
§
Campus physical planning is more commonly addressed by organizations like the Society for College and University Planning (SCUP), and scholarly literature (e.g., in the Journal of the American Planning Association) notes limited APA focus on higher education facilities compared to K-12 schools.
International Building Code Development Schedule
Related:
The New Urban Order: Is the Rise of Homeschooling a Problem?
Do Texas public schools exist to serve the school district? Or do they exist to serve all the children and families in the community? Here is the list of schools discriminating against homeschoolers by not allowing those students to participate in UIL. #txlege…
— Matt Schaefer (@RepMattSchaefer) January 5, 2026
Group E occupancy covers buildings (or portions thereof) used for educational purposes by six or more persons at any time through the 12th grade.
This includes:
Key exceptions and notes:
Colleges and universities do not fall under Group E; higher education facilities typically classify as Group B (Business) for classrooms, offices, and labs, with assembly spaces (e.g., lecture halls, auditoriums) as Group A if they meet assembly criteria.
Section 308 defines Institutional Group I occupancies overall, with Group I-4 specifically addressing day care facilities requiring custodial care.
Group I-4 includes buildings occupied by more than five persons of any age who receive custodial care (supervision and assistance due to age or incapacity) for fewer than 24 hours per day, provided by non-relatives outside the home.
This explicitly covers:
For child day care:
Other notes:
Elementary schools and colleges do not fall under Section 308; elementary schools are Group E (as above), and colleges are typically Group B.
These classifications in the 2024 IBC remain consistent with prior editions (e.g., 2021). Local amendments may apply, so verify with the authority having jurisdiction. For the exact text, consult the official ICC digital codes.
Today at 16:00 UTC we review best practice for engineering and installing the point of common coupling between an electrical service provider its and an purchasing — under the purview of NEC CMP-10.
Committee topical purviews change cycle-to-cycle. Here’s the transcript for today’s session: CMP-10 Second Draft Report (368 pages)
Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
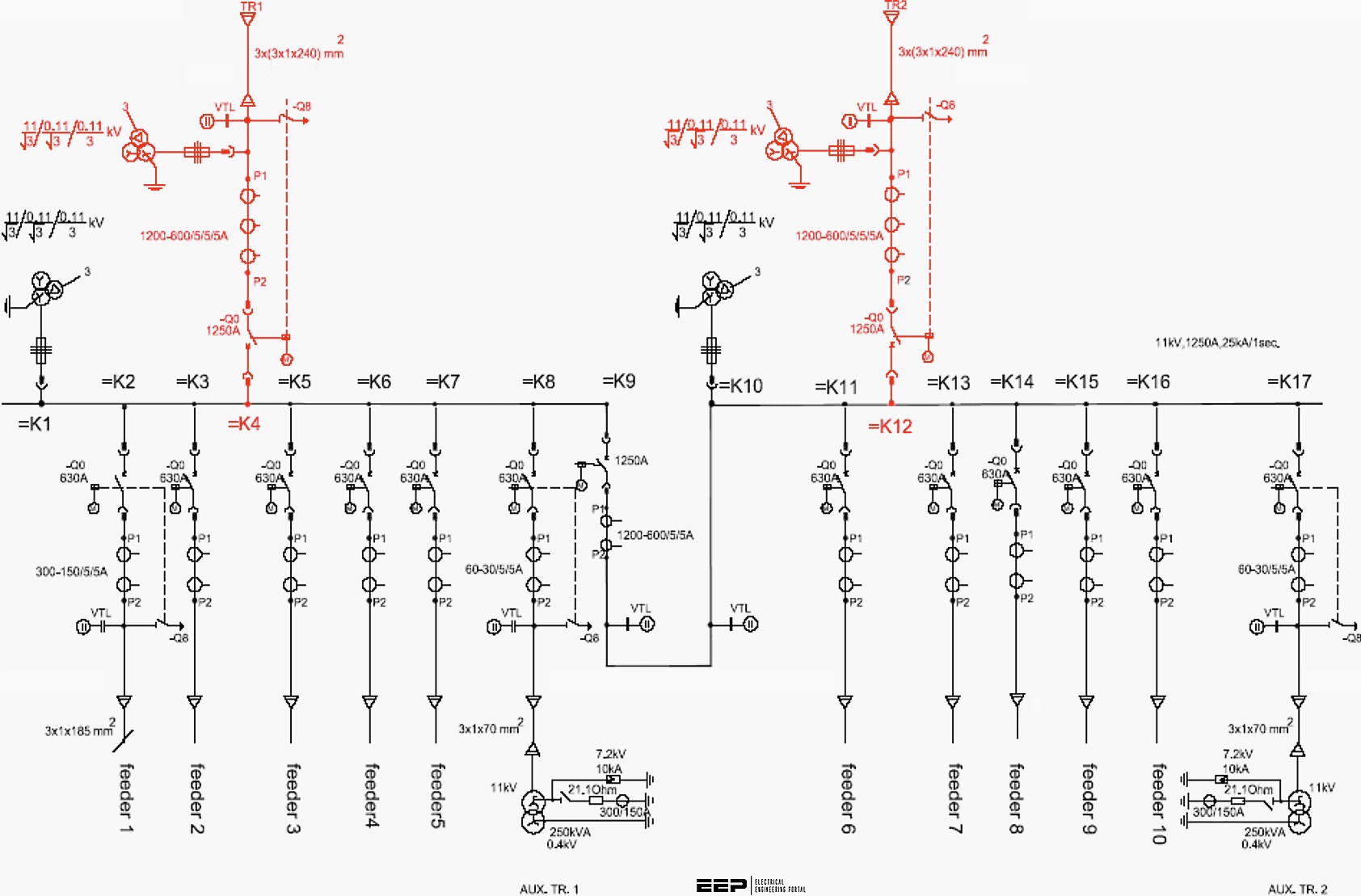
The relevant passages of the National Electrical Code are found in Article 230 and Article 495. We calibrate our attention with the documents linked below. These are only representative guidelines:
University of Michigan Medium Voltage Electrical Distribution
Texas A&M University Medium Voltage Power Systems
University of Florida Medium Voltage Electrical Distribution
Representative standards for regulated utilities for purchased power:
Detroit Edison Primary Service Standards (Green Book)
American Electric Power: Requirements for Electrical Services
Pacific Gas & Electric Primary Service Requirements
The IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee curates a library of documents similar to those linked above.
Design of Electrical Services for Buildings
We are in the process of preparing new (original, and sometimes recycled) proposals for the 2026 National Electrical Code, with the work of Code Panel 10 of particular relevance to today’s topic:
First Draft Meetings: January 15-26, 2024 in Charleston, South Carolina
Electrical meter billing standards are generally regulated at the state or local level, with guidelines provided by public utility commissions or similar regulatory bodies. These tariff sheets are among the oldest in the world. There are some common standards for billing and metering practices, including:
Michigan Public Service Commission | Consumer’s Energy Customer Billing Rules
— Charles Louis de Secondat, Baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu
Heat tracing is a process used to maintain or raise the temperature of pipes and vessels in order to prevent freezing, maintain process temperature, or ensure that products remain fluid and flow through the system properly. Without electric heat tracing; much of the earth would be uninhabitable.
Heat tracing works by using an electric heating cable or tape that is wrapped around the pipe or vessel, and then insulated to help retain the heat. The heating cable is connected to a power source and temperature control system that maintains the desired temperature by regulating the amount of heat output from the cable. Heat tracing is commonly used in industrial applications where temperature control is critical, such as in chemical plants, refineries, and oil and gas facilities.
There are several types of heat tracing, including electric heat tracing, steam tracing, and hot water tracing, each of which have their own unique advantages and disadvantages. The selection of the appropriate type of heat tracing depends on the specific application and the required temperature range, as well as factors such as cost, maintenance, and safety considerations.
Heat Tracing for Piping Specification | NECA Standards (N.B. Link unstable)
2026 NEC CMP-17 Public Input Report | 2026 NEC CMP-17 Second Draft Report
Capturing snow flakes as the fall out of the sky
[📹 Dmitry Dotsenko / dots_foto]pic.twitter.com/e3rwNUGLmK
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) January 29, 2025
Today we review the literature for snow and ice management (and enjoyment) produced by these standards-setting organizations:
Accredited Snow Contractors Association
American Society of Civil Engineers
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
ASTM International
Destructive Deep Freeze Strikes Cold and Hot Regions Alike
Institute of Electrical & Electronic Engineers
Electrical Heat Tracing: International Harmonization — Now and in the Future
Indiana University.
The most beautiful college campus in the country covered in snow. pic.twitter.com/Tp33cQgKuq
— Alex Paul Photo (@alexpaulphoto) January 11, 2025
International Code Council
International Building Code: Chapter 15 Roof Assemblies and Rooftop Structures
National Electrical Contractors Association
National Fire Protection Association
Winter is Coming: Is Your Facility Protected? (Holly Burgess, November 2022)
National Electrical Code: Articles 426-427
National Floor Safety Institute
Snow and Ice Management Association
Underwriters Laboratories
Manufacturers:
Chromalox Electrical Heat Tracing Systems Design Guide
It is a surprisingly large domain with market-makers in every dimension of safety and sustainability; all of whom are bound by state and federal regulations.
Join us at 16:00 UTC with the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
Red surely made the most of his snow day! 🛷 ☃️
Who’s team snow on campus? ❄️ pic.twitter.com/F03KX1XyaR
— The Catholic University of America (@CatholicUniv) January 14, 2025
There have been several recent innovations that have made it possible for construction activity to continue through cold winter months. Some of the most notable ones include:
Overall, these innovations have made it possible for construction crews to work through the winter months more comfortably and safely, which has helped to keep projects on schedule and minimize delays.
Somewhat related:
Capturing snow flakes as the fall out of the sky
[📹 Dmitry Dotsenko / dots_foto]pic.twitter.com/e3rwNUGLmK
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) January 29, 2025
Map showing what states can actually drive in snow pic.twitter.com/qgKEhLtKbr
— Midwest vs. Everybody (@midwestern_ope) February 7, 2025
Much of our assertion that building construction in education communities resembles a perpetual motion machine rests upon innovation in a broad span of technologies that is effectively weather resistant; that along with development of construction scheduling. Today at 16:0 UTC we review the technical, management and legal literature that supports safe and sustainable construction,
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration does not have a specific regulation solely dedicated to building construction in cold winter weather. However, several OSHA standards and guidelines are applicable to address the hazards and challenges of winter construction work. These regulations focus on worker safety, protection from cold stress, proper equipment use, and general site safety. Key applicable OSHA regulations and guidance include:
By following these OSHA standards and implementing additional best practices (e.g., scheduling breaks in heated shelters, providing warm beverages, and encouraging layered clothing), employers can ensure a safer construction environment during winter conditions.
Related:
Electrical heat tracing: international harmonization-now and in the future
#Snowstorms ❄️ are no match for our facilities team. Watch to see what it takes to keep our #Northeastern community safe and our #Boston campus clean. https://t.co/lDcjFRRhlw
— Northeastern U. (@Northeastern) January 20, 2023
“Among famous traitors of history one might mention the weather.”
Ilka Chase, The Varied Airs of Spring
Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures (ASCE/SEI 7-22)
Quick & Dirty Snow Load Calculator
Call for public proposals for the 2028 edition
Roof Snow Load Calculation for Newton High School Nebraska
Brian Rickard@ASCE_SEI
print(“Du Froid”)https://t.co/igfshxpiot pic.twitter.com/Qw5hKy5voE— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) December 22, 2022
“Analysis of a Frame under Snow Load” | Dr. Structurehttps://t.co/6cpz1kyW7s
print(“Du Froid”)https://t.co/Ke7qRmIz6X pic.twitter.com/Sh805RZoBz— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) January 28, 2022
Brown University Electrical Design Criteria | Information Technology Resources Policy
The University of Michigan has supported the voice of the United States education facility industry since 1993 — the second longest tenure of any voice in the United States. That voice has survived several organizational changes but remains intact and will continue its Safer-Simpler-Lower Cost-Longer Lasting priorities on Code Panel 3 in the 2029 Edition.
Today, during our customary “Open Door” teleconference we will examine the technical concepts under the purview of Code Panel 4; among them:
Article 690 Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
Article 691 Large-Scale Photovoltaic (PV) Electric Supply Stations
Article 694 Wind Electric Systems
Article 705 Interconnected Electric Power Production Sources
Article 710 Stand-Alone Systems
Public Input on the 2029 Edition will be received until April 9, 2026.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670
