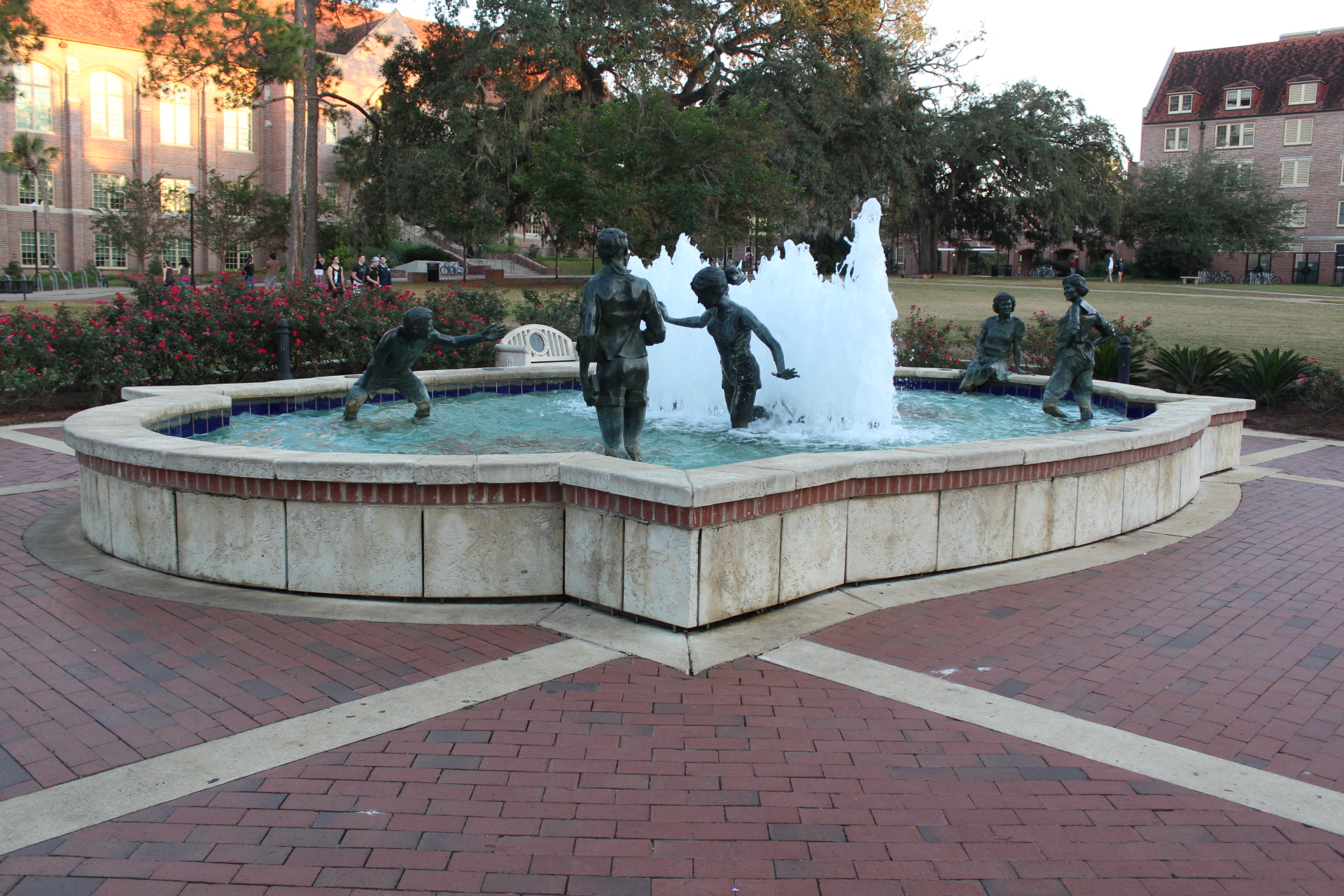Construction Trailer Coffee
- Home Page 97

Keeping Animals Cool
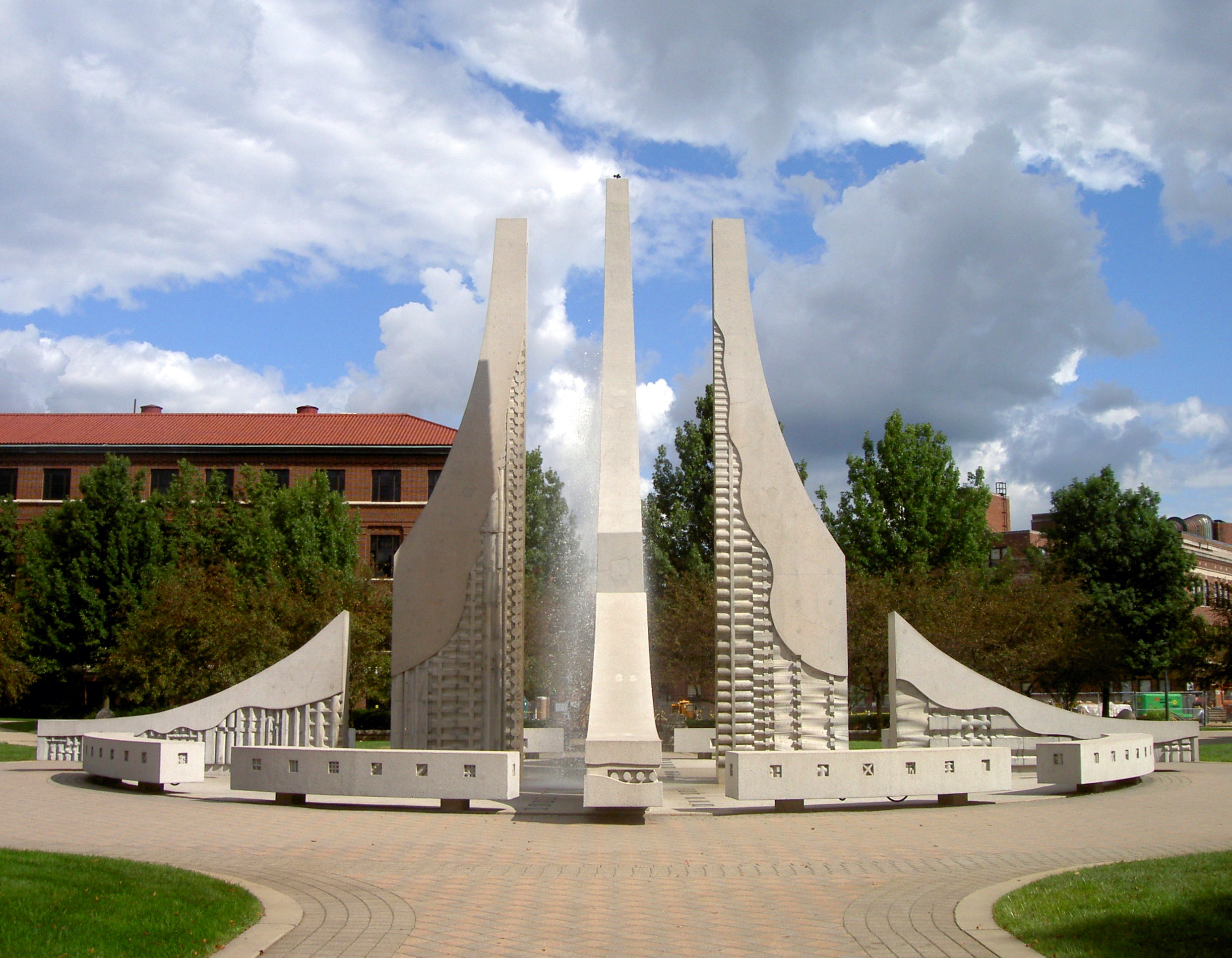
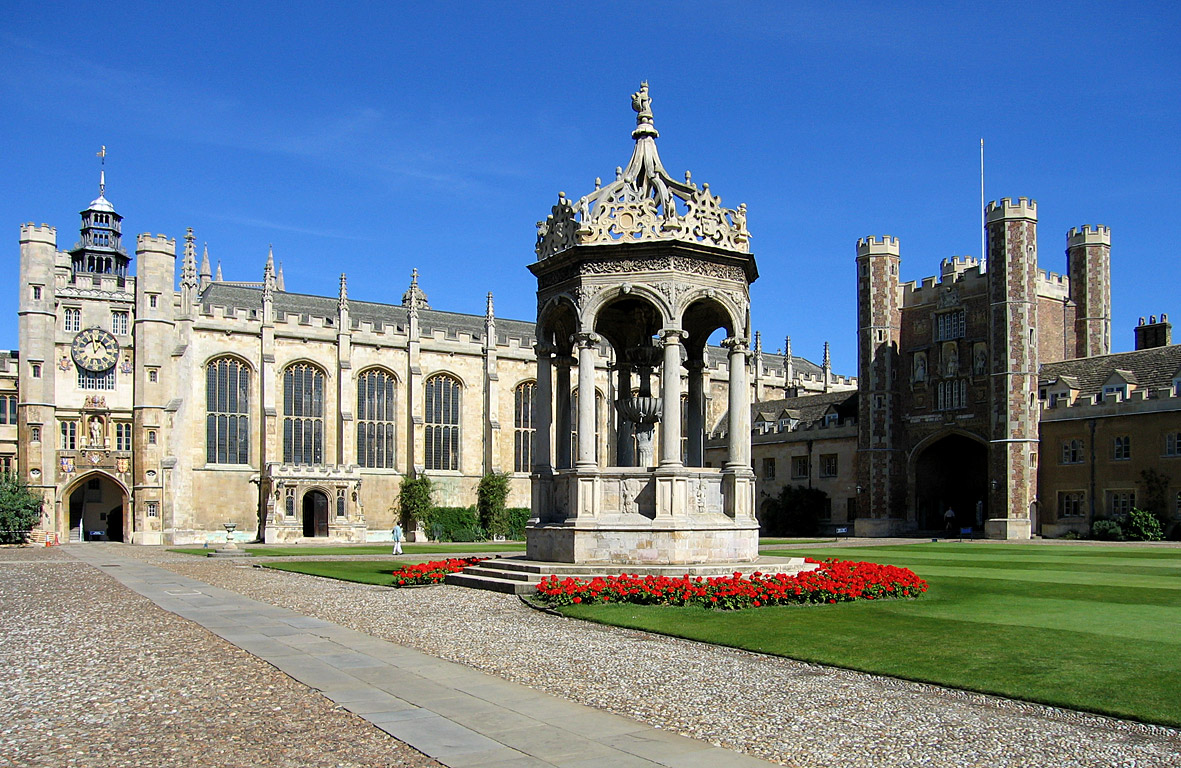
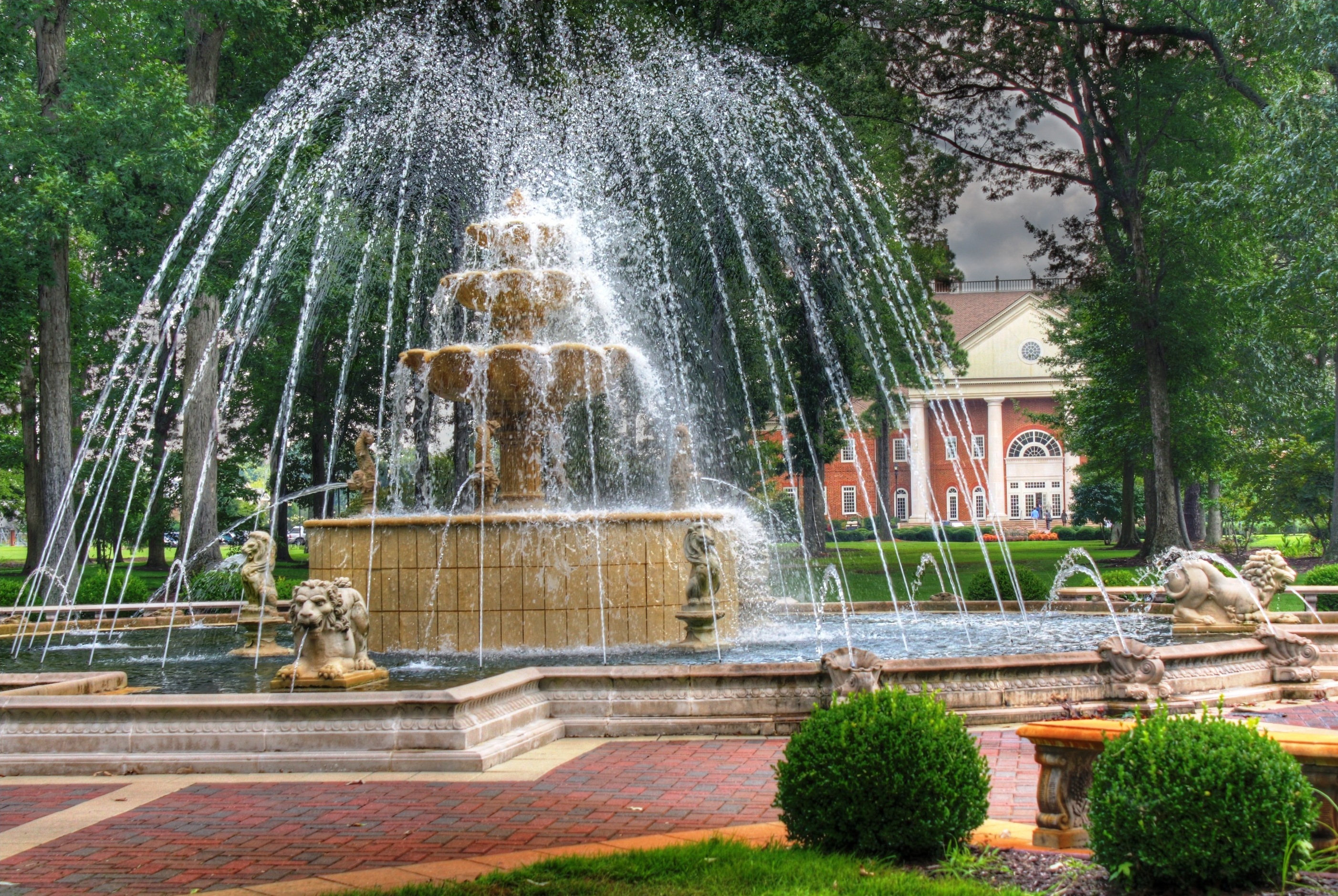
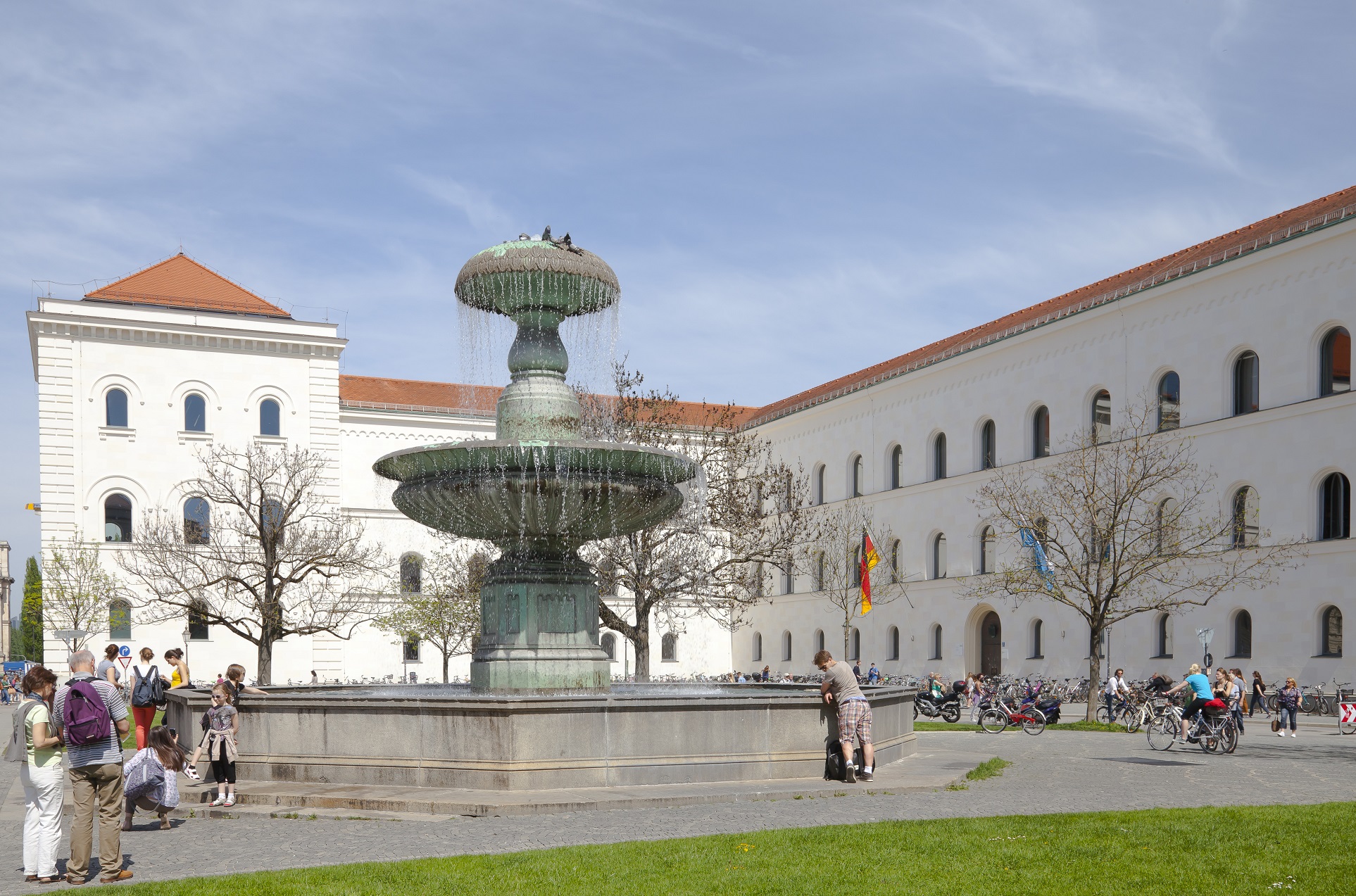
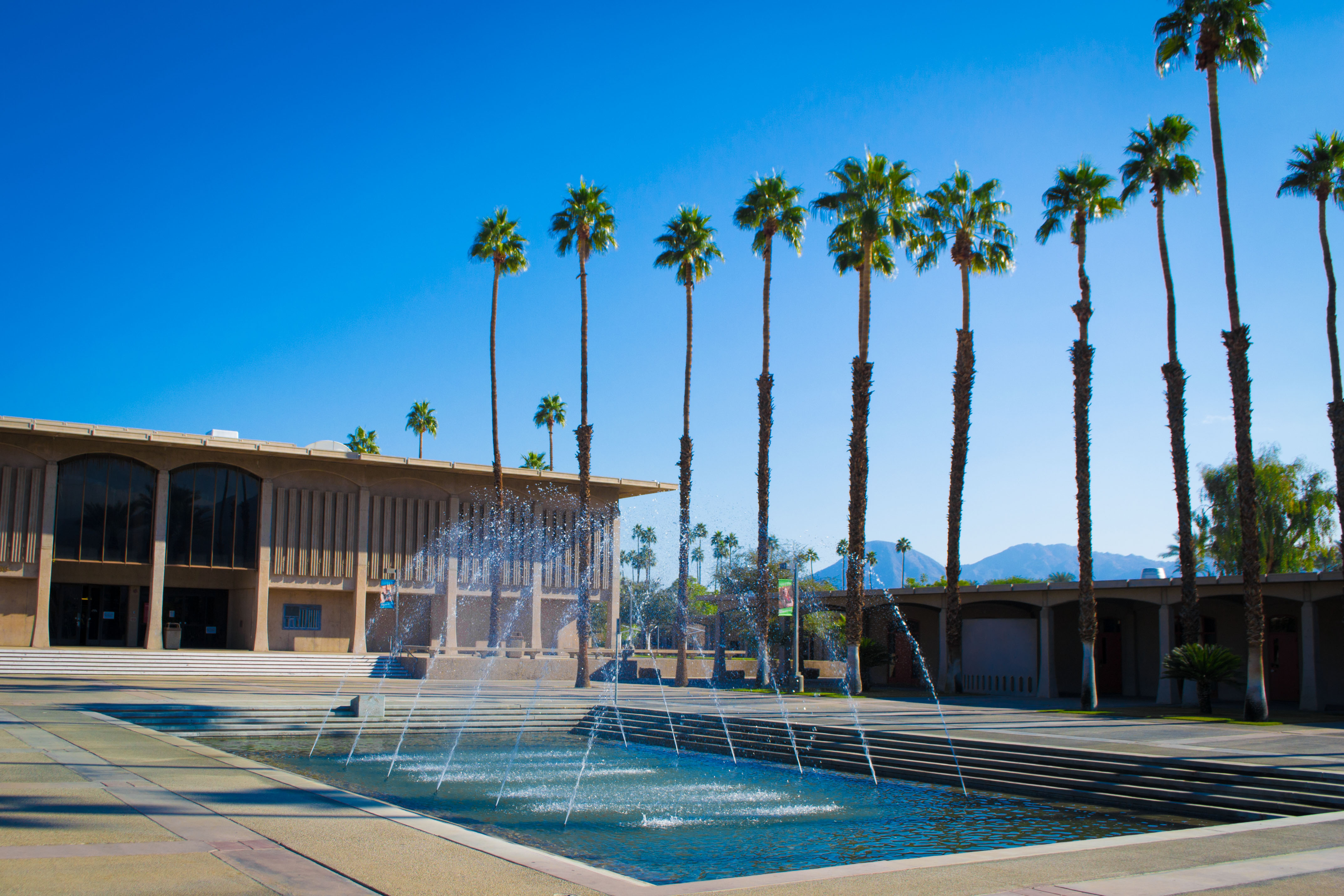
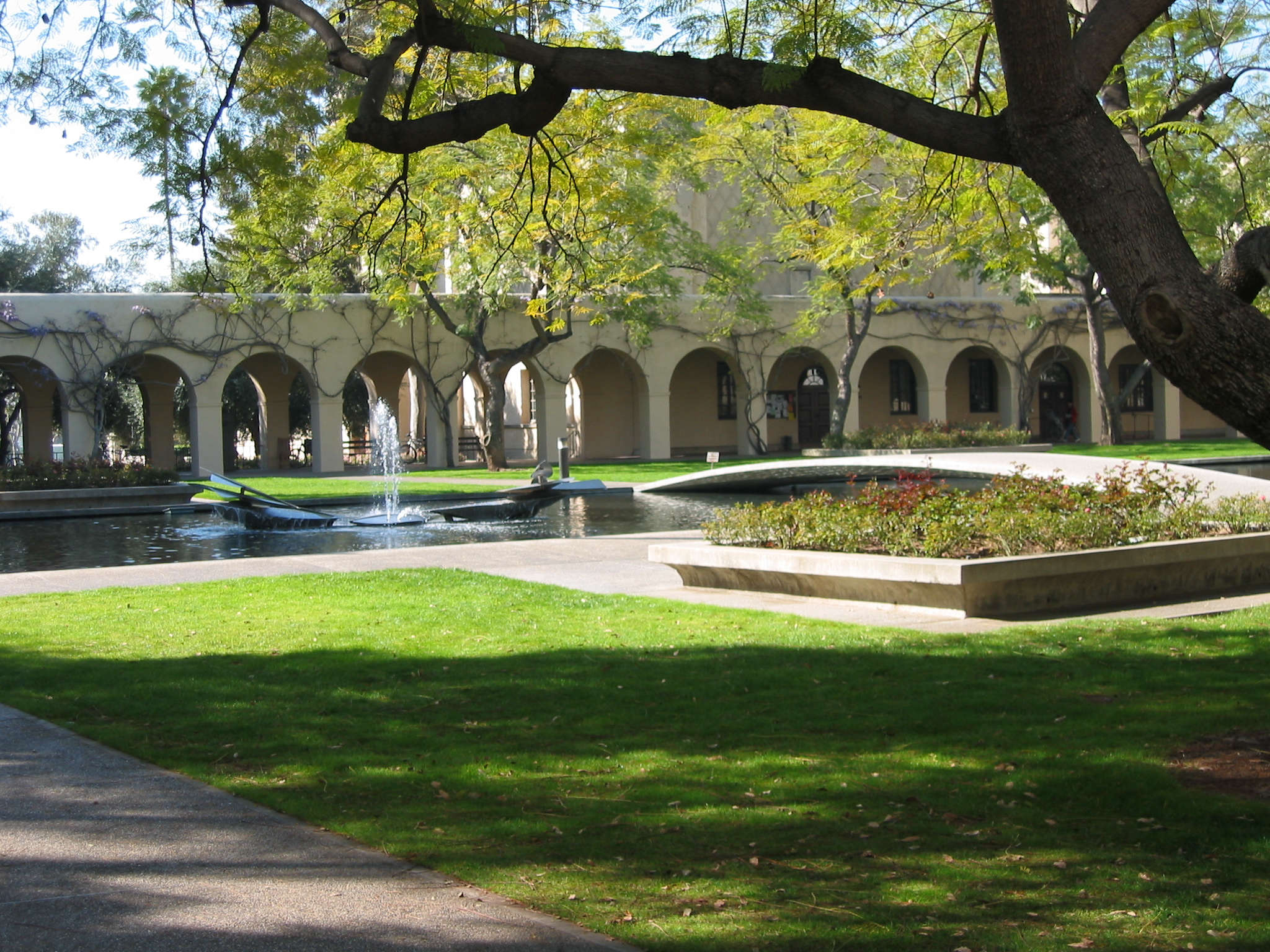
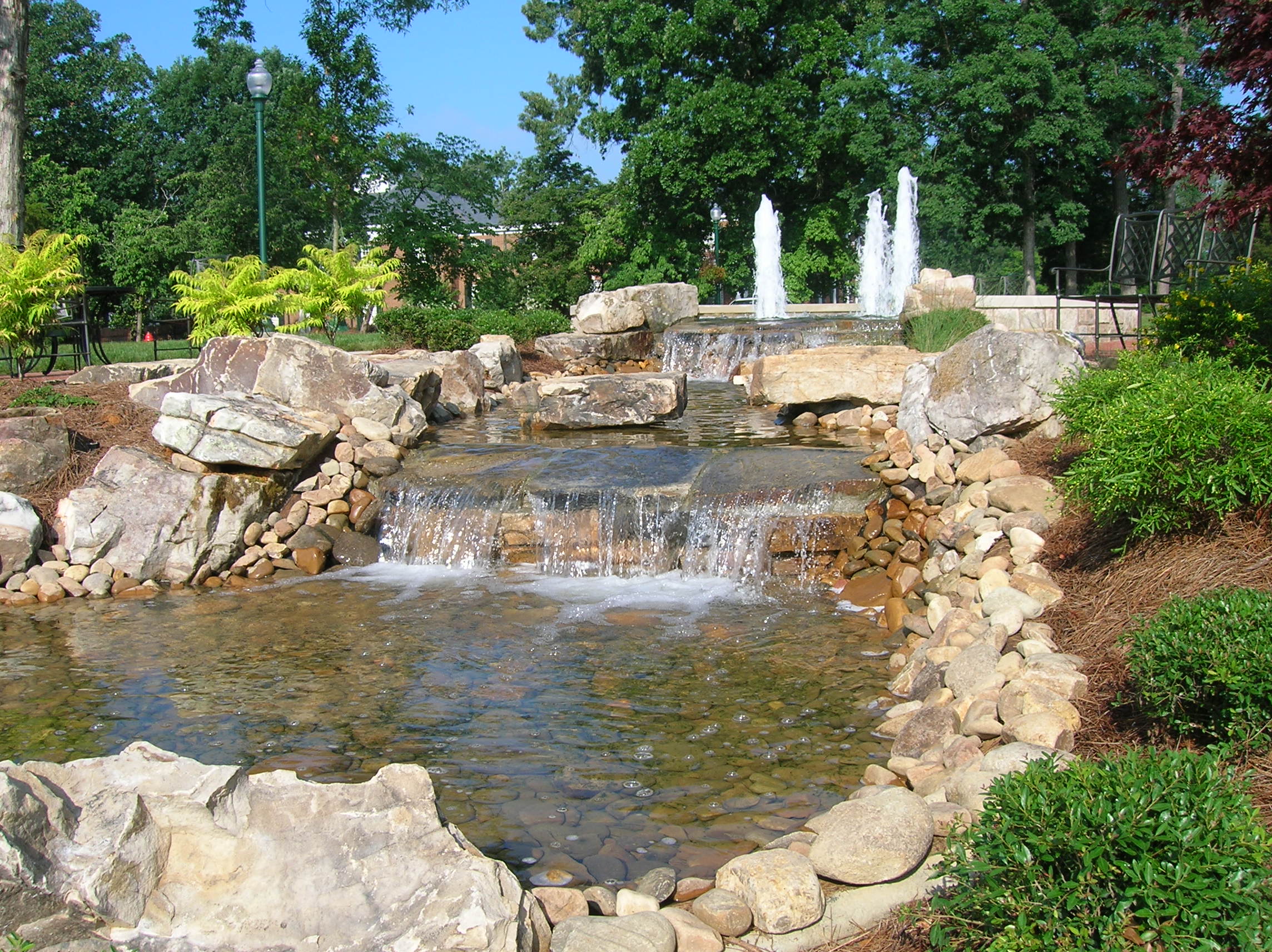
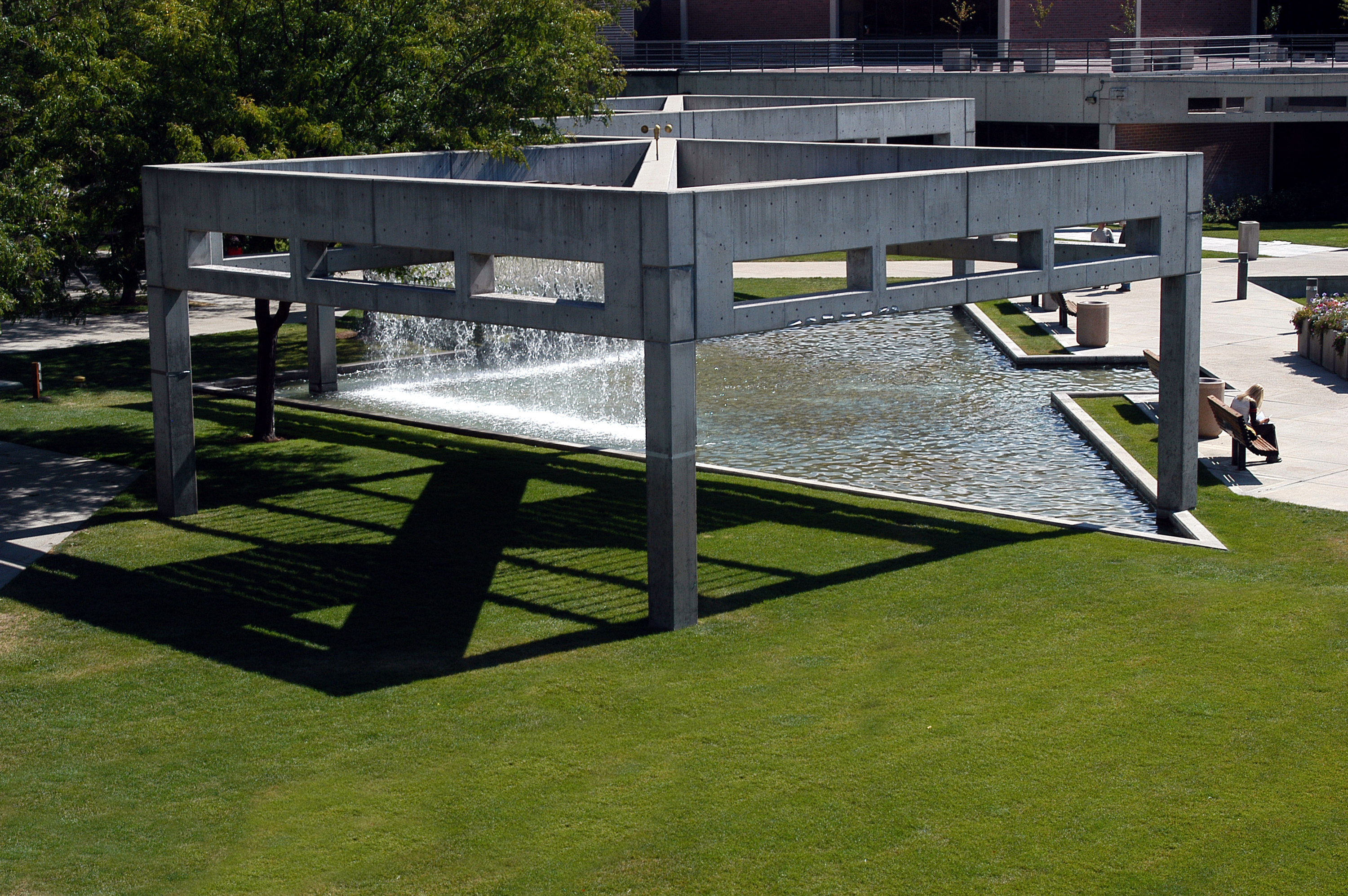
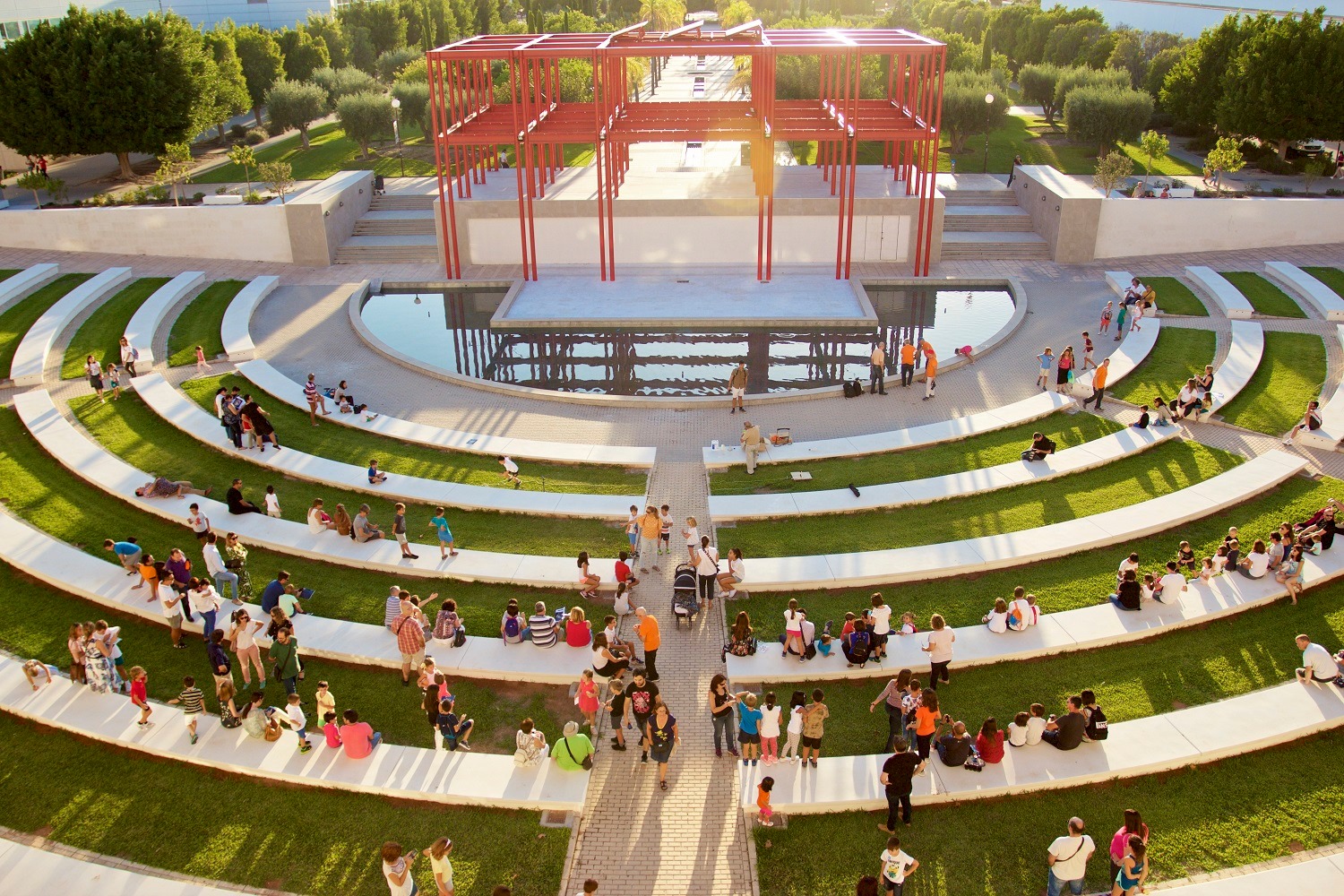
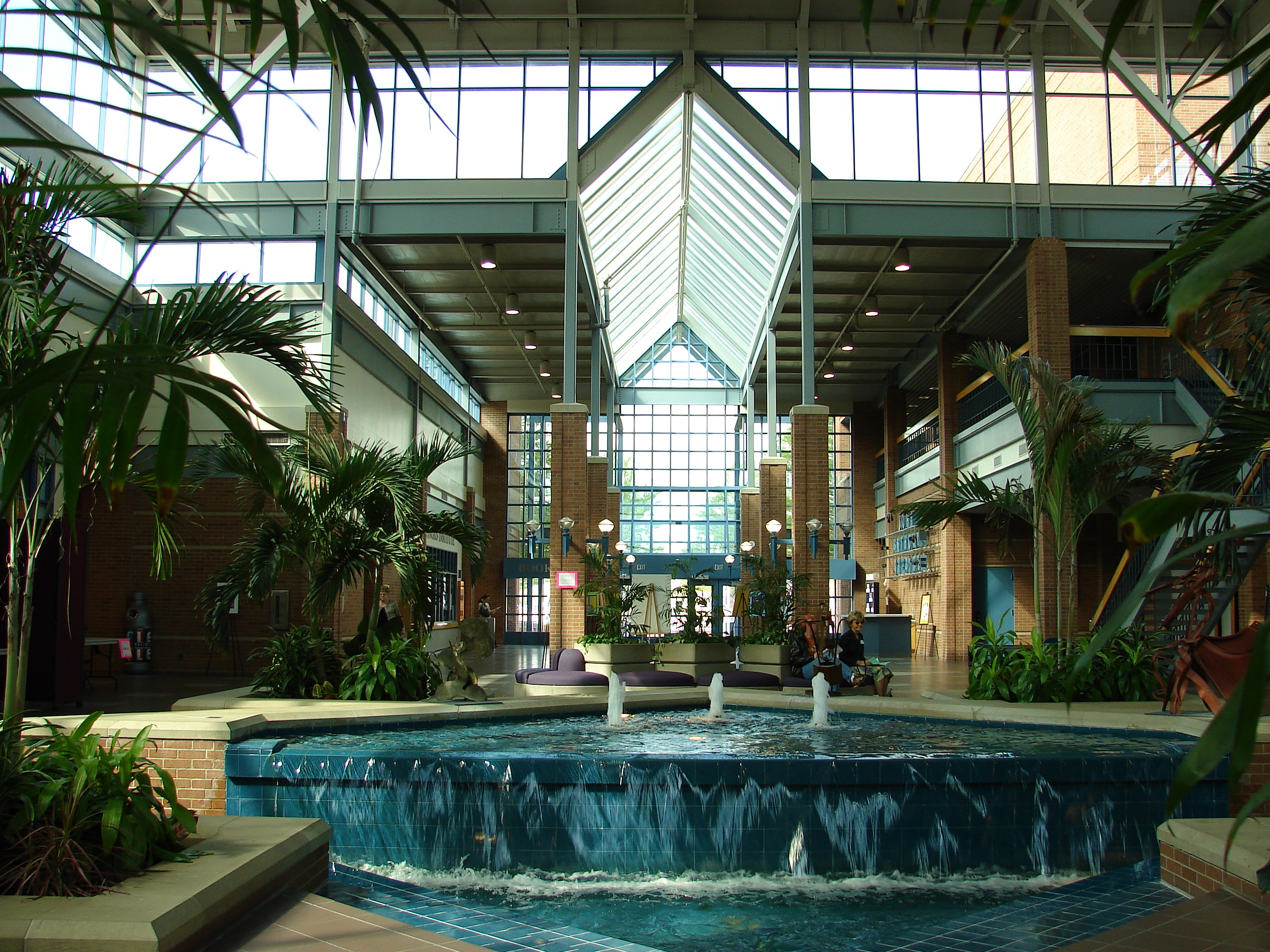
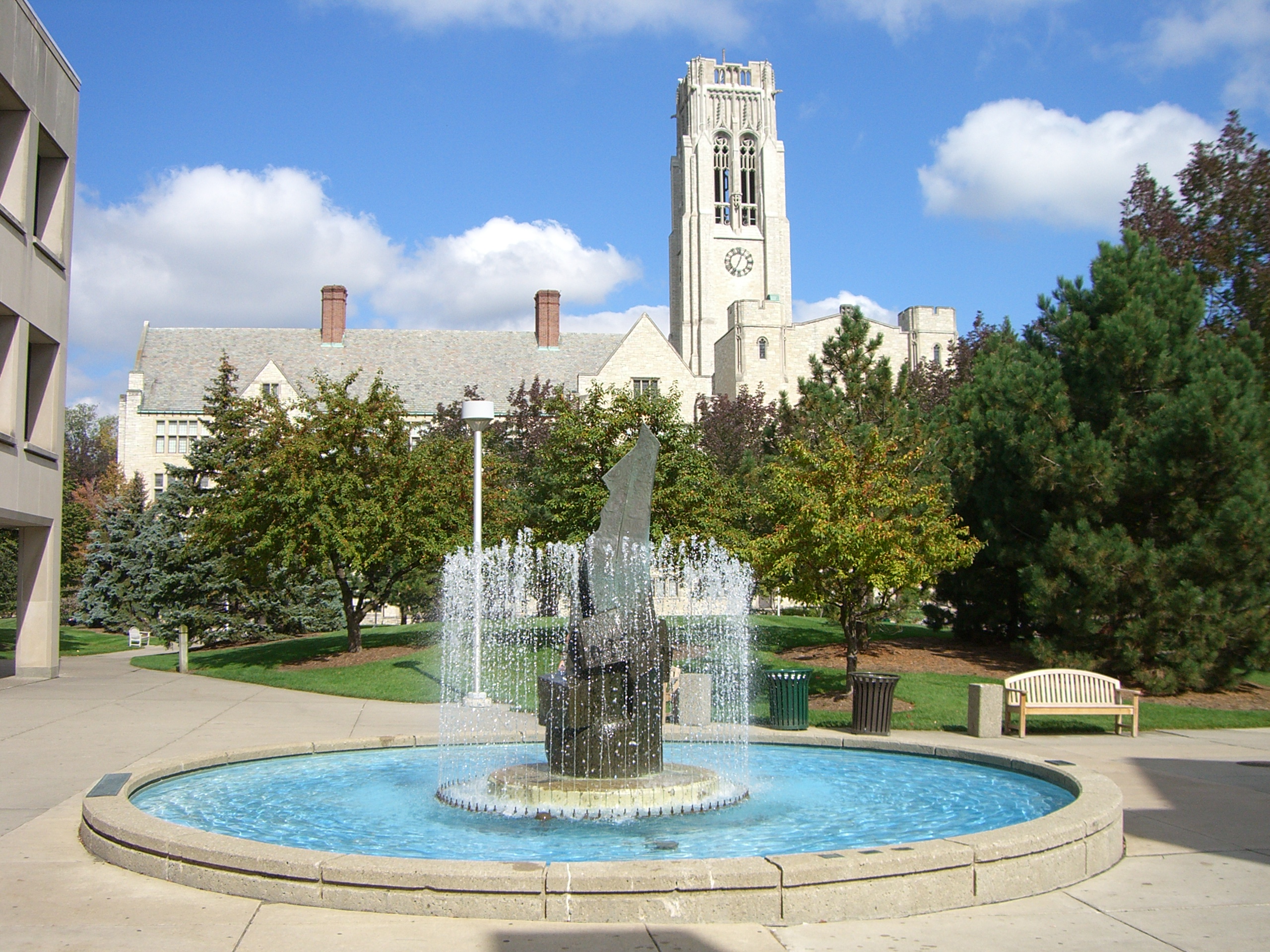
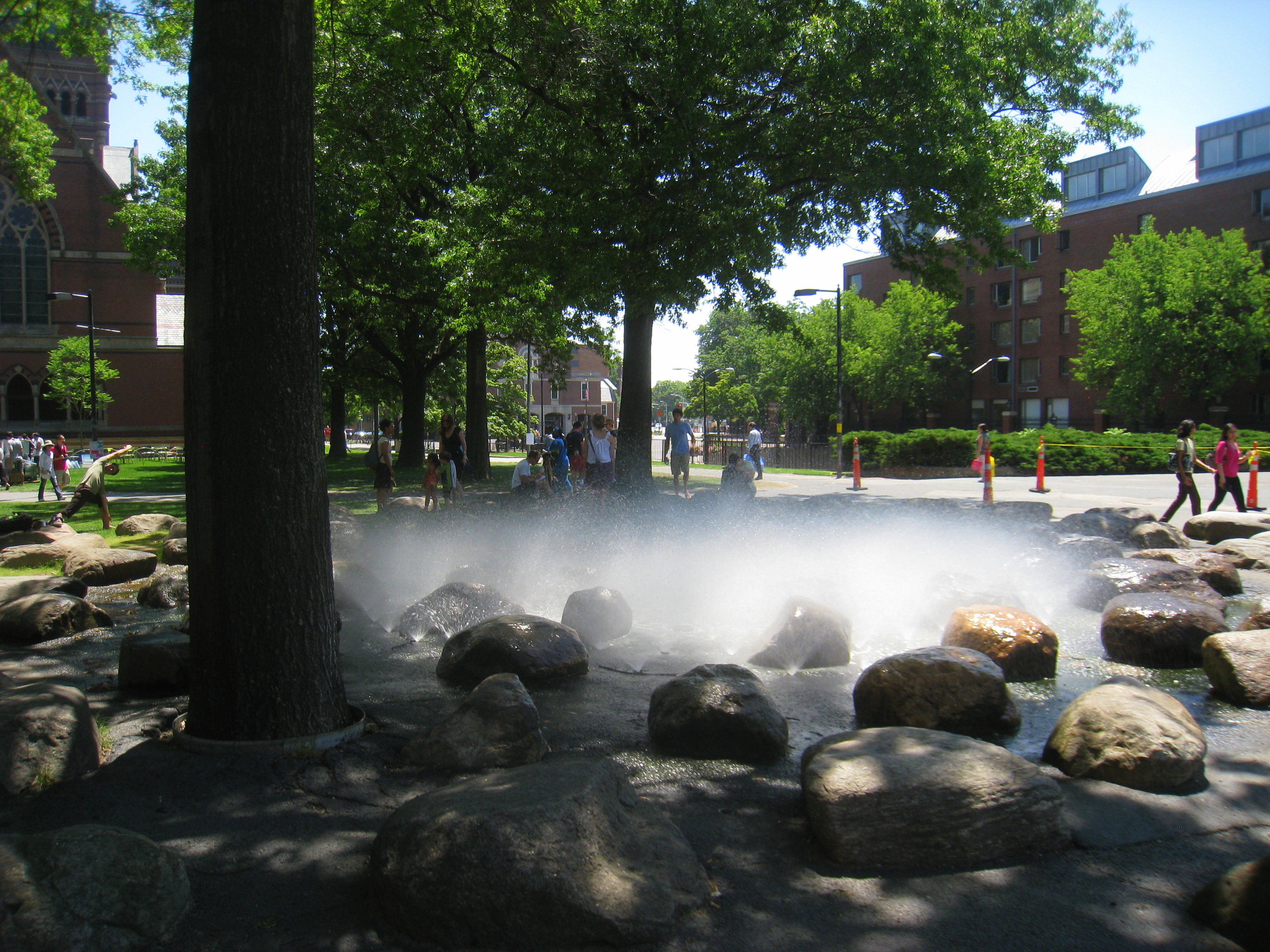
Fountains
From time to time we break from our interest in lowering the cost of our “cities-within-cities” to enjoy the work of our colleagues responsible for seasonal ambience and public art. We have a dedicated post that celebrates the accomplishments of our gardeners and horticultural staff. Today we dedicate a post to campus fountains–a focal point for gathering and a place for personal reflection for which there is no price.
Alas, we find a quickening of standards developing organizations growing their footprint in the spaces around buildings now. They used to confine the scopes of their standardization enterprises to the building envelope. That day will soon be behind us as an energized cadre of water rights social justice workers, public safety, sustainability and energy conservation professionals descend upon campus fountains with prescriptive requirements for evaporation rates, bromine concentrations, training, certification and inspections. In other words regulators and conformity functionaries will outnumber benefactors and fountain designers 1 million to 1.
We will deal with all that when the day comes. For the moment, let’s just enjoy them.
We are happy to walk you through the relevant structural, water safety, plumbing and electrical issues any day at 11 AM EST during our daily standing online teleconferences. Click on any image for author attribution, photo credit or other information.

University of Michigan College of Engineering
Cucumber, Tomato, & Feta Salad
https://www.scu.edu/sustainability/forgegarden/resources/recipes/forge-crafted-recipes/cucumber-tomato–feta-salad.html
Peach Cobbler
Santa Clara University Consolidated Financial Statements | $2.9 billion
Follow #SantaClaraUniversity across platforms to stay up to date with the leading #Jesuit university in #SiliconValley. #DiscoverSCU
📷 Instagram: https://t.co/Vni4SipVEH
👍🏽 Facebook: https://t.co/X1tKW02iZn
💼 LinkedIn: https://t.co/Rhwh4DReVI
😆 TikTok: https://t.co/yqUvfBWbIK pic.twitter.com/mrYtn6G0O6— Santa Clara Univ (@SantaClaraUniv) November 20, 2022
🍑 season is here!! pic.twitter.com/sFVK62dXUk
— Holly (@HTAgronomy) August 9, 2024
Bucolia 400
I hear it in the deep heart’s core.
— William Butler Yeats
Today we walk through literature governing the safety and sustainability of the open space features of education community estates. Unlike the titles for the building envelope, which are known to most design professionals and contractors, the standards for grounds and landscaping are widely scattered; many of them occupational safety related; created, administered and enforced by units of government.
Bucolia 100. We present a broad overview of the dominant standards catalogs incorporated by reference into public safety and sustainability legislation.
Bucolia 200. We drill into technical specifics of the titles in Bucolia 100.
Bucolia 400. We pick through case studies in landscape, garden, tree and water literature. We also track titles about the reclamation of building roofs for permeable surfaces and gardens.
During the winter months (Bucolia 200) in the northern hemisphere we include snow and ice management; while covering summer month technologies for southern hemisphere (and vice-versa). Snowfalls in the southern hemisphere are mainly contained to the highlands and mountain ranges, which are almost exclusively in Victoria and Southern New South Wales, as well as the mountains in Tasmania. Winter does not pose as much of a cost burden to education facilities in the southern hemisphere as it does in the northern hemisphere.
|
Landscape standards refer to guidelines or regulations that specify the requirements for the design, installation, and maintenance of outdoor spaces such as parks, gardens, streetscapes, and public spaces. Landscape standards typically cover various aspects of landscape design, including vegetation selection, planting arrangements, irrigation systems, hardscape materials, and lighting. These standards may be set by government agencies at the federal, state, or local level, or by professional organizations such as the American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA). Landscape standards aim to ensure that outdoor spaces are safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing while also promoting sustainability and environmental protection. Landscape standards may also address issues such as accessibility for people with disabilities, water conservation, stormwater management, and erosion control. They may vary depending on the specific location, climate, and intended use of the outdoor space. Compliance with landscape standards may be required for approval of development projects, public funding, or other permits. |
We track the standards catalog of two ANSI-accredited standards developers:
Tree Care Industry Association
Additional practice titles applicable to accessory systems:
ASABE/ICC 802 Landscape Irrigation Sprinkler and Emitter Standard
ASHRAE 90.1 Energy Standard for Sites and Buildings
Golf Course Superintendents Association of America
National Electrical Code: Article 411 Low-Voltage Lighting
National Electrical Code: Article 225: Outside Branch Circuits and Feeders
Illumination Engineering Society (Lighting Library)
Land F/X: Landscape Lighting, Codes, Guidelines and Techniques
OSHA Landscape and Horticultural Services
Sports Turf Managers Association
As a cross-cutting subjectSports Turf Managers Association ( involving soil and water and sun many other standards developers, and all levels of government, produce best practice literature for today’s topic. We’ll have a look at what’s moving among those.
To join us use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.














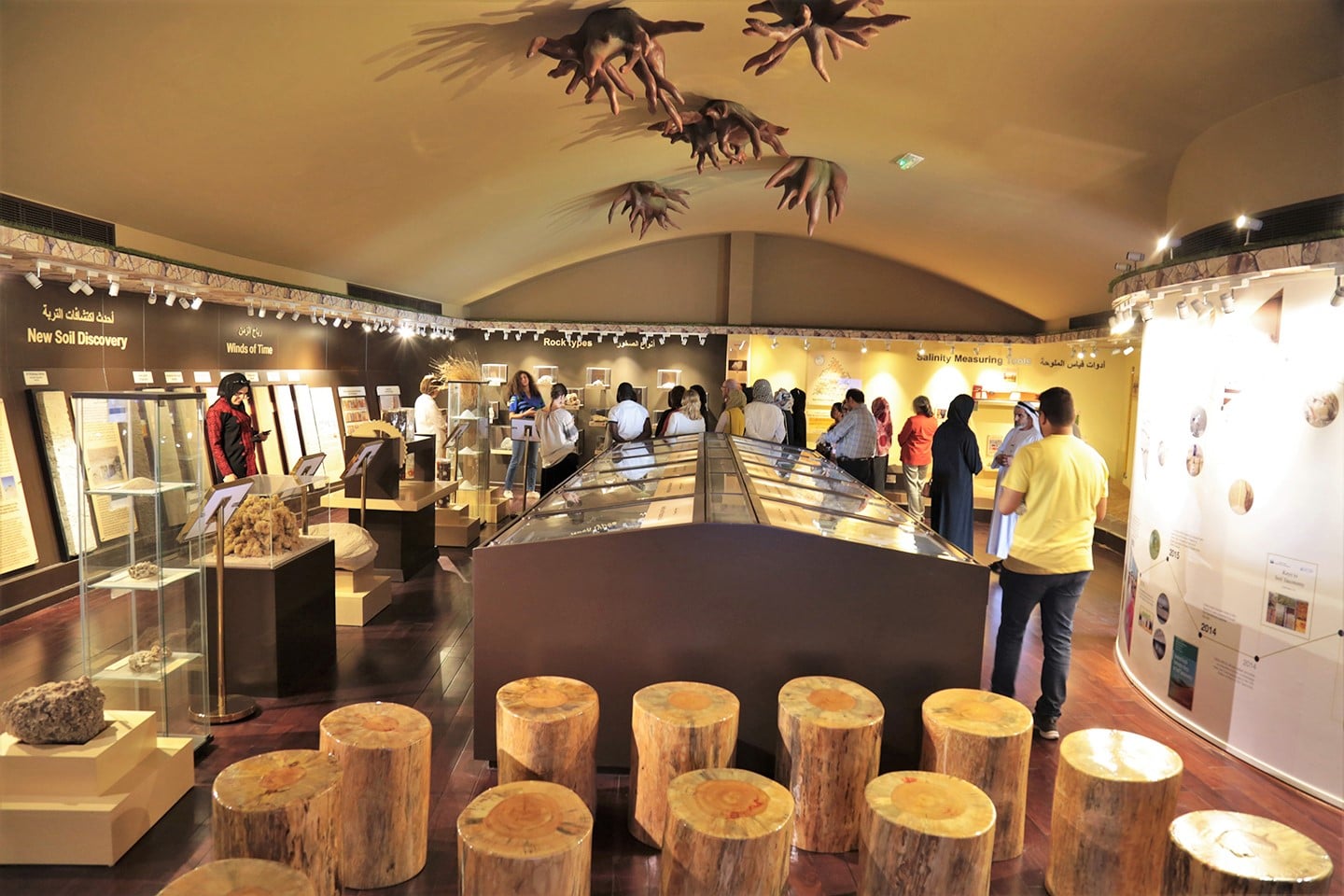
World Soil Museum
The World Soil Museum hosts a range of educational programs and workshops for students, researchers, and other visitors who are interested in learning more about soil science. These programs cover topics such as soil classification, soil management, and soil conservation, and they are designed to help people understand the vital role that soils play in supporting agriculture, ecosystems, and human societies around the world.
Captain Kangaroo
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Fire Safety
Fire safety leadership usually finds itself involved in nearly every dimension of risk on the #WiseCampus; not just the built environment but security of interior spaces with combustibles but along the perimeter and within the footprint of the education community overall.
The Campus Fire Marshal, for example, usually signs the certificate of occupancy for a new building but may be drawn into meetings where decisions about cybersecurity are made. Fire protection systems coincide with evacuation systems when there is no risk and both may be at risk because of cyber-risk.
The job description of a campus fire safety official is linked below offers some insight into why fire safety technologies reach into every risk dimension:
University of California Santa Cruz Office of Emergency Services
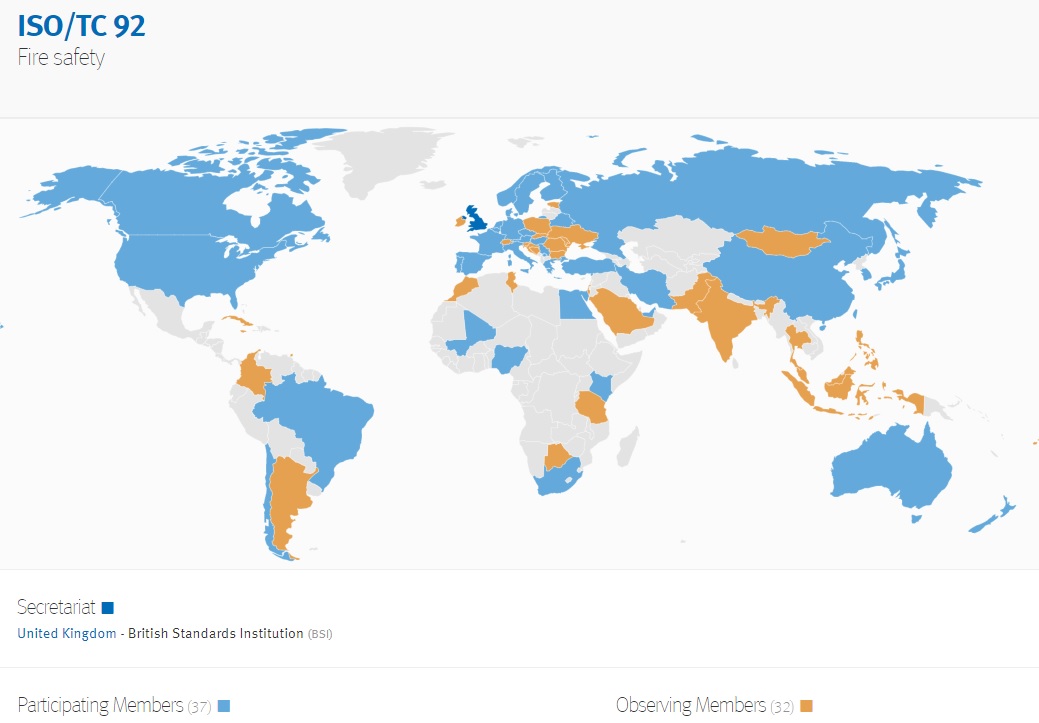
The development of the highest level fire safety consensus product in the world is led by the British Standards Institute, under the administration of the International Standardization Organization, with Committee E05 on Fire Standards of ASTM International as the US Technical Advisory Group Administrator. The business plan and the map of global participants is linked below:
BUSINESS PLAN ISO/TC 92 Fire safety EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The consensus products developed by TC 92 are intended to save lives, reduce fire losses, reduce technical barriers to trade, provide for international harmonization of tests and methods and bring substantial cost savings in design. ISO/TC 92 standards are expected to be of special value to developing countries, which are less likely to have national standards. As with all ISO standards, the TC 92 consensus product is a performance standard suitable for use in prescriptive regulations and provide for a proven route to increased fire safety.
We do not advocate in this standard at the moment; we only track it. The International Fire Code and the Fire Code have been our priorities since 2006. The fire safety space is well populated with knowledgeable facility professionals because conformity budgets in the fire safety world — i.e. the local or state fire marshal — usually has a budget. When you have a budget you usually have people keeping pace with best practice.
We encourage our colleagues in the United States on either the business or academic side of the education facility industry to communicate directly with ANSI’s ISO Team and/or the ASTM Contact: Tom O’Toole, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959 Phone: (610) 832-9739, Email: totoole@astm.org
We maintain this title on the agenda of our periodic Global and Prometheus colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [19-104]
Category: Fire Safety, Fire Protection, International
Contact: Mike Anthony, Joe DeRosier, Alan Sactor, Joshua Elvove, Casey Grant
More:
The Challenges of Storage and Not Enough Space, Alan Sactor
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670