“Chance favors the prepared mind.”
— Louis Pasteur
Agenda
Technical:
Respond to client queries and retainers
Prepare new proposals for the NFPA 2029 National Electrical Code
Prepare comments on the IEEE 2028 National Electrical Safety Code
Recap of activity in the ISO and IEC catalogs. We are members of Healthcare Management. We coordinate our responses to IEC CDV’s with IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee.
2025 “Wins” and “Losses”
“Wins”: All of the references to IEEE research and recommended practices that appear in electrical related titles in the NFPA catalog are the result of Standards Michigan advocacy in collaboration with the IEEE
“Losses”: Persist in getting Article 210 (Soon to be in Chapter 1) 180 VA per outlet requirement down to 150 VA instead of 120 VA in the ASHRAE suite from an energy conservation perspective. This will be the most meaningful and transformative code “win” since our 2014 code “win” in 2014 NEC Section 220.12.
Expansion of user-interest advocacy for the 2028 IEEE National Electrical Safety Code.
Follow up driving electrical safety concepts into the ASHRAE and ICC catalog that cannot, or will not, be incorporated into the NFPA catalog
Continue driving IEEE best practice literature into the NFPA, ASHRAE and IEEE catalog
Electric service reliability data gathering for point of common coupling of merchant utilities and schools, colleges, universities with emphasis on large health care systems. (Bob Arno’s IEEE 493 Gold Book update)
Break out coverage of ASHRAE 90.1 in its entirety in a dedicated content management system now that its scope includes outside/between buildings.
Break out coverage of Chapter 27 (Electrical) of the International Building Code as a “pivot” or “anchor” post for other relevant titles in the ICC catalog.
10-year retrospective on the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee at the May Technical Conference in Montreal
Administrative:
Expansion of our unaccredited for-profit educational mission to Michigan school districts, colleges, universities, trade schools. In the normal course of business we present educational opportunities to faculty and students administered by ANSI, ASME, AWS, ACI, ICC, IEC, IEEE, IEEE, NIST, SAE and others. List of Faculty & Student Standards Education Resources
New signage at our State Street office
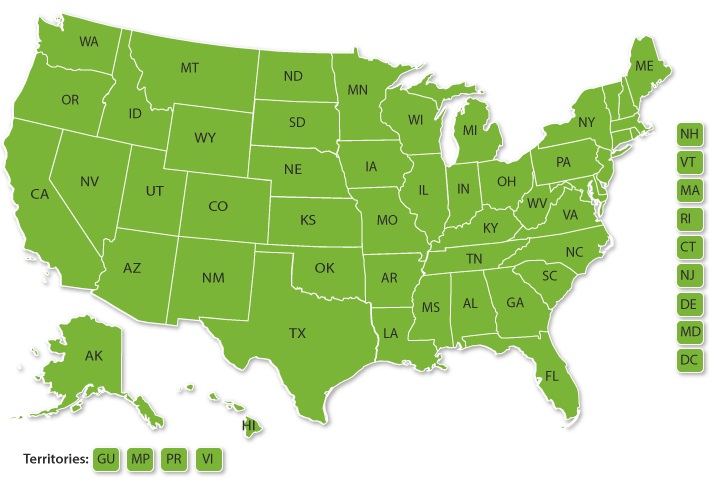
Rollout the platform to at least two more states — we have only one now.
Re-organize web pages to track IEEE, NFPA, ASHRAE, ICC, CSA Group and TIA catalog action more effectively. ASTM and UL catalogs remain “problematic” because their titles are so deeply embedded in products and less so in systems.
List of ANSI Accredited Standards Developers
Other:
Our thanks for the collegiality and wisdom of Larry Spielvogel as he enters retirement
Continued mentorship of electrical engineering students in the IEEE Southeastern Michigan Section. Introduction to mentorship partner Nathan from private industry.
Social Page Rollout: Engagements, Weddings & Births