Fire Protection Engineering Research Projects
- Home Page 190

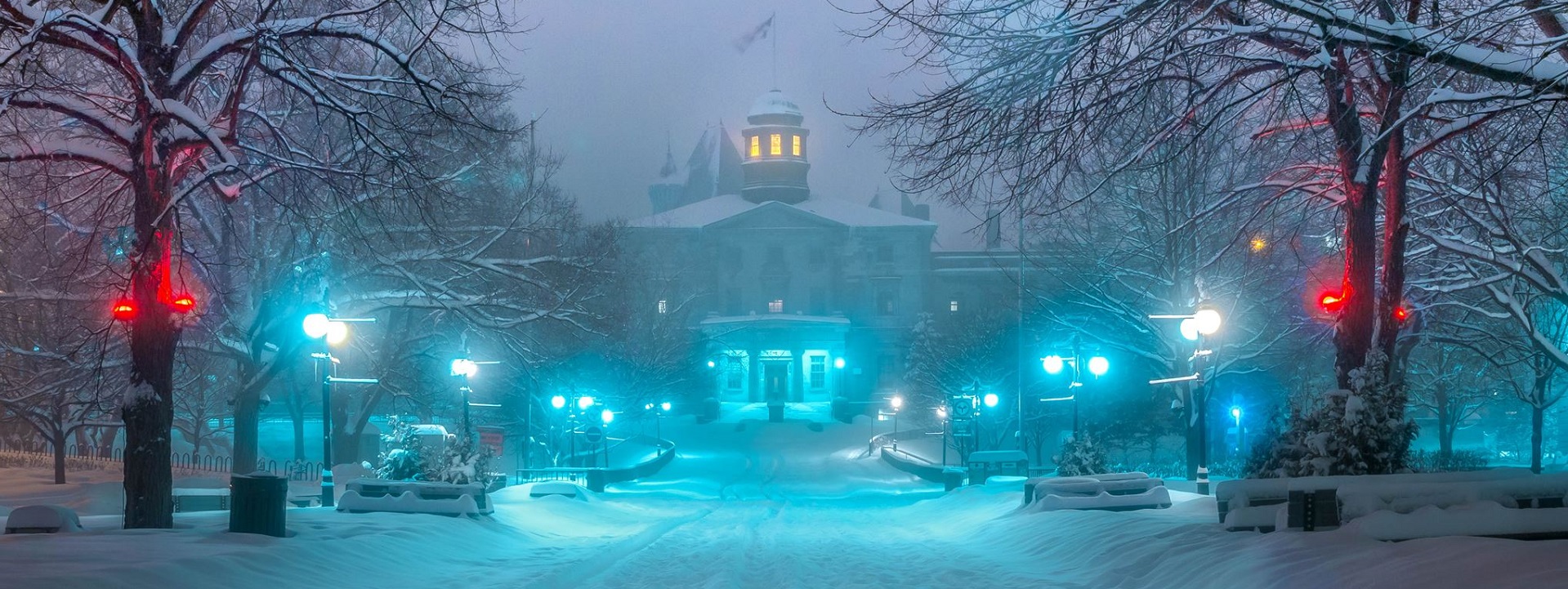
Heat Tracing
The National Electrical Contractors Association best practice catalog features a suite of titles (National Electrical Installation Standards to meet the intent of the National Electrical Code (NEC); particularly where the NEC asserts that an installation be constructed in a “neat and workmanlike manner”. As anyone who has had to reckon with the subjectivity of the local electrical inspector knows, the determination of “neat and workmanlike” can be mighty subjective. The NECA documents are used by construction owners, specifiers, contractors and electricians to clearly illustrate the performance and workmanship standards essential for different types of electrical construction. Because the NEC is intended to be primarily a wiring safety standard, the NEIS suite is referenced throughout the National Electrical Code. Electrical shop foremen and front line electricians take note.
NECA Standards and Publication Development Home Page
One of the NECA products that may be of interest to facility managers and risk management units in the education industry this time of year is NECA 202-2013 Standard for Installing and Maintaining Industrial Heat Tracing Systems. About half of the United States deals with snow and ice half the year.
NECA 202 details procedures for the installation, testing, and documentation of electrical freeze protection and process heat tracing systems. Heat tracing cable types covered by this publication include: self-regulating, constant wattage, and zone heating cables and mineral insulated heating cables. 2 is approved as an American National Standard. The 2013 edition is the current edition and will likely need revisiting/revision/reaffirmation as an American national standard soon.
The technical literature that keeps pipes breaking and roofs failing is complicated space. A common conundrum in the construction industry is which discipline (architectural, mechanical or electrical) should specify application of this technology; especially in value-engineering negotiations when each discipline is trying to reduce its unit costs. Control and communication system add another layer of complexity. Several consensus standards occupy this technology; cross referencing one another and leaving gaps
ASCE 7-10 Snow Load Provisions
UL 515 Standard for Electrical Resistance Trace Heating for Commercial Applications
IEC 62395 Electrical resistance trace heating systems for industrial and commercial applications
National Electrical Code Article 427
There are codes and standards developed by ASTM International, the International Code Council and ASHRAE International that set the standard of care for pipe insulation for energy conservation purposes but we will deal with the interdependence of standard of care set by those documents in a separate post. Organizations such as FM Global typically derive their customer recommendations from consensus standards developers.









Because heat tracing is a cross-disciplinary technology we maintain it on the standing agenda of several colloquia: Power, Water, Bucolia, Snow & Ice and Mechanical See our CALENDAR for the next meeting; open to everyone. You may obtain an electronic copy of this standard from neis@necanet.org. Communicate directly with Aga Golriz, (301) 215-4549, Aga.golriz@necanet.org.
Participation by the public in reviewing other titles in the NEIS bibliography is welcomed and begins at the page linked below:
Issue: [19-24]
Category: Architectural, Electrical, Facility Management, Mechanical, Risk Management,
Colleagues: Eric Albert, Mike Anthony, Jack Janveja, Richard Robben, Larry Spielvogel
More
RESEARCHGATE: HEAT-TRACING OF PIPING SYSTEMS TYPES OF HEAT-TRACING SYSTEMS
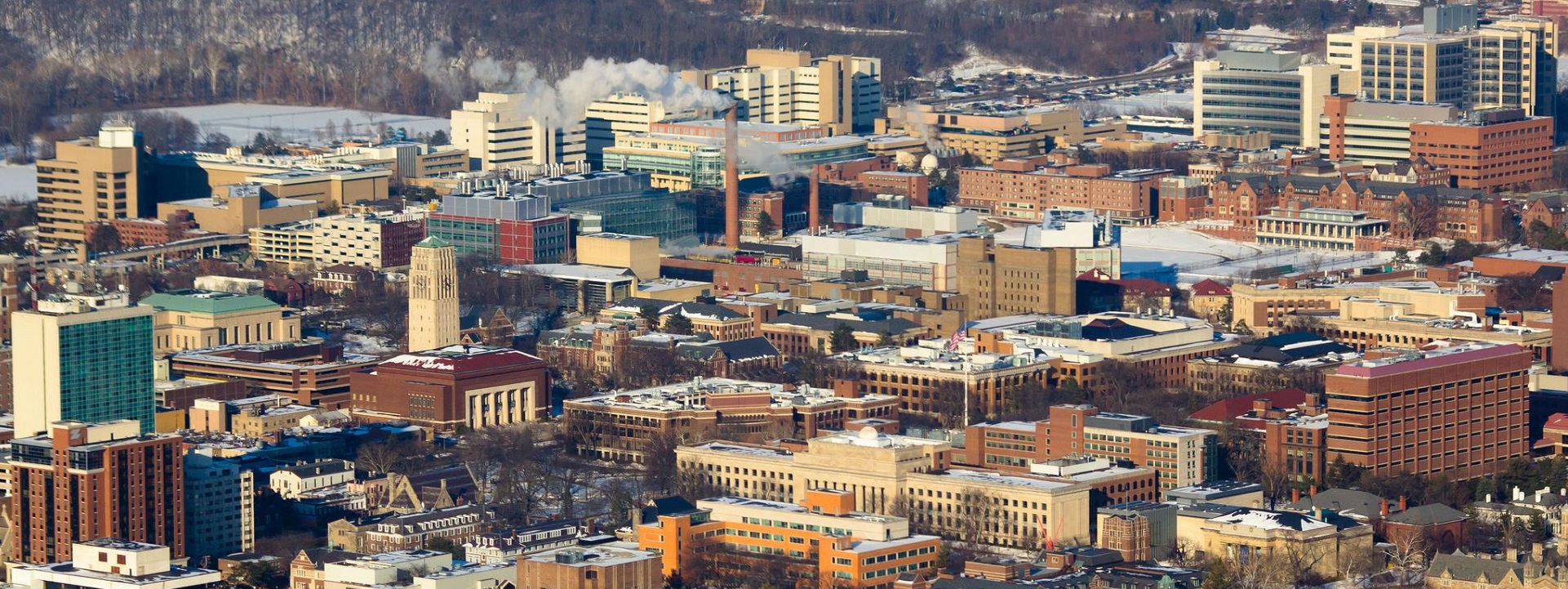

With some 36 million square feet under management — and one of the largest campuses in the United States exposed to extreme low temperatures — building industry professionals at the University of Michigan have some experience managing the competing requirements of safety and economy in heat tracing technology.
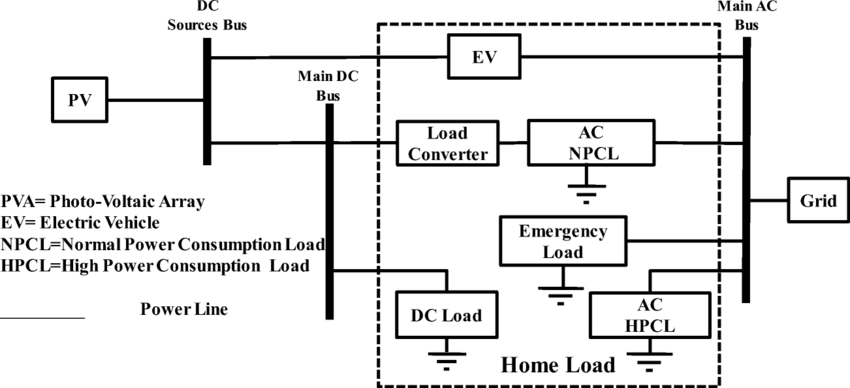
Electric Vehicle-to-Home Emergency Power System
Reliable and Economy Modes of Operation for Electric Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) System
Mahdi Shafaati Shemami, et al
Department of Electrical Engineering, Aligarh Muslim University
Abstract: In developing countries load shedding for hours is very common. Generally, a small power backup source is utilized for necessary loads (emergency lights and emergency loads like fan and small cooler). Nowadays, grid-connected solar inverters that installed on the roof are widely utilized for backup power source in urban cities. Penetration of electric vehicles (EVs) are increasing, so charging of EVs battery through grid increase power grid instability. Solar PV based charging of EVs can be a solution for this problem. However, in the case of a charged battery condition, whenever battery has charged through the grid, the available power from solar PV modules remain unutilized and wasted. The proposed controllers modify the regular, low-cost home inverter into a PV grid-connected inverter that it also has the ability to utilize EV battery energy. It has better control strategy that guarantees the reliability of the power supply. Economy mode and reliable mode has been developed to improve standby power supply, it also maximizes utilization of PV energy. In addition, the customers, don’t need to buy a new expensive solar grid-connected inverter or any other devices to charge the EV battery if they already have a home-based inverter.
Relevant Titles
“Be steady and well-ordered in your life
so that you can be fierce and original in your work.”
― Gustave Flaubert
Education communities are the foundation of every industry in every nation. The United States should have a voice in the development of international management and technology standards that originate from the global standards bodies in Geneva — International Electrotechnical Commission, International Organization for Standardization and the International Telecommunications Union. At the moment the voice of US education communities is relatively weak; even with the sustained involvement of Standards Michigan beginning with the original University of Michigan standards enterprise described in our ABOUT.*
Owing to relationships with scholars and researchers in other nations that is common in academic communities we collaborate with many universities in other nations. We feature their research when appropriate; all of it worthy of admiration. Our primary involvement is with US Technical Advisory Groups administered by the American National Standards Institute. Of the projects listed below we are actively involved in meetings, gathering data and marking up drafts. There are other projects that are nascent, dormant, rejected , abandoned or consolidated with other titles. If the basis of the standardization project has merit; the idea will ultimately find its proper place.
Owing to copyright restrictions we are unable to post specifics on many of them but we are happy to provide a status check during our periodic Global standards colloquia. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
*S. Joe Bhattia, Chairman of the American National Standards Institute, describes that condition at the University of Michigan Ross School of Business:
Automated Sports Court Drawing Bot
The Civil 20's Technology and Security for One World Summit began today. Honourable Governor of Tamil Nadu, Shri. R.N. Ravi, and Swami Amritaswarupananda Puri as a Civil 20 Troika member were at the event. #YouAreTheLight #Civil20India #Civil20 #C20 #G20India #G20 #TST #Amrita pic.twitter.com/4KsIAoSmoj
— Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (@AMRITAedu) May 13, 2023
Arduino based Automated Sports Court Drawing Bot
Rajesh Kannan Megalingam, et. al
Stadium maintenance staff are one of those people who work hard to maintain the court correctly. One of the items that often require rework is the lines drawn on the court for maintenance of track or boundaries or even the entire court when it is football stadium etc. Besides, for indoor stadiums that host volleyball, basketball, tennis, etc., lines need to be drawn. Redrawing the court after each match is one of the major problems of concern. In such a scenario, a system is proposed that can draw the court lines autonomously. The objective of this research work is to present a design of an autonomous sports court drawing bot that can draw the linear lines automatically which can aid in the maintenance work of the sports stadium.
CLICK HERE to order complete paper.
Law on the State of Emergency
“A smooth sea never made a skilled sailor.”
— Franklin D. Roosevelt
University of Melbourne Estate Plan
The criteria and process for declaring a state of emergency can vary depending on the country and its legal framework. However, governments generally consider certain factors and criteria when making such declarations. Here are some common elements that governments use to determine whether to declare a state of emergency:
- Imminent Threat: Governments typically declare a state of emergency when there is an imminent threat to public safety or the normal functioning of society. This could include natural disasters (such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods), severe public health emergencies (like pandemics), acts of terrorism, civil unrest, or other situations that pose a significant risk.
- Scale and Severity: The scale and severity of the situation play a crucial role in declaring a state of emergency. Governments assess whether the event or circumstances are beyond the capacity of regular governmental and emergency response systems to effectively manage and mitigate the impact.
- Public Safety and Welfare: Governments consider the potential impact on public safety, welfare, and infrastructure. If the situation poses a substantial risk to lives, property, critical infrastructure, or essential services, it may warrant a declaration of a state of emergency.
- Legal Framework: Countries typically have legal frameworks in place that outline the conditions and procedures for declaring a state of emergency. Governments assess whether the situation meets the legal requirements and conditions specified in these frameworks.
- Proportionality: The principle of proportionality is often considered, ensuring that the measures taken during the state of emergency are proportional to the threat or situation at hand. Governments aim to strike a balance between protecting public safety and minimizing unnecessary disruption to individual rights and liberties.
- Expert Advice and Recommendations: Governments rely on expert advice and recommendations from relevant authorities, such as emergency management agencies, health organizations, and security agencies, to assess the situation and determine the need for a state of emergency.
It’s important to note that the specific criteria and procedures for declaring a state of emergency can vary significantly between countries. The legal provisions and powers granted to the government during a state of emergency also vary, including the duration, scope of authority, and measures that can be implemented. It’s advisable to consult the specific laws and regulations of the country in question to understand the precise criteria and process involved in declaring a state of emergency.
Blockchain Application for Disaster Management
Blockchain Application for Disaster Management and National Security*
Mohit Singh Panesir
Graduate School of the University at Buffalo, State University of New York
Natural phenomena such as floods, storms, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, landslides have affected our planet in an unpredictable way. However, these phenomena are merely classified as a hazard when they may affect people and the things they value (Cutter, 2005). The involvement of many agencies and the public is important in planning for disaster relief, in rescuing victims, and in managing the event. A lot of individuals are deprived of help due to poor coordination, late assistance and uneven distribution of food, water, medical assistance, clothes, and vehicles. The need for a proper disaster relief plan is crucial to overcome these challenges. On the other hand, identity theft is one of the most bizarre and rapidly growing crimes present in the world. Identity thieves are active more than ever as the e-commerce trading keeps on growing. Earlier the thieves used to buy pieces and parts of someone’s personal identification information but now they could have hold of everything. Similarly there has been an increase in illegal immigration, smuggling of weapons and terrorist activities noticed in last 2 decades in the United States. This study focuses on the current condition of disaster management, identity theft, border security and controlling the misuse of weapon of mass destruction. It proposes the use of advanced technological methods like Blockchain to overcome the loss of time and cost to provide a quick response to the victims and to provide secure ways to store personal identification information and better national security. The study helps to understand how better disaster management and national security can be achieved by using various use cases and implementation models. By implementing these models, the border security can be improved and proper handling of weapons of mass destruction can also take place.
*We have noticed that access to the complete paper has been spotty. You may communicate directly with the author by CLICKING HERE
Parking Lot Lighting Networking
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Leviathan 400
Thomas Hobbes titled his book “Leviathan” (1651) as a metaphorical representation of the powerful and all-encompassing state. In it, he proposed a social contract theory, arguing that individuals willingly surrender some freedoms to a sovereign authority in exchange for protection and order. The Leviathan, a biblical sea monster, symbolizes this sovereign entity’s immense power and control. Hobbes believed that without a strong central authority, human life would be chaotic and marked by a “war of all against all.”
The Leviathan concept underscores his advocacy for the largest possible administrative state to provide jobs that claim to maintain social stability and prevent anarchy. We cover the topic today because insofar as technology standards are concerned, federal involvement has run to excess (ignoring market signals), is just another form of market-making that ignores the limits placed upon us by Mother Nature.
Keep in mind that the American National Standards Institute administers a relatively small part of standards-setting in the United States. (Click here for a complete list; updated frequently. A great deal of ANSI resources are devoted to supporting members that run “conformance shops” essential to safe and fair trade. Other standards setting is done by governments, open-source, and other ad hoc consortia.
The culture of the standards-setting domain in every nation rests upon the culture of conformance. “Standards are the seed corn for conformance revenue” we are fond of saying and most of the expertise in the standards setting domain rests with people who make a living making sure others conform to the standard; whatever that standard may be. Conformance (product testing, installation certification, periodic re-commissioning and audits, etc.) is where the money is so we should not be surprised at the degree to which the user-interest (represented by the third gray column in our logo) is outnumbered.
That much said, having the global standards system is better than not having one at all. This system places a check on oligarchies that make central governments grow. The topic is relevant to our work because a surprising measure of influence over technical standards is undertaken by non-technical people who lack the sensitivity to technical and economic trade-offs — many of them presented by Mother Nature herself.
0. Leviathan.
Office of Management and Budget
United States Department of Education
United States Department of Commerce
United States House of Representative Committees
United States Senate Committees
Health, Education, Labor & Pensions
United States Constitution 10th Amendment
The foregoing block of content will be re-configured to another, more dynamic post that synchronizes with state and county-level standards action. Reminder: We do not advocate with governments at any level; merely follow it since the action of government appears routinely in the leading practice discovery activity of standards setting organizations.
IEEE-USA Government Policy Committees
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670