The student version of an English Breakfast
- Home Page 10

Coffee Society
Annual report and financial statements 31 July 2024 | “Campus” Masterplan
Durham (Dunholm O.E.) as a Northumbrian learning settlement originates with its Cathedral; founded in 995 AD as part of a Benedictine monastery. Monks maintained libraries and created an intellectual hub for the English speaking peoples. Fast forward a millennium and we find “DU Coffee Society” which describes itself as a welcoming space for students to learn about coffee making, latte art and each other.
🗣️Did you miss out on Assembly last week? Don’t worry, our Media Observer, Nicole Ireland, was there to catch all the action!
Check out her report on our website here: https://t.co/lKSFHjhyyu pic.twitter.com/t70D0mKmcn
— Durham SU (@durhamSU) November 29, 2023
FYI:
LSE: “The Benefits and Costs of International Higher Education Students to the UK Economy
PwC: UK Higher Education Financial Sustainability Report
Don’t say ‘right-wing’, say ‘pattern recognizer’ https://t.co/0s5FNnlCOB pic.twitter.com/s0YuVy4jw6
— 𝒩𝒶𝓉𝒶𝓁𝒾𝒶 (@classicspilled) November 3, 2025
Ædificare & Utilization
It has been 20 years since we began following educational facilities construction activity. Starting this month we will examine federal government data together with the best available data about space utilization to enlighten our response to the perfectly reasonable question: “Are we over-building or under-building or building ineffectively”. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
United States: Schools of Architecture
The Society for College and University Planning (Ann Arbor, Michigan)
National Center for Education Statistics
The Financial Impact of Architectural Design: Balancing Aesthetics and Budget in Modern Construction
Homeschooling
2022 International Existing Building Code
 University College London
University College London University of Toronto
University of Toronto 43.0764° N | 87.8816° W
43.0764° N | 87.8816° W University of Waterloo Ontario
University of Waterloo Ontario California Polytechnic University | San Luis Obispo County
California Polytechnic University | San Luis Obispo County Oulun yliopisto | Pohjois-Pohjanmaa
Oulun yliopisto | Pohjois-Pohjanmaa Tulane School of Architecture Louisiana
Tulane School of Architecture Louisiana University of Michigan | Washtenaw County
University of Michigan | Washtenaw County Auburn University | Lee County Alabama
Auburn University | Lee County Alabama University of Kansas School of Architecture | Douglas County
University of Kansas School of Architecture | Douglas County
As reported by the US Department of Commerce Census Bureau the value of construction put in place by May 2025 by the US education industry proceeded at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $135.970 billion. This number does not include renovation for projects under 50,000 square feet and new construction in university-affiliated health care delivery enterprises. Reports are released two months after calendar month. The complete report is available at the link below:
MONTHLY CONSTRUCTION SPENDING August 2025 (released two months after calendar month)
THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHUTDOWN LAST MONTH HAS INTERRUPTED THE RELEASE CADENCE THIS MONTH
Total construction activity for June 2025 ($2,136.2 billion) was 0.4 percent below the revised May 2025 estimate ($2,143.9 billion).
Learn more: https://t.co/ljpaYyKjuX#CensusEconData pic.twitter.com/TS6ewzZhc4
— U.S. Census Bureau (@uscensusbureau) August 1, 2025
This spend makes the US education facilities industry (which includes colleges, universities, technical/vocational and K-12 schools, most university-affiliated medical research and healthcare delivery enterprises, etc.) the largest non-residential building construction market in the United States after commercial property; and fairly close. For perspective consider total public + private construction ranked according to the tabulation most recently released:
$137.604 billion| Education Facilities
$155.728 billion | Power
$69.625 billion | Healthcare
Keep in mind that inflation figures into the elevated dollar figures. Overall — including construction, energy, custodial services, furnishings, security. etc., — the non-instructional spend plus the construction spend of the US education facilities is running at a rate of about $300 – $500 billion per year.
LIVE: A selection of construction cameras at US schools, colleges and universities
![]()
We typically pick through the new data set; looking for clues relevant to real asset spend decisions. Finally, we encourage the education facilities industry to contribute to the accuracy of these monthly reports by responding the US Census Bureau’s data gathering contractors.
As surely as people are born, grow wealthy and die with extra cash,
there will be a home for that cash to sustain their memory and to steer
the cultural heritage of the next generation in beautiful settings.
More
National Center for Educational Statistics
AIA: Billings Index shows but remains strong May 2022
National Center for Education Statistics
Sightlines: Capital Investment College Facilities
OxBlue: Time-Lapse Construction Cameras for Education
US Census Bureau Form F-33 Survey of School System Finances
Global Consistency in Presenting Construction & Life Cycle Costs
High-voltage switchgear and controlgear
The U.S National Committee (USNC) of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) serves as the focal point for U.S parties who are interested in the development, promulgation, and use of globally relevant standards for the electrotechnical industry.
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers: Relevant Recent Research
A study of an approach to the construction of high-power with high-voltage supplies
Fault Clearing Operation in Low-Frequency High-Voltage AC Systems
Guide for Overhead Alternating Current (AC) Transmission Line Design | Comments Due February 2
National Electrical Manufacturers Association: Standards relevant to this topic.
National Fire Protection Association
Underwriters Laboratories: Solutions for Medium & High Voltage Cables
Memorial Church Sunday Service
Hillsdale College | The Theological–Political Problem and the American Founding | Glenn Ellmers
From George Washington to the Hebrew Congregation in Newport, Rhode Island, 18 August 1790
The Best Breakdown of America You’ve Never Heard: Richard Miniter
In Federalist No. 2, John Jay [1764 Graduate of King’s College; now Columbia University] argues that a strong union under the Constitution will promote peace and prosperity, which are conducive to the spread of religion and morality:
“Providence has been pleased to give this one connected country to one united people—a people descended from the same ancestors, speaking the same language, professing the same religion, attached to the same principles of government, very similar in their manners and customs… These considerations, and many others that might be mentioned, prove, and experience confirms it, that artificial distinctions and separations of [America’s] land are essentially unnatural; and that they may be eradicated and extirpated by the united and advisable efforts of individuals and communities…”
The Federalist Papers discuss themes of morality, social order, and the importance of a cohesive society, they do not explicitly emphasize the importance of Christian faith to the American constitutional republic. The authors generally focused on principles of governance, political theory, and the structure of the proposed Constitution.
“The experience of the sacred is a universal phenomenon,
found in all human societies, however primitive or complex.”
— 1957 Mircea Eliade (‘The Sacred and the Profane’)
Harvard’s Memorial Chapel, also known as Memorial Church, was designed by the architectural firm Coolidge, Shepley, Bulfinch, and Abbott. The church was dedicated on Armistice Day, November 11, 1932, as a memorial to Harvard alumni who died in World War I.
 |
Sunday Service Announcements and Music Notes
John Harvard, the namesake of Harvard University, was a 17th-century English minister lived on campus from 1607 – 1638 and conformed to Puritan ideal of dedicating Sundays to worship, prayer, and rest.
Radio Transmission Power & Frequency Allocation
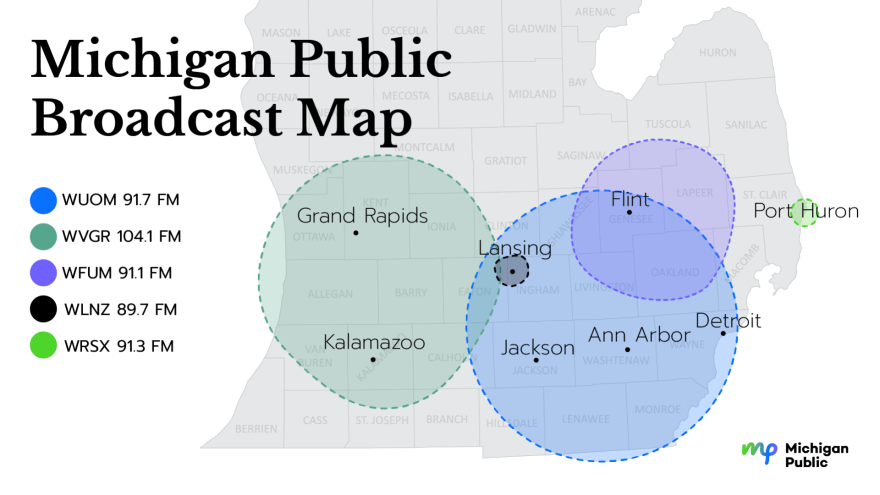
Why are there at least 10 publicly funded radio stations receivable in a 75 mile radius (back and forth, up and down) the I-94/I-75 corridor of Michigan — all of them domiciled in public universities? These stations also receive revenue from other non-profit organizations, unending funding drives and private advertising from multinational financing organizations such as Schwab, Fidelity and other for-profit corporations. Most of them purchase their “content” from the same source; reflecting the same large government bias seen across the entire nation; concentrated in college towns with spotty intellectual history.
Within an approximate 50 mile radius of the University of Michigan, five national public radio stations are receivable:
WUOM University of Michigan Ann Arbor
WEMU Eastern Michigan University
WDET Wayne State University
WKAR Michigan State University
WGTE University of Toledo
Move 25 miles to the northwest and two more are receivable:
WLNZ Landing Community College
Move 25 miles northeast and three more are receivable
WFUM University of Michigan Flint
WMUK Western Michigan University
WAUS Andrews University
FCC ONLINE TABLE OF FREQUENCY ALLOCATIONS: 47 C.F.R. § 2.106
(Revised July 1, 2022)
Standards for radio broadcast coverage can vary depending on factors like location, broadcasting technology, and regulatory requirements. Here’s a general list covering various aspects:
- Technical Standards:
- Transmission Power and Frequency Allocation: Standards set by regulatory bodies like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States or Ofcom in the UK regulate the power levels and frequencies allocated to radio stations to prevent interference.
- Audio Quality: Standards for audio encoding and decoding, such as those defined by organizations like the European Broadcasting Union (EBU) or the Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) standards.
- Antenna Design and Installation: Standards for antenna design, placement, and maintenance to ensure efficient transmission and coverage.
- Content Standards:
- Language and Content Regulations: Regulations on language, decency, and content suitability enforced by regulatory bodies to ensure broadcasts adhere to community standards and do not contain offensive or harmful material.
- Advertising Standards: Guidelines on the content and placement of advertisements to prevent deceptive practices and ensure fairness and transparency.
- Copyright and Licensing: Regulations governing the use of copyrighted material and licensing agreements for broadcasting music, interviews, and other content.
- Emergency Broadcast Standards:
- Emergency Alert Systems (EAS): Standards for implementing emergency alert systems to disseminate important information to the public during emergencies or disasters.
- Public Safety Communications: Standards for communication protocols and procedures to coordinate with emergency services and agencies during crises.
- Accessibility Standards:
- Closed Captioning: Standards for providing closed captioning for the hearing impaired, ensuring accessibility to radio broadcasts.
- Descriptive Video Service (DVS): Standards for providing audio descriptions of visual content for the visually impaired.
- Ethical Standards:
- Journalistic Integrity: Guidelines for ethical reporting and journalism standards, including accuracy, fairness, and impartiality.
- Disclosure of Sponsored Content: Standards for disclosing sponsored or paid content to maintain transparency and trust with the audience.
- Conflict of Interest Policies: Standards for identifying and managing conflicts of interest in news reporting and programming.
- Health and Safety Standards:
- Electromagnetic Radiation Exposure Limits: Standards set by health organizations and regulatory bodies to limit human exposure to electromagnetic radiation emitted by radio transmitters.
- Workplace Safety: Standards for ensuring the safety of radio station personnel and compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
These standards are often enforced by governmental regulatory agencies, industry organizations, and professional associations to ensure the quality, integrity, and safety of radio broadcast coverage.
National Public Radio is the soundtrack of American academia and American academia has always been partial to large government:
“It was always the woman, and above all the young ones who where the most bigoted adherents to the party” — (George Orwell, ‘1984’)
— NPR (@NPR) April 12, 2023
Integrated Planning Glossary
Connections, learnings, and expanded conversations #SCUPNC2022 in #chicago 👍🌟 pic.twitter.com/enPtA7YJsX
— SCUP (@Plan4HigherEd) October 18, 2022
Early operations benefited from administrative support (aegis) provided by the University of Michigan, including office space and resources in Ann Arbor. This arrangement persisted until a financial crisis in the late 1970s (1976–1980), during which SCUP relocated to New York.
The decoupling—marking full operational and administrative independence from the University of Michigan—occurred in 1980, when SCUP returned to Ann Arbor as a self-sustaining nonprofit headquartered at a separate location –1330 Eisenhower Place — less than a mile walk from Standards Michigan‘s front door at 455 East Eisenhower.
* Of the 220 ANSI Accredited Standards Developers, the State of Michigan ranks 3rd in the ranking of U.S. states with the most ANSI-accredited standards developers (ASDs) headquartered there; behind the Regulatory Hegemons of California and ChicagoLand and excluding the expected cluster foxtrot of non-profits domiciled in the Washington-New York Deep State Megalopolis. Much of Michigan’s presence in the private consensus standards space originates from its industrial ascendency through most of the 1900’s.
National Center for Spectator Sports Safety and Security
The legacy of Merry Old England lives on in the American South. pic.twitter.com/ujnDUIz3Q3
— 𝒩𝒶𝓉𝒶𝓁𝒾𝒶 (@classicspilled) October 3, 2025
Exploring the impacts of elite youth sports on family life
Purpose: This study explored the impacts of elite-level youth sport participation on family life.
Methodology: In-depth semi-structured interviews were conducted with parents of youth athletes (N = 17).
Findings: Parents extensively talked about the temporal demands of elite youth sports and necessity of time management. Three domains were found in parents’ accounts including, children’s time, parents’ time, and family’s time; temporal opportunities and challenges were identified within each domain. Time spent on sports was perceived positively, keeping children out of trouble and from video games/time online; however, it left no time for other activities. Although parents sacrificed their own activities to facilitate their child’s sports participation, they used the practice and tournament time to engage in personal interests, such as reading or exercising. Likewise, family’s time was restricted by youth sport schedules, but parents managed to turn car rides or tournament trips into quality family time.
Practical implications: Findings can be used by youth sport practitioners to enhance children and parents’ experiences.
Research contribution: Findings contribute to the literature by assessing the impacts of elite-level youth sports participation on family life.
Originality: The intricacies of how time-on task relates to parents’ relationship with their child’s sport have been understudied.
Berrien Springs
Settled in the Village of Berrien Springs (Population 2043, including students) Andrews University is the flagship educational institution of the Seventh-day Adventist Church, and is made up of the Seventh-day Adventist Theological Seminary, College of Arts and Sciences, School of Business Administration, School of Education, School of Health Professions, and the School of Architecture, Art & Design.
The University is named after John Nevins Andrews (1829–1883), the biggest thinker in the 19th-century Seventh-day Adventist Church. He was also the first sponsored missionary that the Church sent overseas. J.N. Andrews’ example of careful thought and compassionate action in Christian life is something we have taken to heart. Our motto is “Seek Knowledge. Affirm Faith. Change the World.”
Andrews University is honored to be ranked as one of the top 15 Christian universities and the highest ranked Adventist university in the country in the 2024 Niche Best Colleges report. pic.twitter.com/FQb7czeHoL
— Andrews University (@AndrewsUniv) September 27, 2023
Pres. JW Taylor greeted Julianna Magan, her parents, Andy & Cindy Magan, & sister, Clara, at Sutherland House on Aug. 19. Julianna, a transfer student, & Clara are great-great-great-granddaughters of Percy T. Magan, 1 of the 2 major founders of the Andrews Berrien Springs campus. pic.twitter.com/2wqcgUQBdl
— Andrews University (@AndrewsUniv) August 25, 2023
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670