Cookbook: January
- Home Page 28

London Fog
Bowdoin College Statement of Financial Position: June 2023 | $3.046B
Maine Miscellany | State of Maine Building Codes| Bowdoin College Chapel (SGH Architects)
EMMA University of Maine System Revenue Bonds

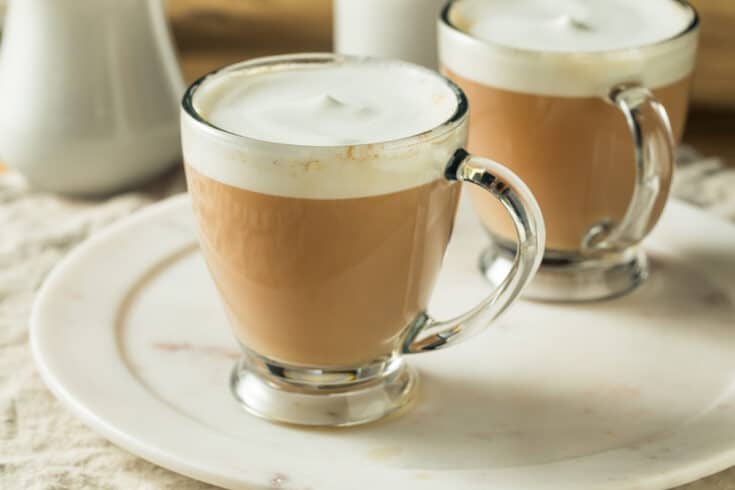
The Cafe’s London Fog | Yield: 16oz
Ingredients
16oz Cup
1 Earl Grey tea bag
1oz Vanilla syrup
11oz Hot water
4oz Steamed milk
Steps
1. Fill the cup with hot water
2. Add vanilla syrup
3. Add tea bag
4. Top with steamed milk
Peter Boghossian (VQ, Portland State University): Critical Thinking, Failing Universities, etc.
Maine is the only rural state led by Democrats | Readings: Self-Reliance
Family Weekend is coming up fast! It is an opportunity for families and friends to connect with campus and to learn about life at Bowdoin. The dates this year are October 21-23rd. Go check out the website here to get details. https://t.co/z1xx28Y2ZX pic.twitter.com/y456C8dhCJ
— Bowdoin College (@BowdoinCollege) October 15, 2022
Big thanks to Glenn Michaels for sharing these beautiful photos with us! pic.twitter.com/8L6nhf4cyT
— Bowdoin College (@BowdoinCollege) November 1, 2024
Chanson de matin Op.15 No. 2
“Chanson de Matin” is characterized by its light, lyrical, and charming melody, which evokes a sense of freshness and optimism associated with the early hours of the day. Elgar is known for his ability to capture various moods and emotions in his compositions.
Anderson University School of Music, Theater, and Dance
Physical Plant | Anderson University
🟠⚫SCHOLARSHIP ALERT
Learn more about our Christian High School and Homeschool scholarship by clicking this link:https://t.co/LTMbl9WfNT pic.twitter.com/GEEr4i1xkv
— Anderson University (@AndersonU) February 13, 2025
Westminster
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Unexpectedly
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Home & Hearth
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Ivy League Graduates Prohibited from Presidency, Congress & Supreme Court
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Hoosier Brunch
Indiana University Bloomington (the main campus, often referred to as IU) operates its student food services (including residential dining halls, retail locations, and campus eateries) in-house through IU Dining & Hospitality, a department under Campus Auxiliaries.
This unit is not run by an external corporation as so many educational settlements do (also known as “outsourcing”). IU handles operations directly, with its own executive director, chefs, staff (including many student employees), and leadership team. They emphasize local sourcing, sustainability, and student-focused menus. :
- In 2018, IU transitioned away from Sodexo (which previously operated some IMU restaurants) to create IU Dining as an internal operation for better control, fresher/local ingredients, and community alignment.
- Residential dining (All You Care to Eat halls like McNutt, Forest, etc.) and most campus food services are run by IU Dining & Hospitality.
- Note: Athletics concessions and game-day food/beverage (at venues like Memorial Stadium and Assembly Hall) are separately handled by Levy (a Chicago hospitality company under Compass Group), starting in summer 2024—but this does not cover general student dining/residential services.
For the Bloomington campus student meal plans and everyday dining, it’s university-managed internally.
Hoosier The Bison is back, baby. Indiana University’s official mascot – Hoosier The Bison – has returned to the IU-Bloomington campus after a nearly 60-year hiatus. The Bison will make its public debut Aug. 30 when Indiana hosts ODU pic.twitter.com/pH3oKB2QSL
— Brett McMurphy (@Brett_McMurphy) July 14, 2025
Indiana girls like this are the backbone of America pic.twitter.com/FCJu7IzcL5
— TastefulLindy (@LindyTasteful) January 1, 2026
Related:
Beach Volleyball
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
“Ave Maria” Franz Biebl
A joint performance during the Morehouse College Glee Club‘s 2013 spring tour led by Conductor David Morrow.
Standards Georgia | Standards New York
Cultural capital of Christian North America is the result of long-term, intergenerational buildup of widely recognized, high-status cultural knowledge, tastes, skills, credentials, behaviors, and social codes that confer advantages in Western democratic societies — the inventors of modernity — that attract internet-connected young people from all over the world.
In Western democracies, centuries of industrialization, mass education, print culture, elite universities, arts institutions, and global cultural dominance have created dense layers of legitimate (“high-status”) cultural capital: familiarity with classical music, modernist literature, specific linguistic registers, art history references, debate styles, bodily hexis (ways of moving/speaking), and credential hierarchies (Oxbridge/Ivy League degrees, etc.). This capital is subtly transmitted through families, schools, and social networks, functioning as an invisible multiplier of economic and political power.
Leaving American large cities aside as a special case, African nations of origin have not yet had the historical time, stable institutional continuity, or global cultural hegemony needed to accumulate equivalent volumes of such internally and internationally valorized cultural capital. Colonial disruption, shorter periods of mass formal education, and the peripheral position in global symbolic production mean that many of the most rewarded cultural codes remain externally imported rather than indigenously accumulated and naturalized across generations.
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670