Stablecoin
- Home Page 142

Herbert Hoover Policy Center
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Fire Safety Developmental Calendar
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
A comparison of the conception of God in the thinking of Paul Tillich and Henry Nelson Wieman
Open Review University Microfilms | Ann Arbor Michigan
Stanford University: Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute
Related:
American Psychological Association Dissertation Standards
Boston University Guide for Writers of Theses and Dissertations
University of Michigan Dissertation Formatting
History of University Microfilms Ann Arbor Michigan
Donut Expedition
“…I found myself in the midst of a civilization that had advanced beyond all the great dreams of my forebears. I had thought my home would be a simple place for pastoral people, people who made their living from agriculture. But it was already a complex place, an iron and steel and railway and grain-exchange city, the gates to the prairie…”
— Saul Bellow, (Nobel Laureate 1976)
The College by the Cup: Grounds of Being
University of Chicago Financial Position 2024: $11.589B | University of Chicago Facilities Services
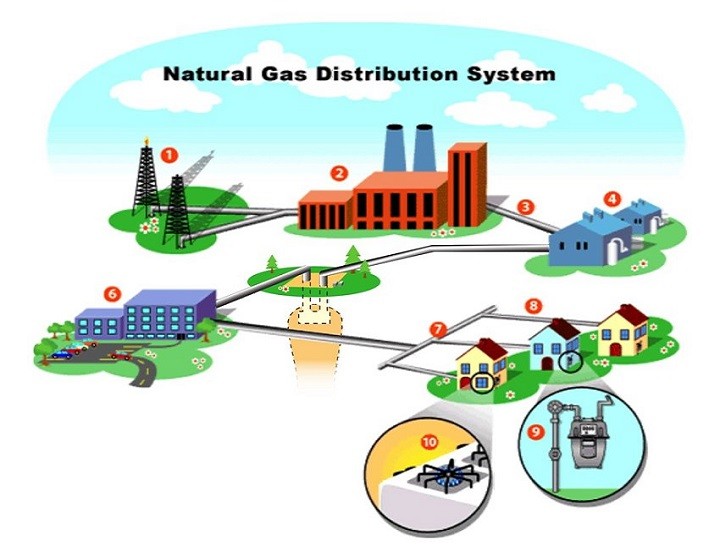
Town Gas
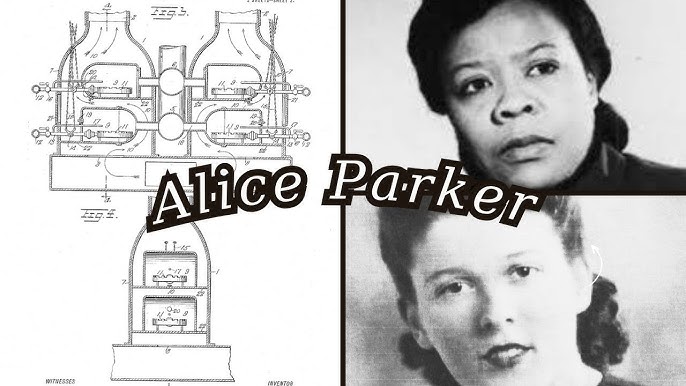
Brought to You by Howard: Alice H. Parker’s historic patent of the gas heater warms the world
Historically, “Town Gas” referred to a manufactured gaseous fuel, primarily produced from coal, that was supplied to homes and businesses in towns and cities for heating and lighting purposes. We use it as a general term for a manufactured gas distributed through educational settlements because of its cleaner and safer properties. Among them:
-
Heating and Cooling – Most settlements use natural gas to power boilers and furnaces for heating buildings during cold months. It also fuels absorption chillers for air conditioning in warmer seasons.
-
Electricity Generation – Settlements with cogeneration (combined heat and power) plants use natural gas to produce electricity while capturing waste heat for heating, improving energy efficiency.
-
Cooking Facilities – Dining halls rely on natural gas for precise and reliable cooking, making meal preparation efficient.
-
Laboratories and Research – Science and engineering labs use natural gas for Bunsen burners, sterilization, and other experimental applications requiring controlled flames.
-
Hot Water Supply – Dormitories, gyms, and other campus facilities use natural gas water heaters to provide a continuous supply of hot water for showers, washing, and sanitation.
-
Transportation – Some universities operate shuttle buses and service vehicles on compressed natural gas (CNG), reducing emissions and fuel costs.
-
Emergency Backup Power – Natural gas generators provide backup power during outages, ensuring critical systems, like research labs and data centers, remain operational.
Glorious gas lamps of London
Their warm glow adds beauty to these winter evenings pic.twitter.com/UgHK8yh2YN
— Conor Lynch (@c_k_lynch) February 18, 2025
Safety and Sustainability Bibliography:
International Standards:
ISO 13686 – Specifies the quality of natural gas for use in various applications.
ISO 14001 – Provides environmental management standards for reducing the environmental impact of natural gas operations.
ISO 50001 – Energy management system standard for improving energy efficiency, including natural gas usage.
IEC 60079 – Covers explosive atmospheres, ensuring safety in handling natural gas in industrial settings.
OHSAS 18001 (now ISO 45001) – Occupational health and safety standards for workplaces dealing with natural gas.
IPCC Guidelines – International standards for measuring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions from natural gas operations.
U.S. Standards:
49 CFR Part 192 – Federal Pipeline Safety Regulations, governing natural gas pipeline transportation.
EPA Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP) – Requires natural gas facilities to report emissions data.
ANSI/GPTC Z380.1, Guide for Gas Transmission, Distribution, and Gathering Piping Systems
NFPA 54 (National Fuel Gas Code) – Covers safe installation and use of natural gas in buildings.
NFPA 58 – Safety regulations for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), including storage and handling.
ASME B31.8 – Pipeline safety code for natural gas transmission and distribution.
Clean Air Act (CAA) – Regulates air emissions from natural gas production and consumption.
California Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) – Encourages sustainable fuel alternatives, including renewable natural gas (RNG).
State of Michigan Technical Standards for Gas Service
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission: Natural Gas Policies
Schools, Colleges, Universities, Hospitals (Educational Settlements)
University of Michigan Design Guidelines
Related:
Architectural “Neighborhoods”
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670