Performance of Buildings
- Home Page 11

Commissioning Process Requirements for New Buildings and New Systems
Standards Michigan ASHRAE Coverage
ASHRAE Standard 202 provides procedures, methods, and documentation for project delivery from predesign through occupancy/operations, ensuring buildings and new systems meet the Owner’s Project Requirements. The standard promotes a uniform, integrated approach to verify performance, deliver quality facilities, and support ongoing successful operation.
International Fire Code
2024 International Fire Code | Free Access
Crosswalk: NFPA Fire Code and ICC International Fire Code
Not to worry, I have a permit. pic.twitter.com/SUp9ztTH2g
— Emily Laudin (@EmilyLaudin) August 4, 2024
2024 GROUP A PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES based on Committee Action Hearings October 2024
2024 GROUP A PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
ICC BCAC | Comments to be presented at October Hearings
Noteworthy Proposals:
IFC 1010.27 Locking arrangements, PDF page 252
IFC 1020.2 Corridor Fire Resistance Ratings. PDF page 356
IFC 915 More Carbon Monoxide Detection Systems, PDF page 1156
IBC 917 Mass notification for Group E occupancies, PDF page 1176
IFC 5701 More Process Hazard Analysis, PDF page 1571
The transcript (Complete Monograph) of Committee Actions should be available by September 5th.
Committee Action Hearings on Proposed Changes: October 23-31 Long Beach, California
“Waking Effectiveness of Alarms for Adults Who Are Hard of Hearing” 2007 Victoria University, Australia
Health Facilities: Navigating IBC and NFPA differences
Posted February 14, 2023
Free access to the latest edition of the IFC is linked below:
Following the ICC Group A revision cycle public consultation on the 2024 International Fire Code will begin. The ICC will announce the development schedule sometime in 2022.
We limit our resources simply tracking the proposals that run through Group E (Educational) and Group I (Institutional) occupancies in the Group A suite with closer attention to the state they are adopted whole cloth or with local exceptions. In many cases, IFC adoption by state and local authorities is delayed by one or more previous code revisions. This delay in adoption may be necessary in order for jurisdictions to evaluate the impact of changes upon the region under their authority.
Public safety budgets historically support the local and state fire marshal and his or her staff. The revenue stream of many trade associations originates from membership, conference attendance, training and certification enterprises that service the public sector stakeholder. Manufacturer sponsorship of trade association conferences is noteworthy.
Unless there is an idea, or proposed regulation that has run off the rails (either in terms of rigor or cost increase) — we place fire safety in the middle of our ranking of priorities. With gathering pace, we find many fires safety goals being met with electrotechnologies where we place our highest priority.
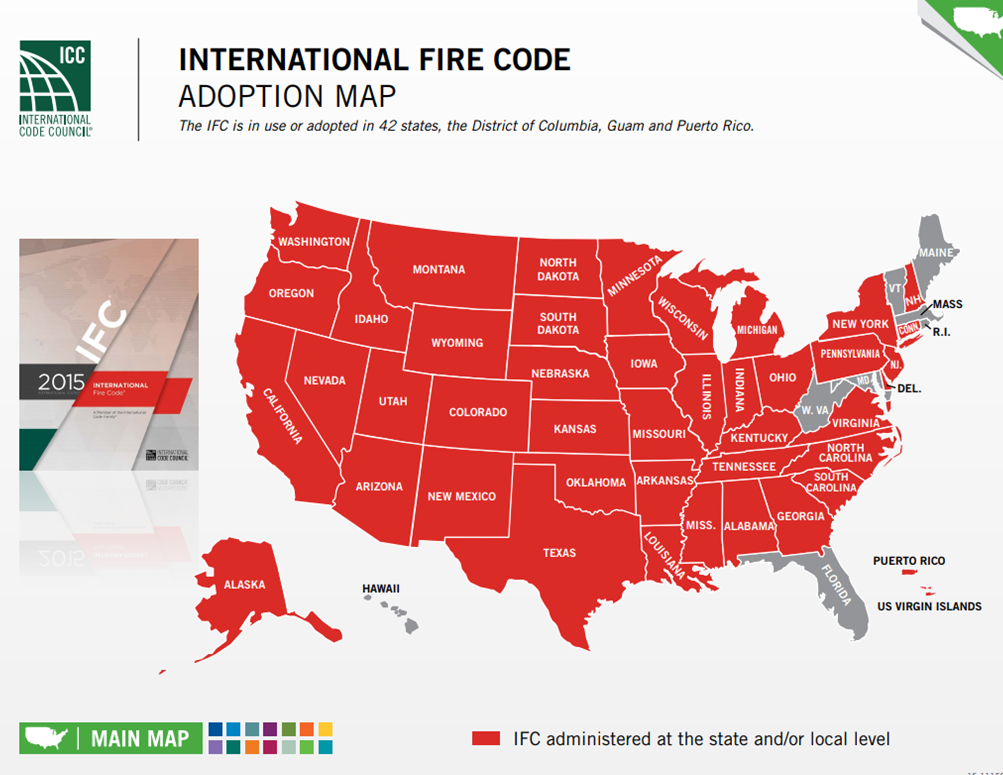
Click on image for more information. The map is updated by expert agencies frequently so we recommend a web search for an update.
Significant code changes rarely happen within a 3-year cycle so it is wise to follow ideas as they travel through the agendas of technical committees through several cycles as administered by the Fire Code Action Committee.
The ICC posts the transcripts of public proposals, technical committee responses to public proposals, public response to the technical committee response and the final balloting in a fair and reasonable fashion as can be seen in the transcripts linked below:
2021 International Fire Code Proposed Changes
2021 International Fire Code Public Comment Agenda
A search on the terms “classroom” or “school” in any of the documents above offers granular insight into the trend of current thinking. We find fire extinguishers placement a perennial concern across several standards suites. You will note the careful consideration of proposals for use of the mass notification systems, now integrated into fire alarm systems and their deployment in active shooter situations.
The transcripts reveal detailed understanding and subtlety.
There are many issues affecting the safety and sustainability of the education facility industry. We add value to the industry because of our cross-cutting perspective on the hundreds of “silos”created by the competition (and sometimes cooperation) among accredited, consortia and open-source standards developers. We have the door open every day at 11 AM Eastern time to enlighten understanding of them all. We also host a breakout teleconference every month to drill into the specifics of standards action on fire safety for the real assets of school districts, colleges and universities. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
Finally, we persist in encouraging education industry facility managers (especially those with operations and maintenance data) to participate in the ICC code development process. You may do so by CLICKING HERE.
The ICC Group B Code Meetings will be hosted soon and open to the public:
The Group B tranche is largely focused on energy, structural, residential and existing building concepts but all of the titles cross-reference the IFC in some way so it is wise to follow how the concepts re-arrange and cross-reference themselves with each cycle.
Issue: [16-169]
Category: Architectural, Facility Asset Management, Space Planning
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Casey Grant, Joshua Evolve, Marcelo Hirschler
More
2021/2022 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE
FINAL ACTION RESULTS ON THE 2018 PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE INTERNATIONAL CODES – GROUP A
2018 GROUP A PROPOSED CHANGES TO THE I-CODES COLUMBUS COMMITTEE ACTION HEARINGS
2018 GROUP A PUBLIC COMMENT AGENDA | INTERNATIONAL BUILDING CODE
2018 GROUP A PUBLIC COMMENT AGENDA | INTERNATIONAL FIRE CODE
2018 REPORT OF THE COMMITTEE ACTION HEARINGS ON THE 2018 EDITIONS OF THE GROUP A INTERNATIONAL CODES
print (“Hello World!”)
Data Points (2023 Estimates for 193 countable nations):
Global Gross Domestic Product (GGDP) ~ $106.17T
Anglosphere (United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand) ~ $31T (or ~32% of GGDP)
United States GDP $27T (or about 1/3rd of GGDP)

“Livres des Merveilles du Monde” 1300 | Marco Polo | Bodleian Libraries, University of Oxford
Today we break down consultations on titles relevant to the technology and management of the real assets of education communities in the United States specifically; but with sensitivity to the global education markets where thousands of like-minded organizations also provide credentialing, instruction, research, a home for local fine arts and sport.
We steer away from broad policy issues and steer toward technical specifics of public consultations presented by national member bodies of the International Electrotechnical Commission, the International Organization for Standardization, the International Telecommunications Union and the American National Standards Institute. If there is a likelihood that the titles published by these workgroups will be incorporated by reference into public safety or sustainability legislation; or integrated into the cost structure of education communities in any other way, we will listen carefully and contribute meaningfully where we can.
Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations | 1961
| “Even apart from the instability due to speculation, there is the instability due to the characteristic of human nature that a large proportion of our positive activities depend on spontaneous optimism rather than on a mathematical expectation, whether moral or hedonistic or economic. Most, probably, of our decisions to do something positive, the full consequences of which will be drawn out over many days to come, can only be taken as the result of animal spirits — a spontaneous urge to action rather than inaction, and not as the outcome of a weighted average of quantitative benefits multiplied by quantitative probabilities. Enterprise only pretends to itself to be mainly actuated by the statements in its own prospectus, however candid and sincere that prospectus may be. Only a little more than an expedition to the South Pole is it based on an exact calculation of benefits to come. Thus if the animal spirits are dimmed and the spontaneous optimism falters, leaving us to depend on nothing but a mathematical expectation, enterprise will fade and die; — though fears of loss may have a basis no more reasonable than hopes of profit had before.”
“The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money” — John Maynard Keynes, 1936 |
American National Standards Institute
Setting the standard: Grange members can be voice of rural users in standardization system
ISO/IEC/ITU coordination – Listing of New Work Items (New: Passwords Required)
New ANSI Education Initiative Supports the Next Generation of Standardization Leaders
International Code Council
2024/2025/2026 ICC CODE DEVELOPMENT SCHEDULE (3/17/2023)
International Electrotechnical Commission
International Electrotechnical Commission | CDV Consultations
IEC Open Consultations: 20 December
IEC 87th General Meeting | Cairo, 22 – 26 October
Results from IEC General Assembly 2022 | San Francisco
Extended Versions Certain standards are required to be read in tandem with another standard, which is known as a reference (or parent) document. The extended version (EXV) of an IEC Standard facilitates the user to be able to consult both IEC standards simultaneously in a single, easy-to-use document.
International Telecommunications Union
The case for standardizing homomorphic encryption
Outcomes of the ITU Plenipotentiary Conference
World Radiocommunication Conference
International Standardization Organization
How ISO codes connect the world
New partnership for ISO and ICC
Must-have skills for the green economy
A partial list of projects with which we have been engaged as an active participant; starting with the original University of Michigan enterprise in the late 1990’s and related collaborations with IEEE and others: (In BOLD font we identify committees with open consultations requiring a response from US stakeholders before next month’s Hello World! colloquium)
IEC/TC 8, et al System aspects of electrical energy supply
IEC/TC 22 Power electronic systems and equipment
IEC/TC 62 Electrical equipment in medical practice
IEC/TC 64 Electrical installations and protection against electric shock
IEC/TC 82 Solar photovoltaic energy systems
IEC/SYC Electrotechnical Aspects of Smart Cities
Standards Michigan Workspace for IEC/ITU Consultations
ISO/IEC JTC 1 Information Technology, et. al
ISO/TC 205 Building environmental design
ISO/TC 229 Nanotechnologies
ISO/TC 232 Education and Learning Services
ISO/TC 260 Human Resource Management
ISO/TC 267 Facility Management
ISO/TC 268 Sustainable cities and communities
ISO/TC 301 Energy management and energy savings
ISO/TC 304 Healthcare organization management
We collaborate with the appropriate ANSI US TAG; or others elsewhere in academia. We have begun tracking ITU titles with special attention to ITU Radio Communication Sector.
main( ) { printf("hello, world\n"); }
We have collaborations with Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, Sapienza – Università di Roma, Universität Zürich, Universität Potsdam, Université de Toulouse. Universidade Federal de Itajubá, University of Windsor, the University of Alberta, to name a few — most of whom collaborate with us on electrotechnology issues. Standards Michigan and its 50-state affiliates are (obviously) domiciled in the United States. However, and for most issues, we defer to the International Standards expertise at the American National Standards Institute
ANSI INTERACTIVE MAP: INTERNATIONAL TRADE & DEVELOPMENT
Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
More
Data Point: Global Construction Market is Expected to Reach $11 trillion by 2031
General Public Participation in ANSI ISO Activities
March 2021 edition of the TMB Communiqué.
ISO/IEC Directives, Part 1, Consolidated ISO Supplement
International Electrotechnical Commission Annual Report 2019
ANSI Education & Training Overview
ITU Digital Technical Standards
* A “Hello, World!” program generally is a computer program that outputs or displays the message “Hello, World!”. Such a program is very simple in most programming languages (such as Python and Javascript) and is often used to illustrate the basic syntax of a programming language. It is often the first program written by people learning to code. It can also be used as a sanity test to make sure that a computer language is correctly installed, and that the operator understands how to use it.
History & Horizon
Our engagement with the ISO catalog began in 2008 at the University of Michigan and, after the 2016 reorganization, was transferred to Standards Michigan, LLC. We start the year reviewing where our voice was heard (with attendance at meetings in Europe) and in written response to calls for public comment. With link to research grant applications for faculty and students.
Standards Australia
Department of Industry, Science and Resources
Tune in to our latest podcast ‘Building a global Quantum Industry: Explaining, Scaling and Standardising Quantum Technologies’ where experts draw upon quantum’s most exciting applications.https://t.co/dFun1MTkDE
— Standards Australia (@standardsaus) November 29, 2023
Evolution of the standards system in Australia is tracking the evolution of the United States standards system administered by the American National Standards Institute. In many economic sectors adherence to Australian Standards is mandated by legislation, however, access to the standards are often cost prohibitive, particularly to small business and sole traders.
Principal petitioner Andrew Gardso, an electrical engineer, states,
“This in essence will force small organisations and sole traders out of business or necessitate services being performed without having access to these standards.”
Access to Standards Australia Construction codes can cost more than $2673 for three years’ access to the National Construction Code set of standards. A petition to the Australian parliament’s House of Representatives seeks free or affordable access to essential standards that govern the safety and consistency of products services and systems, including design and construction.
Survey and Analysis of Current End-User Data Analytics Tool Support
Three ways Artificial Intelligence is transforming agriculture and food
*
Canadian Parliament Debate on Standards Incorporated by Reference
This week, we hosted the @IECStandards #smartcities committee in Sydney. Experts discussed smart tech and #sustainability to tackle #urbanchallenges. Discover more about our efforts to build resilient, sustainable cities: https://t.co/GOjoOBXoc9 pic.twitter.com/gvqvegx4km
— Standards Australia (@standardsaus) February 14, 2025
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670
























