Category Archives: Lively Arts / Media
- Home
- Archive by category "Lively Arts / Media" (Page 2)

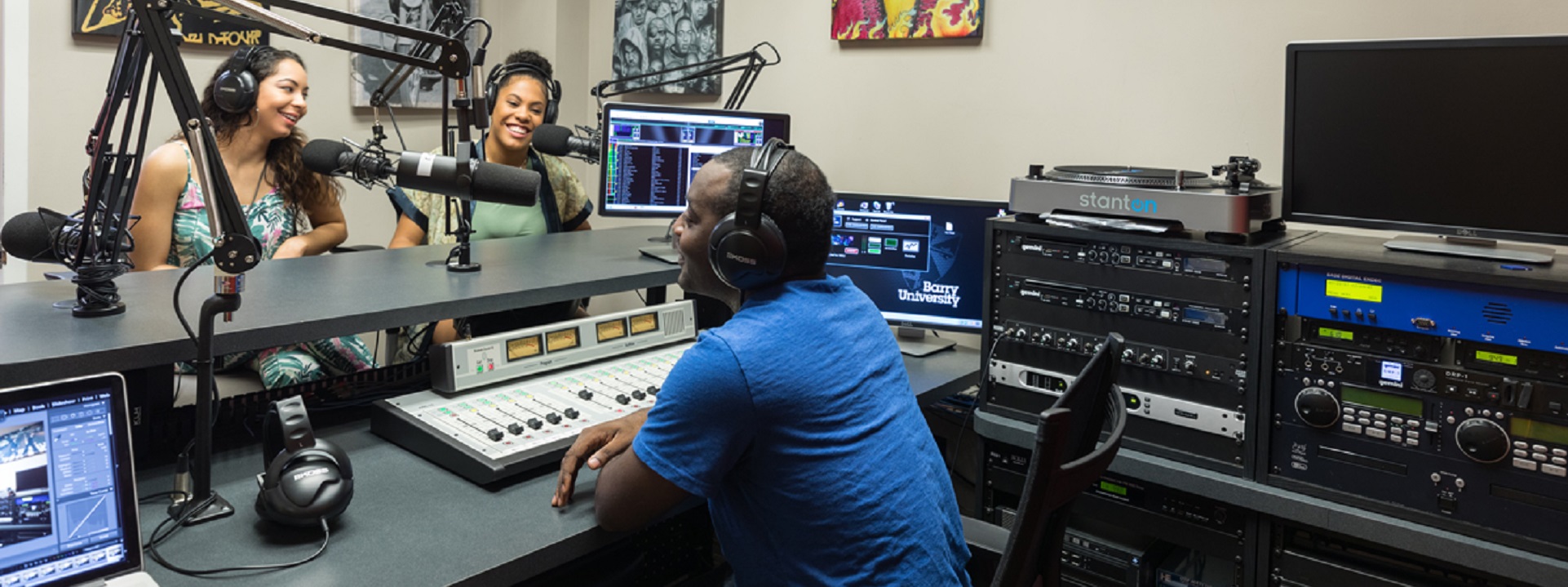
Podcast Production
The term “podcast” is a combination of “iPod,” Apple’s portable media player, and “broadcast.” It originated in the early 2000s when individuals began creating audio content specifically designed for download and playback on portable media players, including the iPod. Over time, the concept has evolved, and podcasts are now a popular and diverse form of digital media covering a wide range of topics, including news, education, entertainment, and more. The key feature of a podcast is its on-demand nature, allowing listeners to access content at their convenience.
Drive Time Bias By Omission
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
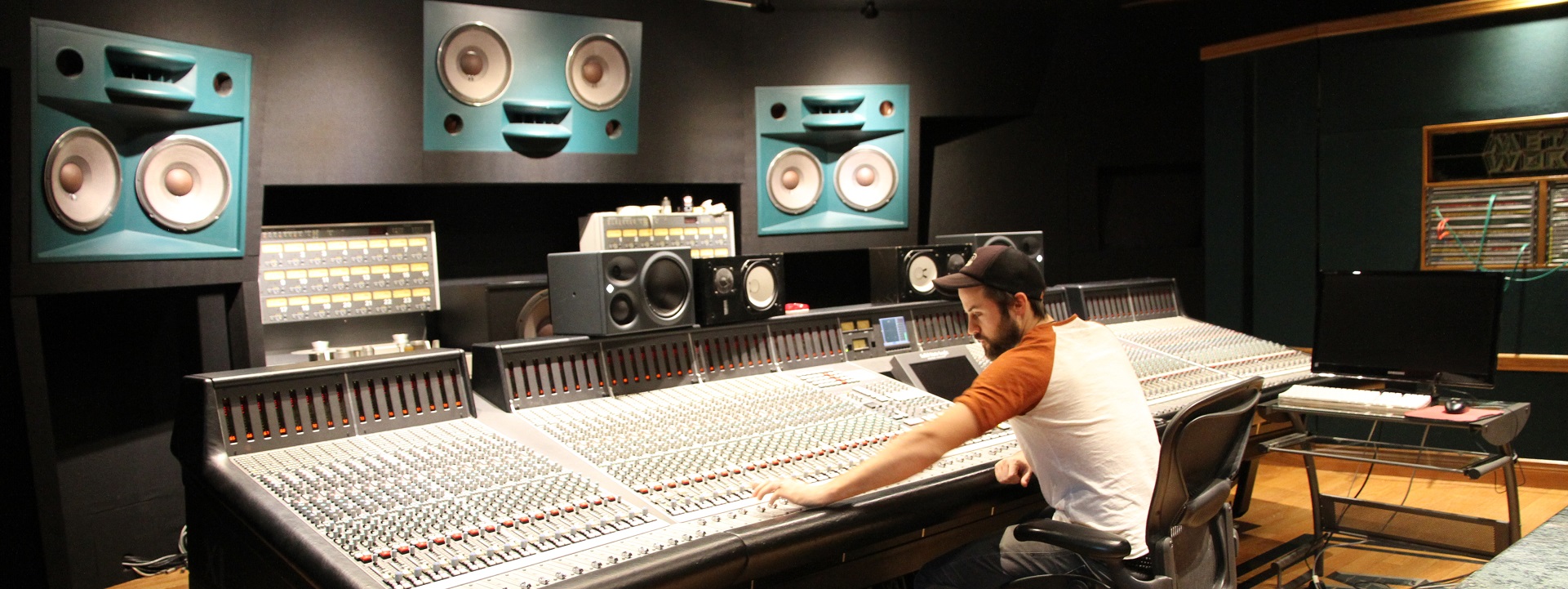
Audio Standards
“The voice of the intellect is a soft one,
but it does not rest until it has gained a hearing.”
— Sigmund Freud
The education industry provides a large market for occupancy classes — athletic stadiums, student assembly spaces, performance theaters, large lecture halls– that depend upon effective audio systems*. To an unexpected degree the structural engineering, specification of materials and electrical system design and operation is informed by acoustical considerations. So does the integration of fire safety and mass notification systems into normal state enterprises so it is wise to follow and, ideally, participate in leading practice discovery and promulgation of audio standards.











The Audio Engineering Society — one of the first names in this space — has a due process platform that welcomes public participation. All of its standards open for public comment completed their revision cycle mid-November as can be seen on its standards development landing page below:
Note that AES permits access to those revision even after the comment deadline. You are encouraged to communicate directly with the Direct communication with the standards staff at Audio Engineering Society International Headquarters, 551 Fifth Avenue, Suite 1225, New York NY 10176, Tel: +1 212 661 8528
We keep the AES suite on the standing agenda of our periodic Lively Arts teleconference. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
This facility class is one of most complex occupancy classes in education facilities industry so we also collaborate with experts active in the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee. Much of the AES suite references, and borrows from, International Electrotechnical Commission system integration and interoperability standards. The IEEE E&H committee meets online again four times monthly in European and American time zones. The meeting dates are available on the IEEE E&H website




Issue: [19-23]
Category: Electrical, Academic, Athletics, Fire Safety, Public Safety, #WiseCampus
Contact: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey
*Mass notification systems are governed by NFPA 72 and, while life safety wiring is separate from other wiring, the management of these systems involve coordination between workgroups with different business objectives and training.
LEARN MORE:
The AES welcomes new Executive Director, Colleen Harperhttps://t.co/r7DfPp6wfE#AESorg #proaudio #audioengineer pic.twitter.com/nTKBf8oHeR
— Audio Engineering Society (@AESorg) January 16, 2019
Requirements for Hybrid Media Production
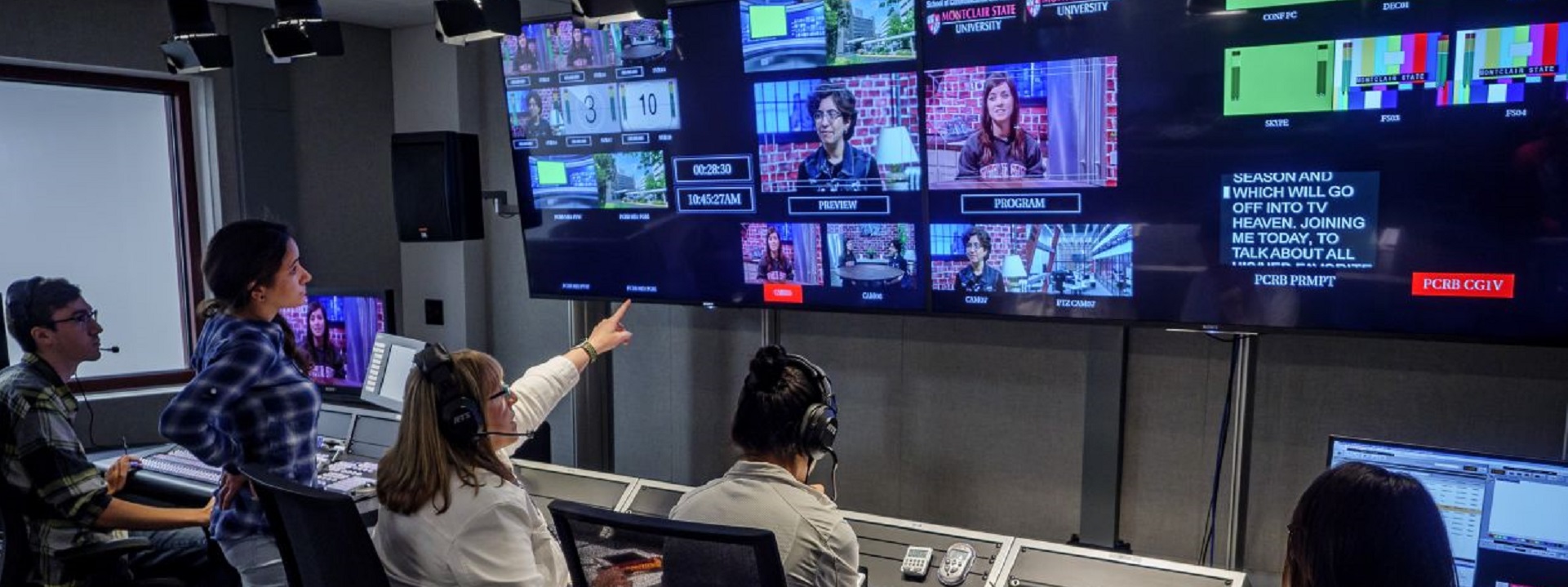
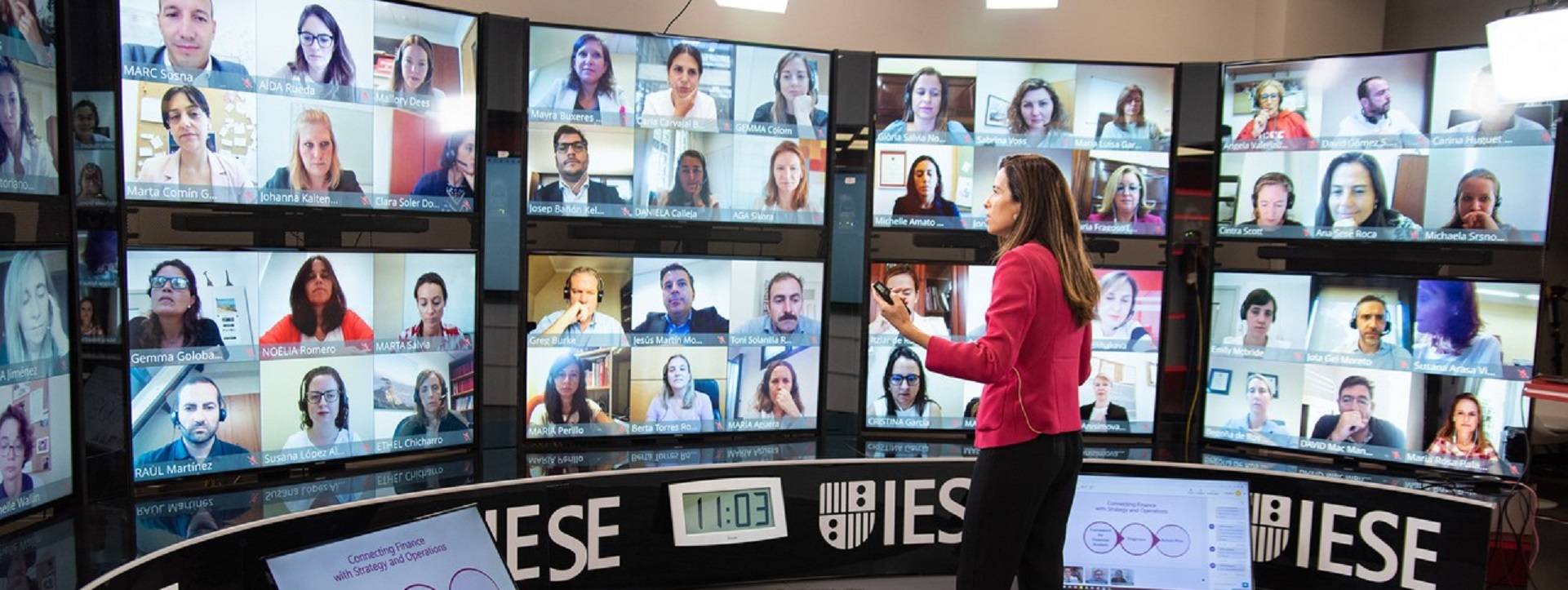
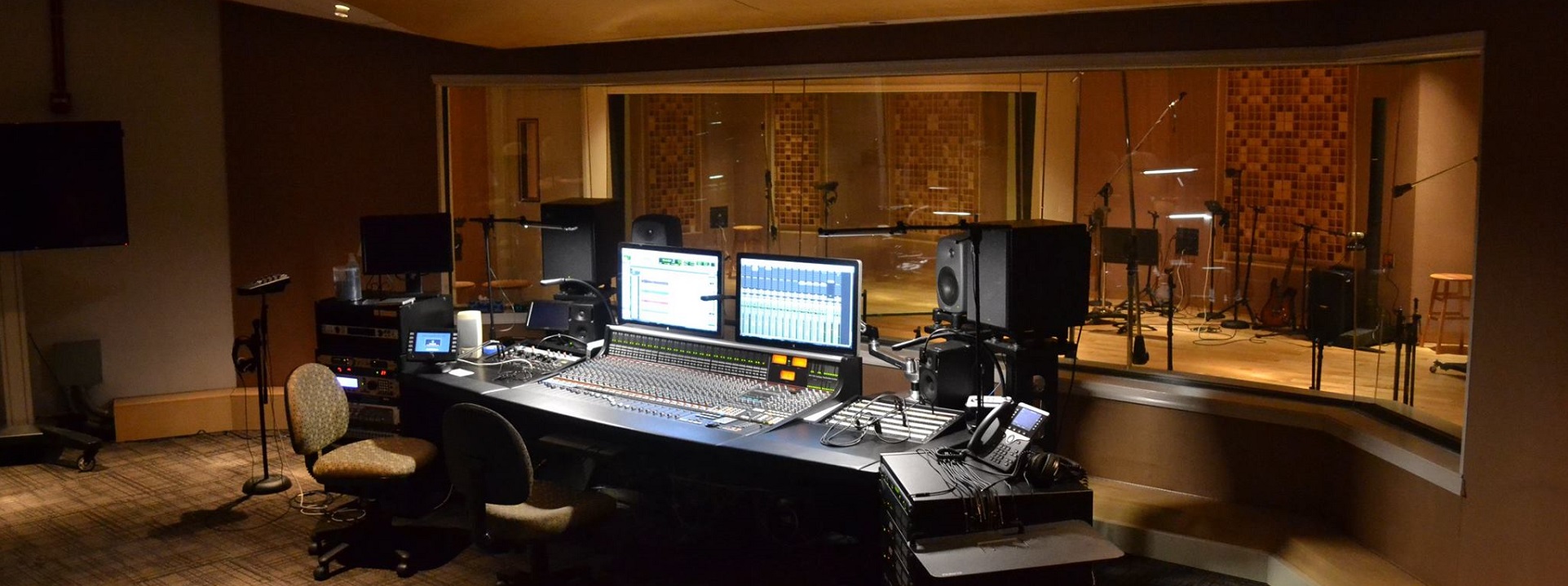






Requirements for the Hybrid Media Production Facility of the Future
Mike Strein – Karl Paulsen
Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers
Abstract: People who began their careers in television broadcasting before the 1990s should have seen television and media technical infrastructures endure three significant transitions: standard definition (SD) analog to SD digital; SD digital to high definition (HD) digital; and HD digital to media carried over an Internet Protocol (IP) network in multiple formats. Each transition involved either an infrastructure replacement or a complete rebuild of their technical facilities. Most of the gear and much of the cabling likely had to be replaced, updated, or refined. As changes to the system were made, compressed video, storage, and data management adjusted accordingly. New terminologies evolved, sometimes heightened by “marketing hype,” that drove users to amend workflows, processes, and capital budgets like revolving doors in a hotel.
We live in an age of continual transformation where formats, transport methods, and delivery have moved in full strength to yet another dimension—the era of IP. Yet again the industry is being thrust into yet another significant change in infrastructure, which now includes cloud, realtime over-the-top (OTT) streaming, and virtualization. How does one design a facility for these kinds of transitions without needing a forklift upgrade every decade? These are serious topics that impact return on investment (ROI), timing, and capital versus operational alterations. This article examines new hybrid models for media production, explores their components, and gives examples of how to compose the media future for live production environments at the studio and enterprise levels.
CLICK HERE to order complete paper
Have you seen the renovations to the @COMatBU studios yet? Students and faculty are super excited by a half-a-million dollar investment in Studio West, podcast studios, and more.
Take a look ➡️https://t.co/N3VPyTD8BY pic.twitter.com/kWFWxH8eLD
— Boston University (@BU_Tweets) September 25, 2023
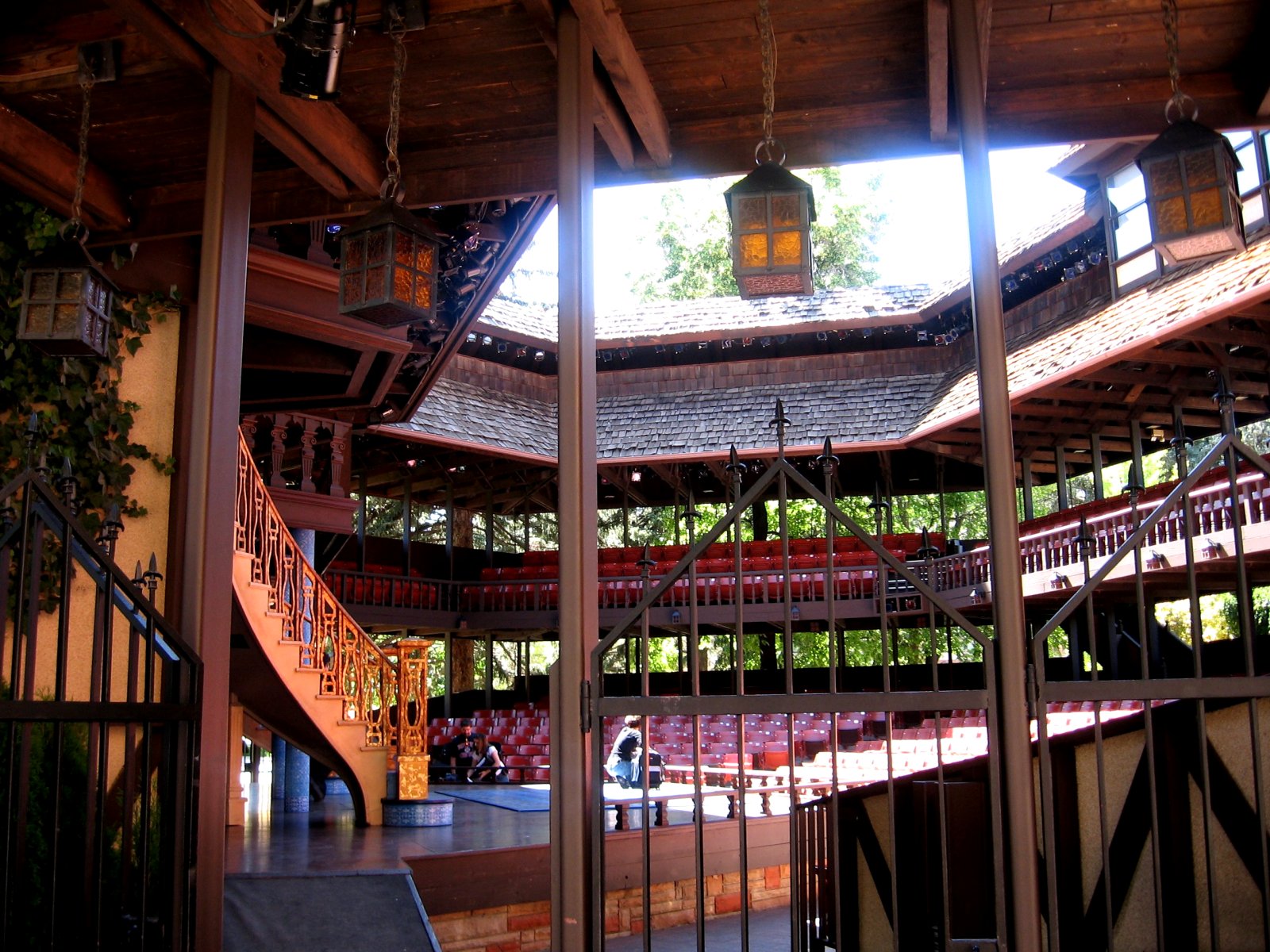
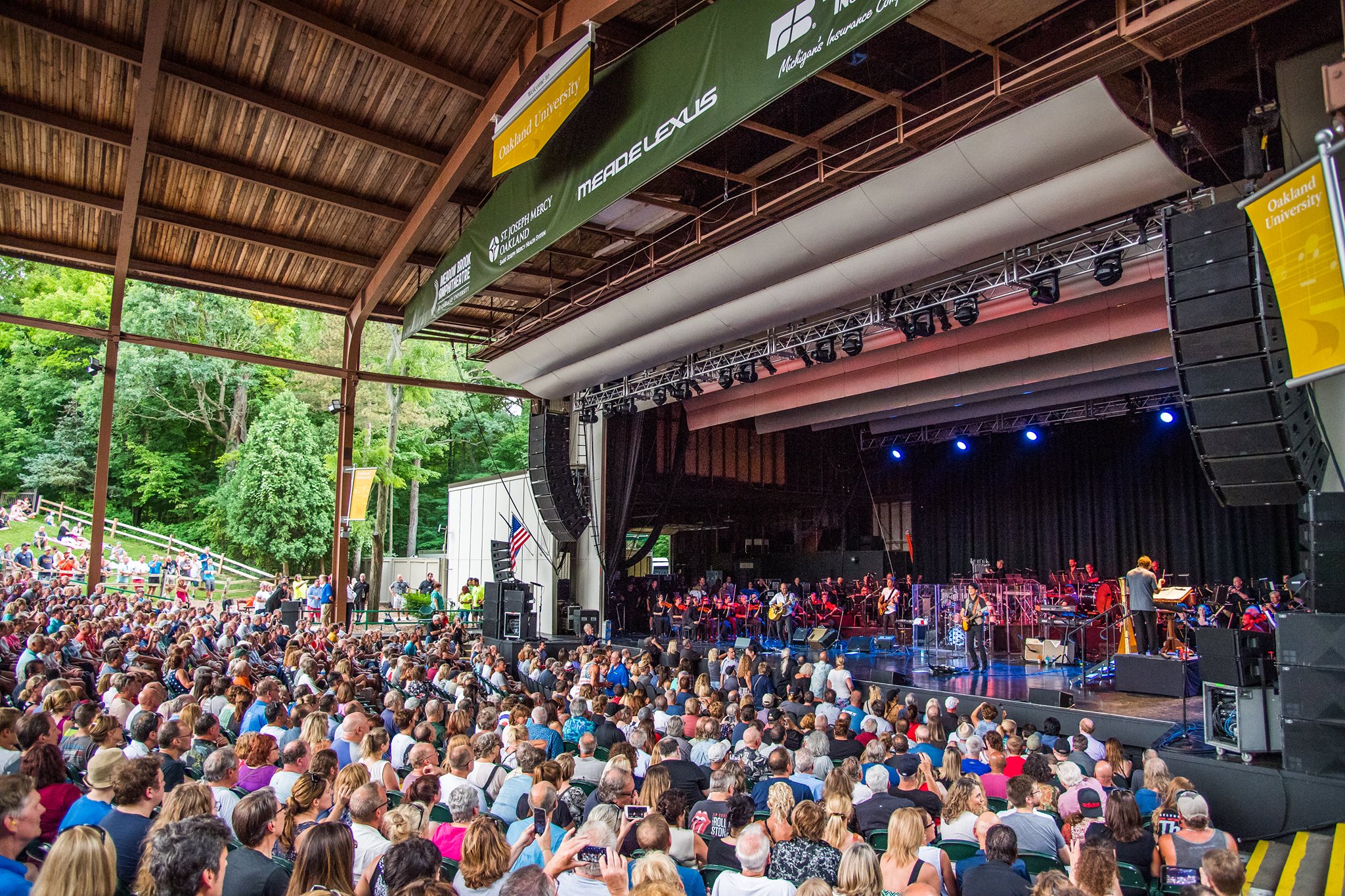
Stage Technical Standards for Outdoor Live Performance Theater
Theatre: Lighting Design
Artificial lighting was first introduced to theater dramatic performance stages in the 17th century. The use of candles and oil lamps initially provided a means to illuminate the stage, allowing performances to take place in the evening and enhancing the visibility for both actors and the audience. Before this development, theatrical performances were typically held during daylight hours due to the reliance on natural light.
In the early 17th century, theaters in England began experimenting with various lighting techniques. Thomas Killigrew’s Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, in London, is often credited as one of the first theaters to use artificial lighting. The use of candles and later oil lamps evolved over time, leading to more sophisticated lighting setups as technology advanced.
The 18th and 19th centuries saw further innovations in stage lighting, including the use of gas lamps. Eventually, the introduction of electric lighting in the late 19th and early 20th centuries revolutionized stage lighting, providing theaters with a more reliable and controllable source of illumination. This allowed for greater creativity in the design and execution of lighting effects, contributing significantly to the overall theatrical experience.
More
Stage Lighting 101 — Everything You Need to Know
Boston University: Theater, Lighting Design
Wayne State University: Lighting Design
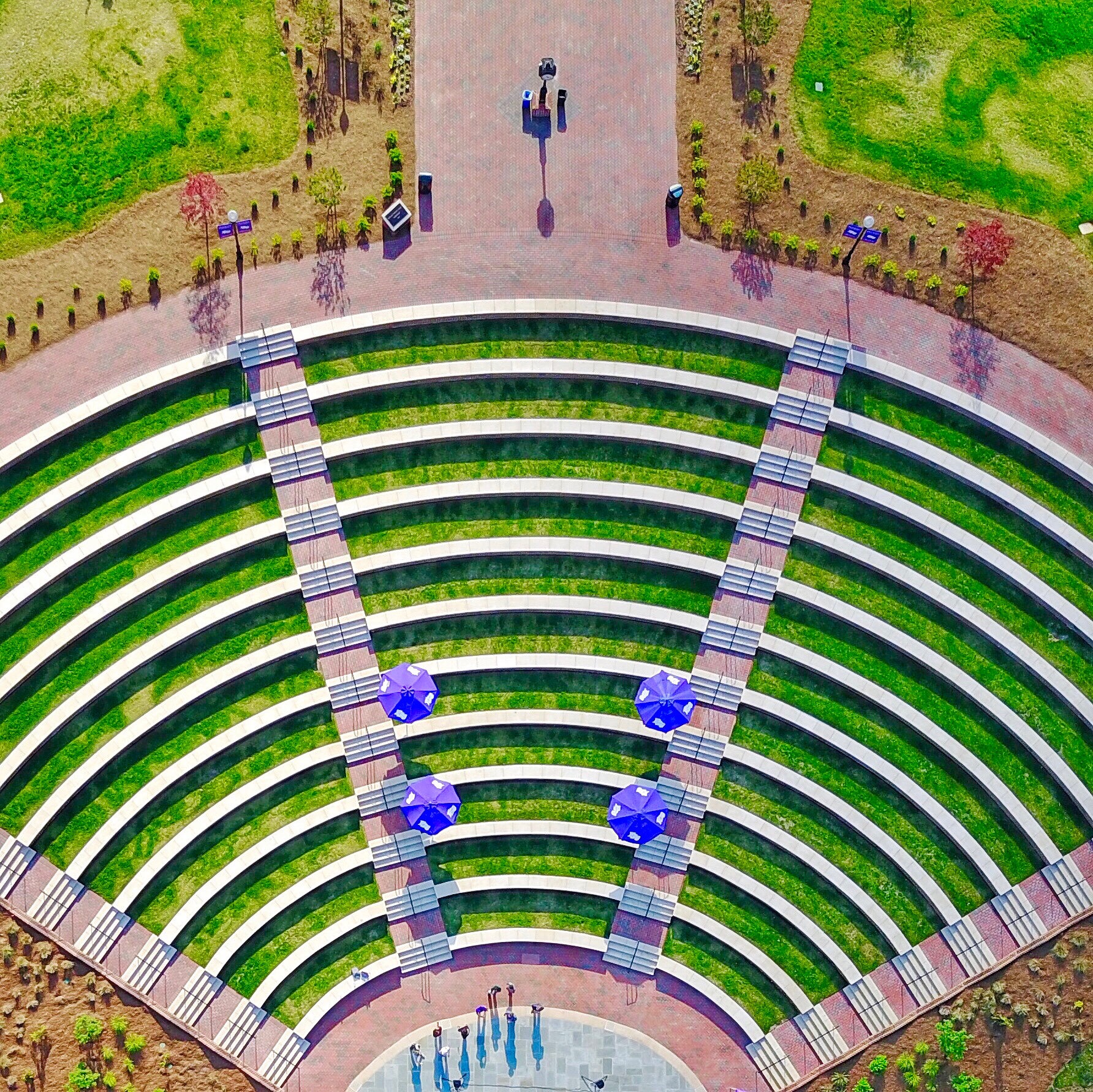
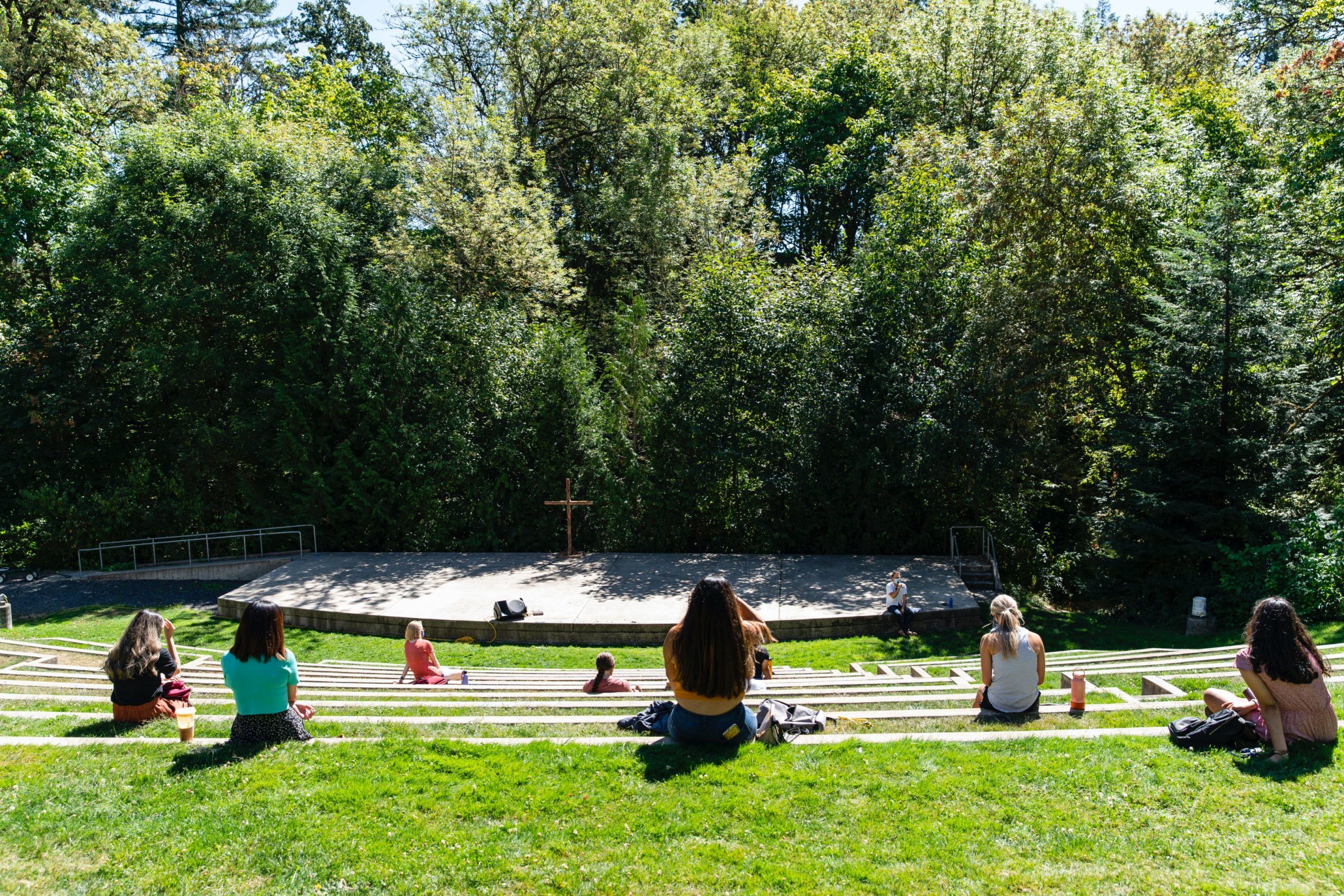
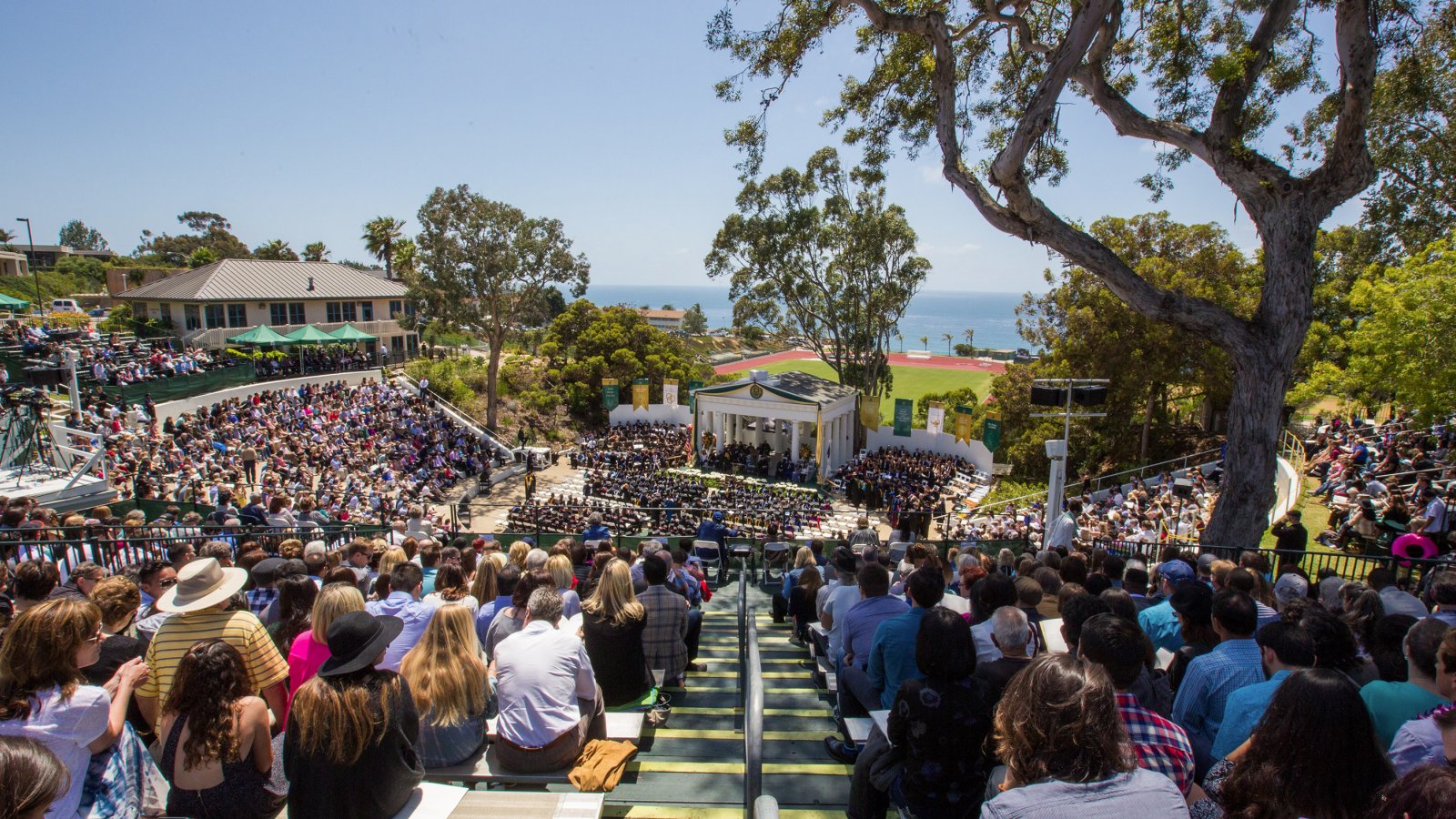
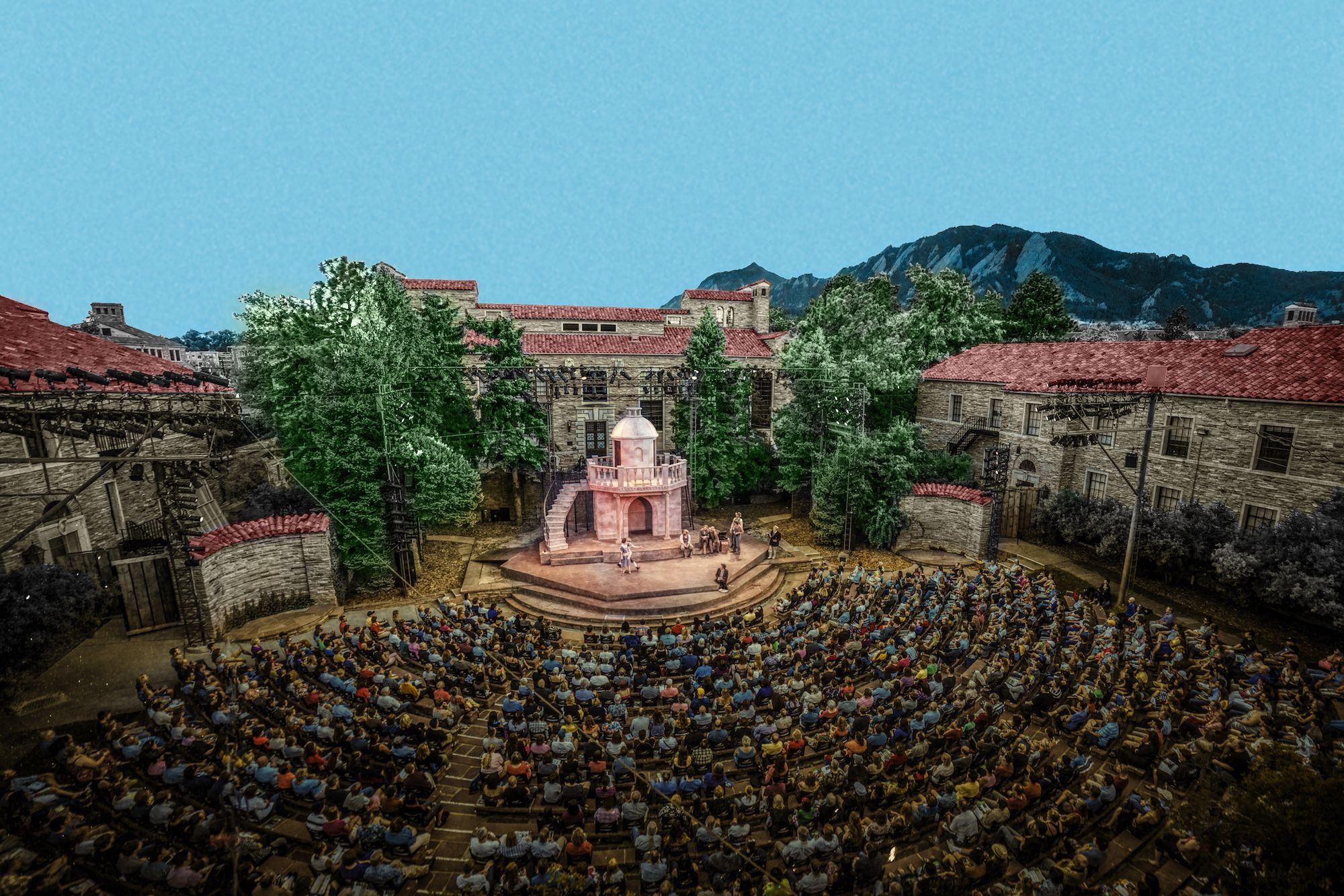
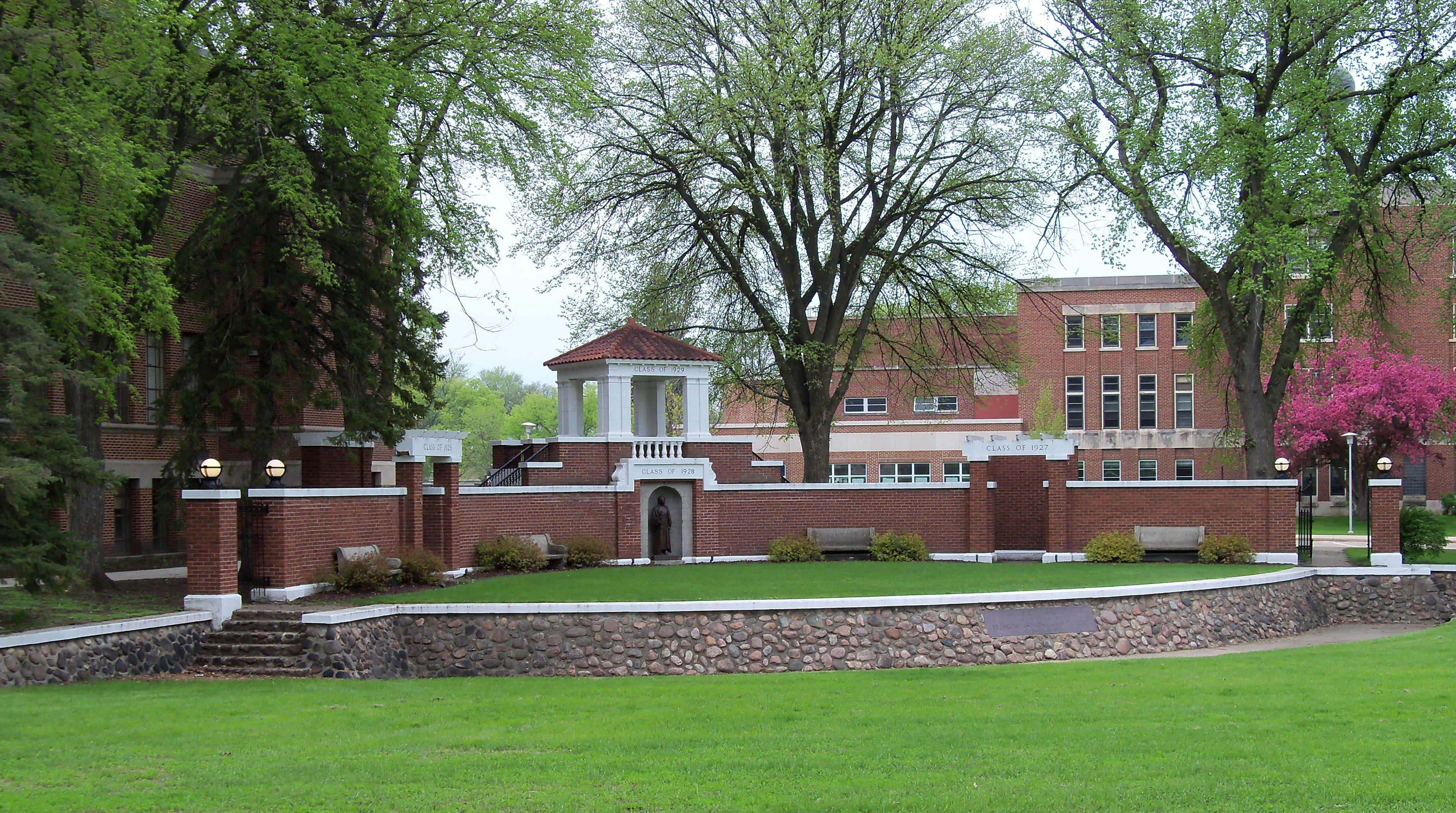
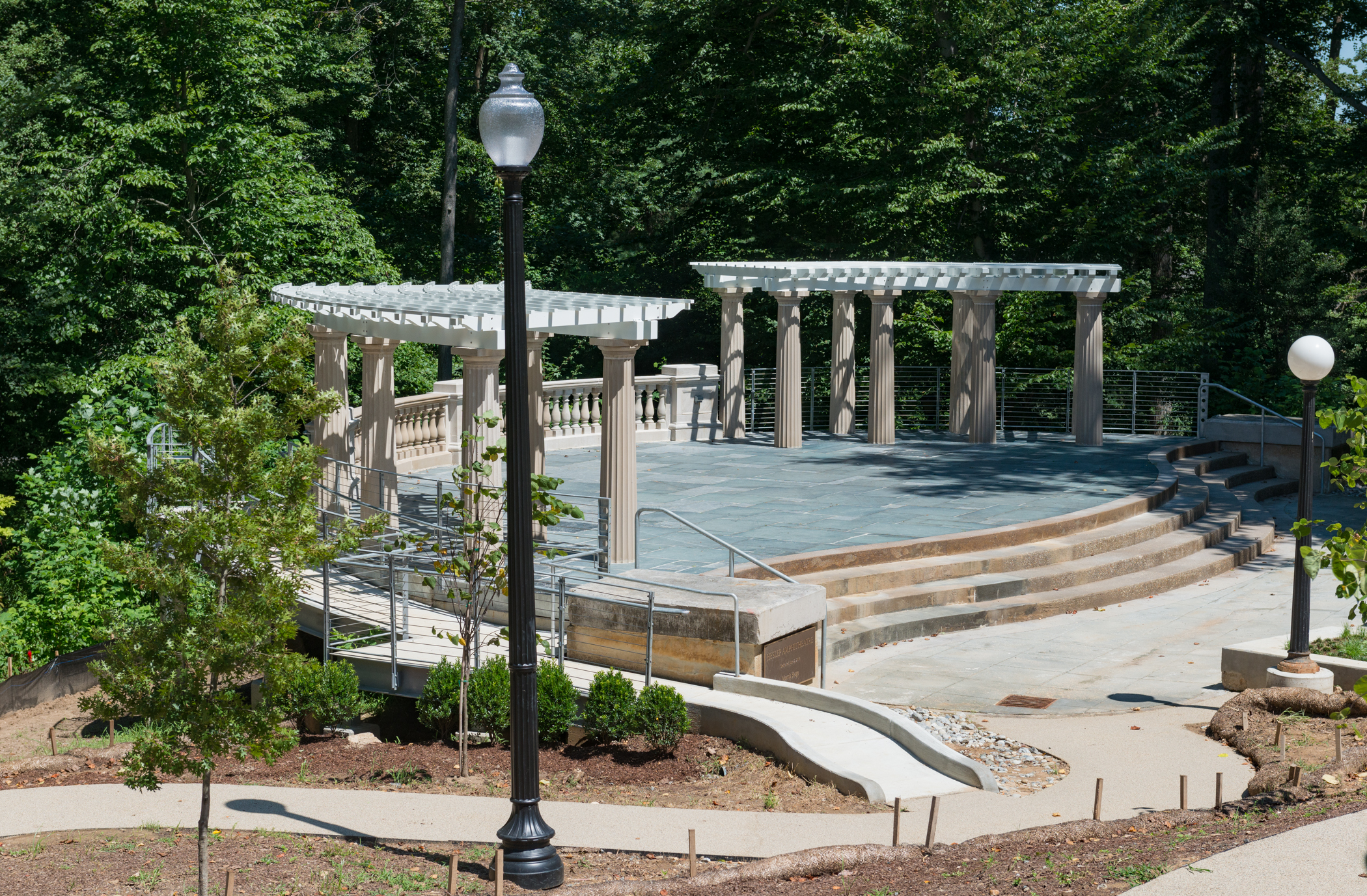
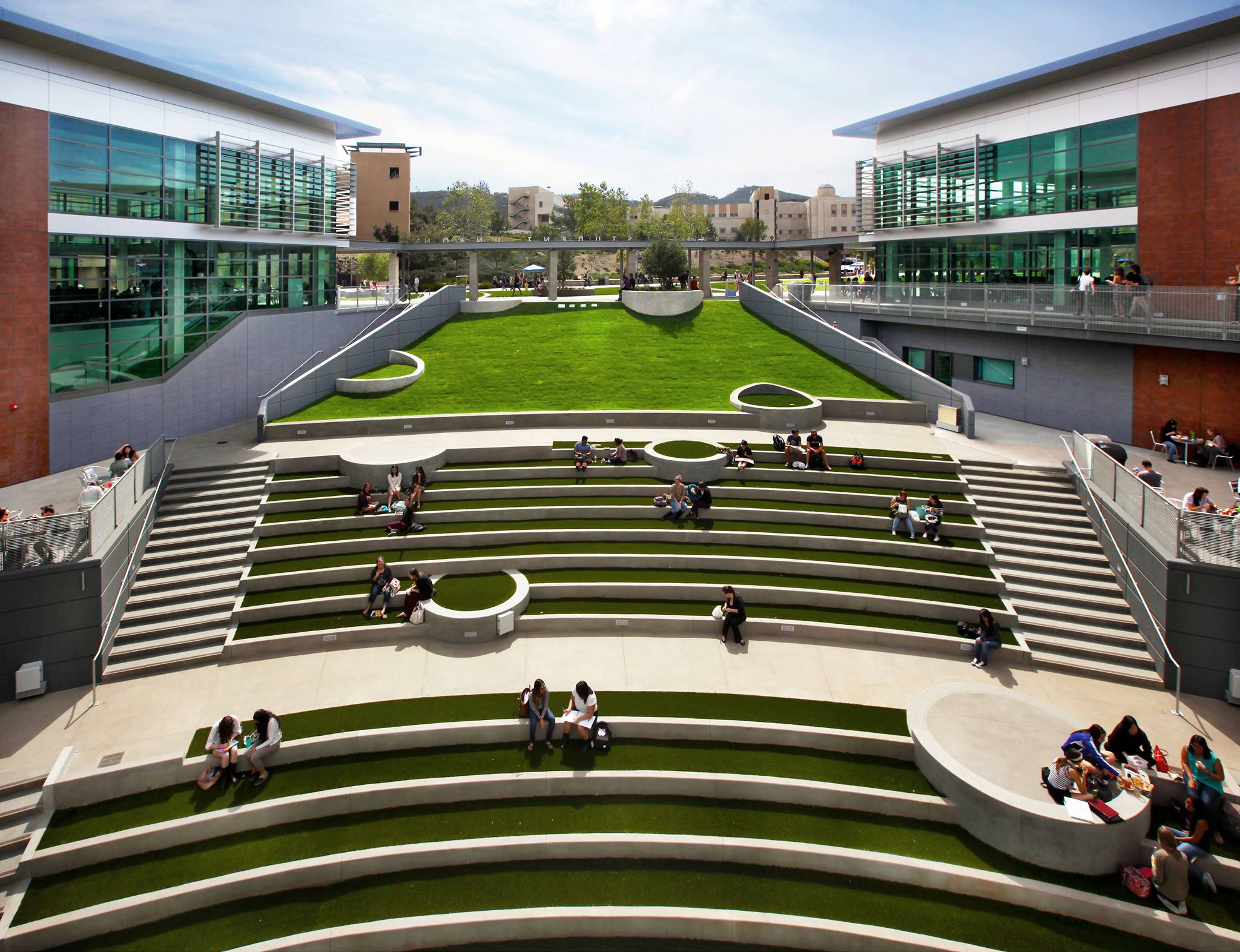
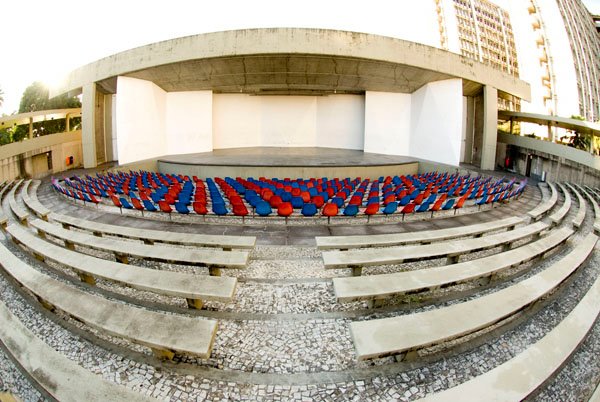
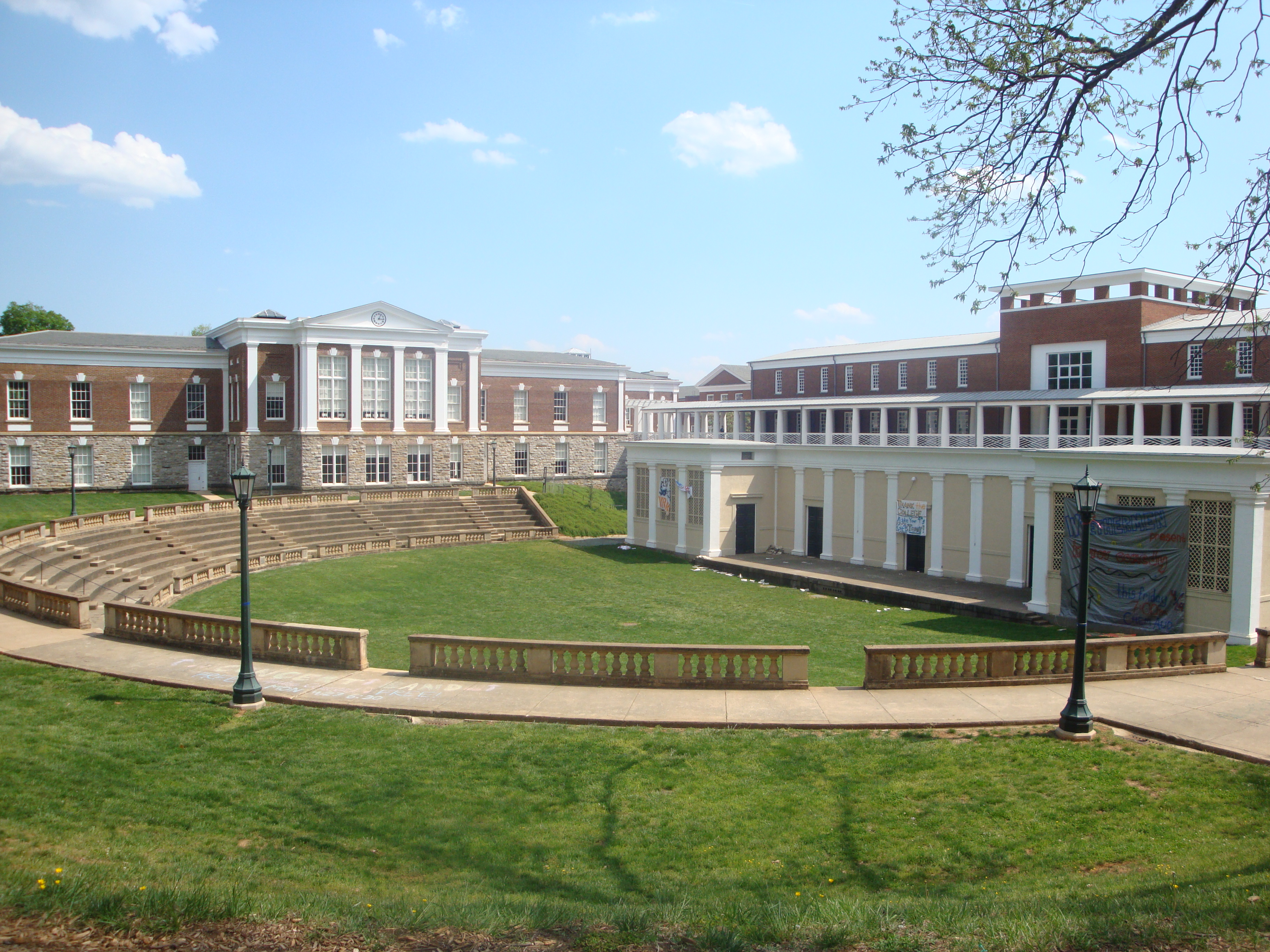
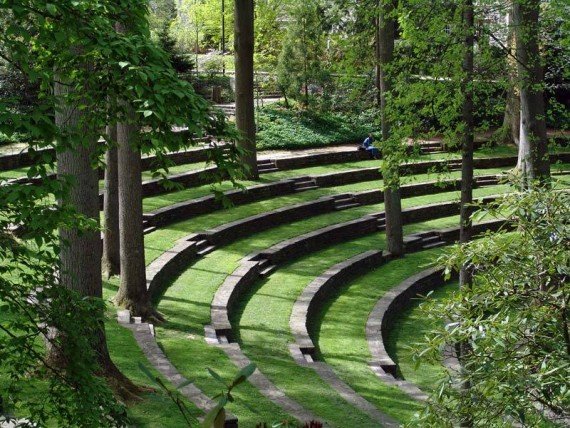
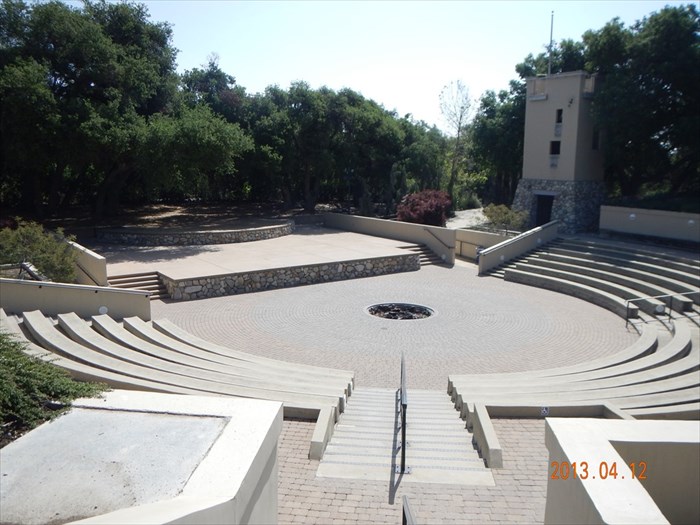
Amphitheaters
From from time to time — particularly in the months of fairer weather, when many events are hosted outdoors — we break form from the grind of responding to c0nsultations to simply enjoy these spaces See our CALENDAR for our periodic Lively c0lloquia when we drill down into technical specifics.
California State University San Marcos![]()

Clemson University
More coming
LEARN MORE:
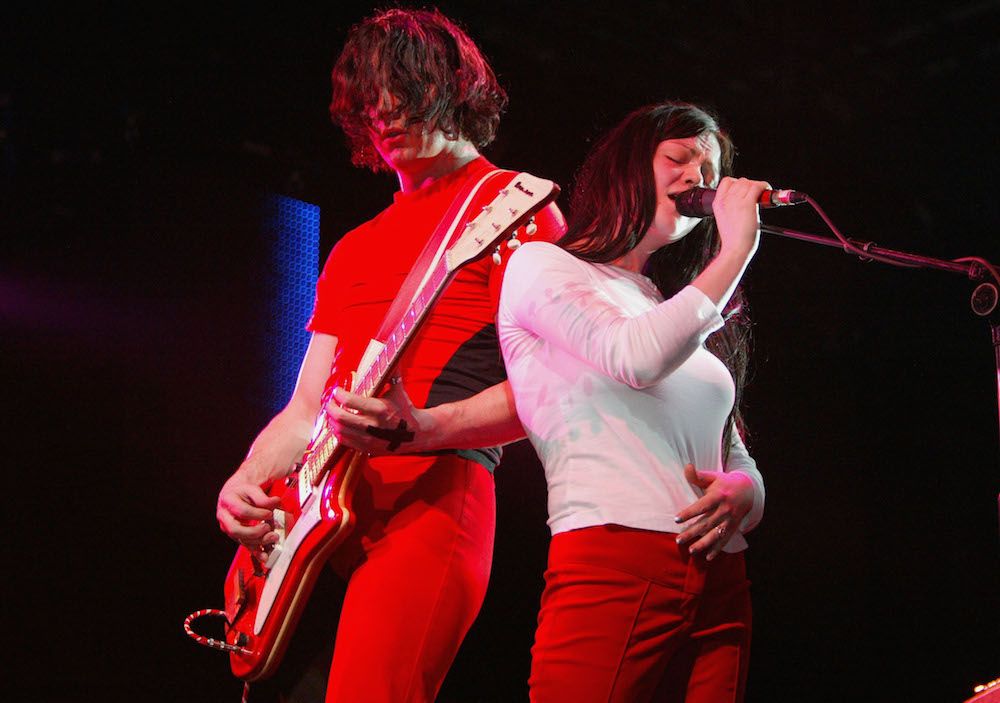
Anthem “Seven Nation Army”
After moonlighting in several underground Detroit bands as a drummer, Jack White founded the White Stripes with fellow Detroit native and then-wife Meg White in 1997. He graduated from Cass Tech High School and attended Wayne State University as a dramatic arts student; thereafter receiving an honorary degree; and since awarded eight Grammy Awards, among them, for his work on the soundtrack of “Cold Mountain”.
Detroit’s Wayne State University introduces world to Dr. Jack White
Rolling Stone: Jack White Saves Detroit Masonic Temple from Foreclosure
“Seven Nation Army” is one of the most iconic and popular songs of the early 21st century and is routinely performed at athletic events at all levels in the United States. Its view count on YouTube is closing in on 1 billion. Several factors contributed to the song’s popularity:
Memorable Guitar Riff: The song is instantly recognizable for its distinctive and powerful guitar riff played by Jack White. The riff, created using a semi-acoustic guitar and an octave pedal, became an anthem for many music enthusiasts.
Catchy Chorus: The song features a catchy and memorable chorus with the repeated lyrics, “I’m gonna fight ’em off, a seven nation army couldn’t hold me back.” This repetition and simplicity added to its appeal and made it easy for listeners to sing along.
Sports and Pop Culture: “Seven Nation Army” transcended the music scene and found its way into various aspects of popular culture. The song became a favorite at sports events around the world, particularly in stadiums and arenas. Its use in sports contexts, such as football chants, contributed to its widespread recognition.
Critical Acclaim: The song received critical acclaim for its raw energy, innovative sound, and Jack White’s distinctive vocals. It won a Grammy Award for Best Rock Song in 2004 and became a defining track for The White Stripes.
Cover Versions and Remixes: The song’s popularity was further fueled by numerous cover versions and remixes by various artists across different genres. This contributed to its longevity and continued relevance in diverse musical contexts.
As a result of these factors, “Seven Nation Army” has endured as a cultural phenomenon, maintaining its popularity long after its initial release.
I’m gonna fight ’em off
A seven nation army couldn’t hold me back
They’re gonna rip it off
Taking their time right behind my back
And I’m talking to myself at night
Because I can’t forget
Back and forth through my mind
Behind a cigarette
And the message coming from my eyes
Says “Leave it alone”
Don’t want to hear about it
Every single one’s got a story to tell
Everyone knows about it
From the Queen of England to the Hounds of Hell
And if I catch it coming back my way
I’m gonna serve it to you
And that ain’t what you want to hear
But that’s what I’ll do
And the feeling coming from my bones
Says “Find a home”
I’m going to Wichita
Far from this opera forevermore
I’m gonna work the straw
Make the sweat drip out of every pore
And I’m bleeding, and I’m bleeding, and I’m bleeding
Right before the Lord
All the words are gonna bleed from me
And I will sing no more
And the stains coming from my blood
Tell me “Go back home”
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670