Updated July 15, 2025
2026 National Electrical Code Table of Contents
2026 NEC First Draft: How Did We Get Here?
Public Input Transcript: First Draft | Public Comment Transcript: Second Draft
2023 National Electrical Code | Current Issues and Recent Research
August 5, 2021
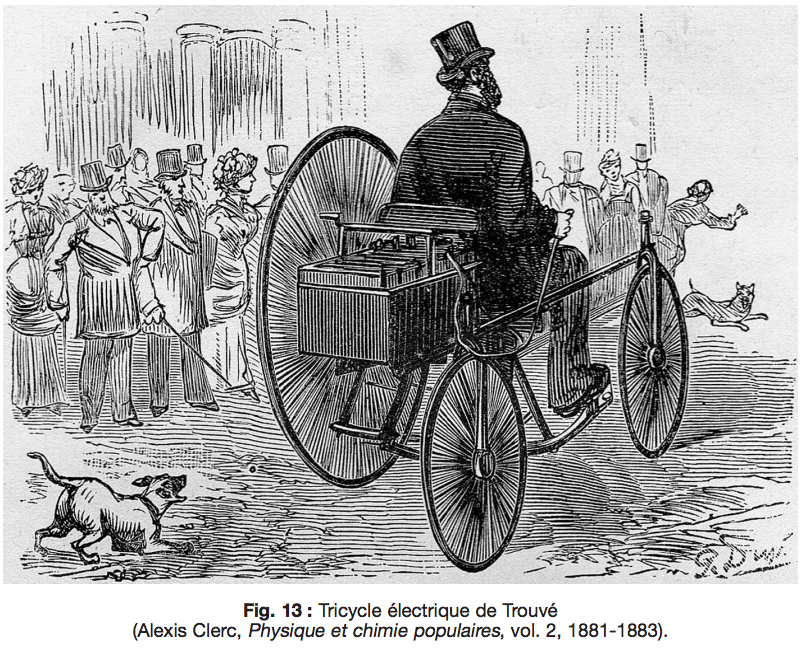
The 2020 National Electrical Code (NEC) contains significant revisions to Article 625 Electric Vehicle Power Transfer Systems. Free access to this information is linked below:
You will need to set up a (free) account to view Article 625 or you may join our colloquium today.
Public input for the 2023 Edition of the NEC has already been received. The work of the assigned committee — Code Making Panel 12 — is linked below:
NFPA 70_A2022_NEC_P12_FD_PIReport_rev
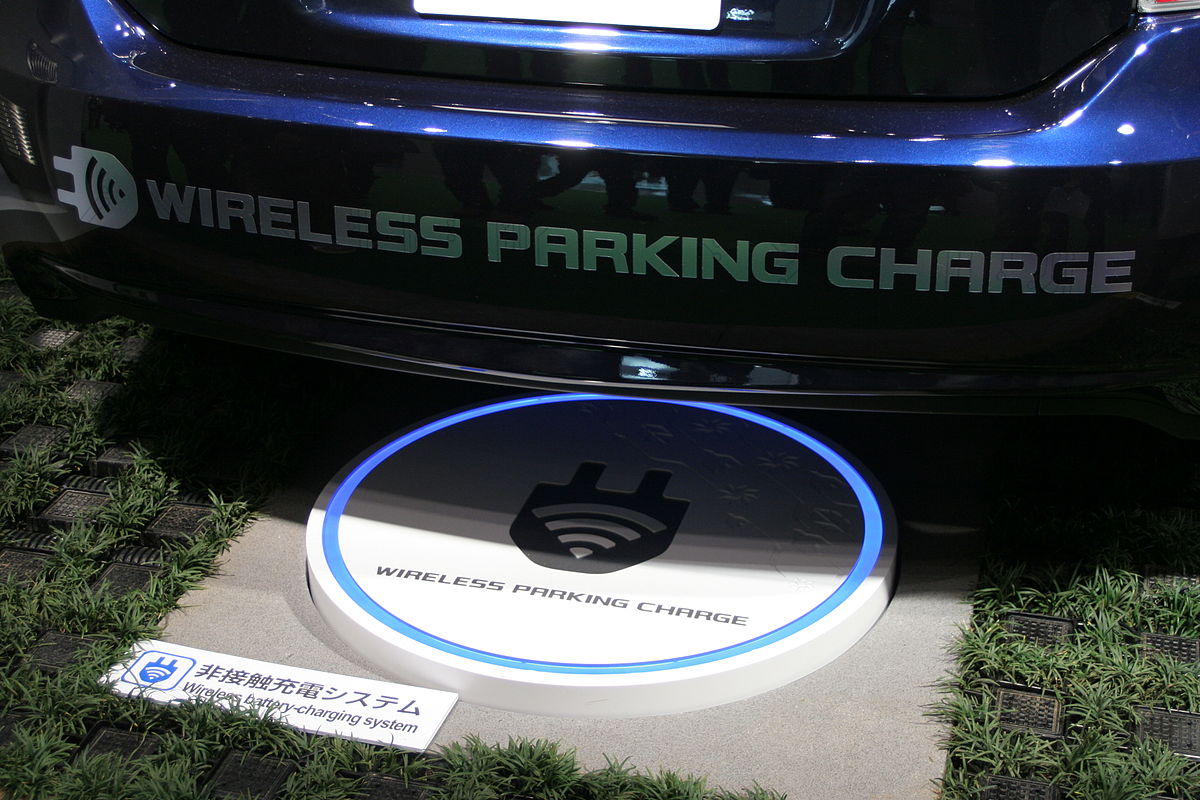
Mighty spirited debate. Wireless charging from in-ground facilities employing magnetic resonance are noteworthy. Other Relevant Articles:
- Article 240: Overcurrent Protection: This article includes requirements for overcurrent protection devices that could be relevant for EV charging systems.
- Article 210: Branch Circuits: General requirements for branch circuits, which can include circuits dedicated to EVSE.
- Article 220: Load Calculations: Guidelines for calculating the electrical load for EVSE installations.
- Article 230: Services: General requirements for electrical service installations, which can be relevant for EVSE.
- Article 250: Grounding and Bonding: Requirements for grounding and bonding, which are critical for safety in EVSE installations.
Technical committees meet November – January to respond. In the intervening time it is helpful break down the ideas that were in play last cycle. The links below provide the access point:
Public Comment Report Panel 12
We find a fair amount of administrative and harmonization action; fairly common in any revision cycle. We have taken an interest in a few specific concepts that track in academic research construction industry literature:
- Correlation with Underwriters Laboratory product standards
- Bi-Directional Charging & Demand Response
- Connection to interactive power sources
As a wiring safety installation code — with a large installer and inspection constituency — the NEC is usually the starting point for designing the power chain to electric vehicles. There is close coupling between the NEC and product conformance organizations identified by NIST as Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories; the subject of a separate post.
After the First Draft is released June 28th public comment is receivable until August 19th.
We typically do not duplicate the work of the 10’s of thousands of National Electrical Code instructors who will be fanning out across the nation to host training sessions for electrical professionals whose license requires mandatory continuing education. That space has been a crowded space for decades. Instead we co-host “transcript reading” sessions with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee to sort through specifics of the 2020 NEC and to develop some of the ideas that ran through 2020 proposals but did not make it to final ballot and which we are likely to see on the docket of the 2023 NEC revision. That committee meets online 4 times monthly. We also include Article 625 on the standing agenda of our Mobility colloquium; open to everyone. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting
Issue: [16-102]
Category: Electrical, Transportation & Parking, Energy
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey
More
U.S. NATIONAL ELECTRIC VEHICLE SAFETY STANDARDS SUMMIT | DETROIT, MICHIGAN 2010