New Construction Release Schedule: https://www.census.gov/construction/c30/release.html
Reports are usually released at 10 AM EST the first day of every month.
There’s been a significant redesign of the look and feel of the monthly Census Bureau reports construction activity. Today we sort through the rather more granular statistics that inform our recommendations for facility spend.
December 1, 2025
It has been 20 years since we began tracking educational settlement facility spend. Starting this month we will examine federal government data together with the best available data about space utilization to enlighten our response to the perfectly reasonable question: “Are we over-building or under-building or building ineffectively”. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
United States: Schools of Architecture
The Society for College and University Planning (Ann Arbor, Michigan)
National Center for Education Statistics
The Financial Impact of Architectural Design: Balancing Aesthetics and Budget in Modern Construction
Homeschooling
2022 International Existing Building Code
As reported by the US Department of Commerce Census Bureau the value of construction put in place by August 2025 by the US education industry proceeded at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $137.604 billion. This number does not include renovation for projects under 50,000 square feet and new construction in university-affiliated health care delivery enterprises. Reports are released two months after calendar month. The complete report is available at the link below:
MONTHLY CONSTRUCTION SPENDING August 2025 (released two months after calendar month)
This spend makes the US education facilities industry (which includes colleges, universities, technical/vocational and K-12 schools, most university-affiliated medical research and healthcare delivery enterprises, etc.) the largest non-residential building construction market in the United States after commercial property; and fairly close. For perspective consider total public + private construction ranked according to the tabulation most recently released:
$137.604 billion| Education Facilities
$155.728 billion | Power
$69.625 billion | Healthcare
Keep in mind that inflation figures into the elevated dollar figures. Overall — including construction, energy, custodial services, furnishings, security. etc., — the non-instructional spend plus the construction spend of the US education facilities is running at a rate of about $300 – $500 billion per year.
LIVE: A selection of construction cameras at US schools, colleges and universities

Architectural Billings
We typically pick through the new data set; looking for clues relevant to real asset spend decisions. Finally, we encourage the education facilities industry to contribute to the accuracy of these monthly reports by responding the US Census Bureau’s data gathering contractors.
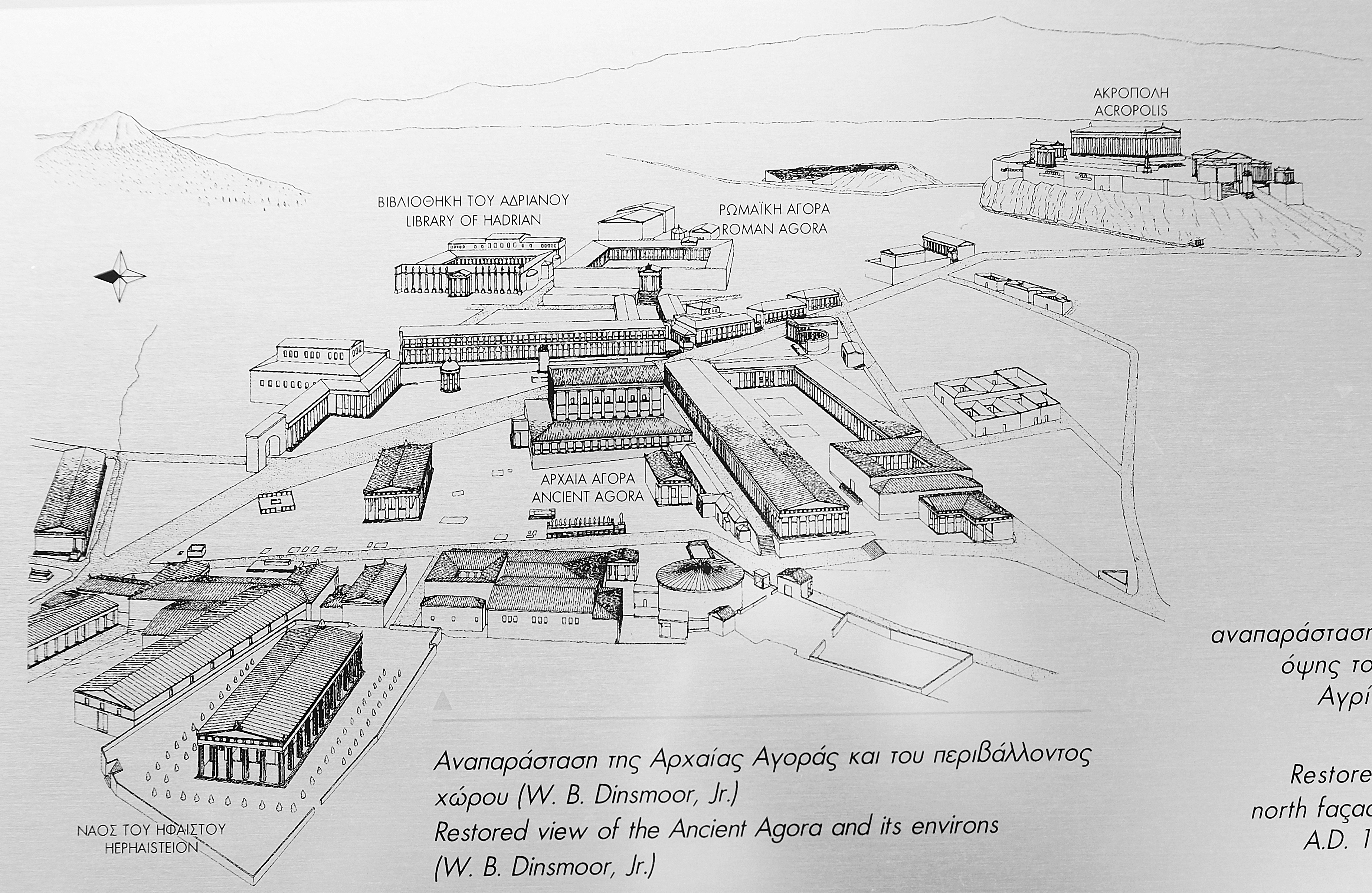
Reconstruction of Ancient Agora
As surely as people are born, grow wealthy and die with extra cash,
there will be a home for that cash to sustain their memory and to steer
the cultural heritage of the next generation in beautiful settings.


More
National Center for Educational Statistics
AIA: Billings Index shows but remains strong May 2022
National Center for Education Statistics
Sightlines: Capital Investment College Facilities
OxBlue: Time-Lapse Construction Cameras for Education
Architectural Billing Index
IBISWorld Education Sector
US Census Bureau Form F-33 Survey of School System Finances
American School & University
New Report from Occuspace Finds U.S. Campuses Face Significant Underutilization
Global Consistency in Presenting Construction & Life Cycle Costs
Carnegie Classifications





































