Anixter
- Home Page 36

“The Grave Dancer”
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Fine Arts 300
Public Input on the 2029 Edition will be received until January 6, 2027
“Wir haben Kunst, damit wir nicht
an der Wahrheit zugrunde gehen”
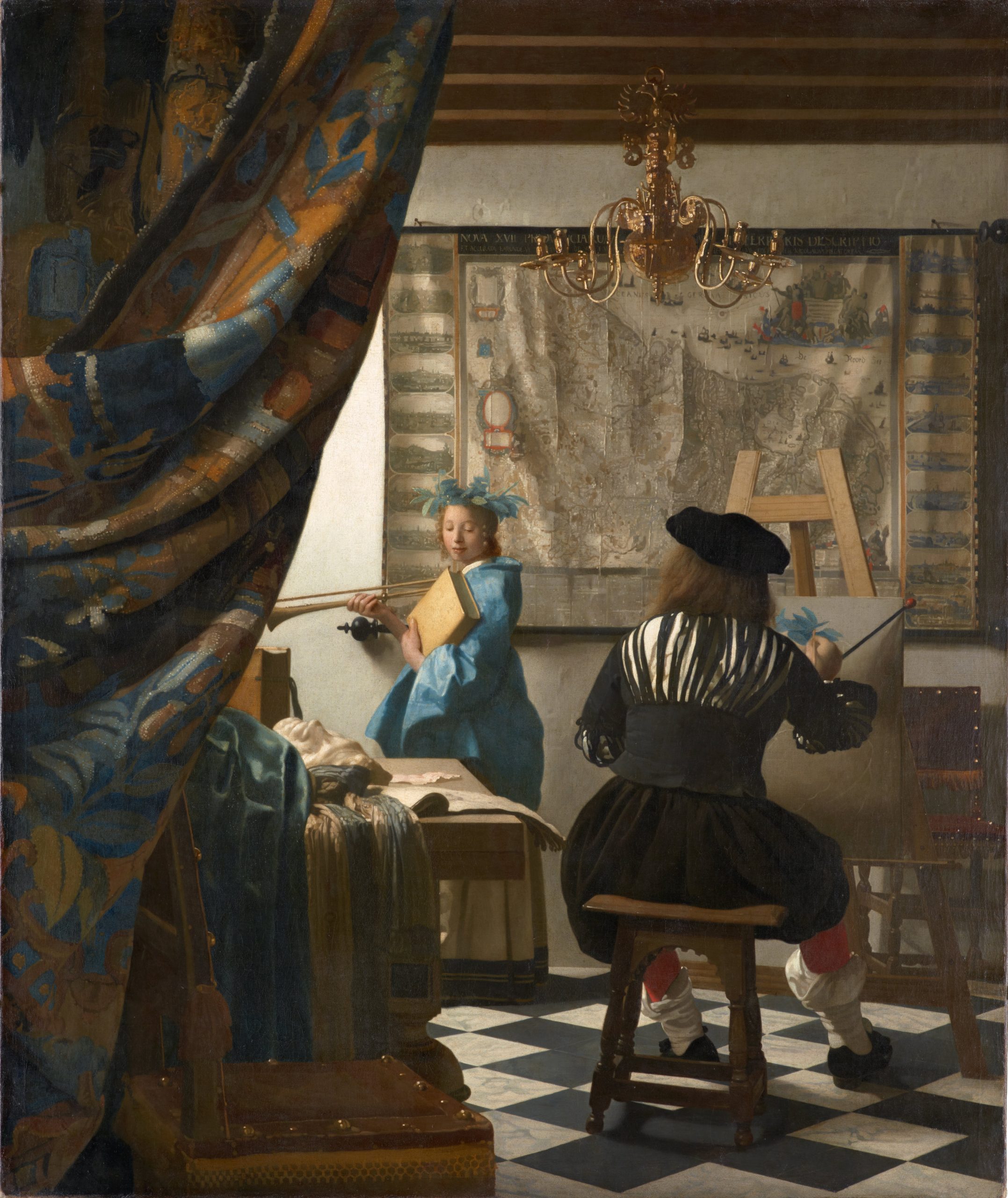
Not every student is passionate about Graph Algorithms, Green Policy or coding the Internet of Things but wants to devote their energy and talent to making the world a better place by making the world a more beautiful place. Spaces for the “creatives” among them are elevated risk spaces. Today we examine the literature for designing, building and maintaining these occupancies in the safest and most sustainable way; among them the spaces for textile research and fashion design; usually co-mingled with drawing, painting, and textile creation space.
The garment industry is multi-disciplinary and is larger than the energy industry. It contributes to the standard for civilization; even though subtly so. For this reason, starting 2023, we will break down our coverage of the literature that supports the fashion industry from the fine arts domain in separate colloquia every quarter.
Fine Arts 200. Exploration of best practice for spaces used for various forms of creative expression that are appreciated for their artistic or aesthetic value, often involving skills and techniques that require specialized training and expertise.
-
- Painting: The application of pigment to a surface, such as canvas or paper, to create images or visual compositions using techniques like oil, acrylic, watercolor, or tempera.
- Sculpture: The creation of three-dimensional artworks by shaping and manipulating materials such as stone, wood, metal, or clay.
- Drawing: The use of lines, marks, or other materials to create images or representations on paper, canvas, or other surfaces.
- Printmaking: The creation of multiple copies of an image from a master plate or block, using techniques like engraving, etching, lithography, or screen printing.
- Photography: The use of a camera to capture and create visual images, often through techniques such as exposure, composition, and processing.
- Architecture: The design and construction of buildings and structures, involving artistic elements such as form, space, materials, and aesthetics.
- Ceramics: The creation of pottery or ceramic objects using techniques like wheel throwing, hand-building, or glazing.
- Mixed media: The combination of different artistic materials or techniques in a single artwork, such as collage, assemblage, or installations.
- Conceptual art: The creation of artworks that prioritize ideas, concepts, and intellectual or philosophical aspects over traditional aesthetic or material considerations.
Fashion 300. Best practice literature for the spaces needed for the creation of artworks using textiles and fibers, such as weaving, quilting, or embroidery. Research and teaching spaces in this domain; at the foundation of the garment industry — one of the largest sectors in the economy in any nation — present surprising challenges
See our CALENDAR for a schedule of those session.
US-based standards developers with a footprint in the fine arts domain:
Committee D13 on Textiles Celebrates a Century
2021 International Building Code: Section 305 Educational Group E
Underwriters Laboratories
Lorem ipsum (product testing: kiln heat specifications, fabric and paint flammability, wet and dry fire extinguishing systems, etc.)
National Fire Protection Association
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
Leveraging User-Provided Noisy Labels for Fashion Understanding
Institutional Guidelines
Federal Regulations & Recommendations
Environmental Health and Safety in the Arts Guide for K-12 School, Colleges and Artisans
Global standard developers: (partial list)
Open to everyone. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
🌤️🌺⛲🌳 pic.twitter.com/bRL7eIY4gg
— Cranbrook Academy of Art (@cranbrookart) July 3, 2023
Public Art Program
More
Texas Education Agency: Fine Arts Standards
Texas Tech: Facilities Planning & Construction
“Public art is form of street life, a means to articulate the implicit values of a city when its users occupy the place of determining what the city is.” — Malcolm Miles
Museum Collections Security
Law & Crime Network: Bizarre Details of Louvre Heist That Shocked the World
Several universities host federal enterprises (laboratories, wildlands, Presidential libraries*, etc.) that must conform to Title 40 United States Code, Public Buildings, Property, and Works Paragraph 486(c) provides statutory authority for the head of each executive agency to issue orders and directives necessary to manage the Government’s property.
Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) 41 Federal Property Management Regulations Part 101, Subpart 20.5 “Physical Protection”, prescribes policies and methods for physically protecting buildings and grounds operated by GSA and other Federal Executive agencies. The Department of the Interior’s property management regulations are in Part 114 of CFR 41.
Museum Management Chapter 14: Museum Collections Security
Standard Methods of Fire Tests for Flame Propagation of Textiles and Films
* There are only a few education communities that host Presidential Libraries:
Herbert Hoover Presidential Library and Museum – West Branch, Iowa (Hoover Institution, Stanford University)
Lyndon B. Johnson Presidential Library and Museum – Austin, Texas (The University of Texas at Austin)
Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library and Museum – Ann Arbor, Michigan (The University of Michigan)
George H. W. Bush Presidential Library and Museum – College Station, Texas (Texas A&M University)
Cultural Resource Properties
Public Input on the 2029 Edition will be received until January 6, 2027
Books cannot be killed by fire. People die, but books never die
No man and no force can put thought in a concentration camp forever
— Franklin Roosevelt
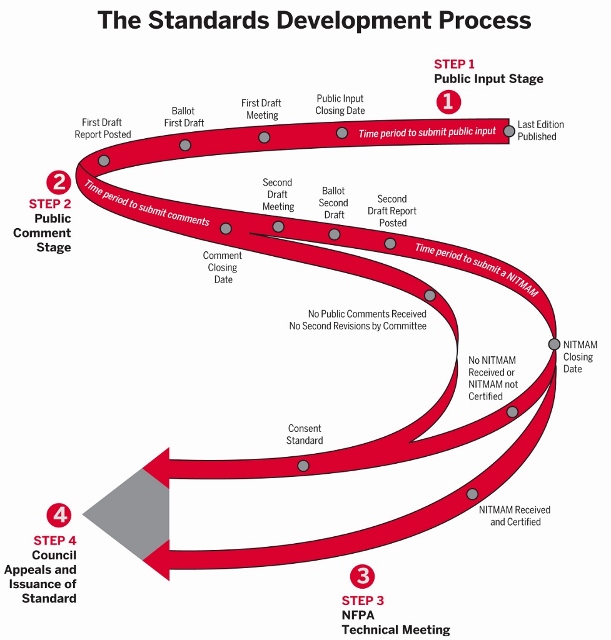
Many education communities build and maintain cultural resource properties whose safety and sustainability objectives are informed by local adaptations of consensus products developed by the International Code Council (ICC) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). We need to understand the ICC and NFPA product suites as a pair. For most real assets in the education industry they move “roughly” in tandem even though they are produced by different organizations for a different set of customers. Sometimes the out-of-step condition between NFPA and ICC permits subject matter experts on technical committees to make the best possible decisions regarding the safety and sustainability agenda of the interest group they represent; but not always.
Occupancy classification is always a first consideration and both the NFPA and the ICC have a claim to some part of this occupancy concept*. In the ICC suite we find code requirements for many “cultural places of worship” tracking in the following sections of the International Building Code (IBC):
Section 303 Assembly Group A-3
Section 305 Educational Group E
Section 308 Institutional Group I
Note that Sections 305 and 308 recognize the accessory and multi-functional nature of occupancy types in the education industry – i.e child care and adult care function can marge and be an accessory to a place of worship. The general rule in the IBC is that accessory religious educational rooms and religious auditoriums with occupant loads of less than 100 per room or space are not considered separate occupancies. Other standards developers are guided by this rule.







Close coupled to the IBC for this occupancy class is NFPA 909 Code for the Protection of Cultural Resource Properties – Museums, Libraries, and Places of Worship. From the document prospectus:
• This code describes principles and practices of protection for cultural resource properties (including, but not limited to, museums, libraries, and places of worship), their contents, and collections, against conditions or physical situations with the potential to cause damage or loss.
• This code covers ongoing operations and rehabilitation and acknowledges the need to preserve culturally significant and character-defining building features and sensitive, often irreplaceable, collections and to provide continuity of operations.
• Principles and practices for life safety in cultural resource properties are outside the scope of this code. Where this code includes provisions for maintaining means of egress and controlling occupant load, it is to facilitate the evacuation of items of cultural significance, allow access for damage limitation teams in an emergency, and prevent damage to collections through overcrowding or as an unintended consequence of an emergency evacuation.
• Library and museum collections that are privately owned and not open to the public shall not be required to meet the requirements of this code.







Since we are hard upon release of the 2021 Edition of NFPA 909 let us take a backward look at the current (2017) version of NFPA 909 Code for the Protection of Cultural Resource Properties – Museums, Libraries, and Places of Worship. Chapter 14 covers “Museums, Libraries and their Collections”. Chapter 15 covers “Places of Worship”
The 2025 Edition is now open for public input. Let us pick through proposals for the 2021 Edition to inform our approach to its improvement by referencing the technical committee transcripts linked below:
Public Input Report: January 12, 2023
N.B. We find committee response (accepted in principle) to Standards Michigan proposal to articulate conditions in which places of worship and libraries are used as community disaster relief support facilities. We consider this a modest “code win”.
Circling back to the ICC suite we find elevated interest in hardening community owned facilities to tornadoes, hurricane and floods and other storm related risk in the structural engineering chapters of the International Building Code.















Leadership and facility managers for enterprises of this type are encouraged to contribute obtain their own (free) NFPA public participation account in order to directly participate in the 2025 revision of NFPA 909 by logging in here: https://www.nfpa.org/login.
Public consultation on the First Draft of the 2025 Edition closes January 4, 2024.
This document is also a standing item on our periodic Prometheus, Lively and Fine Arts teleconference. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.![]()
Issue: [15-258]
Category: Fire Safety, Public Safety
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Josh Elvove, Joe DeRosier
*See NFPA 101 Life Safety Code
LEARN MORE:
Guidelines for the Security of Rare Books, Manuscripts, and Other Special Collections, Association of College & Research Libraries, American Library Association, 50 East Huron Street, Chicago, IL 60611-2795.
“A Legal Primer on Managing Museum Collections,” Malaro, Marie, second edition 1998
“Risk and Insurance Management Manual for Libraries,” Mary Breighner and William Payton, edited by Jeanne Drewes, ALA 2005 ISBN 0-8389-8325-1.
Wisconsin Historic Building Code, Madison, WI:Wisconsin Administrative Code.
Laboratories 400
ASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide, Second Edition
Classification of Laboratory Ventilation Design Levels
ISO/DIS 22544Laboratory design — Vocabulary (Under Development)
The Haldane Principle § “On Being the Right Size” J.B.S Haldane
We break down our coverage of laboratory safety and sustainability standards thus:
Laboratories 100 covers a broad overview of the safety and sustainability standards setting catalogs; emphasis on titles incorporated by reference into public safety laws.
Laboratories 200 covers laboratory occupancies primarily for teaching
Laboratories 300 covers laboratories in healthcare clinical delivery.
Laboratories 400 covers laboratories for scientific research; long since creating the field of environmental health and safety in higher education and a language (and acronyms of its own: CSHEMA)
In the most recent fiscal year, the National Institutes of Health had a budget of approximately $47.7 billion. A substantial portion of this budget is allocated to research at colleges and universities. Specifically, about 83% of NIH’s funding, which translates to roughly $39.6 billion, is awarded for extramural research. This funding is distributed through nearly 50,000 competitive grants to more than 2,500 universities, medical schools, and other research institutions across the United States
The cost to build a “standard” classroom runs about $150 to $400 per square foot; a scientific research laboratory about $400 to $1200 per square foot.
Laboratories 500 is broken out as a separate but related topic and will cover conformity and case studies that resulted in litigation. Both Laboratories 200 and 400 will refer to the cases but not given a separate colloquium unless needed.
At the usual time. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
February 27, 2023
Research findings related to laboratory safety:
- Identifying and Evaluation Hazards in Research Laboratories
- “Evaluating the Efficacy of Laboratory Hazard Assessment Tools for Risk Management in Academic Research Laboratories” – This study from 2021 evaluated the effectiveness of various laboratory hazard assessment tools in academic research laboratories, and found that a combination of tools and approaches may be most effective for managing risks.
- “A Framework for Assessing Laboratory Safety Culture in Academic Research Institutions” – This 2020 study developed a framework for assessing laboratory safety culture in academic research institutions, which can help identify areas for improvement and promote a culture of safety.
- “Enhancing Laboratory Safety Culture Through Peer-to-Peer Feedback and Coaching” – This 2020 study found that peer-to-peer feedback and coaching can be an effective way to enhance laboratory safety culture, as it encourages open communication and feedback among colleagues.
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Laboratory Safety Training Programs for Graduate Students” – This 2019 study evaluated the effectiveness of laboratory safety training programs for graduate students, and found that interactive and hands-on training was more effective than traditional lecture-based training.
- “Improving Laboratory Safety Through the Use of Safety Climate Surveys” – This 2018 study found that safety climate surveys can be an effective way to improve laboratory safety, as they provide insight into employee perceptions of safety culture and identify areas for improvement.
- Chemistry laboratory safety climate survey (CLASS): A tool for measuring students’ perceptions of safety
These recent research findings suggest that laboratory safety culture can be improved through a variety of approaches, including hazard assessment tools, peer-to-peer feedback and coaching, interactive training, and safety climate surveys. Some of these findings will likely set the standard of care we will see in safety standards incorporated by reference into public safety regulations.
Related:
November 29, 2021
Today we break down the literature setting the standard of care for the safety and sustainability of instruction and research laboratories in the United States specifically; and with sensitivity to similar enterprises in research universities elsewhere in the world. We will drill into the International Code Council Group A titles which are receiving public input until January 10, 2022.
Join us by clicking the Daily Colloquia link at the upper right of our home page.
The original University of Michigan Workspace for [Issue 13-28] in which we advocate for risk-informed eyewash and emergency shower testing intervals has been upgraded to the new Google Sites platform: CLICK HERE
Related:
September 20, 2021
Today we break down the literature setting the standard of care for the safety and sustainability of instruction and research laboratories in the United States specifically; and with sensitivity to similar enterprises in research universities elsewhere in the world.
Classification of Laboratory Ventilation Design Levels – ASHRAE
ASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide
Join us by clicking the Daily Colloquia link at the upper right of our home page.
May 10, 2021
Today we will poke through a few proposals for the 2021/222 revision of the International Code Council’s Group A Codes. For example:
IFC § 202 et. al | F175-21| Healthcare Laboratory Definition
IBC § 202 et. al | E7-21| Collaboration Room
IBC § 1110.3 et. al | E143-21| Medical scrub sinks, art sinks, laboratory sinks
. . .
IFGC § 403, etl al| G1-21| Accessibility of fuel gas shut off valves
IBC § 307 Tables | G36-21| For hazardous materials in Group B higher education laboratory occupancies
IBC § 302.1 et. al | G121-21| Separation from other nonlaboratory areas for higher education laboratories
And about 20 others we discussed during the Group A Hearings ended last week. We will have until July 2nd to respond. The electrotechnology proposals will be referred to the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee which is now preparing responses to this compilation by Kimberly Paarlberg.
March 15, 2021
Today we break down action in the literature governing the safety and sustainability of instruction and research laboratories in the United States specifically; but also with sensitivity to similar enterprises in research universities elsewhere in the world. “Everyone” has an iron in this fire:
International Building Code Chapter 38: Higher Education Laboratories
ASCE Structural Engineering Institute (so that the foundations and “bone structure” of laboratories survive earthquakes, floods and other Force majeure mayhem)
National Electrical Code Chapter 5: Special Occupancies
ASHRAE Laboratory Design Guide
NFPA 45 Standard on Fire Protection for Laboratories Using Chemicals
IEEE Electrical Safety in Academic Laboratories
…and ISEA, AWWA, AIHA, BIFMA, CLSI, LIA, IAPMO, NSF, UL etc. among ANSI accredited standards developing organizations…
..and addition to NIST, Federal code of Regulations Title 29, NIH, CDC, FEMA, OSHA etc
…and state level public health regulations; some of them adapted from OSHA safety plans
Classroom and offices are far simpler. Laboratories are technically complicated and sensitive area of concern for education communities not only responsible for the safety of instructional laboratories but also global communities with faculty and staff that must simultaneously collaborate and compete. We have been tip-toeing through the technical and political minefields for nearly 20 years now and have had some modest success that contributes to higher safety and lower costs for the US education community.
Colloquium open to everyone. Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
More
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
National Institutes of Health
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
NFPA Fire Code requirements for laboratories at colleges and universities
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
National Conference of Standards Laboratories
National Institute of Standards and Technology/Information Technology Laboratory
World Standards Week 2025
2025 ANSI Innovation Summit: Where standards power progress

89th IEC General Meeting | 15-19 September 2025 | New Delhi, India
Slide decks from 2021 October ANSI Company Member Forum:
ANSI 2021 CMF-Tretler_20211013 International
ANSI WSW 2021 Standards as Digital Data Rupert
ANSI CMF WSW 2021 – Ali slides
ANSI CMF WSW 2021 – Lippert slides RE USNA IEC
Micah 4:3
Michigan West | Chapel Sermons at Calvin University
That single verse has become a tattoo, a protest sign, and a life motto for millions of Gen Z and Millennials precisely because it’s the opposite of cringe: it’s simple, doable, and refuses to let privilege or power excuse cruelty. Micah also dreams of a world where “everyone sits under their own vine and fig tree” and “no one makes them afraid” (4:4)—a vision of safety, dignity, and peace that resonates deeply with a generation facing climate anxiety, gun violence, and economic precarity. Micah says: your rage at injustice is valid, but channel it into real fairness and kindness, not just tweets.
If you treat the miracles as symbolic wisdom only, you are doing exactly what Greco-Roman intellectuals did with their own myths—and the New Testament writers explicitly reject that move. If you treat them as literal history, you are at odds with the consensus of modern historical-critical scholarship and with post-Enlightenment views of nature.
Do you accept the Bible’s own claim that it is reporting actual divine invasions of history, or do you place it, against its own self-understanding, into the same genre as the myths that surrounding cultures themselves often admitted were not historical? Most young people today instinctively lean toward the symbolic/spiritual-poetry reading because it feels sophisticated and non-threatening. But that reading would have baffled (and angered) Micah, Jesus, and Paul, who staked everything on the claim that these things really happened.
Laboratory Design
ISO/DIS 22544Laboratory design — Vocabulary (Under Development)
International Building Code Chapter 38: Higher Education Laboratories
Update: 6 June 2024
Update: 28 September 2023
Update: 10 May 2023
Update: 27 February 2023
Updated: September 20, 2021
Original Post: May 25, 2019
Colleagues in the US education facility industry who collaborated with the original University of Michigan codes and standards advocacy enterprise ahead of the launch of ISO TC 276 Biotechnology standard in 2015 may recall how the University of Michigan recommended that ANSI request removal of “facilities” from the scope of the proposed biotechnology standard; administered by the Deutsches Institut für Normung committee.
Our recommendation was accepted; thereby partitioning the science of biotechnology from the facilities that supported that activity as much as possible. Back in the early 2000’s we found the US research community in higher education was indifferent to participation in international standards of any kind; despite the concentration of chemical, energy, environmental air, electrical and fire safety risk aggregations.
Now the scope of this standard appears to recover some of the facility scope in another title; a few of the key details linked here.
Since the beginning of the original University of Michigan standards advocacy enterprise described in our ABOUT we found the US research community indifferent to participation in standards development of any kind; much less international standards. To a large degree it remains so. Perhaps in the fullness of time, respected voices will join ours.
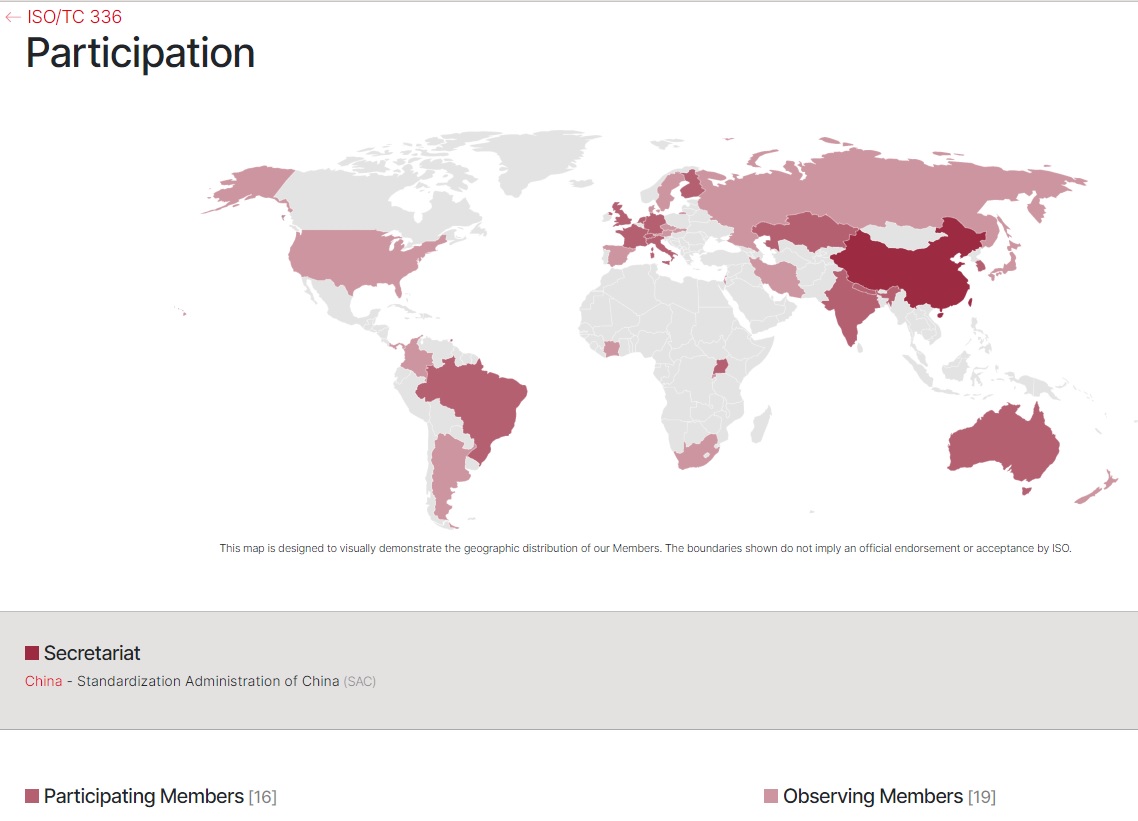
The Standards Administration of China is the Global Secretariat. The American National Standards Institute participates as an Observer. The business plan posted in 2019 is linked below:
ISO TC 336 Laboratory Design 22 March 2023 336 L
ISO TSP 290 (Laboratory Design) | 2019 (Shown for reference only)
You may communicate directly with Steve Cornish: scornish@ansi.org on any matter regarding this project.
Starting 2023 we are breaking up our coverage of laboratory-related best practice titles accordingly:
Laboratories 100 will cover all relevant standardization catalogs with special attention to titles that are incorporated by reference into public safety and sustainability laws.
Laboratories 200 will cover laboratory occupancies primarily for teaching and healthcare clinical delivery.
Laboratories 400 will cover laboratories for scientific research including medical research.
Laboratories 500 is broken out as a separate but related topic and will cover conformity and case studies that resulted in litigation. Both Laboratories 200 and 400 will refer to the cases but not given a separate colloquium unless needed.
We maintain titles from the project on the standing agendas of our periodic Global and Laboratories conversations open to everyone. Always at 15:00 UTC.













Issue: [19-134]
Category: Academic, International
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Christine Fischer, Jack Janveja, Richard Robben, Markus Scheufele, Larry Spielvogel
Source: ANSI Standards Action | Page 33
ANSI-Accredited U.S. Technical Advisory Groups (TAGS) to ISO
LINK TO ORIGINAL UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN ISO STANDARDS WORKSPACE
Reposted by ANSI July 13, 2020
Last week the American National Standards Institute notified stakeholders that the Standardization Administration of China (SAC) — the ISO member body for China — has submitted a proposal for a new field of ISO technical activity on “Laboratory Design”. The proposal bears resemblance to a notice of public consultation that was posted last year; now linked below:
ISO TSP 290 (Laboratory Design)
Comments on the (apparently revised) proposal are due at ANSI offices on August 3rd.
We refer you to Steve Cornish (scornish@ansi.org) and/or Henry Cheung (HCheung@ansi.org) at the American National Standards Institute.
We maintain consensus products of this nature on our Global and Laboratory teleconferences; open to everyone. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
Originally posted May 25, 2019
“Science, my boy, is made up of mistakes,
but they are mistakes which it is useful to make,
because they lead little by little to the truth.”
― Jules Verne, Journey to the Center of the Earth
The Standardization Administration of China (SAC) — the ISO member body for China — has submitted a proposal for a new field of ISO technical activity on “Laboratory Design” with the following scope statement:
“…Standardization in the field of laboratory design including site selection and design planning, the functional division of experimental areas, the determination of scientific and technological processes, layouts and design of furniture, and the scientific design of the facility taking into account environmental conditions and impact. Excluded:
– IEC/TC 64 (Electrical installations and protection against electric shock);
– IEC/TC 81 (Lightning protection);
– IEC/TC 66 (Safety of measuring, control and laboratory equipment);
– IEC/TC 85 (Measuring equipment for electrical and electromagnetic quantities).
Once the new TC is established, liaisons with other relevant ISO technical committees will be established, including ISO/TC 48(laboratory equipment), ISO/TC 212 (Clinical laboratory testing and in vitro diagnostic test systems)and CASCO as well as relevant IEC technical committees (IEC/TC 45(Nuclear instrumentation), IEC/TC 62 (Electrical equipment in medical practice), IEC/TC 65 (Industrial-process measurement, control and automation), IEC/TC 76 (Optical radiation safety and laser equipment) and IEC/TC 104 (Environmental conditions, classification and methods of test). Note: the TC will support the contribution of the laboratory design industry to UN Sustainable Development Goals and enable countries to address a wide range of global issues including eradication of hunger and poverty, health, climate change and economic development….”
“…The new TC will stipulate technical design requirements for a diverse range of laboratories with different functions and responsibilities. It will include, but not limited to:
1. site selection and design planning;
2. layouts and design of furniture (e.g workbenches, fume hoods, safety showers, biological safety cabinets, etc);
3. electrical, water and gas supply systems, drainage, fire prevention, HVAC, auto-control and decoration;
4. laboratories featuring bio-safety, constant temperature and humidity, and other special laboratories;
5. laboratory safety, staff health, environmental protection, and energy saving;
6. Smart laboratory (use of new technologies such as big data, cloud computing, block chain, etc. to empower laboratories, e.g. increase the depth and width of services provided to clients, improve the servicing level during the consulting, design and maintenance phases.)…”
“…The setting up of laboratory design TC and establishment of laboratory design standards will benefit organizations and groups as follows:
-
-
- Laboratory owners (including governments, scientific agencies and enterprises, etc.): Laboratory owners will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design for better management of laboratory design, construction, acceptance and operation. The investment budget will have a reference basis; construction cost will be better controlled; investment risk will be lowered; project quality can be better evaluated; construction cycle will be shortened; capital usage efficiency will be raised;
-
-
-
- Laboratory designers: Laboratory designers will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design, and will have standards to follow and verify by, make fewer design faults and ensure laboratory design to be more scientific and professional; laboratory environmental facility will be improved in terms of safety, energy conservation, environmental friendliness, as well as impacts on human health and well-being.
-
-
-
- Laboratory constructors: Laboratory constructors will have construction and acceptance standards to refer to; the construction quality will be raised; technology advancement will be promoted; the industry will be further regulated.
-
-
-
- Laboratory users: Laboratory users will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design; stakeholders can communicate with each other in a more informed way and evaluate laboratories based on common standards, making laboratory use, operation and management more scientific and regulated. Smart laboratories will allow more functions and add value by integrating technologies of big data, cloud computing and internet of things, etc.
-
-
-
- Laboratory operators: Laboratory operators will understand the principles and methods of laboratory design, which will facilitate the maintenance of laboratories; Smart laboratories will enable the remote digital control of laboratory operation and facilitate reliable, efficient and convenient maintenance.
-
-
-
- Society: The society will be able to cultivate more professional personnel in the field of laboratory design; a more sound and fair development of laboratory design and construction both home and abroad will be facilitated; more energy-saving and environmental-friendly design will promote the sustainable development of the society; the premium laboratories will inspire the creativity of researchers and promote the advancement and development of technologies. Smart laboratories will facilitate technological progress, product quality improvement, data recognition as well as international trade….”
-
If the proposal is accepted, China is willing to undertake the work of secretariat of the new TC and will provide all necessary resources including financial and human resources as well as facility supports. A partnership agreement between China and France at committee level is foreseen.
Anyone wishing to review the proposal can request a copy by contacting ANSI’s ISO Team (isot@ansi.org), with a submission of comments to Steve Cornish (scornish@ansi.org) by close of business on Friday, June 28th
N.B. This proposal will be featured in an ANSI Online news story and open for public review and comments from relevant US stakeholders via notice in Standards Action. In addition, ANSI will conduct targeted outreach to gather input on this proposal. Based on the input received from US stakeholders, a recommended ANSI position and any comments will be developed and presented to the AIC for approval before the ISO voting deadline of August 13, 2019. Contact Steve Cornish (scornish@ansi.org)
ANSI’s due process requirements were applied to this ISO/SIA/AFNOR proposal and comment from US stakeholders were consulted. It appears that most US stakeholders do NOT want to participate in the development of this standard as currently written. The public comments are available from Henry Cheung (HCheung@ansi.org) who has also prepared a draft statement from ANSI.
Comments on the draft statement are due August 2nd.
Perspective: We have been down this road before. The original University of Michigan user-interest advocacy enterprise — through ANSI — was persuasive in having “facilities” struck from the scope of the original ISO TC/276 Biotechnology project proposal (Global Secretariat: Deutsches Institut für Normung) in 2012. Now we circle back to a proposal that captures the facility component as an articulated enterprise which, in large research colleges and universities, is a delicate risk aggregation that generates significant revenue.
As always, we are happy to discuss any best practice title from anywhere on earth that affects the safety and sustainability agenda of education communities. Just click the login credentials at the upper right of our home page any day at 11 AM Eastern time. We also sweep through the status of international consensus products emerging from ISO, IEC and ITU technical and management committees. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [19-134]
Category: Academic, International
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Christine Fischer, Jack Janveja, Richard Robben, Markus Scheufele, Larry Spielvogel
Source: ANSI Standards Action | Page 33
LINK TO ORIGINAL UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN ISO STANDARDS WORKSPACE
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670