IEEE Standards Association Public Review
Related Issues and Recent Research | Federal Legislation
This title sets the standard of care for construction, operation and maintenance of power and telecommunication infrastructure on the supply side of the point of common coupling. It is the first title to contemplate when weather disasters happen; with most public utilities bound to its best practice assertions by statute. Pre-print of Change Proposals for changes to appear in 2028 Edition will be available by 1 July 2025; with 24 March 2026 as the close date for comments on proposed changes.
Project Introduction for the 2028 Edition (2:39 minutes)
Changes proposals for the Edition will be received until 15 May 2024
Project Workspace: Update Data Tables in IEEE Recommended Practice for the Design of Reliable Industrial and Commercial Power Systems
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission: Electrical Resource Adequacy
NARUC Position on NFPA (NEC) and IEEE (NESC) Harmonization
The standard of care for electrical safety at high and low voltage is set by both the NEC and the NESC. There are gaps, however (or, at best “gray areas”) — the result of two technical cultures: utility power culture and building fire safety culture. There is also tradition. Local system conditions and local adaptation of regulations vary. Where there is a gap; the more rigorous requirement should govern safety of the public and workers.
The 2023 National Electrical Safety Code (NESC)– an IEEE title often mistaken for NFPA’s National Electrical Code (NEC) — was released for public use about six months ago; its normal 5-year revision cycle interrupted by the circumstances of the pandemic. Compared with the copy cost of the NEC, the NESC is pricey, though appropriate for its target market — the electric utility industry. Because the 2023 revision has not been effectively “field tested” almost all of the available support literature is, effectively, “sell sheets” for pay-for seminars and written by authors presenting themselves as experts for the battalions of litigators supporting the US utility industry. Without the ability to sell the NESC to prospective “insiders” the NESC would not likely be commercial prospect for IEEE. As the lawsuits and violations and conformance interests make their mark in the fullness of time; we shall see the 2023 NESC “at work”.
Office of the President: Economic Benefits of Increasing Electric Grid Resilience to Weather Outages
Change Proposals are now being accepted from the public for revisions to the 2023 Edition of the National Electrical Safety Code® #NESC through 15 May 2024.
Learn more: https://t.co/jbxWtLPS6r pic.twitter.com/FRvZly1DoH
— IEEE Standards Association | IEEE SA (@IEEESA) April 11, 2024
“Science can amuse and fascinate us all, but it is engineering that changes the world.”
– Isaac Asimov pic.twitter.com/IDl3dWLVgn— World of Engineering (@engineers_feed) February 26, 2024
Research Tracks:
Reliability of Communication Systems needed for the autonomous vehicle transformation
- Smart Grid Technologies:
- Investigating advanced technologies to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of power grids.
- Energy Storage Systems:
- Researching and developing new energy storage technologies to improve grid stability and accommodate intermittent renewable energy sources.
- Distributed Generation Integration:
- Studying methods to seamlessly integrate distributed energy resources such as solar panels and wind turbines into the existing power grid.
- Grid Resilience and Security:
- Exploring technologies and strategies to enhance the resilience of power grids against cyber-attacks, natural disasters, and other threats.
- Demand Response Systems:
- Researching ways to improve demand-side management and develop systems that allow consumers to actively participate in grid balancing.
University of Groningen: Smart Grid Blockchains
- Researching ways to improve demand-side management and develop systems that allow consumers to actively participate in grid balancing.
- Advanced Sensors and Monitoring:
- Developing new sensor technologies and monitoring systems to enhance grid visibility, detect faults, and enable predictive maintenance.
- Power Quality and Reliability:
- Studying methods to improve power quality, reduce voltage fluctuations, and enhance overall grid reliability.
- Integration of Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Researching the impact of widespread electric vehicle adoption on the grid and developing smart charging infrastructure.
- Grid Automation and Control:
- Exploring advanced automation and control strategies to optimize grid operations, manage congestion, and improve overall system efficiency.
- Campus Distribution Grid Selling and Buying
Standards:
Presentation | FERC-NERC-Regional Entity Joint Inquiry Into Winter Storm Elliott
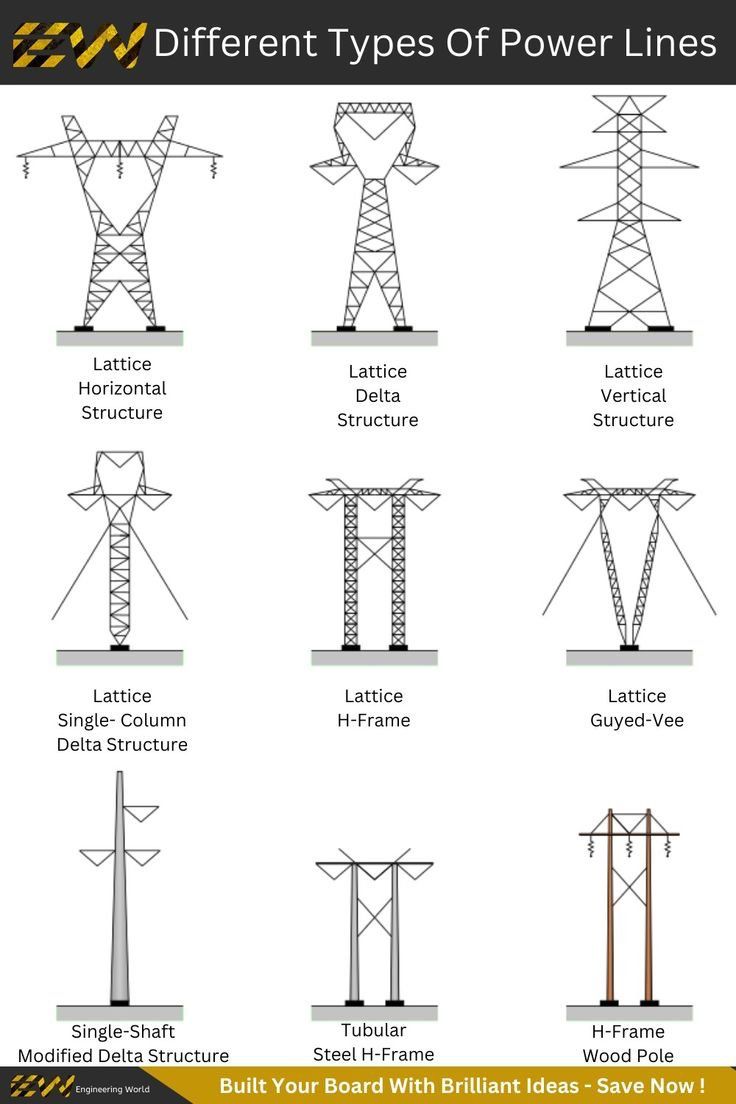
IEEE Guide for Joint Use of Utility Poles with Wireline and/or Wireless Facilities
NESC Rule 250B and Reliability Based Design
NESC Requirements (Strength and Loading)
Engineering Analysis of Possible Effects of 2017 NESC Change Proposal to Remove 60′ Exemption
Joint Use of Electric Power Transmission & Distribution Facilities and Equipment
A Framework to Quantify the Value of Operational Resilience for Electric Power Distribution Systems
Technologies for Interoperability in Microgrids for Energy Access
National Electrical Safety Code: Revision Cycles 1993 through 2023
February 24, 2023
The new code goes into effect 1 February 2023, but is now available for access on IEEE Xplore! Produced exclusively by IEEE, the National Electrical Safety Code (NESC) specifies best practices for the safety of electric supply and communication utility systems at both public and private utilities. The bibliography is expanding rapidly:
NESC 2023: Introduction to the National Electrical Safety Code
NESC 2023: Safety Rules for Installation and Maintenance of Overhead Electric Supply
NESC 2023: Rules for Installation and Maintenance of Electric Supply Stations
October 31, 2022
The IEEE NESC technical committee has released a “fast track” review of proposed changes to fault-managed power system best practice:
CP5605 Provides a definition of new Fault Managed Power System (FMPS) circuits used for the powering of
communications equipment clearly defines what constitutes a FMPS circuit for the purposes of application of the NESC
Rules of 224 and 344
https://ieee-sa.imeetcentral.com/p/eAAAAAAASPXtAAAAADhMnPs
CP5606 Provides new definitions of Communication Lines to help ensure that Fault Managed Power Systems (FMPS)
circuits used for the exclusive powering of communications equipment are clearly identified as communications lines
and makes an explicit connection to Rule 224B where the applicable rules for such powering circuits are found.
https://ieee-sa.imeetcentral.com/p/eAAAAAAASPXpAAAAAFfvWIs
CP5607 The addition of this exception permits cables containing Fault Managed Power System (FMPS) circuits used for
the exclusive powering of communications equipment to be installed without a shield.
https://ieee-sa.imeetcentral.com/p/eAAAAAAASPXuAAAAAEEt3p4
CP5608 The addition of this exception permits cables containing Fault Managed Power System (FMPS) circuits used for
the exclusive powering of communications equipment to be installed without a shield.
https://ieee-sa.imeetcentral.com/p/eAAAAAAASPXvAAAAAGrzyeI
We refer them to the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee for further action, if any.
August 5, 2022
We collaborate closely with the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee (IEEE E&H) to negotiate the standard of care for power security on the #SmartCampus since many campus power systems are larger than publicly regulated utilities. Even when they are smaller, the guidance in building the premise wiring system — whether the premise is within a building, outside the building (in which the entire geography of the campus footprint is the premise), is inspired by IEEE Standards Association administrated technical committees.
Today we begin a list of noteworthy changes to be understood in the next few Power colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
- New rules 190 through 195 cover photovoltaic generating stations. Rule 116c adds an exception for short lengths of insulated power cables and short-circuit protection if the situation involves fewer than 1,000 volts.
- Rule 320B has been revised to clarify separations that apply to communications and supply in different conduit systems.
- Table 410-4 is based on the latest arc flash testing on live-front transformers.
- Rule 092A adds an exception allowing protection, control, and safety battery systems to not be grounded.
- Rules 234 B1, C1, D1 were revised to better present vertical and horizontal wind clearances, and to coordinate requirements with the new Table 234-7.
- Rule 120A was revised to provide correction factors for clearances on higher elevations.
- Table 253-1 has been revised to reduce the load factor for fiber-reinforced polymer components under wire tension—including dead ends—for Grade C construction.
- Rule 410A now requires a specific radio-frequency safety program for employees who might be exposed.
- In the Clearances section, as well as in the specification of the Grade of Construction in Table 242-1, the Code further clarifies the use of non-hazardous fiber optic cables as telecom providers continue to expand their networks.
- Revisions in the Strength & Loading sections include modified Rule 250C, which addresses extreme wind loading for overhead lines. Two wind maps are now provided instead of the previous single one. A map for Grade B, the highest grade of construction, with a Mean Recurrence Interval (MRI) of 100 years (corresponding to a one percent annual probability of occurrence) is provided in place of the previous 50–90-year MRI map. For Grade C construction, a separate 50-year MRI (two percent annual probability of occurrence) map is now provided. In the previous Code, a factor was applied to the 50–90-year MRI map for application to Grade C.
- Changes were also made to the method of determining the corresponding wind loads, consistent with the latest engineering practices as an example of a Code revision focused on public safety, the ground end of all anchor guys adjacent to regularly traveled pedestrian thoroughfares, such as sidewalks, and similar places where people can be found must include a substantial and conspicuous marker to help prevent accidents. The previous Code did not require the marking of every such anchor guy.
- Significant revisions were made in Section 14 covering batteries. Previous editions of the code were based on lead-acid technology and batteries only used for backup power. The 2023 Code incorporates the new battery technologies and addresses energy storage and backup power.
- A new Section 19 of the code covers photovoltaic generating stations, with sections addressing general codes, location, grounding configurations, vegetation management, DC overcurrent protection, and DC conductors. These new rules accommodate large-scale solar power projects.
- In the Clearances section, all rules for wireless antenna structures have been consolidated in the equipment section (Rule 238 and 239), which makes the Code more user-friendly.
- A new subcommittee was created focusing on generating stations, with the original subcommittee continuing to address substations.
- A working group is investigating Fault Managed Power Systems (FMPS) cables as the technology may be used for 5G networks. The team is looking at possible impacts, including clearances and work rules.
After "slipping a pole" in its revision cadence (owed to the circumstances of the pandemic) the 2023 NESC is rolling out for incorporation by reference into public safety laws relevant to education communities with #WiseCampus ambitions.@ieee_pes @IEEESAhttps://t.co/7EaTBgxa8X pic.twitter.com/jPvZNYzWBi
— IEEECampus (@IEEECampus) August 5, 2022
February 18, 2021
Several proposals recommending improvements to the 2017 National Electrical Safety Code (NESC) were submitted to the IEEE subcommittees drafting the 2022 revision of the NESC. Some of the proposals deal with coordination with the National Electrical Code — which is now in its 2023 revision cycle. Keep in mind that that NESC is revised every 5 years at the moment; the NEC is revised every 3 years.
The original University of Michigan standards advocacy enterprise has been active in writing the NESC since the 2012 edition and set up a workspace for use by electrical professionals in the education industry. We will be using this workspace as the 2022 NESC continues along its developmental path:
The revision schedule — also revised in response to the circumstances of the pandemic — is linked below::
NESC 2023 Edition Revision Schedule*
The NESC is a standing item on the 4-times monthly teleconferences of the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities committee. The next online meeting is shown on the top menu of the IEEE E&H website:
We have a copy of the first draft of the 2023 NESC and welcome anyone to join us for an online examination during any of Power & ICT teleconferences. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
Business unit leaders, facility managers and electrical engineers working in the education facilities industry may be interested in the campus power system reliability database. Forced outages on large research campuses, for example, can have enterprise interruption cost of $100,000 to $1,000,000 per minute. The campus power system forced outage database discriminates between forced outages attributed to public utility interruptions and forced outages attributed to the university-owned power system. The E&H committee will convey some of the discipline applied by the IEEE 1366 technical committee into its study of campus power systems and, ultimately, setting a benchmark for the standard of care for large university power systems.
* The IEEE changed the nominal date of the next edition; likely owed to pandemic-related slowdown typical for most standards developing organizations.
Issue: [16-67]
Contact: Mike Anthony, Robert G. Arno, Lorne Clark, Nehad El-Sharif, Jim Harvey, Kane Howard, Joe Weber, Guiseppe Parise, Jim Murphy
Category: Electrical, Energy Conservation & Management, Occupational Safety
ARCHIVE: University of Michigan Advocacy in the NESC 2007 – 2017
The 2023 National Electrical Safety Code (#NESC) will be published this August. Stay tuned for new resources from #IEEE coming soon! Read about the upcoming changes here:https://t.co/VLXCNaf74S
— IEEE Educational Activities (@IEEEeducation) June 8, 2022
LEARN MORE:
P1366 – Guide for Electric Power Distribution Reliability Indices
University Design Guidelines that reference the National Electrical Safety Code