Perfect Irish Coffee
- Home Page 155

Eggnogg
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
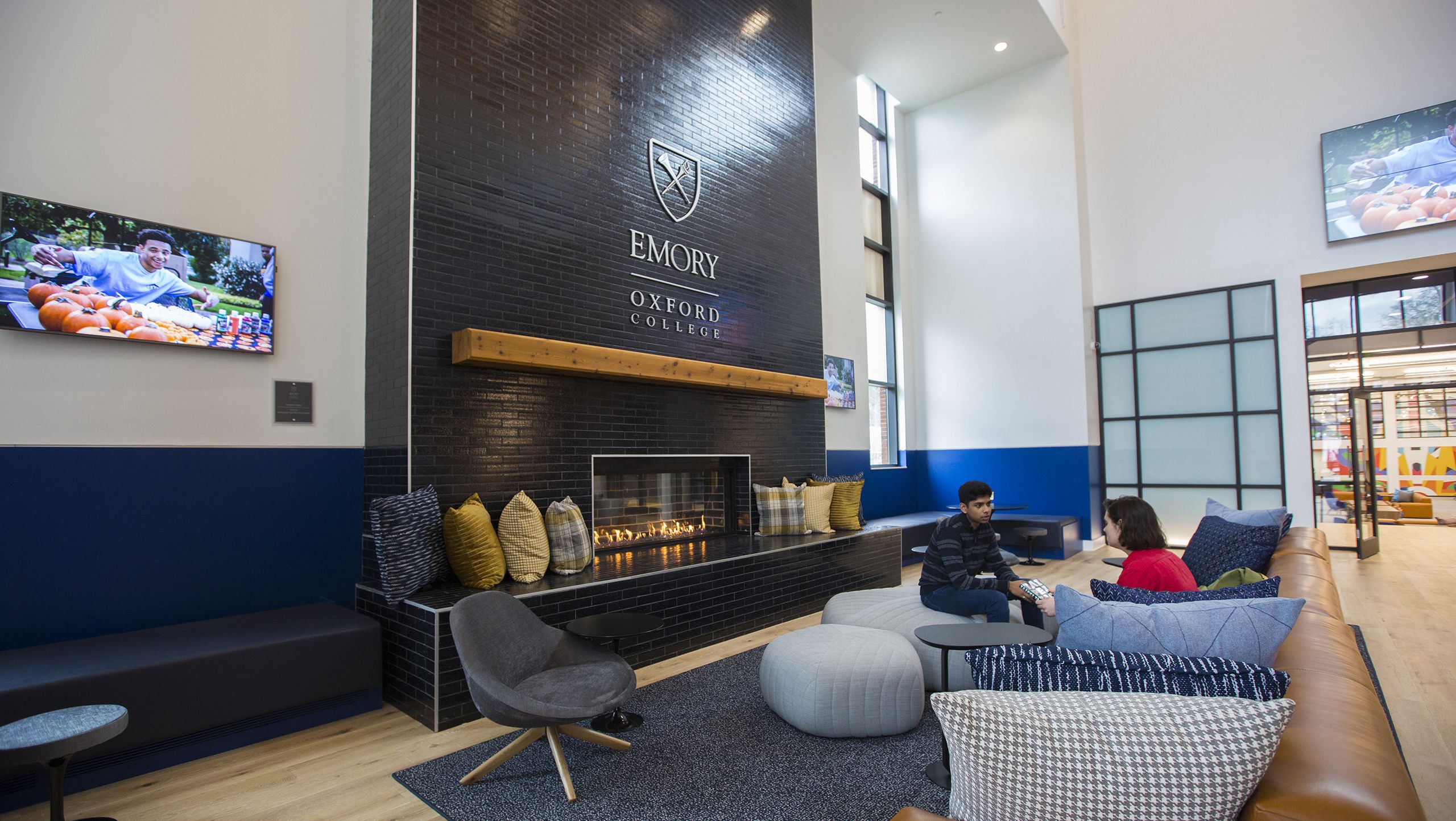
Oxford College Student Center
Emory University Facilities Management
💙 Atlanta quad, late winter. 💛
Photo by Emory College student Khushi Niyyar pic.twitter.com/pv3qiEngvM
— Emory University (@EmoryUniversity) February 19, 2024
What an incredible weekend for our swimming & diving teams! The women’s and men’s teams dominated at the UAA conference championships, with both bringing home their 25th consecutive conference titles! Women’s recap: https://t.co/ByXJDpa61F Men’s recap: https://t.co/GTPzPEHyOo pic.twitter.com/yT3UJME2Cd
— Emory University (@EmoryUniversity) February 19, 2024
“Midnight Train To Georgia” 1973 | written in his spare time by Jim Weatherly star football quarterback @OleMiss
https://t.co/Yj1iMkLZRK
print(“Lunch Hour 1600 UTC”)\n weekday(2)
print(“American Standard”)@SchoolofRockUSAhttps://t.co/yjhiCTCPoS pic.twitter.com/BfIE0wwjWz— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) October 25, 2023
International Building Code: Chapter 27 Electrical
§ 2701.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter and NFPA 70 shall govern the design, construction, erection and installation of electrical components, appliances, equipment and systems used in buildings and structures covered by this code. The International Fire Code, the International Property Maintenance Code and NFPA 70 shall shover the use and maintenance of electrical components, appliances, equipment and systems. The International Existing Building Code and NFPA 70 shall govern the alteration, repair, relocation, replacement and addition of electrical components, appliances, or equipment and systems.
Physical Security of Water Utilities
Many school districts, colleges and universities are affected by annual spring flooding in the Central United States; seasonal inspiration for revisiting the technical and management codes and standards to avoid and/or mitigate water damages that may be originate with host municipality water supply and control authorities.
The standards developed by the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) and its affiliate institute — Environmental Water Resource Institute (EWRI) — should appear in the design guidelines given to professional services firms retained by the facility construction, operations and maintenance workgroups. We encourage our colleagues in these units to update their design guidelines with the latest versions of the documents linked below:
ASCE/EWRI 56: Guidelines for the Physical Security of Water Utilities. These water utility guidelines recommend physical and electronic security measures for physical protection systems to protect against identified adversaries, referred to as the design basis threats (DBTs), with specified motivation, tools, equipment, and weapons.
ASCE/EWRI 57: Guidelines for the Physical Security of Wastewater/Stormwater Utilities. These wastewater/stormwater utilities guidelines recommend physical and electronic security measures for physical protection systems to protect against identified adversaries, referred to as the design basis threats (DBTs), with specified motivation, tools, equipment, and weapons. Additional requirements and security equipment may be necessary to defend against threats with greater capabilities.
Note that these documents are “paired” for the obvious reason that potable water systems must be separate from all other water systems.
No redlines that are in the upper tier of our priority rankings are open for public comment at this time; though there are two that might interest building contractors:
Standards currently accepting Public Comments include:
Public Comment for ASCE-SEI 24 Flood Resistant Design and Construction (Comment Deadline 9/26/24)
Public Comment for ASCE/SEI 32-01 Design and Construction of Frost-Protected Shallow Foundations (Comment Deadline 8/05/2024
Public Comment on ASCE 7-22 Supplement for Chapter 5 (Comment Deadline 1-15-2023)
Public Comment on ASCE 7-22 Supplement for Referenced Standards (Comment Deadline 1-15-2023)
We encourage direct engagement by education industry leaders, their engineering consultants, or municipal water management experts to participate in the development of these standards through the ASCE standards portal:
ASCE Standards Public Comment Page
You will need to set up an access account. You may also communicate directly with the American Society of Civil Engineers, 1801 Alexander Bell Dr., Reston, VA 20191. Contact: James Neckel (jneckel@asce.org).
We keep water-related ASCE titles on the standing agenda of our Water colloquium. See our CALENDAR for the next teleconference; open to everyone.
Issue: [18-52]
Category: Civil Engineering, Water, #SmartCampus
Colleagues: Jack Janveja, Richard Robben, Steve Snyder, Larry Spielvogel
LEARN MORE:
Student Health and Wellness Center
The Center provides comprehensive healthcare services to students. Located on the Logan campus, the clinic offers a range of medical services including general health check-ups, vaccinations, mental health support, and chronic disease management. Staffed by experienced physicians, nurse practitioners, and support staff, the clinic aims to address both physical and mental health needs. Students can access acute care for illnesses and injuries, preventive care, women’s health services, and counseling.
The clinic also provides lab services, prescriptions, and referrals to specialists when needed. With a focus on promoting wellness and healthy lifestyles, the USU Student Health Clinic ensures that students receive quality care in a supportive environment, contributing to their overall well-being and academic success. The clinic operates on an appointment basis, with some walk-in availability, and is committed to maintaining confidentiality and respect for all students.
Abiit sed non oblita | Margaret Wise Brown
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Guidance for Grants and Agreements
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670