Sport and Wellbeing | Standards Scotland
The term “curling” is thought to derive from the way the stone moves and “curls” as it travels over the ice. The key feature of curling that sets it apart from other ice sports is the deliberate rotation, or “curl,” applied to the stones as players release them. This rotation causes the stone to curve or “curl” on its path down the ice, adding an element of strategy to the game.
The precise origin of the term is not definitively known, but it likely emerged organically as people described the action of the stones on the ice. The word “curling” has been associated with the sport for centuries, and as the game evolved and gained popularity, the term became firmly established.
The concept of curling is integral to the sport’s strategy, as players use the curl to navigate the stones around guards and other stones strategically placed on the ice. The unique way in which the stones move and interact with the playing surface is one of the defining characteristics of curling, and the name captures this distinctive feature
World Curling Mixed Championship 2024
Scientific American: Why Do Curling Stones Curl?
A curling facility typically consists of several key components to support the sport and provide a suitable environment for players and spectators:
- Flooding equipment, refrigeration for 3 degrees C, fine mist sprayers, ice planer, infrared thermometers.
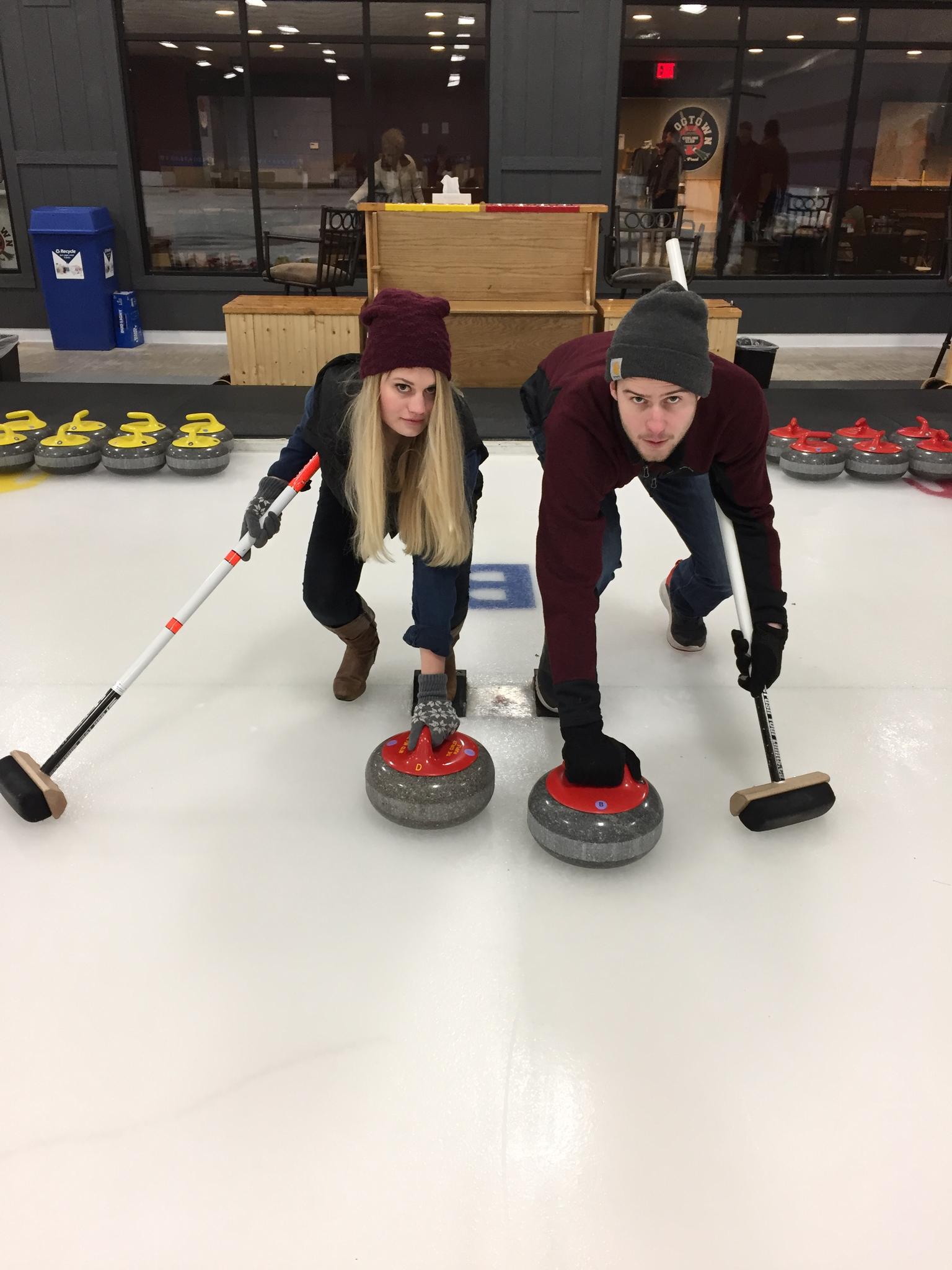
- The playing surface is called a “sheet,” and it is a rectangular area of ice where the game is played. Each sheet is divided into several sections called “curling houses,” which are the target circles.
- Curling stones are made of granite and weigh around 38 to 44 pounds. Each team has eight stones, and players take turns sliding them down the ice towards the target area, known as the House.
- The house is the target area with concentric circles marked on the ice. The center of the house is the “button,” and the circles are used for scoring points.
- The hacks are footholds on either end of the sheet where players push off to slide the stones. The player in control of the stone uses the hack as a starting point for their delivery.
- Brooms, also known as brushes, are used by players to sweep the ice in front of the sliding stone. Sweeping can affect the stone’s trajectory and speed.
- A scoreboard is essential for keeping track of the score in a curling game. It typically displays the current score, the end in progress, and other relevant information.
- Players use locker rooms for changing into their curling attire and storing their personal belongings.
- A designated area where players can warm up before a game. It may include stretching space and possibly a small practice sheet.
- A facility usually has a clubhouse or main building that includes amenities such as viewing areas, meeting rooms, a bar, and possibly a restaurant. In the case of the Windsor Curling Club: Scotch Whiskey
- Equipment like ice resurfacers or Zambonis are used to maintain the quality of the ice surface between games.