Tennis Court Lighting
- Home Page 74

Report
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Solar Panels on King’s College Chapel Roof
“…The solar panels will populate the gothic chapel roof, producing an approximate 105,000 kWh of energy a year – enough to run the chapel’s electricity, and saving around £20,000 in energy bills per year. The college confirmed that any excess energy would be sold off to the national grid.
Solar Panels on King’s College Chapel Roof
Solar panels perform better when listening to music:
A 2013 study by researchers at Imperial College London and Queen Mary University of London showed that solar panels actually work better when exposed to music, of multiple genres. Scientists at the university proved that when exposed to high pitched sounds, like those found in rock and pop music, the solar cells’ power output increased by up to 40 percent. Classical music was also found to increase the solar cells’ energy production, but slightly less so than rock and pop, as it generally plays at a lower pitch than pop and rock. Whether they know it or not, British band Coldplay are just one of the artists benefitting from this research. During their 2021 tour, they installed solar photovoltaic panels in the build-up to each show, “behind the stage, around the stadium and where possible in the outer concourses”…
BS 7671 Requirements for Electrical Installations
The Major Differences in Electrical Standards Between the U.S. and Europe
Representative Calculation: (WAG)
To determine how much electrical power and lighting 12 kilowatts (kW) will provide for an educational facility, we need to consider the following factors:
-
- Power Distribution: How the 12 kW will be distributed across different electrical needs such as lighting, computers, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), and other equipment.
- Lighting Requirements: The specific lighting requirements per square foot or room, which can vary based on the type of facility (classrooms, libraries, laboratories, etc.).
- Efficiency of Lighting: The type of lighting used (e.g., LED, fluorescent, incandescent) as this affects the power consumption and lighting output.
We start with lighting.
-
- Lighting Efficiency:
- LED lights are highly efficient, typically around 100 lumens per watt.
- Fluorescent lights are less efficient, around 60-70 lumens per watt.
- Lighting Power Calculation:
- 12 kW (12,000 watts) of LED lighting at 100 lumens per watt would provide: 12,000 watts×100 lumens/watt=1,200,000 lumens
- Illumination Requirements:
- Classroom: Approximately 300-500 lux (lumens per square meter).
- Library or laboratory: Approximately 500-750 lux.
- Area Coverage:
- If we target 500 lux (which is 500 lumens per square meter), we can calculate the area covered by the lighting: (1,200,000 lumens)/ 500 lux=2,400 square meters
- Lighting Efficiency:
Now we need to allocate power to other loads.
-
- Lighting: Assuming 50% of the 12 kW goes to lighting:
- Lighting Power: 6 kW (6,000 watts)
- Using the previous calculation: 6,000 watts×100 lumens/watt=600,000 lumens
- Area Coverage for lighting (at 500 lux): (600,000 lumens)/500 lux=1,200 square meters
- Other Electrical Needs:
- Computers and equipment: Typically, a computer lab might use around 100 watts per computer.
- HVAC: This can vary widely, but let’s assume 4 kW is allocated for HVAC and other systems.
- Lighting: Assuming 50% of the 12 kW goes to lighting:
Breakdown:
-
- Lighting: 6 kW
- Computers/Equipment: 2 kW (e.g., 20 computers at 100 watts each)
- HVAC and other systems: 4 kW
Summary
-
- Lighting: 12 kW can provide efficient LED lighting for approximately 1,200 square meters at 500 lux.
- General Use: When distributed, 12 kW can cover lighting, a computer lab with 20 computers, and basic HVAC needs for a small to medium-sized educational facility.
The exact capacity will vary based on specific facility needs and equipment efficiency.
Audio Standards
“The voice of the intellect is a soft one,
but it does not rest until it has gained a hearing.”
— Sigmund Freud
The education industry provides a large market for occupancy classes — athletic stadiums, student assembly spaces, performance theaters, large lecture halls– that depend upon effective audio systems*. To an unexpected degree the structural engineering, specification of materials and electrical system design and operation is informed by acoustical considerations. So does the integration of fire safety and mass notification systems into normal state enterprises so it is wise to follow and, ideally, participate in leading practice discovery and promulgation of audio standards.











The Audio Engineering Society — one of the first names in this space — has a due process platform that welcomes public participation. All of its standards open for public comment completed their revision cycle mid-November as can be seen on its standards development landing page below:
Note that AES permits access to those revision even after the comment deadline. You are encouraged to communicate directly with the Direct communication with the standards staff at Audio Engineering Society International Headquarters, 551 Fifth Avenue, Suite 1225, New York NY 10176, Tel: +1 212 661 8528
We keep the AES suite on the standing agenda of our periodic Lively Arts teleconference. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
This facility class is one of most complex occupancy classes in education facilities industry so we also collaborate with experts active in the IEEE Education & Healthcare Facilities Committee. Much of the AES suite references, and borrows from, International Electrotechnical Commission system integration and interoperability standards. The IEEE E&H committee meets online again four times monthly in European and American time zones. The meeting dates are available on the IEEE E&H website




Issue: [19-23]
Category: Electrical, Academic, Athletics, Fire Safety, Public Safety, #WiseCampus
Contact: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey
*Mass notification systems are governed by NFPA 72 and, while life safety wiring is separate from other wiring, the management of these systems involve coordination between workgroups with different business objectives and training.
LEARN MORE:
The AES welcomes new Executive Director, Colleen Harperhttps://t.co/r7DfPp6wfE#AESorg #proaudio #audioengineer pic.twitter.com/nTKBf8oHeR
— Audio Engineering Society (@AESorg) January 16, 2019
Eagles’ Nest
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
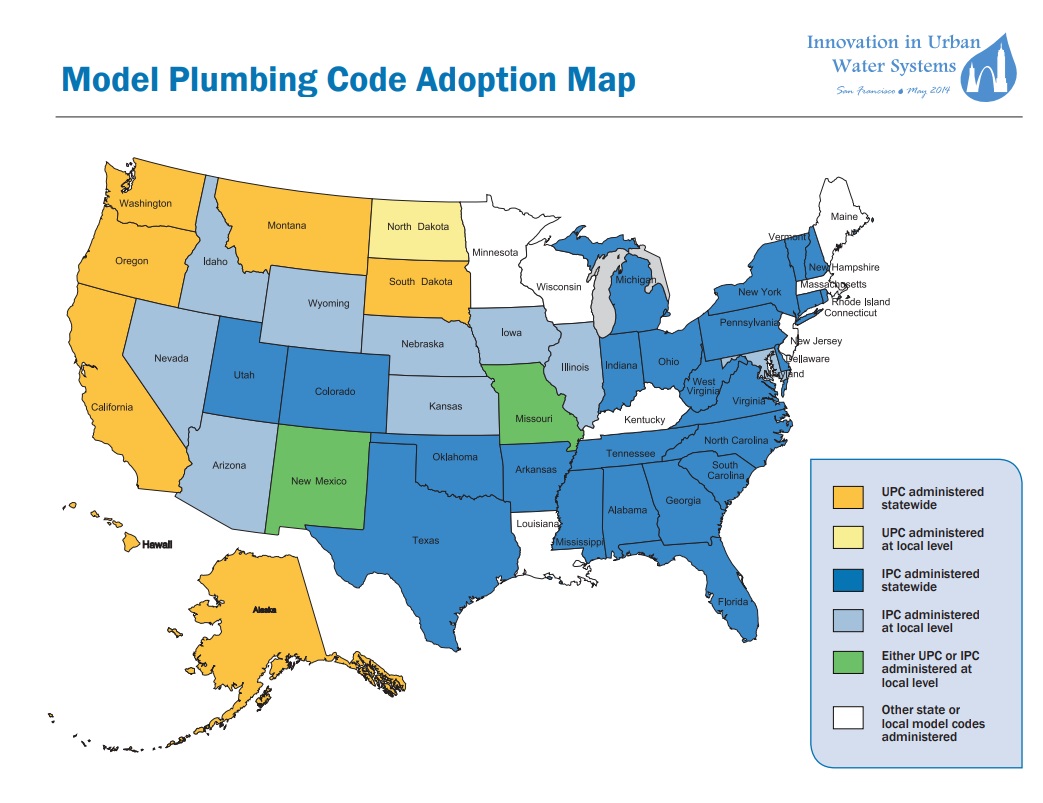
International Plumbing Code
The International Plumbing Code (IPC) is developed to harmonize with the full span of ICC’s family of building codes. The IPC sets minimum regulations for plumbing systems and components to protect life, health and safety of building occupants and the public. The IPC is available for adoption by jurisdictions ranging from states to towns, and is currently adopted on the state or local level in 35 states in the U.S, the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico.
CLICK HERE for the 2021 Public Access Edition
The IPC is developed in the ICC Group A Code development framework and concluded its revision cycle in late 2021 under the circumstances of the pandemic. The 2023 International Plumbing Code revision cycle will not begin until early 2023 but it is never too soon to understand the issues from previous revision cycles to enlighten approaches to the forthcoming Group A revision cycle. The complete monograph of the Group A Codes is linked below, with comments on IPC proposals starting on Page 1417 of this 1613 page document:
2021 IPC | Group A Public Comment Monograph
Because transgender issues are on the agenda of many facility managers we direct you to Page 1424 of the rather large document linked above.
As always, we persist in encouraging education industry facility managers (especially those with operations and maintenance data) to participate in the ICC code development process. You may do so by CLICKING HERE.
Real asset managers for school districts, colleges, universities and technical schools in the Las Vegas region should take advantage of the opportunity to observe the ICC code-development process during the upcoming ICC Annual Conference in Las Vegas, October 20-23 during which time the Group B c Public Comment Hearings will take place. Even though the IPC has moved farther along the ICC code development process it is still enlightening to observe how it work. The Group B Hearings are usually webcast — and we will signal the link to the webcast when it becomes available — but the experience of seeing how building codes are determined is enlightening when you can watch it live and on site.
Issue: [16-133]
Category: Plumbing, Water, Mechanical
Colleagues: Eric Albert, Richard Robben, Larry Spielvogel
#StandardsNewMexico
LEARN MORE:
Neutral Public Bathroom Design
— Leslie (@Hopeleslie1234) August 10, 2024
Uniform Plumbing Code
Although the 2024 Revision is substantially complete there are a number of technical and administrative issues to be resolved before the final version is released for public use. Free access to the most recent edition is linked below.
2027 UPC/UMC CODE DEVELOPMENT TIMELINE
Report on Comments for the 2024 Uniform Plumbing Code
— Leslie (@Hopeleslie1234) August 10, 2024
Infotech 100
“The more abundant the information in the world,
the more economics becomes the science of allocating attention.”
— George Gilder
Today we break down the literature for building, maintaining and supporting the computing infrastructure of education communities. We use the term “infotech” gingerly to explain action for a broad span of technologies that encompass enterprise servers and software, wireless and wired networks, campus phone networks, and desktop computers that provide administrative services and career tech video production. The private sector has moved at light speed to respond to the circumstances of the pandemic; so have vertical incumbents evolving their business models to seek conformance revenue in this plasma-hot domain.
Starting 2023 we break down the topic accordingly:
Infotech 100: Survey of the principal standards developing organizations whose catalogs are incorporated by reference into federal and state legislation. Revision cycles.
Infotech 200: Campus computing facilities for research and education
Infotech 300: Communication networks, wired and unwired at the demarcation point; crucial for defining the responsibilities and boundaries between the service provider and the customer.
Infotech 400: System, middleware and application for education and research
We have begun to track case studies of satellite-based internet services to rural and remote schools and community colleges.
Throughout 2025 we will expand our inquiry in this time slot. There are obvious global security issues to enlighten approaches to assuring communication security if, for example, undersea cables are maliciously destroyed.
The literature radiates continually by consortia, open-source, or ad hoc standards-setting domains rather than the private standards system administered by global and standards setting bodies; to wit:
International:
IEC (EN 50600), IET, ISO, ITU
Vocabulary
United States:
Data Center Operations and Maintenance Best Practices
Everywhere else:
3GPP & 3GPP2, Apache Software Foundation, ISTE, OneM2M, Uptime Institute
The ICT domain is huge, replacing physical libraries. The foregoing is a highly curated sample.
We continue to include teaching and learning media standards on our colloquia however it is likely that will break up this topic into at least two related colloquia as 2023 proceeds; with primary focus on the design, construction and maintenance of the physical ICT infrastructure. Much depends upon the interest of our clients, colleagues and other stakeholders. We collaborate closely with the IEEE Education and Healthcare Electrotechnology Committee.
Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.











New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670