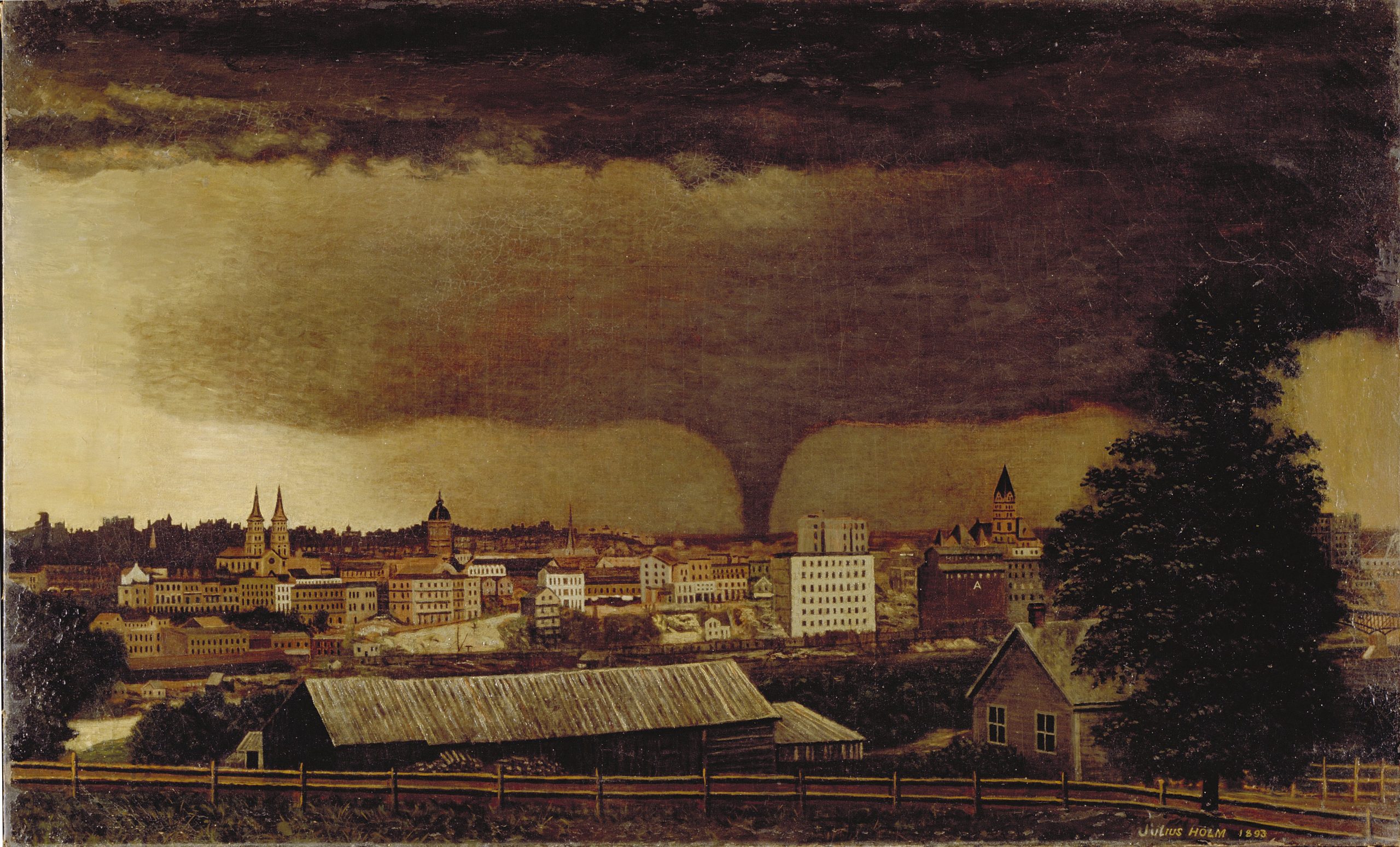
Disaster 500


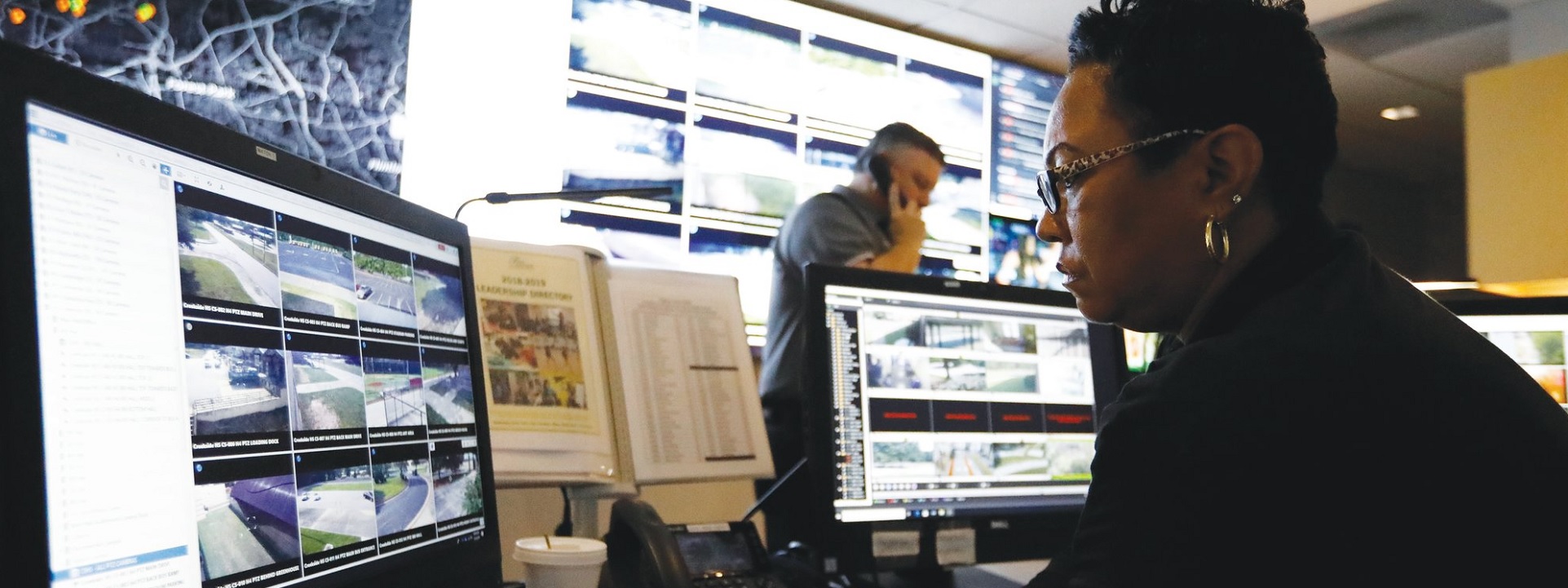
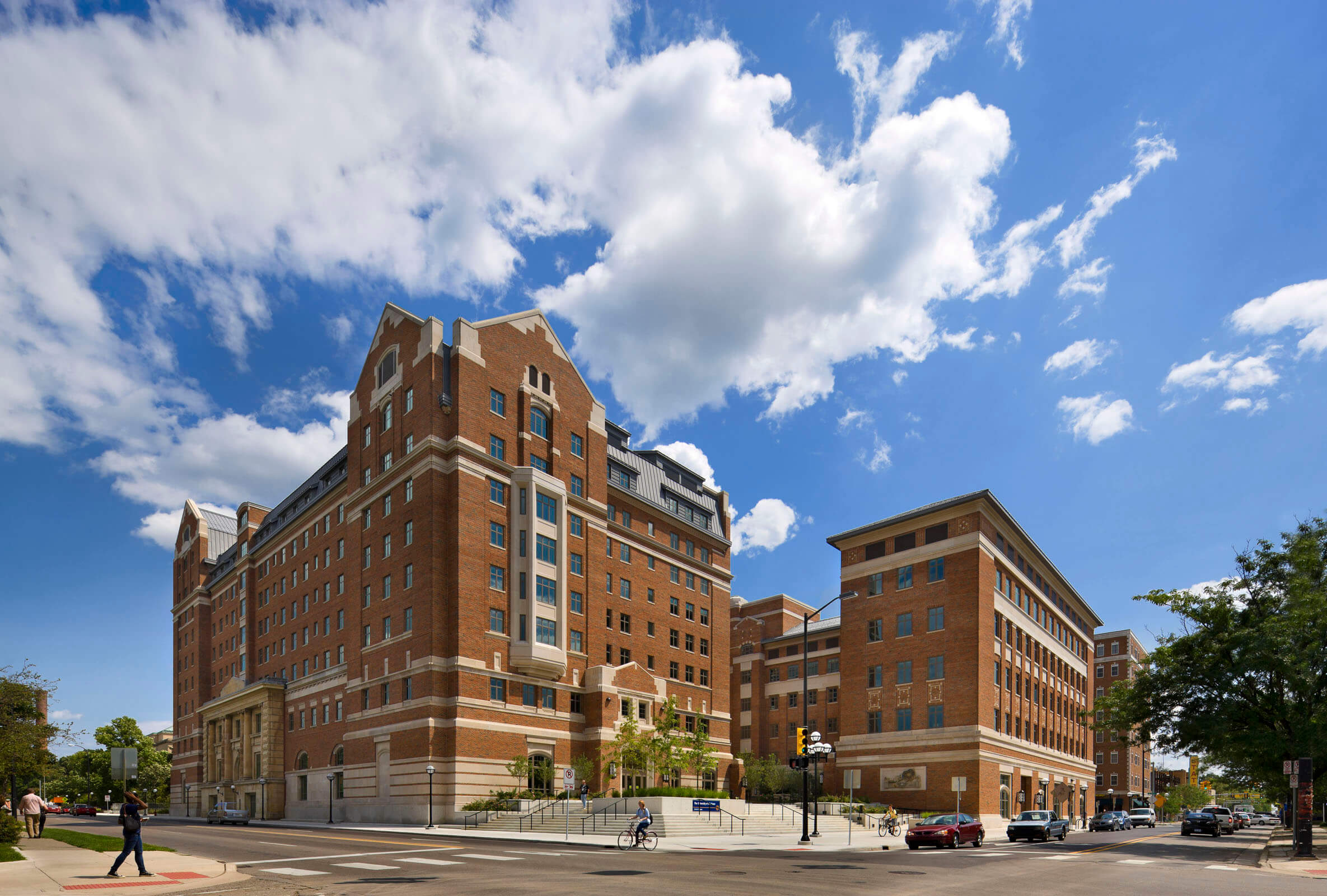
The original University of Michigan codes and standards enterprise advocated actively in Article 708 Critical Operations Power Systems (COPS) of the National Electrical Code (NEC) because of the elevated likelihood that the education facility industry managed assets that were likely candidates for designation critical operations areas by emergency management authorities.
Because the NEC is incorporated by reference into most state and local electrical safety laws, it saw the possibility that some colleges and universities — particularly large research universities with independent power plants, telecommunications systems and large hospitals — would be on the receiving end of an unfunded mandate. Many education facilities are identified by the Federal Emergency Management Association as community storm shelters, for example.
As managers of publicly owned assets, University of Michigan Plant Operations had no objection to rising to the challenge of using publicly owned education facilities for emergency preparedness and disaster recovery operations; only that meeting the power system reliability requirements to the emergency management command centers would likely cost more than anyone imagined — especially at the University Hospital and the Public Safety Department facilities. Budgets would have to be prepared to make critical operations power systems (COPS) resistant to fire and flood damages; for example.
Collaboration with the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Industrial Applications Society began shortly after the release of the 2007 NEC. Engineering studies were undertaken, papers were published (see links below) and the inspiration for the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee developed to provide a gathering place for power, telecommunication and energy professionals to discover and promulgate leading practice. That committee is now formally a part of IEEE and collaborates with IAS/PES JTCC assigned the task of harmonizing NFPA and IEEE electrical safety and sustainability consensus documents (codes, standards, guidelines and recommended practices.

Transcripts of 2026 Revision:
Public Input Report CMP-13
Public Comment Report CMP-13
The transcript of NEC Code Making Panel 13 — the committee that revises COPS Article 708 every three years — is linked below:
NEC CMP-13 First Draft Balloting
NEC CMP-13 Second Draft Balloting
The 2023 Edition of the National Electrical Code does not contain revisions that affect #TotalCostofOwnership — only refinement of wiring installation practices when COPS are built integral to an existing building that will likely raise cost. There are several dissenting comments to this effect and they all dissent because of cost. Familiar battles over overcurrent coordination persist.
Our papers and proposals regarding Article 708 track a concern for power system reliability — and the lack of power — as an inherent safety hazard. These proposals are routinely rejected by incumbent stakeholders on NEC technical panels who do not agree that lack of power is a safety hazard. Even if lack of power is not a safety hazard, reliability requirements do not belong in an electrical wiring installation code developed largely by electricians and fire safety inspectors. The IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee (IEEE E&H) maintains a database on campus power outages; similar to the database used by the IEEE 1366 committees that develop reliability indices to enlighten public utility reliability regulations.
Public input on the 2026 revision to the NEC will be received until September 7th. We have reserved a workspace for our priorities in the link below:
2026 National Electrical Code Workspace
Colleagues: Robert Arno, Neal Dowling, Jim Harvey

LEARN MORE:
IEEE | Critical Operations Power Systems: Improving Risk Assessment in Emergency Facilities with Reliability Engineering
Consuting-Specifying Engineer | Risk Assessments for Critical Operations Power Systems
Electrical Construction & Maintenance | Critical Operations Power Systems
International City County Management Association | Critical Operations Power Systems: Success of the Imagination
Facilities Manager | Critical Operations Power Systems: The Generator in Your Backyard