standardization in the field of laboratory design including site selection and design planning, the functional division of experimental areas, the determination of scientific and technological processes, layouts and design of furniture, and the scientific design of the facility taking into account environmental conditions and impact. Excluded:
– IEC/TC 64 (Electrical installations and protection against electric shock);
– IEC/TC 81 (Lightning protection);
– IEC/TC 66 (Safety of measuring, control and laboratory equipment);
– IEC/TC 85 (Measuring equipment for electrical and electromagnetic quantities).
Once the new TC is established, liaisons with other relevant ISO technical committees will be established, including ISO/TC 48(laboratory equipment), ISO/TC 212 (Clinical laboratory testing and in vitro diagnostic test systems)and CASCO as well as relevant IEC technical committees (IEC/TC 45(Nuclear instrumentation), IEC/TC 62 (Electrical equipment in medical practice), IEC/TC 65 (Industrial-process measurement, control and automation), IEC/TC 76 (Optical radiation safety and laser equipment) and IEC/TC 104 (Environmental conditions, classification and methods of test). Note: the TC will support the contribution of the laboratory design industry to UN Sustainable Development Goals and enable countries to address a wide range of global issues including eradication of hunger and poverty, health, climate change and economic development….”
“…The new TC will stipulate technical design requirements for a diverse range of laboratories with different functions and responsibilities. It will include, but not limited to:
1. site selection and design planning;
2. layouts and design of furniture (e.g workbenches, fume hoods, safety showers, biological safety cabinets, etc);
3. electrical, water and gas supply systems, drainage, fire prevention, HVAC, auto-control and decoration;
4. laboratories featuring bio-safety, constant temperature and humidity, and other special laboratories;
5. laboratory safety, staff health, environmental protection, and energy saving;
6. Smart laboratory (use of new technologies such as big data, cloud computing, block chain, etc. to empower laboratories, e.g. increase the depth and width of services provided to clients, improve the servicing level during the consulting, design and maintenance phases.)…”
“…The setting up of laboratory design TC and establishment of laboratory design standards will benefit organizations and groups as follows:
-
-
- Laboratory owners (including governments, scientific agencies and enterprises, etc.): Laboratory owners will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design for better management of laboratory design, construction, acceptance and operation. The investment budget will have a reference basis; construction cost will be better controlled; investment risk will be lowered; project quality can be better evaluated; construction cycle will be shortened; capital usage efficiency will be raised;
-
-
-
- Laboratory designers: Laboratory designers will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design, and will have standards to follow and verify by, make fewer design faults and ensure laboratory design to be more scientific and professional; laboratory environmental facility will be improved in terms of safety, energy conservation, environmental friendliness, as well as impacts on human health and well-being.
-
-
-
- Laboratory constructors: Laboratory constructors will have construction and acceptance standards to refer to; the construction quality will be raised; technology advancement will be promoted; the industry will be further regulated.
-
-
-
- Laboratory users: Laboratory users will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design; stakeholders can communicate with each other in a more informed way and evaluate laboratories based on common standards, making laboratory use, operation and management more scientific and regulated. Smart laboratories will allow more functions and add value by integrating technologies of big data, cloud computing and internet of things, etc.
-
-
-
- Laboratory operators: Laboratory operators will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design, which will facilitate the maintenance of laboratories; Smart laboratories will enable the remote digital control of laboratory operation and facilitate reliable, efficient and convenient maintenance.
-
-
-
- Society: The society will be able to cultivate more professional personnel in the field of laboratory design; a more sound and fair development of laboratory design and construction both home and abroad will be facilitated; more energy-saving and environmental-friendly design will promote the sustainable development of the society; the premium laboratories will inspire the creativity of researchers and promote the advancement and development of technologies. Smart laboratories will facilitate technological progress, product quality improvement, data recognition as well as international trade….”
-
If the proposal is accepted, China is willing to undertake the work of secretariat of the new TC and will provide all necessary resources including financial and human resources as well as facility supports. A partnership agreement between China and France at committee level is foreseen.
Anyone wishing to review the proposal can request a copy by contacting ANSI’s ISO Team (isot@ansi.org), with a submission of comments to Steve Cornish (scornish@ansi.org) by close of business on Friday, June 28th
N.B. This proposal will be featured in an ANSI Online news story and open for public review and comments from relevant US stakeholders via notice in Standards Action. In addition, ANSI will conduct targeted outreach to gather input on this proposal. Based on the input received from US stakeholders, a recommended ANSI position and any comments will be developed and presented to the AIC for approval before the ISO voting deadline of August 13, 2019. Contact Steve Cornish (scornish@ansi.org)
ANSI’s due process requirements were applied to this ISO/SIA/AFNOR proposal and comment from US stakeholders were consulted. It appears that most US stakeholders do NOT want to participate in the development of this standard as currently written. The public comments are available from Henry Cheung (HCheung@ansi.org) who has also prepared a draft statement from ANSI.
Comments on the draft statement are due August 2nd.
Perspective: We have been down this road before. The original University of Michigan user-interest advocacy enterprise — through ANSI — was persuasive in having “facilities” struck from the scope of the original ISO TC/276 Biotechnology project proposal (Global Secretariat: Deutsches Institut für Normung) in 2012. Now we circle back to a proposal that captures the facility component as an articulated enterprise which, in large research colleges and universities, is a delicate risk aggregation that generates significant revenue.
As always, we are happy to discuss any best practice title from anywhere on earth that affects the safety and sustainability agenda of education communities. Just click the login credentials at the upper right of our home page any day at 11 AM Eastern time. We also sweep through the status of international consensus products emerging from ISO, IEC and ITU technical and management committees. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [19-134]
Category: Academic, International
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Christine Fischer, Jack Janveja, Richard Robben, Markus Scheufele, Larry Spielvogel
Source: ANSI Standards Action | Page 33
LINK TO ORIGINAL UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN ISO STANDARDS WORKSPACE