At the 1853 New York World’s Fair Elisha Otis amazed a crowd when he ordered the only rope holding the platform on which he was standing cut by an axeman. The platform fell only a few inches before coming to a halt; thus proving the safety locking mechanism he had invented will work. These elevators quickly became the type in most common usage and made vertical living possible.

Elisha Graves Otis shows his first elevator in the Crystal Palace, New York City, 1853. — Image by © Bettmann/CORBIS
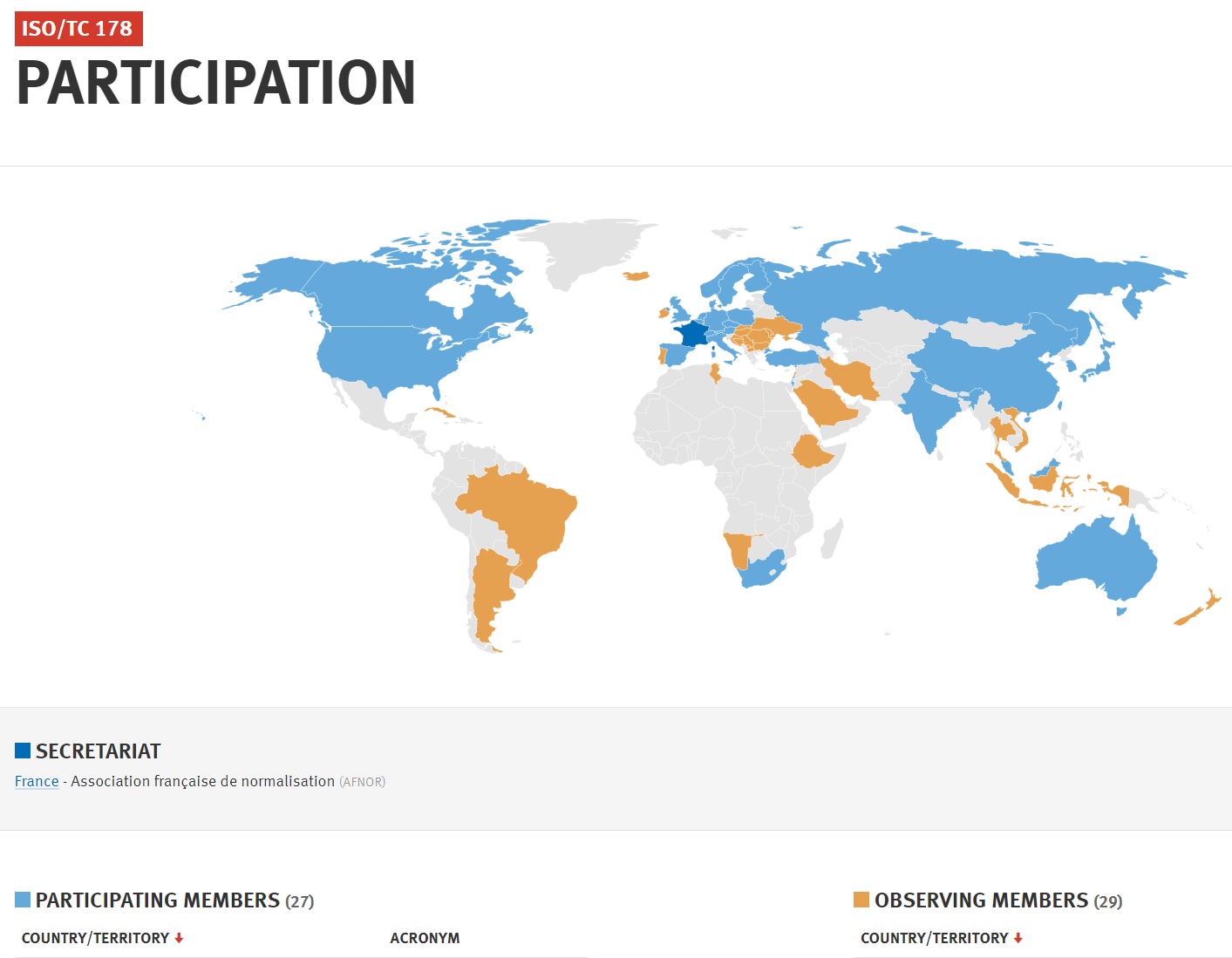
Most large research universities have 100 – 1000 elevators that are highly regulated, maintained by highly regulated service personnel and inspected by highly trained conformance operatives; thus our primary interest in state-specific regulations. We have a secondary interest in innovation in the technology generally. Many sustainability goals urged in academic circles — which include greater population density in smaller areas — are challenged by mobility issues.
From the project prospectus:
“…The main feature of these products is that they are an integral part of industrial, residential or public buildings. Consequently, they should be adaptable to the technical and architectural constraints of such buildings. They must also meet the capacity requirements imposed by the intended use of the building. These products are considered as means of transport and therefore represent an essential component of the functional life of the buildings in which they are installed. Contrary to most public means of transport, they are intended for free use and operation by their passengers, which makes the integration of safety an essential concern…”
STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLAN ISO/TC178: Lifts, escalators and moving walks
The Association française de normalisation (AFNOR) is the global Secretariat. ANSI’s US Technical Advisory Group Administrator is the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. Stakeholders in US-based education communities are encouraged to communicate directly with ASME; CLICK HERE.
We maintain the work products of this committee on the standing agendas of our Mechanical, Elevator and Global colloquia; open to everyone. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting.
Issue: [11-50]
Category: Mechanical, Mobility, Global
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Larry Spielvogel