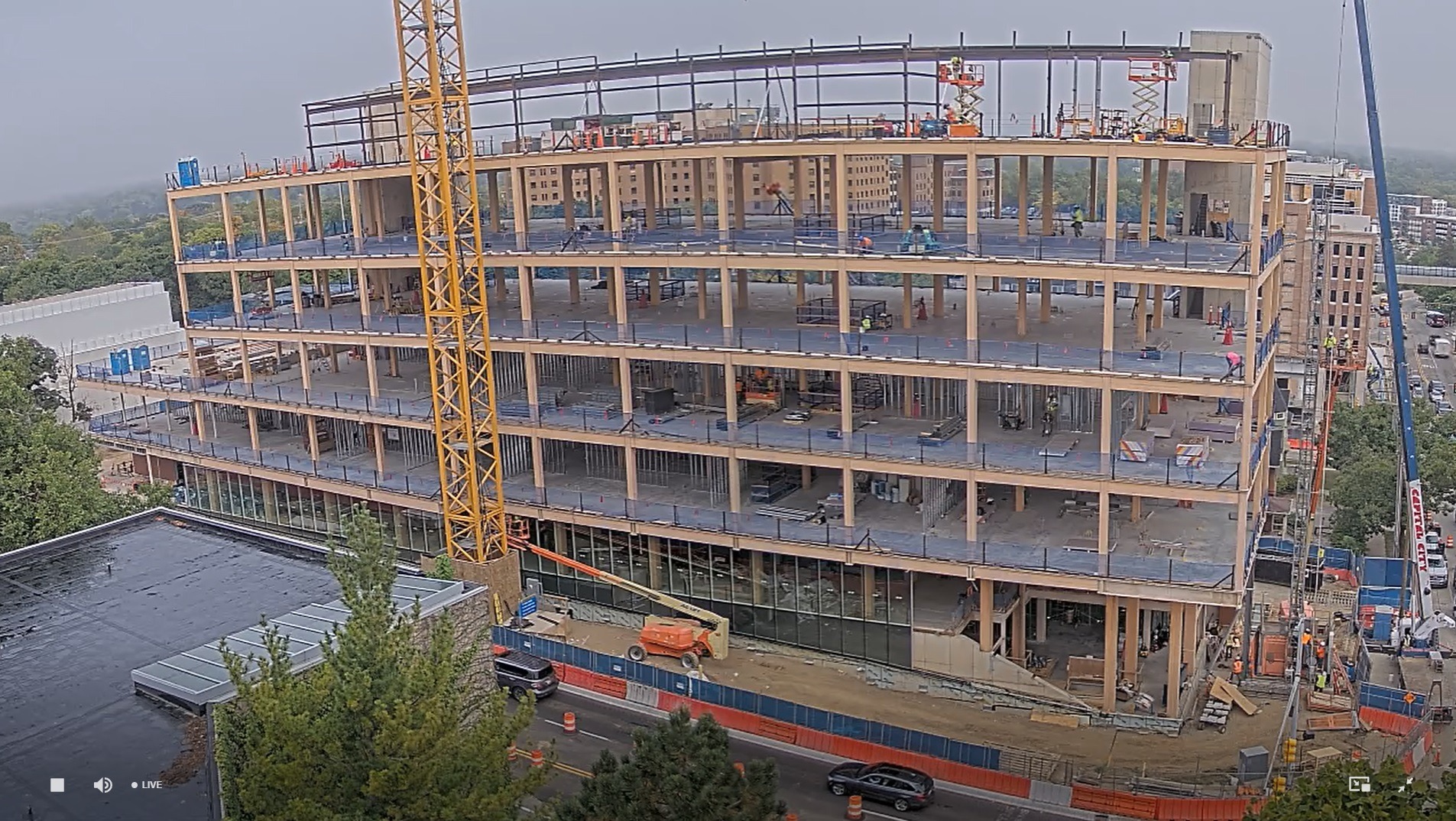
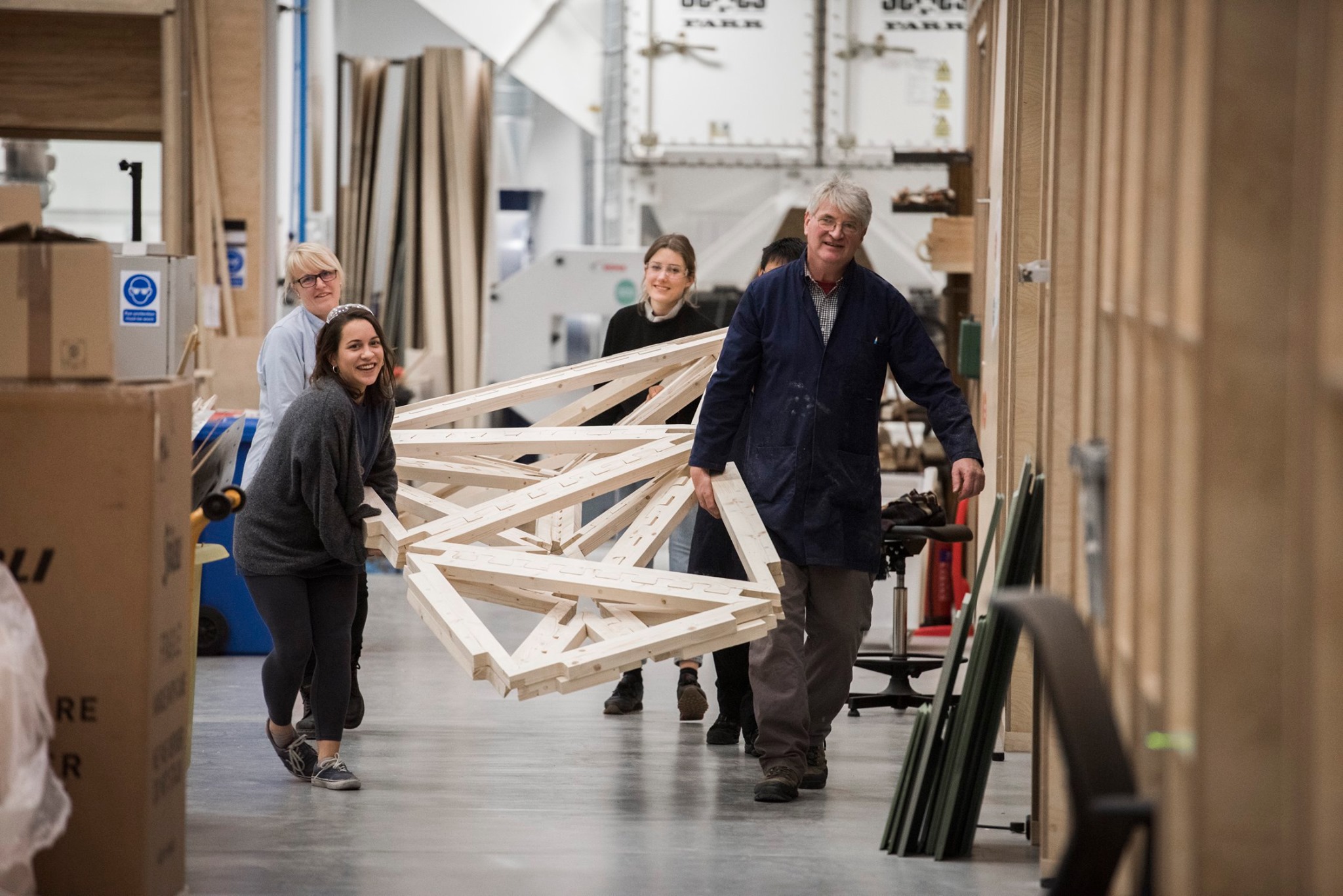
Timber construction offers numerous benefits for university buildings, combining sustainability, aesthetics, and functionality. One of the primary advantages is its environmental impact. Timber is a renewable resource, and modern forestry practices ensure sustainable harvesting. Timber construction also has a lower carbon footprint compared to steel or concrete, as it sequesters carbon dioxide, helping mitigate climate change.
Aesthetically, timber provides a warm, natural look that can enhance the campus environment, creating inviting and inspiring spaces for students and faculty. It can be used in various architectural styles, from traditional to contemporary, offering versatility in design.
Functionally, timber is a strong and durable material. Engineered wood products, such as cross-laminated timber (CLT), provide excellent structural integrity, allowing for larger spans and innovative architectural designs. Timber construction is often faster than traditional methods, reducing construction time and minimizing disruption on campus.
Additionally, timber buildings offer superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs. The acoustic properties of wood also enhance the learning environment by dampening noise and creating quieter spaces.
Related: