What Presidents Are Celebrated on Presidents’ Day? https://t.co/GGKvlPYiWu
— Home Quirer (@homequirer) February 19, 2024
Secretary of State Marco Rubio’s full speech today at the 2026 Munich Security Conference.
Excerpt:
“At the time of that first (1963 Munich Security Conference) gathering, Soviet communism was on the march. Thousands of years of Western civilization hung in the balance. At that… pic.twitter.com/YsE59U2dQU
— Paul Villarreal (AKA Vince Manfeld) (@AureliusStoic1) February 14, 2026
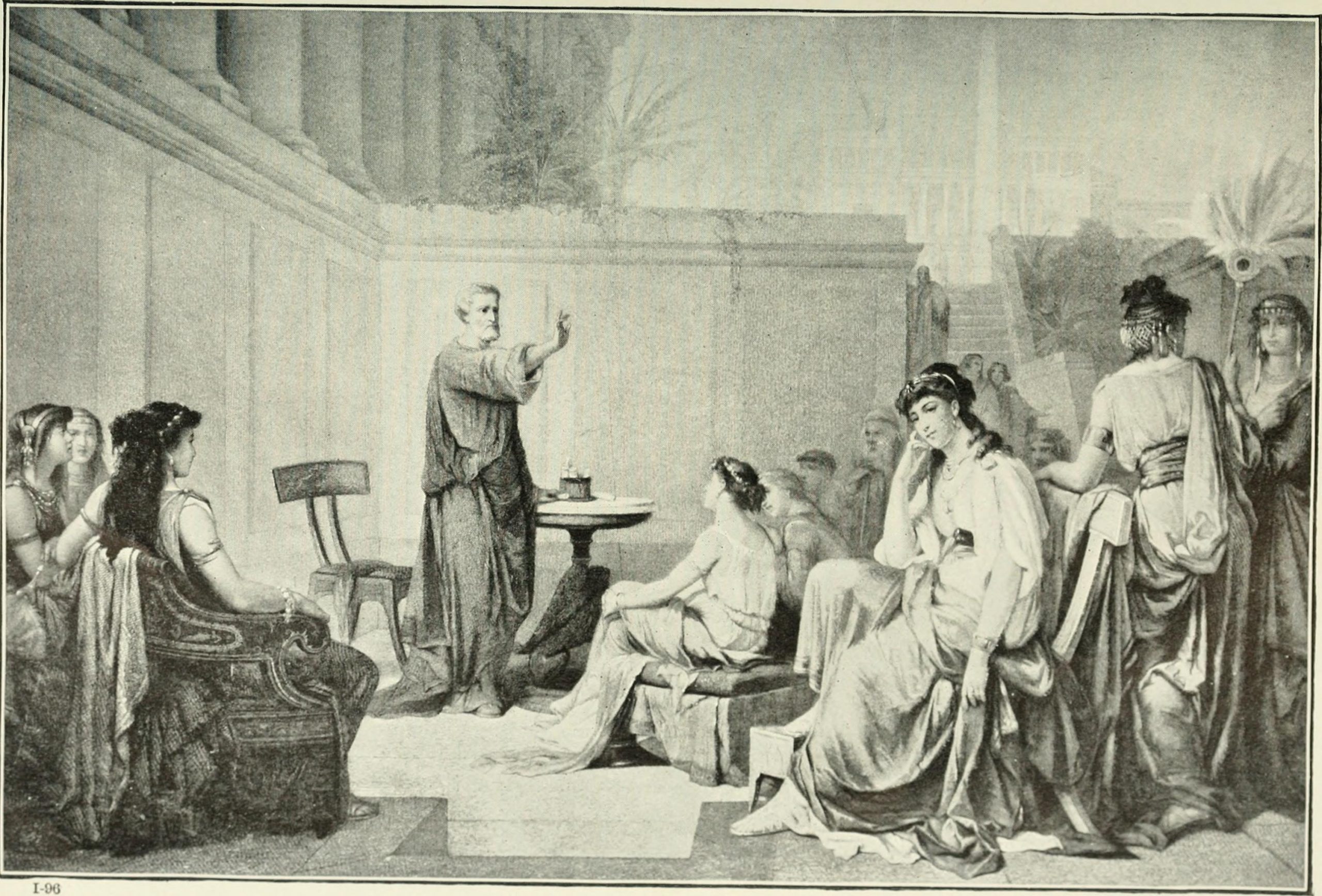
Illustration from 1913 showing Pythagoras teaching a class of women. Pythagoras believed that women should be taught philosophy as well as men and many prominent members of his school were women.Our practice is fairly structured as our Syllabus reveals. Once a month we like to break form and throw our agenda “open”. Unstructured. Completely determined by the interest of our clients, colleagues and followers. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
“Reflections on the motive power of fire: | Sadi Carnot
* Lyndon B. Johnson played a significant role in the passage of the Education Acts of 1965, which consisted of two key pieces of legislation: the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) and the Higher Education Act (HEA).
As President of the United States, Johnson made education reform a priority of his administration and saw it as a means of addressing poverty and inequality in America. He signed the ESEA into law in April 1965, which was designed to provide funding to schools serving low-income students and aimed to close the achievement gap between disadvantaged students and their more affluent peers. The ESEA also provided funds for teacher training and other educational programs.
In November of the same year, Johnson signed the HEA into law, which provided funding for college and university education and sought to make higher education more accessible to all Americans.
Together, these Education Acts of 1965 were a significant achievement for Johnson’s administration and played a crucial role in expanding educational opportunities for millions of Americans. They marked a major shift in federal education policy and helped to establish the federal government’s role in shaping education policy in the United States.
National Institutes of Health (Library of Medicine)
Dr. Jill Jacobs-Biden: Student Retention at the Community College: Meeting Student’s Needs
Michelle Obama: Princeton-Educated Blacks and the Black Community
Dr. Claudine Gay: Taking charge: Black electoral success and the redefinition of American politics
Hilary Clinton: There is Only the Fight…
John Kennedy: Appeasement at Munich
John Nash: Non-Cooperative Games
Thomas Sowell on School Choice and the Price Our Children Pay for Bad Ideas