Barbering & Cosmetology Academies
- Home Page 144

“Forty Days and Forty Nights”
当会では、下記記事にご登場の佐藤様がご登壇されるセミナーを開催いたします。
【規格説明会】
2025年03月19日(水) 13:00~17:00
活力ある超高齢社会に向け企業が気を付けるべきポイントと自治体の取り組み~ウェルビーイング社会に向けて~https://t.co/92jKs1Scu7https://t.co/DOM0F4tzHL— 日本規格協会 (@jsainfra) March 4, 2025
Swedish Meat Balls
This content is accessible to paid subscribers. To view it please enter your password below or send mike@standardsmichigan.com a request for subscription details.
Jazz Standard “Alfie”
“Alfie” 1966 | Burt Bacharach & Hal David, sung by Daisy@WokingCollege @AndrewShephard
print(“Evensong”)https://t.co/nRaoJGi3E5 pic.twitter.com/uSKZdodfwl— Standards Michigan (@StandardsMich) February 12, 2023
Form and Structure: The song doesn’t follow a standard verse-chorus pop structure. Instead, it’s more through-composed, with a flowing, almost conversational quality that mirrors the introspective lyrics by Hal David. It’s built around a series of melodic phrases that evolve rather than repeat predictably, giving it a cinematic feel suited to the film’s narrative. The AABA form is loosely present, but Bacharach stretches it with irregular phrase lengths and unexpected transitions.
Time Signature and Rhythm: Alfie is in 4/4 time, but Bacharach plays with rhythmic fluidity. The phrasing often feels asymmetrical—some measures stretch to five or six beats’ worth of melody over the 4/4 pulse, creating a sense of suspension. The tempo is moderate, around 60-70 BPM, allowing the vocalist room to linger on notes and emote.
Harmony:Bacharach’s harmonic language is where the technical brilliance shines. The song is in C major but frequently ventures into chromatic territory. It’s loaded with extended chords—think 7ths, 9ths, and 11ths—and passing modulations that keep the ear guessing. For example, the opening line (“What’s it all about, Alfie?”) starts with a simple Cmaj7 but quickly pivots to a G7 with a flat 9, then resolves unpredictably. These shifts create tension and release, mirroring the song’s questioning tone.
Melody: The melody is deceptively simple but fiendishly clever. It spans a wide range (over an octave), with leaps and stepwise motion that demand vocal control. Take the phrase “Is it just for the moment we live?”—it starts low, climbs a major 7th, then descends gracefully. Bacharach avoids repetition, so each line feels like a new thought, pulling the listener deeper into the philosophical musing.
Dynamics and Phrasing: The song ebbs and flows dynamically. It begins softly, almost whispered, then builds to a gentle climax around “Are we meant to take more than we give?” before retreating. Warwick’s delivery—smooth, with a touch of restraint—amplifies this. Bacharach’s conducting ensured the band followed her phrasing, not the other way around, giving it an organic, live feel.
Key Changes and Modulations: While the song stays rooted in C major, Bacharach sprinkles in momentary key shifts. For instance, the bridge (“As sure as I believe there’s a heaven above, Alfie”) flirts with A minor and F major, adding a bittersweet flavor before resolving back home. These subtle modulations keep the music unpredictable, reflecting the uncertainty of the lyrics.
Bacharach famously struggled to get this song right—recording it multiple times before settling on Warwick’s take after 18 tries. His perfectionism paid off: the interplay of technical complexity (those jazzy chords and odd phrase lengths) with musical accessibility (a singable, memorable melody) is what makes Alfie timeless. It’s not just a song; it’s a miniature drama, unfolding note by note.
Maths and Sport
The use of “maths” instead of “math” is a difference in British English compared to American English. In British English, the word “mathematics” is often referred to as “maths,” with the added “s” signifying the plural form. This is consistent with how British English commonly shortens many words by adding an “s” to the end. For example, “physics” becomes “phys, “economics” becomes “econs,” and so on.
In contrast, American English typically shortens “mathematics” to “math” without the additional “s,” following a different pattern of abbreviation.
The reason for these linguistic differences is rooted in the historical development of the English language and regional linguistic variations that have evolved over time. British English and American English have diverged in certain aspects of vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar, resulting in variations like “maths” and “math.” It’s important to note that neither is inherently correct or incorrect; they are just regional preferences.
|
Gresham College is a higher education institution located in London, UK. It was founded in 1597 under the will of Sir Thomas Gresham, a financier and merchant who left funds for the establishment of a college in the heart of the city. The college’s original aim was to provide free public lectures in a range of subjects, including law, astronomy, geometry, and music. The lectures were intended to be accessible to anyone who was interested in learning, regardless of their background or social status. Over the centuries, Gresham College has remained true to this mission, and today it continues to offer a range of free public lectures and events that are open to all. |
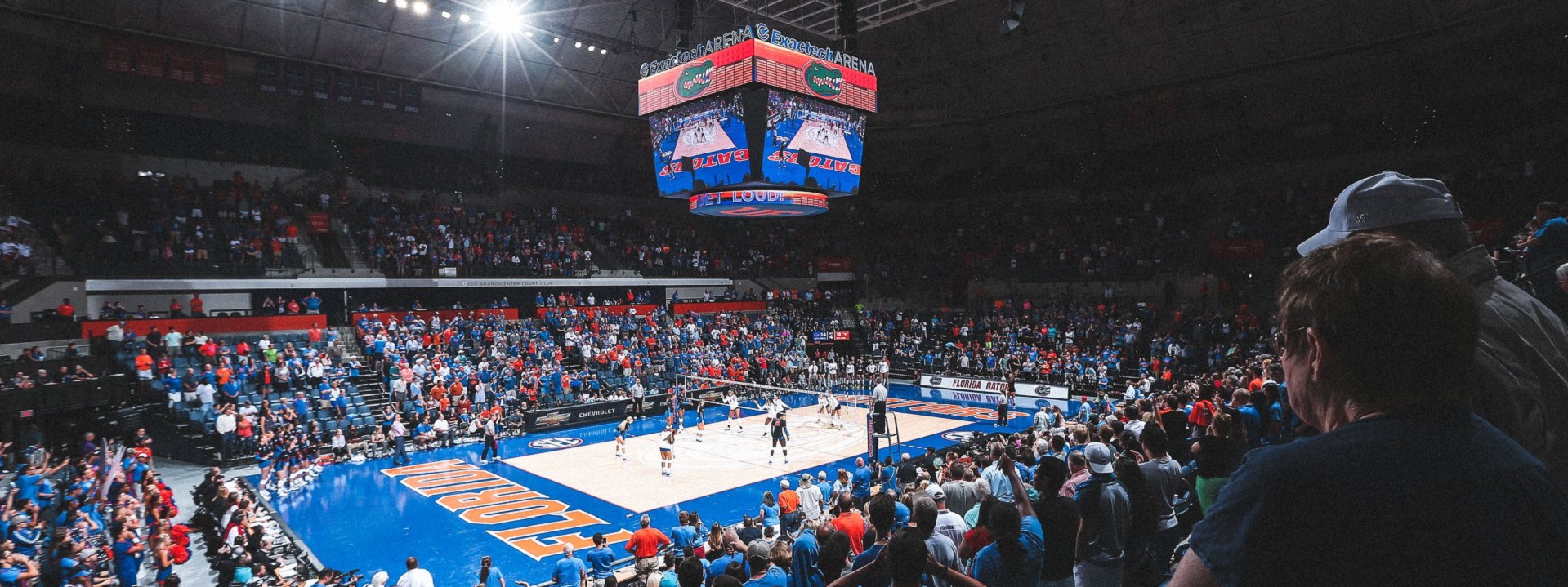
Volleyball Court Lighting
After athletic arena life safety obligations are met (governed legally by NFPA 70, NFPA 101, NFPA 110, the International Building Code and possibly other state adaptations of those consensus documents incorporated by reference into public safety law) business objective standards come into play. The illumination of the competitive venue itself figures heavily into the quality of digital media visual experience and value.
For almost all athletic facilities, the consensus documents of the Illumination Engineering Society[1], the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers[2][3] provide the first principles for life safety. For business purposes, the documents distributed by the National Collegiate Athletic Association inform the standard of care for individual athletic arenas so that swiftly moving media production companies have some consistency in power sources and illumination as they move from site to site. Sometimes concepts to meet both life safety and business objectives merge.
The NCAA is not a consensus standard developer but it does have a suite of recommended practice documents for lighting the venues for typical competition and competition that is televised.
It welcomes feedback from subject matter experts and front line facility managers.
Our own monthly walk-through of athletic and recreation facility codes and standards workgroup meets monthly. See our CALENDAR for the next online Athletics & Recreation facilities; open to everyone.
Issue: [15-138]*
Category: Electrical, Architectural, Arts & Entertainment Facilities, Athletics
Colleagues: Mike Anthony, Jim Harvey, Jack Janveja
92,003 in attendance.@HuskerVB breaks the world record for the largest crowd ever at a women’s sporting event 👏 @espnW | #ThatsaW pic.twitter.com/ChyhUCvaAZ
— ESPN (@espn) August 31, 2023
This may be the rally of the week and we haven't even made it to Friday yet!#NCAAVB #SCtop10
(via @SFA_Volleyball)pic.twitter.com/2h6OvVB1ty— NCAA Women's Volleyball (@NCAAVolleyball) November 2, 2018
[1] Illumination Engineering Handbook
[2] IEEE 3001.9 Recommended Practice for Design of Power Systems for Supplying Lighting Systems for Commercial & Industrial Facilities
[3] IEEE 3006.1 Power System Reliability
* Issue numbering before 2016 dates back to the original University of Michigan codes and standards advocacy enterprise
Aggregate Pathways
As cities-within-cities, education communities are a large market for concrete manufacturers and installation contractors. The pathways built from aggregates (“sidewalks”) are central to the function and character of the campus. Construction and maintenance of these pathways — the cost of which depends upon the appropriate specification and application of aggregate technologies — are a significant cost center. They can also present pathway travel hazards and drainage problems.
The application of permeable pavements in recent years has gathered pace. Permeable pavements typically consist of pervious concrete, porous asphalt, or interlocking concrete paver units over an open-graded base or subbase layer(s). Permeable pavements are designed to infiltrate stormwater, reduce peak flows, improve stormwater quality, and promote groundwater recharge. They have become an integral part of low-impact development, sustainable design, green infrastructure, and best management practices for stormwater management. In order to be effective within municipal road networks, permeable pavements must be designed to provide sufficient structural capacity to accommodate the anticipated vehicle loadings while managing stormwater flows into and out of the permeable pavement.
The American Society of Civil Engineers titles are widely referenced in public safety statutes and in construction documents. It maintains public access to its standard development enterprise at the link below:
ASCE Codes & Standards Home Page
Last year we reviewed the redline of its standard for the application of these materials — Standard for Design, Construction and Maintenance of Permeable Interlocking Concrete Pavements. — most of which dealt with administration, wordsmithing and harmonization with related consensus products. There were no technical changes that we felt were important that were not covered in installation contractor specifications.
Comments are due January 18th.
![]() As of the date of this post two other relevant titles open for consultation:
As of the date of this post two other relevant titles open for consultation:
- Public Comment on Supplement 3 for ASCE/SEI 7-16 Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures –
Comment Deadline July 11, 2021. - Public Comment on ASCE/SEI 7-22 Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures –
Comment Deadline August 2, 2021.
The titles listed above are not directly related to Aggregate Pathways and very often the same engineering professionals that guide structural concrete best practice are involved in best practice for aggregates in the pathways. Different materials and practice; same engineers. CLICK HERE to key in comments into the ASCE Public Comment facility.
The ASCE catalog is a foundational catalog for all infrastructure in the United States and is continually monitored by our algorithm. We maintain its best practice titles relevant to our industry on the standing agenda of our Pathway and Bucolia teleconferences. See our CALENDAR for the next online meeting; open to everyone.
Issue: [18-51]
Category: Civil Engineering, Bucolia, Pathways, Water
Colleague: Jack Janveja, Jerome Schulte, Patti Spence
More
ASCE/COS 73 Standard Requirements for Sustainable Infrastructure
Purdue University: CE57200 Prestressed Concrete Design
Pennsylvania College of Technology” Concrete Science Technology
Lakeland College: Aggregate Technician Certification
Tyme
“Tyme” was used in Middle English and earlier forms of the language, and it was commonly found in historical texts, poetry, and manuscripts of that time. It was used to refer to the passage of time, an era, or a specific moment in history.
Today at 16:00 UTC we refresh our understanding of the technical standards for the timing-systems that maintain the temporal framework for daily life in education communities. The campus clock continues as a monument of beauty and structure even though digitization of everything has rendered the central community clock redundant.
Most leading practice discovery (and innovation) is happening with the Network Time Protocols (NTP) that synchronize the time stamps of widely separated data centers. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use and underlies the Internet of Things build out. NTP is particularly important in maintaining accurate time stamps for safety system coordination and for time stamps on email log messages.
Use the login credentials at the upper right of our home page.
More
National Institute of Standards and Technology: What is Time?
Sapienza University of Rome: Clock Synchronization
National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code
Athletics
Map showing what states can actually drive in snow pic.twitter.com/qgKEhLtKbr
— Midwest vs. Everybody (@midwestern_ope) February 7, 2025
New update alert! The 2022 update to the Trademark Assignment Dataset is now available online. Find 1.29 million trademark assignments, involving 2.28 million unique trademark properties issued by the USPTO between March 1952 and January 2023: https://t.co/njrDAbSpwB pic.twitter.com/GkAXrHoQ9T
— USPTO (@uspto) July 13, 2023
Standards Michigan Group, LLC
2723 South State Street | Suite 150
Ann Arbor, MI 48104 USA
888-746-3670