Fire Drills
- Home Page 76

Spaghetti and Meatballs
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Media Production Facilities
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Ultrasonic cold brew
#UQ ranked 41st in the world in the QS World University Rankings: Sustainability, which recognises an institution’s efforts across areas including environmental sustainability, education, research, and health and wellbeing.@worlduniranking pic.twitter.com/CJDfgqsqjs
— UQ News (@UQ_News) December 18, 2024
Wood
International Building Code Chapter 23: Wood
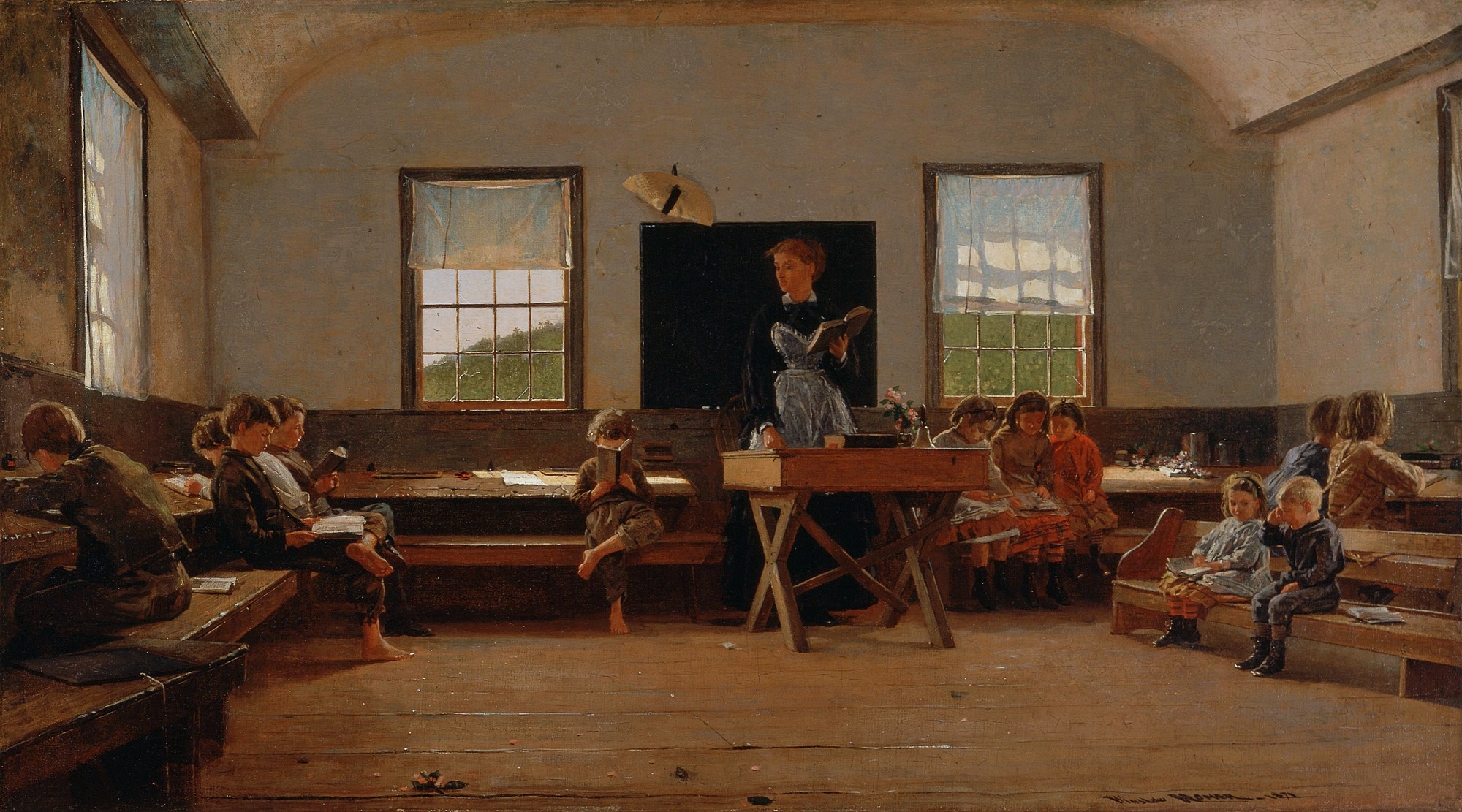
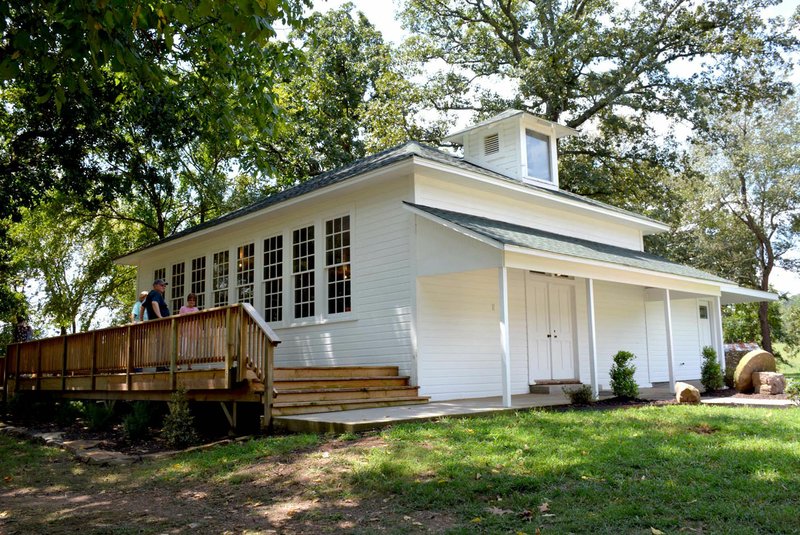
Building schoolhouses with wood in the United States had significant practical and cultural implications, particularly during the 18th and 19th centuries. Wood was the most readily available and cost-effective material in many parts of the country. Abundant forests provided a plentiful supply, making it the logical choice for construction. The use of wood allowed communities to quickly and efficiently build schoolhouses, which were often the first public buildings erected in a new settlement.
Wooden schoolhouses were emblematic of the pioneering spirit and the value placed on education in early American society. These structures were often simple, reflecting the modest means of rural communities, but they were also durable and could be expanded or repaired as needed. The ease of construction meant that even remote and sparsely populated areas could establish schools, thereby fostering literacy and learning across the nation.
Moreover, wooden schoolhouses became cultural icons, representing the humble beginnings of the American educational system. They were often the center of community life, hosting social and civic events in addition to serving educational purposes. Today, preserved wooden schoolhouses stand as historical landmarks, offering a glimpse into the educational practices and community life of early America. Their construction reflects the resourcefulness and priorities of the early settlers who valued education as a cornerstone of their communities.
Building schoolhouses with wood presents several technical challenges, including durability, fire risk, maintenance, and structural limitations. Here are the key challenges in detail:
- Durability and Weather Resistance:
- Rot and Decay: Wood is susceptible to rot and decay, especially in humid or wet climates. Without proper treatment and maintenance, wooden structures can deteriorate rapidly.
- Pests: Termites and other wood-boring insects can cause significant damage, compromising the integrity of the building.
- Fire Risk:
- Combustibility: Wood is highly flammable, increasing the risk of fire. This was a significant concern in historical and rural settings where firefighting resources were limited.
- Safety Standards: Ensuring that wooden schoolhouses meet modern fire safety standards requires additional measures, such as fire-retardant treatments and the installation of fire suppression systems.
- Maintenance:
- Regular Upkeep: Wooden buildings require frequent maintenance, including painting, sealing, and repairing any damage caused by weather or pests.
- Cost: Ongoing maintenance can be costly and labor-intensive, posing a challenge for communities with limited resources.
- Structural Limitations:
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Wood has limitations in terms of load-bearing capacity compared to materials like steel or concrete. This can restrict the size and design of the schoolhouse.
- Foundation Issues: Wooden structures can experience foundation issues if not properly designed and constructed, leading to uneven settling and potential structural damage.
- Environmental Impact:
- Deforestation: The widespread use of wood for construction can contribute to deforestation, which has environmental consequences. Sustainable sourcing practices are essential to mitigate this impact.
- Insulation and Energy Efficiency:
- Thermal Insulation: Wood provides moderate thermal insulation, but additional materials and techniques are often required to ensure energy efficiency and comfort for students and staff.
Despite these challenges, wooden schoolhouses were popular in the past due to the availability of materials and ease of construction. Addressing these technical challenges requires careful planning, use of modern materials and techniques, and regular maintenance to ensure the longevity and safety of wooden schoolhouses.
Related:
Eurocode 5 (EN 1995): Design of timber structures
Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures
National Design Specification for Wood Construction
The 2024 National Design Specification for Wood Construction was developed by AWC’s Wood Design Standards Committee and approved as a standard by ANSI (American National Standards Institute) on October 16, 2023. The 2024 NDS is referenced in the 2024 International Building Code.
International Code Council Mass Timber: Outcomes of the ICC Tall Wood Ad Hoc Committee
Related:
Researchers Make Wood Stronger than Steel
Mass Timber Primed for Wider Use? ( November 19, 2024). This article from the University of Florida’s Warrington College of Business explores the expanding use of mass timber in construction, including a planned mass timber building on the University of Florida’s Gainesville campus. It highlights CLT development and regional advantages in the Pacific Northwest, with examples from University of Oregon research.
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) (August 13, 2024). From Auburn University’s College of Forestry, Wildlife and Environment, this piece details the college’s involvement in mass timber research and construction through the university’s Mass Timber Collaborative. It emphasizes CLT’s growth in the Southeast US using southern pine, with multidisciplinary efforts in forestry, architecture, and engineering for campus and regional projects.
The Meteoric Rise of Cross-Laminated Timber Construction: 50 Projects that Use Engineered-Wood Architecture (November 18, 2024) Published by ArchDaily, this overview of CLT projects worldwide includes US examples like the Albina Yard in Portland (a pioneering CLT building), and discusses its application in sustainable campus and institutional structures, promoting domestic wood use in educational settings.
Almost time to celebrate our Terps! 💛 #UMDGrad🎓
Find the ceremony live stream and more info: https://t.co/O253YinItK pic.twitter.com/dz2MxK94Eb
— Univ. of Maryland (@UofMaryland) May 22, 2025
Construction Technology Careers: Carpentry, HVAC, Plumbing
Construction Technology Careers: Carpentry, HVAC, Plumbing
One study, published in the Journal Social Forces in 2012, found that women’s educational preferences for a potential partner have been changing over time. The study found that in the 1960s and 1970s, women were more likely to prefer men with higher levels of education than themselves, while in the 1990s and 2000s, women were more likely to prefer partners with similar levels of education. The study also found that women’s educational preferences were influenced by their own educational attainment and the gender ratio of their college campus.
Another study, published in the journal Demography in 2015, found that women’s educational preferences for a potential partner varied depending on their own educational background and the gender ratio of their local area. The study found that women with higher levels of education were more likely to prefer men with similar levels of education, while women with lower levels of education were more likely to prefer men with higher levels of education. The study also found that women in areas with a higher ratio of men to women were more likely to prefer men with higher levels of education.
While these studies suggest that young women’s preferences for college-educated men as marriage partners may be influenced by a variety of factors, it is important to recognize that individual preferences and behaviors can vary widely and are influenced by a wide range of factors. Additionally, any generalizations about the preferences of “young women” or any other group should be approached with caution, as these preferences can vary widely depending on factors such as age, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status.
Split Pea Soup
Split Pea Soup
https://eat-move-save.extension.illinois.edu/eat/recipes/split-pea-soup
Butter Tarts
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670